Experimental study on the effect of Huangqi and Danshen ultramicro gel on vascular healing of wound in rats based on network pharmacology
2021-11-04YikangYuKaiYuBochengLiangDongpengTuWenKaiZhangChaoXuZhengLiuYiPengBinZhang
Yikang Yu, Kai Yu, Bocheng Liang, Dongpeng Tu, WenKai Zhang, Chao Xu,2, Zheng Liu, Yi Peng, Bin Zhang
1 Second Clinical Medical School, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Zhejiang 310053, China.
2 Department of Orthopaedics, Xinhua Hospital of Zhejiang Province, Zhejiang 310003, China.
Abstract Objective:To explore the effective components of Huangqi (Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.)Bge.) and Danshen (Salvia miltiorrhizaBge.) and predict their potential functional targets, to explore the effect and mechanism of Huangqi and Danshen ultrafine granule gel on wound vascular healing in rats by network pharmacology and experimental verification.Methods: Using the TCMSP database to screen the active components of two herbs and their potential targets, to search the target related to vascular injury through the Gene Card database, and to select the gene target with correlation coefficient greater than 10%.Then map the disease related target to the potential target of the compound, to obtain the common target, and to import the information to the String online analysis platform and Cytoscape to make the PPI map, and to carry on the topological analysis, KEGG and GO enrichment analysis through Metascape platform.The expression analysis of the main target genes of network pharmacology was verified by pathological section staining and optical density method to determine the content of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in tissues, the number of tissue new capillaries, and the wound healing rate.Results:A total of 115 active components and 297 target genes were selected from Huangqi and Danshen, and 123 target genes were intersected with vascular injury, among which IL6, AKT1, INS, VEGFA, TNF, EGF, CASP3, MAPK1, TP53 were the active genes with the highest intersection value.The pathways involved are mainly related to AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications, MAPK signaling pathway, Pathways in cancer, human cytomegalovirus infection, Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis, Endocrine resistance, foxo signaling pathway etc.We experimentally validated VEGFA based on the primary target of vascular regeneration, the experimental results showed that there was different expression of VEGFA proteins in wound vascular healing process, and the quercetin, daidzein, luteolin, apigenin, tanshinone i of 115 active components were selected as the main compounds acting on the VEGFA.Conclusion:This study systematically reveals the material basis and mechanism of Huangqi and Danshen regulating wound vascular healing through multi-component, multi-target and multi-pathway and provides theoretical and scientific basis for the clinical application of Huangqi and Danshen.
Keywords: Wound healing, Network pharmacology, Huangqi(Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.)Bge), Danshen (Salvia miltiorrhizaBge.), VEGFA
Background
Skin injury is a common form of trauma, and wound healing is one of the important links in the treatment of traumatic diseases, pre-chronic refractory wounds have also become a major challenge in the management of trauma patients.In the process of wound healing, angiogenesis and neovascularization are important factors to determine the growth of wound tissue, but most of the chronic refractory wounds are accompanied by abnormal angiogenesis [1, 2].Different approaches have been developed to promote angiogenesis, natural components derived from plants and animals can be used to enhance neovascularization to promote angiogenesis and wound healing in chronic wounds [3, 4].Huangqi (Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.)Bge.)and Danshen (Salvia miltiorrhizaBge.) are a couple of common drugs used in traditional Chinese medicine.Many studies have confirmed that the active components of two herbs are beneficial to cardiovascular diseases and cerebrovascular diseases to varying degrees, but there are no relevant reports on the effect of wound healing [5, 6].Chronic non-healing wounds belong to the category of "sore" in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), and chronic non-healing wounds are not well healed or slow to heal due to various reasons, which is often associated with the pathological state of deficiency of qi and blood, qi stagnation and blood stasis in patients [7-9].Huangqi has been used as an important medicine for tonifying qi since ancient times.And Danshen as a drug to promote blood circulation, since ancient times.Danshen has a good effect of tonifying blood and activating blood circulation.Huangqi and Danshen, as a couple of common clinical drugs, are famous for tonifying qi and activating blood, and has good clinical effect on the treatment of chronic non-union wound.
