Impact of high-speed railway construction on spatial relationships in the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration
2021-12-20HuilingZhengXiaoshuCao
Huiling Zheng,Xiaoshu Cao,*
aSchool of Geography and Tourism,Shaanxi Normal University,Xi’an,710119,China
bCenter for Resources Research in Northwest China/Institute of Transport Geography and Spatial Planning/Urbanization and Environment Simulation Key Laboratory in Northwest China,Shaanxi Normal University,Xi’an,710119,Shaanxi,China
ABSTRACT
The Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration is a response to the Belt and Road Initiative in Northwest China that aims to promote regional development.The direct impact of high-speed railway construction is to shorten the spatial-temporal distance among regions,improve the accessibility of regional transportation,and promote socioeconomic linkages.From the perspective of accessibility,this study analyzes the impact of high-speed railway construction on the spatial patterns and county-level economic relationships of the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration.The results show that the construction of high-speed railway significantly improves regional accessibility,increases the potential for urban economic development,and gradually narrows the gaps in economic potential among cities.The construction of high-speed railway has increased the intensity of external economic relations among numerous counties in the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration,and most of the areas with increased connections are located in the direction of routes extension.The development of the internal economic network of the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration is unbalanced,and a complex network is gradually emerging with a few large cities at the core,but the construction of high-speed railway is changing the structure of the economic network.In general,a certain degree of intrinsic coupling exists between regional accessibility change and the evolution of economic relations caused by high-speed railway,reflecting the requirements of the regional overall development strategy.
ARTICLEINFO
Keywords:
High-speed railway
Accessibility
Spatial relation pattern
Road network
Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration
1.Introduction
The 21stcentury ushered in a period of global social transformation.During this period,China’s economy,society,and institutional structure have rapidly changed and influenced the development of urban agglomerations(Gu,2011).Yao and Zhu(2001)suggested that an urban agglomeration can be defined as a city with a considerable number of different properties,types,and scales within a specific geographical range.Urban agglomerations arise in certain natural environments in which one or two megacities serve as the core of the regional economy.Moreover,modern transportation and highly developed information networks have aided the development of intrinsic links among urban individuals,constituting a relatively complete urban “aggregate”(Yao and Zhu,2001).Thus,transportation plays an important role in the development of urban agglomerations by linking regions.High-speed railway lines have driven changes through their strong conveyance capacity,rapid speed,security,and comfort.The spatial-temporal compression created by high-speed railway lines can accelerate the spread of social and economic forces,break the traditional“core-periphery”accessibility space pattern,and reshape regional spatial structure of the connected regions(Vickerman et al.,2013;Rosik et al.,2020).Due to the complexity of social and economic development and other transportation modes, the impact of high-speed railway on regional economic patterns must be further explored.It is thus of great theoretical and practical significance to apply concrete case analysis to examine the impact of high-speed railway construction on accessibility and economic relationship patterns in order to improve the efficiency of investments in high-speed railway and optimize the spatial layout of the economy.
Accessibility is a highly important factor in transportation infrastructure for regional social and economic development.This term primarily refers to the convenience of using a specific transportation system to reach a place of activity from a given location(Morris et al.,1979).In attempts to identify the main indicators of transportation infrastructure and economic connection,scholars have studied the relationship between accessibility and economic development(Cascetta et al.,2020).Researches on accessibility changes caused by high-speed railway lines have focused on three scales:transnational,national,and regional.At the transnational scale,scholars have examined the impact of the European high-speed railway network and the Madrid-Barcelona-French border line on the spatial linkages of neighboring countries and regions(Guti′errez,2001;Ma et al.,2015).At the national scale,researchers have mainly studied the impact of high-speed railway construction on changes in accessibility from certain cities to central areas(Chen and Hall,2012;Sanchez-Mateos and Givoni,2012;Moyano et al.,2018)and the impact of high-speed railway construction on provincial accessibility and spatial patterns(Jin and Wang,2004;Coto-Mill′an et al.,2007;Feng et al.,2013;Zhong et al.,2015).At the regional scale,studies have examined changes in accessibility and spatial patterns in cities along the line and urban agglomerations in the metropolitan area(He and Yang,2013;Jiang et al.,2014;Yang,2014;Wang and Zhang,2015;Yu and Fan,2018;Liang et al.,2020).At the same time,some scholars have comprehensively considered the impact of high-speed railway lines on changes in the accessibility of large-and medium-sized cities at the national,regional,and local levels(Ure~na et al.,2011).
Research on the impact of the spatial-temporal compression effect of high-speed railway construction on economic development(Guimaraes,2020;Jain and Jehling,2020)has taken a macro perspective to assert that high-speed railway construction may have the following impacts on regional economic patterns,namely polarization(Ure~na et al.,2011;Jia and Qin,2015;Chen and Haynes,2017),equilibrium(Ortega et al.,2012,2014),or an unclear impact(Sanchez-Mateos and Givoni,2012).By analyzing the previous studies on the impact of high-speed railway lines on the overall level of economic development(Chen and Hall,2011,2012;Chen and Vickerman,2017;Vickerman,2017;Liu and Zhang,2018;Chacon-Hurtado et al.,2020),the level of industrial structure(Ure~na et al.,2011;Qin and Yang,2017;Shao et al.,2017),population and employment flow(Kim,2000;Li et al.,2014;Long and Meng,2015),and the spatial structure of tourism(Yin et al.,2019),we conclude that transportation accessibility is positively related to a region’s overall level of economic development.Central cities have close economic linkages,but the economic relationships between peripheral cities are obviously insufficient.The direction of economic connections has changed from the directivity of central cities to the directivity of geographically adjacent locations.The optimization sequence of the industrial structure follows the order of secondary industry,tertiary industry,and primary industry.Labor and employment flow benefits from the construction of high-speed railway,which gradually promote the process of urbanization.Most research has provided quantitative and qualitative analyses of the economic impact of high-speed railway based on regional characteristics.With the improvement of the transportation network,production factors between regions flow more smoothly. Researchers have tended to quantitatively reveal relationships between regions and within regions through“relationship”data(Hou et al.,2009;Tang et al.,2013).The social network analysis method facilitates this research.The core of the method examines structural issues(behavior,politics,or social and economic structure)from the perspective of“relationships”(Sarlas et al.,2020).
Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration is a newly proposed area in the Guanzhong-Tianshui Economic Zone.“Guanzhong Plain Urban Agglomeration Development Plan”aims to promote urbanization in China through the development of urban agglomerations.Scholars have conducted an analysis of road network accessibility in the Guanzhong-Tianshui Economic Zone(Bai et al.,2012),including the economic connection pattern(Huang and Huang,2016)and county-level economic relationships based on accessibility(Wang and Cao,2016a,b).The results showed that an effective transportation infrastructure network can promote the development of the regional central city and neighboring cities.Economic relationships in the Guanzhong-Tianshui Economic Zone have a“core-periphery”pattern,and the network development is uneven but increasingly dense and complex.Among various modes of transportation,scholars have focused on the spatial-temporal effect of high-speed railway.According to the“Guanzhong Plain Urban Agglomeration Development Plan”,five high-speed railway lines will be constructed in this area.What influence will these lines have on accessibility within the region,and how can economic relationship patterns evolve under the influence of accessibility?Quantitative analysis based on the social network analysis method can clearly reveal changes in economic network patterns and provide a scientific basis for further strengthening regional spatial relationships of the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration.Therefore,this study used the gravity model to establish the strength of the county’s economic connections without high-speed railway,in 2016(when a partial high-speed railway lines were opened)and in 2035(when the planned high-speed railway lines will be completed).The social network analysis method was used to compare the impact of high-speed railway construction on network connectivity and economic connection structures.
2.Study area and methods
2.1.Study area
The “Guanzhong Plain Urban Agglomeration Development Plan”was approved in January 2018 to build a national-level urban agglomeration.This strategy was adopted to plan the core of the development of the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration for Northwest China.The planning scope of the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration includes several districts and counties in Shaanxi,Shanxi,and Gansu provinces.The total area covers 1.07×105km2with a permanent population of 3.86×107at the end of 2016 and a regional GDP of 1.59×1011CNY,accounting for 1.12%,2.79%,and 2.14% of the national total,respectively.This urban agglomeration in Northwest China has a high level of development,but it also has large regional differences.The administrative units involved in this study include 90 county units,which are abstracted as 90 nodes to calculate regional accessibility.
The socioeconomic data used in this study come from the Shaanxi Statistical Yearbook(Shaanxi Provincial Bureau of Statistics,2017),Shanxi Statistical Yearbook(Shanxi Provincial Bureau of Statistics,2017),Gansu Yearbook(Gansu Provincial Bureau of Statistics,2017),and China County Statistical Yearbook(National Bureau of Statistics,2017).The space administrative boundary vector data were extracted from the 1:4,000,000 Chinese electronic map supplied by the latest National Geomatics Center of China(http://www.ngcc.cn/ngcc/html/1/index.html) and were corrected through the digitized mapping of the China Provinces Series Atlas(Shaanxi,Gansu,and Shanxi).The road network data were collected by digitizing the scanned map using ArcGIS 10.1.To avoid the boundary effect of the spatial analysis,we applied a 100 km buffer to the study area,and extended the traced network data to the range boundary of the 100 km buffer.The road network data outside the study area boundary were only used in the data calculation.According to previous researches(Wang et al.,2014,2016;Tao et al.,2016)on the processing methods for road data at different times,we studied the road network data based on the 2016 digital road network(national road,provincial road,county road,highway,railway,and high-speed railway).Then,we calculated the shortest travel time without the use of high-speed railway lines based on the basic road network of ordinary railways,expressways,national highways,provincial roads,and county roads in 2016.We also calculated the shortest travel time in 2016 based on the actual digitized road network,and the shortest travel time in 2035 based on the basic road network in 2016 and the high-speed railway network in 2035.The population and GDP data before and after the completion of the proposed routes in 2016 were used to determine the impact of high-speed railway construction on the accessibility and economic relationship pattern of the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration.
2.2.Study methods
2.2.1.Economic potential
The construction of transport infrastructure leads to the improvement of accessibility,which is evaluated by a series of indicators,while economic potential mainly considers interactions between regions due to their attractiveness.The accessibility of a node in a network is proportional to the spatial interaction among the nodes and is inversely proportional to the distance from the node to the destination(Guti′errez et al.,1996).The formula is given as follows:

where Pirepresents the economic potential value of node i,such that the higher the potential value,the greater the potential advantage of the central city;Dijrepresents the shortest time from node i to node j;α is the distance coefficient of friction and generally takes on a value of 1;Mjis the quality of the central city;n is the total number of nodes except node i;GDPjrepresents the gross domestic product of node j;and POPUjrepresents the population size of node j.