In this study, the target and signal pathway involved in wound vascular healing were studied by network pharmacology and experimental verification, and the direct effects of the main target genes were predicted.
Network pharmacology to predict the mechanism of Huangqi and Danshen on vascular healing
Potential target prediction and network construction of main active components in Huangqi and Danshen
Chemical composition and molecular information of Huangqi and Danshen were obtained by searching pharmacology database of Traditional Chinese Medicine System and analysis Platform (TCMSP, http://ibts.hkbu.edu.hk/lsp/tcmsp.php) database [10].
Screening of active molecules: The composition of traditional Chinese medicine is complex, through the preparation process and in vivo process, screening possible efficacy substances and active molecules, because of the later experimental verification of the treatment method of external application of Chinese medicine particles, the selected compounds were liposoluble transdermal absorption, the adjusted screening conditions are as follows: Drug-likeness ≥ 0.18, AlogP ≥ 5.0 and MW ≥ 500.
Use the Uniprot database (https://www.uniprot.org/) to standardize the target name through the prediction target information provided by the platform.
Construction of compound-target network: Use the TCMSP database to obtain target related genes, the compound-target network was constructed by Cytoscape 3.8.0 software [11].
Gene ontology function (GO) annotation and KEGG enrichment analysis
Use the gene cards database (https://www.gene cards.org/) to retrieve "vascular injury", download the obtained target gene, and select the gene with correlation coefficient >10% as the main target.
The target genes related to vascular injury and compounds were screened, imported into the String database (https://string-db.org/), and the PPI network was constructed to download the network information, and the top 20% of the values in the network were selected as the key target genes.
The key target genes were analyzed by Metascape platform (http://metascape.org/gp/) to obtain GO annotation and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis.
Results of network pharmacology
Through the screening of the potential targets of the main active components in Huangqi and Danshen, one hundred fifteen active components were selected, including 25 components of Huangqi and 90 components of Danshen, with no duplicate compounds.A total of 297 targets were selected, including 173 targets of Huangqi and 231 targets of Danshen, and 117 common targets of two herbs, and we constructed a compound-target network action map, see Figure 1.The left side is the schematic diagram of Huangqi composition-target action, in which the HQ is the abbreviation of the Chinese phonetic Pinyin HuangQi, representing a compound of Huangqi, and the right side is the schematic diagram of Danshen compositiontarget action, the DS is the abbreviation of the Chinese phonetic Pinyin DanShen, representing a compound of Danshen.The common targets of Huangqi and Danshen are in the middle side, all components and targets show different areas according to their connectivity degree values.
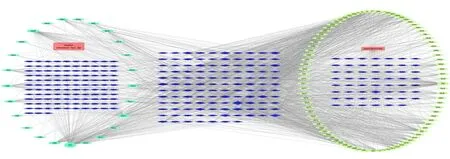
Figure 1.Compound-target network action map.
The related genes of vascular injury were 6886, and 731 main target genes were obtained after screening, of which 123 (key target genes) were intersected with Huangqi and Danshen compounds.The network diagram protein-protein interaction network, PPI intersection genes was obtained by String database, and import to Cytoscape according to the value (Figure 2).According to the different Degree values, the key target genes of the intersection between the target of Huangqi and Danshen compounds and vascular injury showed different area sizes, among which, the target gene value of the circular center part of the net was the highest, and the value of the outer part of the net was lower.
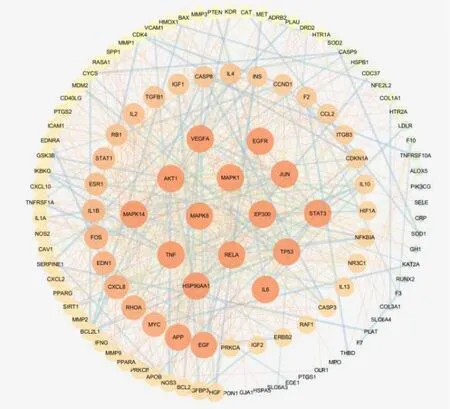
Figure 2.Protein-protein interaction network and key target genes.