To measure the shortest time distance,we must convert the space distance into the time distance and set the speed and time cost values for different roads.According to the Technical Standard of Highway Engineering(JTG B01–2014)(Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China,2014),we determined the speed of the road at all levels in the area in combination with the actual road conditions of the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration.The current designed speeds are listed as follows:250 km/h for high-speed railway,100 km/h for highway,90 km/h for ordinary railway,80 km/h for national road,60 km/h for provincial road,40 km/h for county road,and 30 km/h for village road.The planned high-speed railway lines are established according to their planned speeds,with the Guanzhong Intercity Line at 200 km/h,the Xi’an-Yinchuan High-Speed Railway at 250 km/h,the Xi’an-Yan’an High-Speed Railway at 350 km/h,the Xi’an-Ankang High-Speed Railway at 350 km/h,and the Xi’an-Wuhan High-Speed Railway at 350 km/h.
2.2.2.Economic relation intensity
The direct effect of regional accessibility enhancement is to strengthen socioeconomic relations between regions,and this is an indicator used to measure the strength of economic relations between regions that can reflect the radiation capacity of the economic center to the surrounding areas and the acceptability of the surrounding areas to the economic center’s radiation capacity.Considering the relationship between the economic potential of cities and the real economic links,the economic relationships between the two cities are not equal(Wang et al.,2006;Hou et al.,2009;Tang et al.,2013),such that the proportion of urban GDP to the sum of GDP of the two linked cities is used to correct the economic contact,which can be expressed as follows:


where Rijis the economic relation intensity between region i and region j;POPUiand POPUjare the population sizes of region i and region j,respectively;GDPiand GDPjare the regional gross domestic product of region i and region j,respectively;Dijis the minimum time based on the road network between region i and region j;kijrepresents the contribution rate of region i to Rij;and Riis the total amount of foreign economic relations of region i.
2.2.3.Measure of economic network structure characteristic
The social network model is primarily used to analyze the characteristics of a network,determine types of network nodes,and explore the role of network node members in the network.This method can characterize complex contact attributes between nodes and exhibit diversity depending on the node.This paper selected network density,centrality,and cohesive subgroups to analyze the economic network connection characteristics of 90 county units in the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration.
Network density.This index refers to the closeness of relationships among all nodes in the urban network,which is obtained by comparing the actual contact value with the ideal contact value.This indicator reflects not only the impact of the overall network on individuals in the network,but also the interaction among individuals in the network.The greater the value of the network density,the more the network will affect the members,and the closer the relationship will be among network members.
Centrality.This topic is discussed from two aspects:the individual centrality and the overall central potential.The centrality measures the status and importance of a node in the network,including the degree centrality,closeness centrality,and betweenness centrality.Degree centrality is a relatively simple index.If a point is directly connected to many points,the point has a higher degree of centrality.Closeness centrality is not controlled by other points.If the point is located at a short distance from all other points in the network,the point is said to have a higher degree of closeness.The measurement of this indicator requires the network graph to be fully linked,because it is highly correlated with the degree of centrality;it is therefore rarely used.Betweenness centrality is an indicator of a node’s ability to act as a mediator.If one point is located on the shortest route to many other peers,the node has a higher betweenness centrality.The central potential represents the overall integration of the network,that is,the extent to which the entire network is centralized.Analyzing the center potential of the network allows the asymmetry and the imbalance degree of economic relations between cities to be judged.The closer the value is to 1,the stronger the degree of network concentration and the higher the degree of disequilibrium.
Cohesive subgroup.This indicator primarily analyzes the actual existence or potential relationship pattern among social members and shows how many cohesive subgroups exist in the network,the relationship between each of the cohesive subgroups,and the characteristics of the relationship among the members of the cohesive subgroups.Judgements are based on whether a relatively strong direct and close relationship exists between subgroups and subgroup nodes that constitute a cohesive subgroup.If there are many cohesive subgroups in the network but a lack of connection between them,it is not conducive to the development of the entire network.
The social network analysis method is based on relational data.Therefore,the conversion of attribute data into relational data and the construction of a network of relationships between city cluster counties are a prerequisite and foundation for network analysis.The economic linkage strength matrix is constructed for the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration in the years without high-speed railway,2016,and 2035.The mean values of Rwithouthigh-speedrailway,R2016,and R2035were calculated for the economic linkage strength between each inter-county node,with(Rwithouthigh-speedrailway+R2016+R2035)/3 as the threshold(9996.857)for discriminating effective intercounty links.A value greater than this value is coded 1,and a value less than the threshold value is coded 0.An undirected,unweighted[0,1]adjacency matrix is established to analyze the network characteristics.
3.Urban spatial connection patterns and their evolution
3.1.High-speed railway construction boosts a city’s economic potential
The vector accessibility method was used to calculate the accessibility of each county unit under three scenarios of Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration:without high-speed railway,partial high-speed railway lines access in 2016,and completion of the planned highspeed railway lines in 2035.According to the calculation of the potential formula,combined with the Kriging interpolation method,it is found that the economic potential of each county unit presents an obvious core-periphery structure in spatial distribution(Fig.1).
When the high-speed railway is not available,the overall economic potential(PA)of the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration is low,and most areas are concentrated in the range of 2500–5000(Fig.1a).A clear core-periphery structure is formed in space.The PA values of districts and counties with Xi’an City as the core are high,while some districts and counties under the jurisdiction of Tianshui City and Pingliang City are limited to the level of economic development and marginal location factors with low PA values.
In 2016,some high-speed railway lines were in operation,such as the Longhai Railway,Datong-Xi’an High-Speed Railway,Lanzhou-Xi’an High-Speed Railway,and Zhengzhou-Xi’an High-Speed Railway.The PA of most areas remained at 2500–5000,but high-value areas increased(Fig.1b).Spatially,the high-value center of Beilin District,Xincheng District,and Lianhu District of Xi’an City gradually decreases toward the periphery,and the main area of change is the extension of the railway.
In 2035,after the planned high-speed railway lines are completed,the PA of most county units of the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration will exceed 5000(Fig.1c).The economic changes will be more obvious.Comparing the changes in PA before and after the construction of the high-speed railway,Yijun County,Yaozhou District,Fuping County,Sanyuan County,Zhashui County,and other areas along the Xi’an-Baotou and Xi’an-Ankang High-Speed Railway will undergo the most obvious changes.In the northeast of the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration,Huozhou City,Hongtong County,Fushan County,Xia County,and Tianshui City will experience the smallest changes,which could be due to the absence of planned high-speed railway lines in these areas,as they then can only benefit from the indirect effects of high-speed railway planned in other regions.
Under the three examined scenarios,the coefficients of variation of PA are 0.5854,0.5878,and 0.5429,respectively.This shows that the opening of some high-speed railway lines will increase regional differences.After the planned routes are completed,regional differences in economic potential will decrease(Jiang et al.,2015).
3.2.Changes in county-level economic connections,directions,and structure
3.2.1.Urban external economic relations:significant changes in the total amount
Taking the county as the economic center node,this study measured the total number of external economic relationships for 90 districts and counties in the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration according to the formula of the gravity model.From without highspeed railway to completion of the planned high-speed railway lines in 2035,there was a significant increase in the total amount of external economic relations in all regions.Yanta District is the place with the largest number of external economic links.Without a highspeed railway,the total number of economic connections is 18.21×106,which increases to 19.44×106in 2016 and reaches 20.06×106in 2035(Table 1).The overall change range is 10.18%.Taibai County is the place with the smallest number of external economic links.When there is no high-speed railway,the total degree of economic connections is 1432,increasing to 1506 in 2016 and reaching 1783 in 2035.The overall change range is 24.55%.
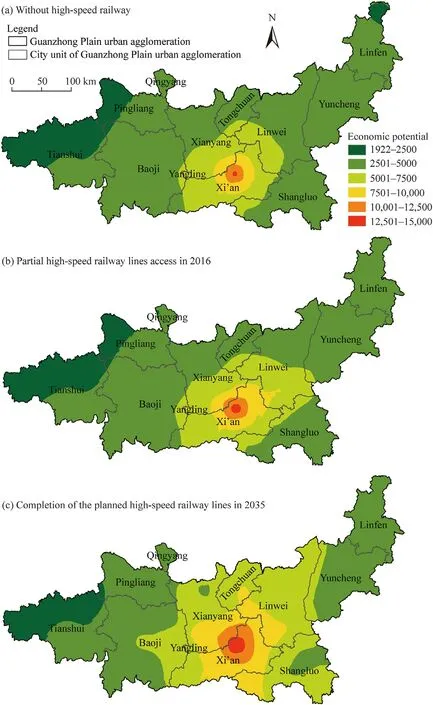
Fig.1.County level economic potential of Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration under three scenarios.(a),without high-speed railway;(b),partial high-speed railway lines access in 2016;(c),completion of the planned high-speed railway lines in 2035.
Cities with a high number of external economic relationships are concentrated in the main urban areas under the jurisdiction of Xi’an City.Before and after the completion of high-speed railway,the ranking of the top 10 districts regarding economic relationship intensity does not change significantly.Gaoling District rises to the 10th position after completion of the planned high-speed railway lines(Table 1).The reason for this is that while Gaoling District’s original external economic relationship is 5.7 × 105economic degrees,ranking 13th,the proposed Xi’an-Baotou High-Speed Railway will establish a site in Gaoling District,and the Xi’an-Hancheng Intercity Railway will also pass through the Gaoling District.A good basis for external contact and convenient traffic conditions serves to increase the rank of Gaoling District.
3.2.2.Direction of change in county economic relations:extension with the direction of high-speed railway
The connection between cities is closely related to the level of economic development and traffic conditions.By drawing the spatial pattern of the intensity of economic links above 0.01×106economic degrees,it can be seen that a complete economic network pattern has not been formed among the cities in the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration.Before the opening of the high-speed railway,there were 419 pairs of cities with economic links above 0.01×106,which increased to 465 in 2016.After completion of the planned highspeed railway lines in 2035,682 pairs of cities will have economic connections in excess of 0.01×106(Fig.2).The overall increase is 62.77%.
Before the opening of high-speed railway, the direction of economic links among the cities was mainly based on Xi’an City as the core area,though these links gradually dispersed and extended in all directions.After completion of the planned high-speed railway lines in 2035,in the extension direction of the Xi’an-Yinchuan,Xi’an-Baotou,Xi’an-Wuhan,Xi’an-Ankang High-Speed Railway,and the Xi’an-Hancheng Intercity Railway,many cities will establish economic links of over 1.0 × 104with Xi’an City,such as Xifeng District,Bin County,Jintai District,Zhashui County,Danfeng County,and Hancheng City.As the East-West-linked economic structure is broken,the economic relation pattern along the direction of the planned high-speed railway construction gradually emerges.