The topological analysis of the network shows that the 24 active genes with the highest value are Interleukin-6 (IL6), RAC-alpha serine/threonine- protein kinase (AKT1), Insulin (INS), Vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA), Tumor necrosis factor (TNF), Epidermal growth factor (EGF), Caspase-3 (CASP3), Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 (MAPK1), Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53) etc.see Table 1, and the correlation degree of the target genes of vascular injury is synthesized, and the VEGFA is taken as the main index of the later experimental verification.
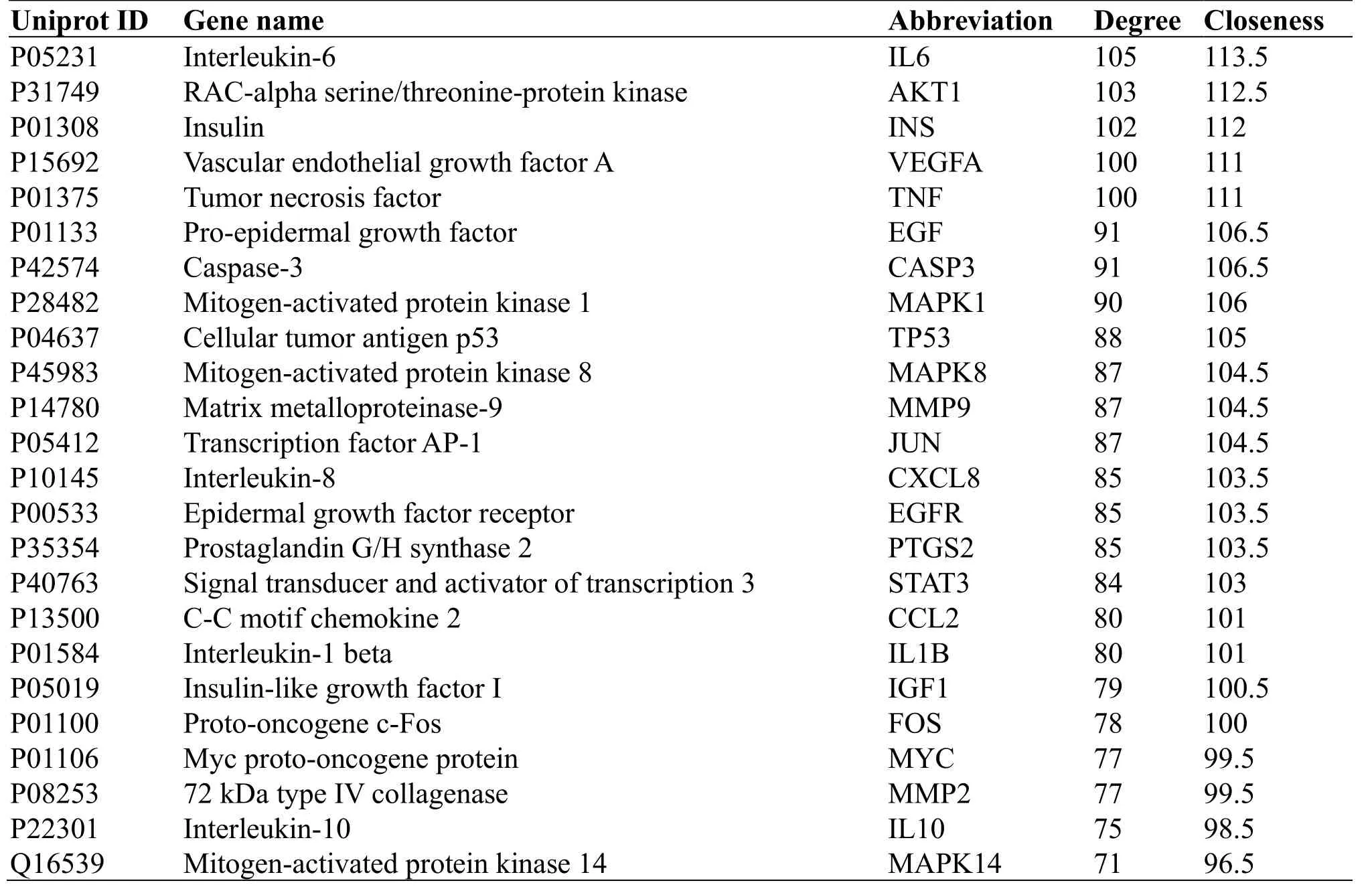
Table 1.Main Intersection Gene of Huangqi and Danshen
The GO annotation and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis were obtained by introducing the intersection gene into the Metascape platform, see Figure 3.It is concluded that the pathway involved in the intervention of Huangqi and Danshen in vascular healing is mainly as: AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications, MAPK signaling pathway, Pathways in cancer, human cytomegalovirus infection, Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis, Endocrine resistance, foxo signaling pathway etc.as shown in Table 2.