3.2.3.Economic network structure:incomplete but increasingly perfect
Taking the average value of economic relationship strength of each inter-county node in the three scenarios as the threshold(9996.857),this study analyzed the structure of the county economic network of Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration using Ucinet 6.When there is no high-speed railway, the economic relationship network density of the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration is 0.0523,increasing to 0.0581 in 2016 and 0.0851 after completion of the planned high-speed railway lines in 2035.Overall,the economic network density among the cities within the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration is low,and the interaction between cities is not sufficient.After completion of the planned high-speed railway lines,the density of the urban economic relationship network will increase and the connections between cities will be strengthened,which is conducive to the coordinated development of the economy.
In social network analysis,changes in a node’s degree centrality indicate changes in its status in the network.When the high-speed railway is not available, the degree centrality of 26 cities in the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration is 0. In 2035, the degree centrality of seven cities increases significantly,and the degree centrality of 19 cities is 0.Their mean value increases from 6.067 to 6.889 in 2016,and will increase to 10.222 in 2035.The opening of the high-speed railway has significantly improved the status of cities in the region,but there are still some cities whose status in the economic network is not obvious,showing a trend of polarization.
To further examine the impact of the high-speed railway on the control of the flow of resource capacity of cities in the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration,it is necessary to analyze changes in the betweenness centrality of each city in different stages(Table 2).Overall,the betweenness centrality of the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration is low,and the completion of the high-speed railway lines will increase this value.Before the opening of the high-speed railway,the economic relationship of most cities is enacted through intermediary cities such as Yanta District and Xingping City.In 2016,the betweenness centrality value of Yanta District increased significantly,which promotes its dominant position in economic links.In 2035,Yanta District will become the absolute leader of economic relations among cities in the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration.The mean value of“brokers”for which each city serves as an economic link within the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration is 0.389 without high-speed railway.This value increased to 0.495in 2016,and will increase to 0.588 after the completion of the proposed high-speed railway lines in 2035.Therefore,the number of core cities with intermediary functions will increase,rendering the structure of the urban economic linkage networks increasingly effective.
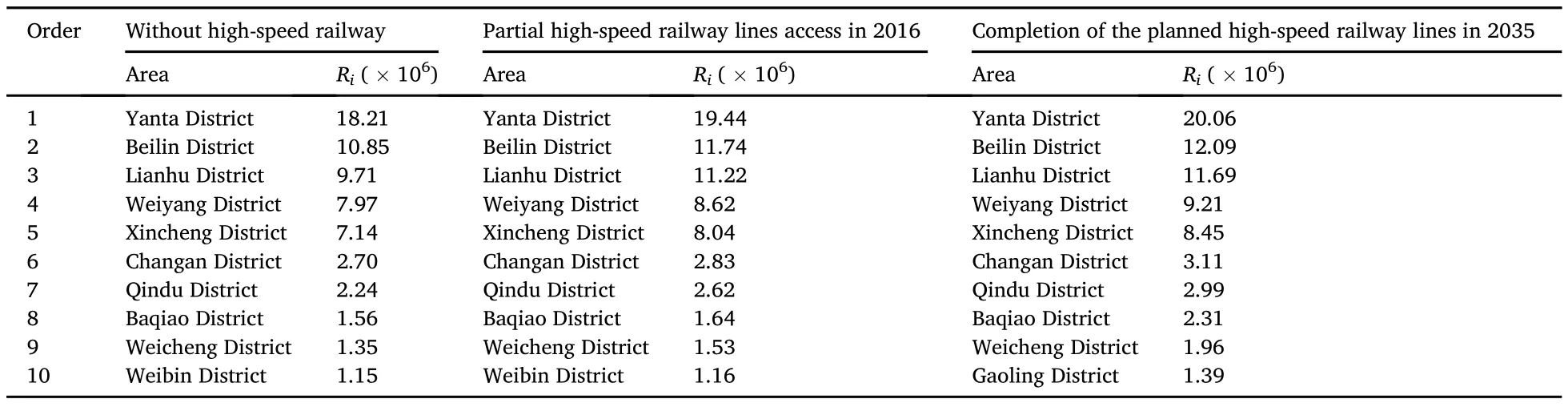
Table 1Top 10 districts in the total amount of external economic relations in different stages of high-speed railway construction in the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration.
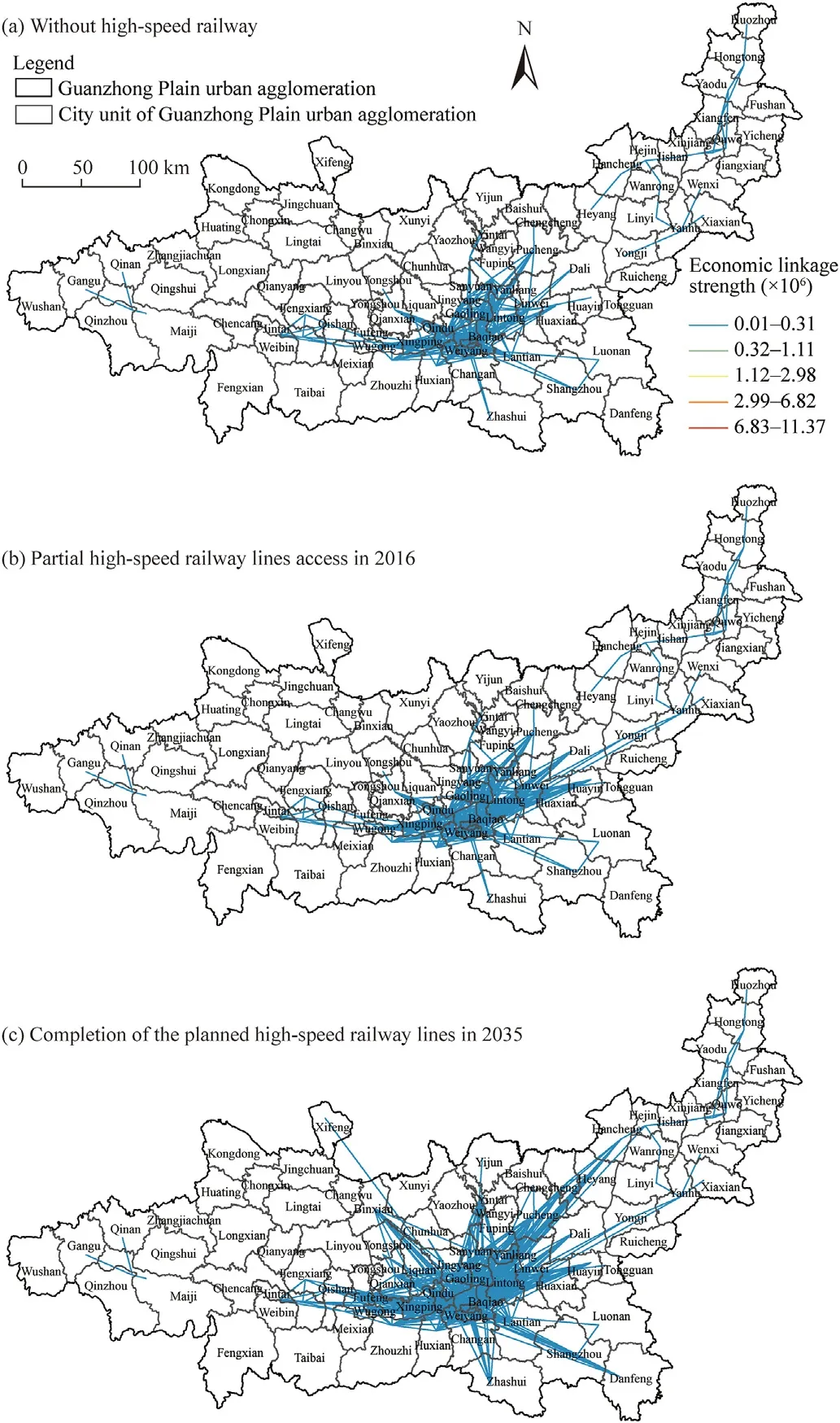
Fig.2.County level economic relation pattern of Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration under three scenarios.(a),without high-speed railway;(b),partial high-speed railway lines access in 2016;(c),completion of the planned high-speed railway lines in 2035.The data of economic linkage strength are concentrated in the range of 0.01–0.31,the rest of the data are less and the spatial distance is similar,so the former data are basically in the figure.
In the social network analysis method,centrality indicators can measure the degree of network centralization.A comparison of the central potential of the overall economic network of the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration in different periods shows that the central potential value of the network has increased,indicating that the asymmetry and imbalance of internal economic relations have increased.Because of the spatial-temporal compression effect of high-speed railway construction,the frequency of contacts between regions with geographical advantages has increased.Taking Yanta District as an example,the central position of this area in the network is more obvious.Small marginal cities benefit from the opening of high-speed railway lines,as the level of economic development and external contact increase.On the whole,changes in the central potential value indicate that after the opening of the high-speed railway in the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration,the economic connection network has an obvious tendency to concentrate on the Yanta District of Xi’an City.
Focusing on the strength of the economic relationships among cities,the CONCOR algorithm of Ucinet 6 was used to investigate the phenomenon of small group aggregation in cities within the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration.The results show that the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration contains four cohesive subgroups at the second level and seven cohesive subgroups at the third level(Tables 3–5).With the completion of the high-speed railway lines in 2035,the locations of the cities in the third level will change.
The first cohesive subgroup is the core of Xi’an City,including the Xincheng District,Weiyang District,Yanta District,and Chang’an District.The first cohesive subgroup is divided into two subgroups with 25 county units at the third level.After completion of the planned high-speed railway lines,the number of subgroups is found to increase to 33 county units.Fufeng County,Bin County,Zhashui County,Wangyi District,and Yintai District are categorized as part of the core subgroup.However,Dali County is categorized in the second cohesive subgroup,because Xi’an City is the best node city for the development of Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration.Although Yaozhou District,Wugong County,Zhouzhi County,and Tongguan County do not belong to Xi’an City in terms of administrative divisions,the actual economic links show close contact with Xi’an City.
The second cohesive subgroup contains nine county units at the second level,with two subgroups at the third level.The second subgroup consists of the eastern portion of Hua County,Huayin City,Dali County,and the western portion of Yangling District,Mei County,and Fufeng County.The urban agglomeration characteristics within this subgroup are not obvious.In 2035,the scope of this cohesive group includes 20 county units,and the additional cities are mostly located in the direction of the planned high-speed railway lines.Cities such as Hejin City,Hancheng City,Danfeng County,Shangzhou District,Zhashui County,and Bin County are included in the subgroup.This result suggests that a potential link exists among the 20 county units,and the planned high-speed railway project could lead to the formation of such a potential linkage model.
The third cohesive subgroup consists of 30 county units and is divided into two subgroups at the third level,consisting of closely connected subgroups such as Huozhou City,Xiangfen County,and Wanrong County in the east and closely connected subgroups including Gangu County,Maiji District,Wangyi District,Qishan County,and Fengxiang County in the west of Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration.There are 12 county units in the third cohesive subgroup that form part of the second cohesive subgroup,while the remaining 18 county units still take Xi’an City as the boundary,forming closely connected subgroups in the East and West.The obvious changes in the third cohesive subgroup indicate that completion of the high-speed railway lines will increase economic links among subgroups.