Table 3.Compounds directly targeting VEGF in Huangqi and Danshen
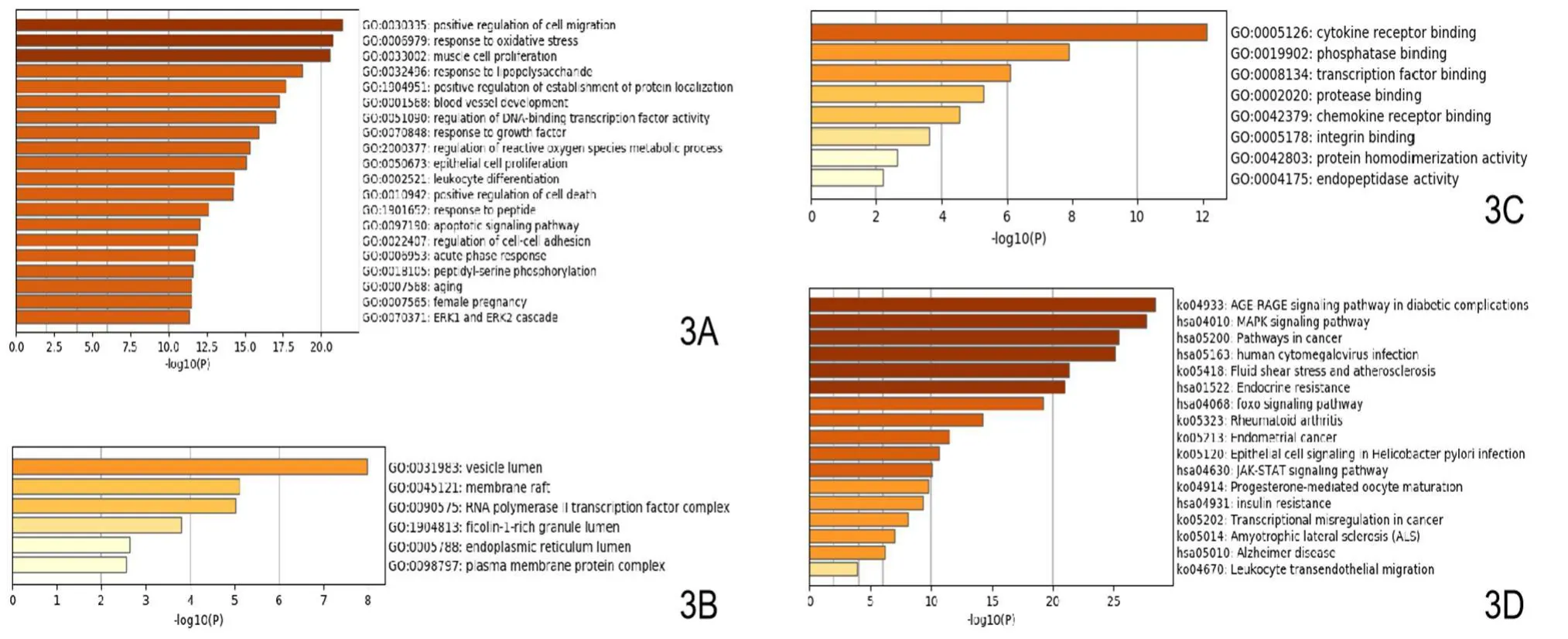
Figure 3.The GO annotation and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis.
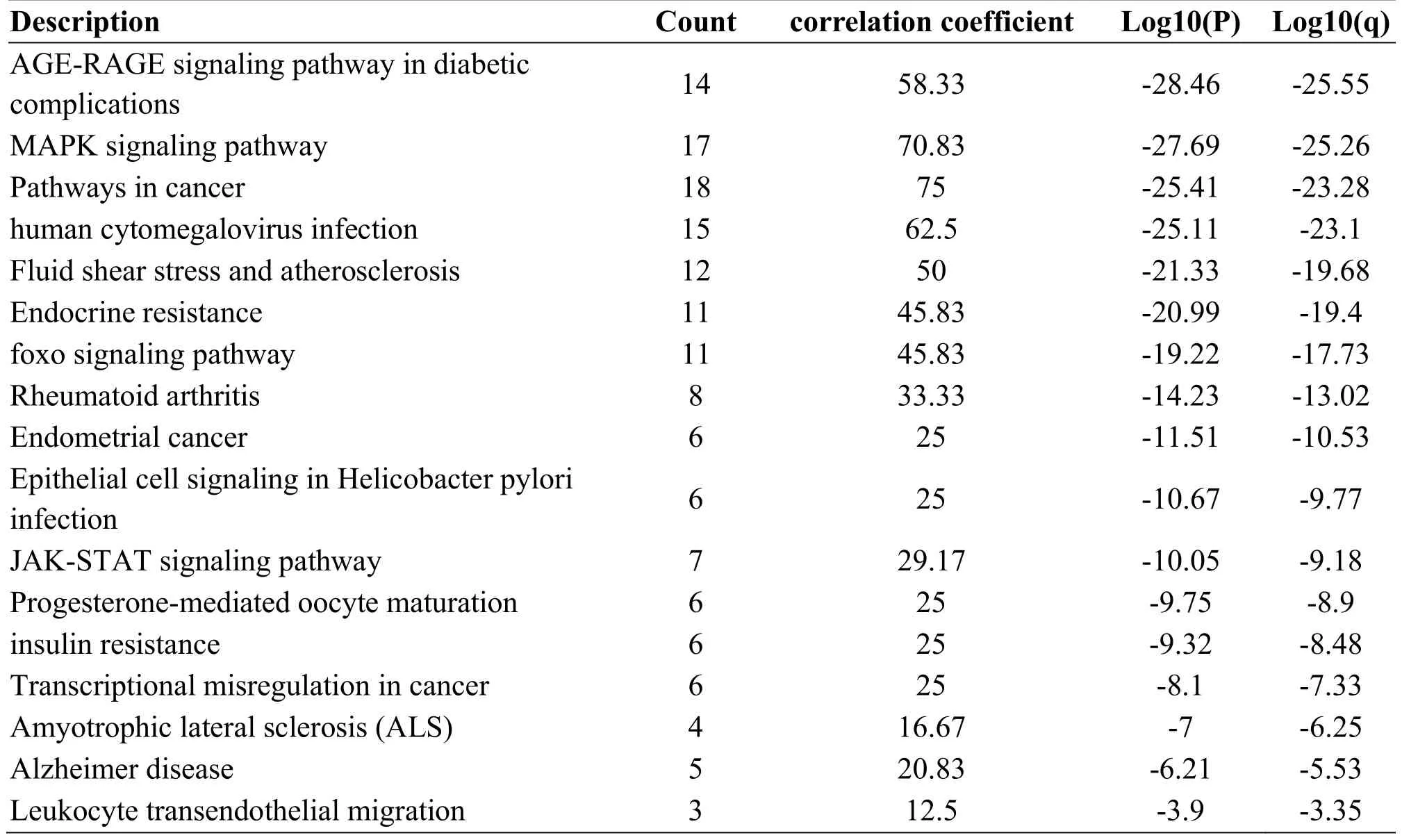
Table 2.KEGG analysis results of the main intersection genes of Huangqi and Danshen and vascular injury
Effect of Huangqi and Danshen Ultramicro Granule Gel on Wound Healing in Rats
Materials and instruments
AnimalsThere are 90 healthy SD rats aged 8-10 weeks, half male and half female, body quality 225-250g, purchased from Shanghai BK Co., Ltd.Experimental Animal Certificate No.ACXK (Shanghai)2018-0198.Animal feeding and disposal are carried out in the Animal Experimental Research Center of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University.The feeding environment is quiet, natural lighting, room temperature 22-26℃.The experimental scheme was approved by the Medical Animal Experimental Ethics Committee.