The fourth cohesive subgroup is the northwestern cohesive group centered on Kongdong District,Huating County,Long County,Qianyang County,Lingtai County,and Jingchuan County.Due to geographical proximity,the economic development level of this subgroup is poor.In addition,the planned high-speed railway does not pass through the area.Although there are seven county units indirectly affected by the reduction in time costs in the third cohesive subgroup,the overall pattern of the western cohesive subgroup remained unchanged.
A comparison of the network contact density matrix of the seven subgroups at the third level shows that the connections among cities within the subgroups are relatively close,but the connections among subgroups are not strong.After the completion of high-speed railway lines,the location of the first cohesive subgroup at the second level will change,increasing not only the connection density between the inner cities of the subgroup,but also that between the subgroup and other subgroups.Moreover,the contact density will increase between the second subgroup and the fourth subgroup;the third subgroup and the fourth,fifth,and sixth subgroups;the fourth subgroup and the second and fifth subgroups;and the fifth subgroup and the third and fourth subgroup at the third level.It will decrease between the second subgroup and the first,third,and sixth subgroups;the third subgroup and the second subgroup;the fourth subgroup and the first and third subgroups;the fifth subgroup and the sixth subgroup;and the sixth subgroup and the second,third,and fifth subgroups at the third level(Table 6).This shows that the construction of high-speed railway lines will change the economic network connection between cities in the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration.The economic core status of some cities becomes moreprominent.
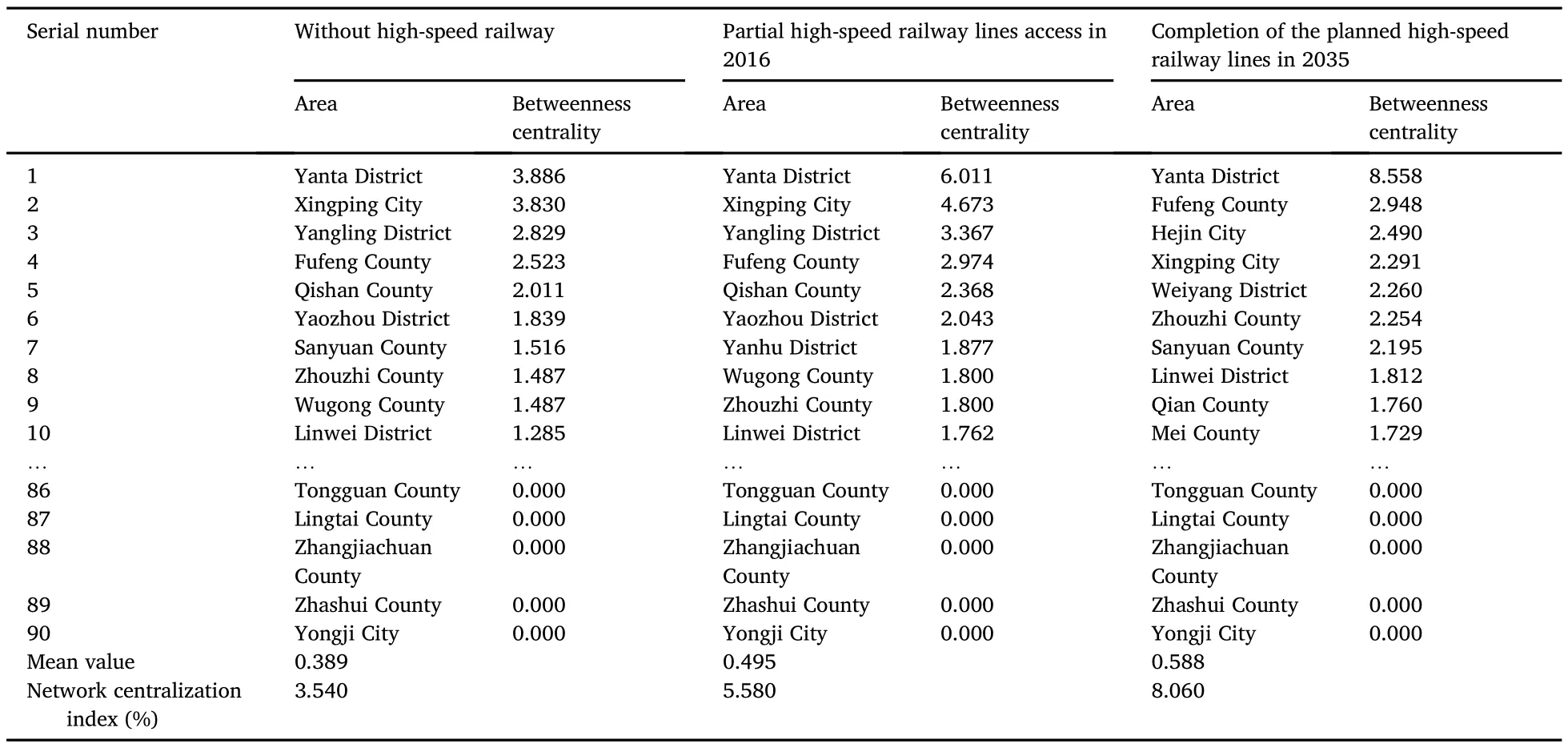
Table 2Network’s betweenness centrality and network centralization in the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration.
Table 3Cohesive subgroups in the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration under the scenario of without high-speed railway.
Table 4Cohesive subgroups in the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration under the scenario of partial high-speed railway lines access in 2016.

Table 5Cohesive subgroups in the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration under the scenario of completion of the planned high-speed railway lines in 2035.

Table 6Network’s density matrix in the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration.
4.Discussion and conclusions
In this paper,PA was used as an indicator to measure the accessibility of the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration under three scenarios to evaluate the impact of high-speed railway on the improvement of regional accessibility.Combined with changes in the total economic amount,direction,and network structure of external economic connections of the county unit,the impact of the spatialtemporal compression effect produced by the construction of high-speed railway on urban economic spatial connection patterns was further analyzed.
The planned high-speed railway lines result in a significant spatial-temporal compression for regional accessibility.The regional economic development potential is significantly improved after completion of the planned high-speed railway lines.In terms of space,the typical core-periphery model is transformed into an elliptical pattern with Xi’an City as the center,extending outward along the planned high-speed railway lines in a “meter”shape.The results of the coefficient of variation indicate that gaps in economic potential among cities will narrow after the completion of the high-speed railway.
The construction of the high-speed railway lines will increase county-level economic relations within the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration,and most of the affected areas are located in the extension directions of the routes.The east-west economic connection pattern in the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration is broken,but the direction of the proposed high-speed railway forms a radiationlike economic relationship pattern with Xi’an City as the core.This provides a certain degree of intrinsic coupling between regionalaccessibility change and the evolution of economic relationships caused by the construction of high-speed railway lines.
The network of county-level economic relationships within the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration is unbalanced,but the overall structure will gradually improve. The network density within the urban agglomeration itself is relatively low. With the completion of the high-speed railway lines,the value of network density and economic linkages will increase.The counties under the jurisdiction of Xi’an City and neighboring cities,such as Yangling District and Fufeng County,have a high degree of betweenness centrality,giving them an important intermediary role in the network.However,the intermediary roles of the network nodes in Yanta District are too polarized,which has led to the prominent position of Xi’an City as a regional core and hub,while the intermediary status of other regions in the network needs to be further improved.Before the construction of high-speed railway,the economic relationships within the urban subgroup are relatively close,but the linkage between the subgroups was less close.The completion of high-speed railway will gradually change this pattern.The relationship among urban subgroups will become closer,and the economic relationships between urban subgroups will also change.
Since the “Guanzhong-Tianshui Economic Zone Development Plan”was put forward,the Guanzhong-Tianshui Economic Zone has become a hot area of academic research.In 2018,after the development area of the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration was demarcated,an increasing amount of research was conducted on the area.Existing studies mainly focus on population urbanization(Xiao et al.,2020),coordinated urban development,tourism and the spatial structure of urban systems(Zhan et al.,2020),and ecosystem services(Zhao et al.,2018;Zhang et al.,2019).From the perspective of traffic accessibility, the analysis is mainly based on the gravity model,focusing on the interaction between different cities.Based on existing research,we further used the social network analysis method to analyze changes in urban spatial connection patterns,including the improvement of the city’s own economicpotential and the total amount,direction,and network structure changes of urban external economic relations.
Combining the “One Circle,One Axis,and Three Belts”spatial development framework proposed in the Guanzhong Plain Urban Agglomeration Development Plan,high-speed railway lines can inject momentum into the construction of this development framework.The Xi’an(Xianyang)Metropolitan Circle has been formed in a preliminarily manner,and the completion of the Guanzhong Intercity Line will further strengthen the core status of the Metropolis Circle of Xi’an City.Relying on the Longhai Railway,Lianyungang-Khorgos Expressway,Zhengzhou-Xi’an High-Speed Railway,and Xi’an-Lanzhou High-Speed Railway,the three radiation axis belts are not obvious.The planned Xi’an-Hancheng Intercity Railway,combined with the Datong-Xi’an High-Speed Railway and the Xi’an-Chengdu High-Speed Railway,can improve the development of the Beijing-Kunming Development Belt,while the planned lines of the Xi’an-Yinchuan High-Speed Railway and Xi’an-Wuhan High-Speed Railway can strengthen economic relationships in the Fuzhou-Yinchuan Development Belt,and the proposed Xi’an-Baotou High-Speed Railway and Xi’an-Ankang High-Speed Railway can promote the development of the Baotou-Maoming Development Belt.Overall,the planned high-speed railway lines can increase the radiation capacity of the core city,promote the rapid development of three radiation belts,and further improve regional economic relationships.
Finally,this paper has certain shortcomings that must be further strengthened in future research.Due to the lack of flow data regarding the urban population,transportation,economy,and other factors,the urban economic spatial connection network based on the gravity model is inevitably bound to the real network.In addition,the proposed high-speed railway lines will be completed in 2035,but its actual opening date and influence on county-level accessibility and economic relationship patterns require further investigation.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(41831284).
杂志排行
区域可持续发展(英文)的其它文章
- Purchase willingness of new energy vehicles:A case study in Jinan City of China
- Assessing the adequacy and sustainability performance of multi-family residential buildings in Anambra State,Nigeria
- Effect of future climate change on the water footprint of major crops in southern Tajikistan
- Exploration of the dynamic water resource carrying capacity of the Keriya River Basin on the southern margin of the Taklimakan Desert,China
- Spatial pattern and drivers of urbanization in China’s mid-level developing urban agglomeration:A case study of Chang-Zhu-Tan
- Dynamics of NDVI and its influencing factors in the Chinese Loess Plateau during 2002–2018