Reagents and InstrumentsHuangqi and Danshen were purchased from Binjiang Medical Clinic, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University; Sodium pentobarbital (Shanghai Chemical Reagent Company); 4% paraformaldehyde; HE staining kit; Immunohistochemical reagent antibody-ARC10513 anti-VEGF antibody; ab64238 DAB of antibodies; Immunohistochemical pen; goat serum (Shanghai Silk Dragon Biotechnology Co., Ltd); Sodium hyaluronate injection(Shandong Ph.D.Renfreda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd); ALLEVYN Wet application (Smith & Nephew); RM -2015 paraffin cutter;LEICADM500 triocular biological microscope; FSX-10-15 Image Signal Acquisition and Analysis System (Leica); DNP-9162 thermostatic incubator (Shanghai Yiheng Scientific Instruments); photon microscope (Olympus); Tissue-Tek VIP5Jr tissue dehydrator (Sakura); KP-90N integrator (KOIZUMI).
Methods
Preparation of Huangqi and Danshen Ultrafine GelThe pieces of Huangqi and Danshen were sent to Shandong Jinan Da Micro Machinery Co., Ltd., and the pieces were processed into ultrafine particles of 3μm diameter with XDW-6 low temperature cell grade ultrafine pulverizer, and mixed well according to the quality ratio of 1:1.The mixture of Haungqi and Danshen granules and sodium hyaluronate injection were mixed in proportion of 50 mg:2mL to make gel preparation, sealed, 0.5g per bag.The prepared gel preparation was sent to the Institute of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences of Zhejiang University for cobalt 60-γ radiation disinfection.The radiation standard was carried out in accordance with the "60 Co irradiation dose Standard for traditional Chinese Medicine" issued by the Ministry of Health in 1997.
Animal grouping and modellingThe rats were divided into model group, control group and gel group with 30 rats in each group.After 2 weeks of routine feeding, 3% pentobarbital sodium was injected intraperitoneally (1.5 mL*kg-1).Referring to the whole skin defect method of Zhao Jingyu [12], a circular whole skin with a diameter of about 1.8 cm was made on the back of the rat to remove the open wound and reach the fascia.
Experimental interventionGauze was used to stop bleeding, iodophor was used to disinfect the wound.The wound in the model group was bandaged with sterile gauze, the wound in the control group was bandaged with ALLEVYN Wet application, the wound in the gel group was smeared with 0.5g Huangqi and Danshen Ultrafine Gel and then wrapped with sterile gauze.After the rats were awake, they were fed in groups, fed freely and drank water, and changed medicine and applications every two days.
Sample collectionSix rats were randomly selected from each group on day 1, day 3, day 7 and day 11.The wound was covered with acetic acid paper and marked with marker along the edge of the wound.The picture was saved to calculate the wound healing rate.Then 1% pentobarbital sodium was injected intraperitoneally, the whole skin tissue was cut along the normal skin wound edge of the rat.On the 15th day after modeling, the wound range of the remaining 6 rats in each group was recorded according to the above method, and the rats were killed after the wound was completely healed.
Determination of experimental indicators
Wound healing rateThe area marked on acetic acid paper was measured by quadrature instrument, and the wound healing rate was calculated.Wound healing rate = [(Wound area at first-Wound area at last/wound area at first] ×100% [13].
Number of new capillaries in wound tissue After 24h, the whole skin tissue was fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, ethanol gradient dehydration, and then embedded in paraffin.Before HE staining, the slices were placed in a 60℃ thermostatic oven for 2 h.The steps are as follows: xylene dewaxing 3 times, 5 mins every time, ethanol gradient dehydration.After dewaxing and dehydration, wash them 2 times by pure water, 3 mins every time, dyeing for 5 mins of hematoxylin dye and pure water rinse.Then differentiated with 1% ethanol hydrochloride for several seconds, staining by 0.5% eosin solution for 1-3 mins.The final step is dehydration seal.Each slice takes images of 10 fields in a 200x magnifier, statistics the number of newborn capillaries and its mean value.
Content of vascular endothelial growth factor in wound repair tissueParaffin sections were dewaxed and rehydrated and incubated with PBS buffer for 5 mins.The antigen surface was repaired with 3% hydrogen peroxide solution in the slice, and the wet box was incubated for 10 mins and washed with PBS for 3 times, 5 mins every time.The residual hydrogen peroxide was washed.Place the slice in 0.01 mL citrate buffer, keep the medium firepower of microwave oven to boiling, keep boiling for 8 mins, and then drop to room temperature, repeat twice.Wash for 5 mins by PBS, add 10% goat serum, close in wet box for 30-60 mins at room temperature and a drop of anti-working fluid, incubate overnight in the refrigerator at 4℃.After removing the resistance, the next day, clean it with PBS, add the II Anti-working fluid.Wash using PBS after 30 mins incubation at room temperature, DAB hematoxylin redye for 2-5 mins after color development.Then differentiated with 1% HCl for a few seconds, dehydration seal after washed with flowing water.Observe and ingest the image under microscope.Based on brown - yellow particles in cytoplasm and membrane, determinate the content of vascular endothelial growth factor using optical density method in Image Pro Plus software.
Statistics analysisSPSS24.0 software was used for statistical analysis of data.Single factor ANOVA was used to compare the wound healing rate and the number of new capillaries and VEGF contents in the wound repair tissues of the three groups at different time points after modeling, and LSD-t test was used to compare the two groups.Inspection level α = 0.05.
Results of experiment
Wound healing rateOn the first day after the model was established, there was still blood leakage in the wound surface of rats in each group, and edema was seen on the edge of the wound, as shown in Figure 4A.On the 3rd day after modeling, most rats had no active bleeding, local swelling subsided, the wound was clean and dry, and no obvious inflammatory reactions such as redness, swelling and heat were found.Compared with the other 2 groups, the edge fold of the wound in gel group was more and the contraction was obvious.On the 7th day after modeling, the wounds of each group were scabbed, the scab was dark black, and the soft tissue around the scab in the gel group was wrinkled and the scab area was smaller than that in the other 2 groups.On the 11th day after modeling, the wounds of the gel group were healed, only a small amount of scab was attached, and the remaining 2 groups were left with scab surface.On the 15th day after modeling, the wounds of the gel group were all healed, and the wounds were covered with hair.The wounds of the other 2 groups were not healed, and a small amount of scab was still seen in the wounds.At the end of the experiment, the wounds of the three groups were healed, and there was no wound infection and death.On the first day after modeling, there was no obvious change in the wound surface of each group, and the wound healing rate was not calculated.There were significant differences in wound healing rate between the 3rd, 7th, 11th and 15th days after the model (P< 0.05).The 3rd, 7th, 11th and 15th days after modeling, the wound healing rate of gel group was higher than that of model group (P< 0.05).The wound healing rate of the control group was higher than that of the model group on the 3rd day after the making (P< 0.05).On the 7th, 11th and 15th model group and control group, the difference of wound healing rate was not statistically significant (P> 0.05), as shown in Figure 4B.

Figure 4.Healing state of rat skin at different time points.
Number of new capillaries in wound repair tissueOn the 3rd day after modeling, a large number of inflammatory cell infiltration was observed in the wound repair tissue of the model group, mainly neutrophils, macrophages and so on.There were more neutrophils in the wound repair tissue of the control group, and a large number of inflammatory cells infiltrated in the wound repair tissue of the gel group, mainly neutrophils, and a few lymphocytes and macrophages scattered in the wound repair tissue.The number of new capillaries was more than that of the other 2 groups, see Figure 5A.On the 7th day after modeling, the number of new capillaries in gel group was more than that in in the other 2 groups, and the number of new capillaries in the control group was significantly increased than before.At the other time points, there was no significant difference in HE staining results of wound repair tissue in group 3.
On day1, day3, day7 and day11, the total number of new capillaries in wound repair tissues of the 3 groups were statistically significant (P< 0.05).On days 1, 3, 7 and 11, the number of new capillaries in the wound repair in gel group was higher than that in model group (P< 0.05).There was no significant difference between model group and application group in the number of new capillaries in wound repair tissues (P> 0.05), see Figure 5B.
Content of VEGF in wound repair tissueImmunohistochemical staining showed that in the three groups of rats on the third day after modeling, the VEGF content in the wound tissue of the gel group was significantly higher than that of the other two groups, as shown in Figure 6A.VEGF contents in wound repair tissues of 3 groups were statistically significant on day 1, day 3, day 7 and day 11.At the 1st, 3rd, 7th and 11th days after mold making, the content of VEGF in repair tissue in gel group were higher than those in model group and control group (P< 0.05).At the 1st and 3rd day after mold making, there was no statistically significant difference in VEGF content between model group and control group (P> 0.05).At the 7th and 11th day, the VEGF content of wound repair tissue in the application group was higher than that in the model group (P< 0.05), as shown in Figure 6B.
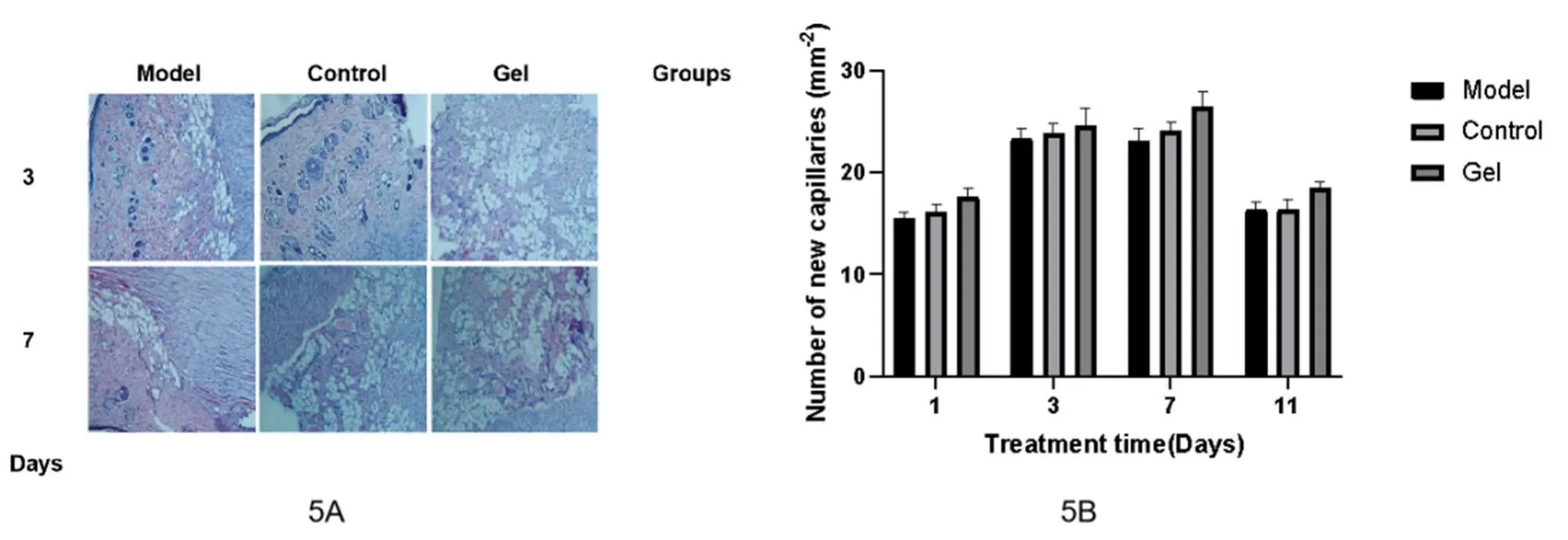
Figure 5.Angiogenesis of the rat wound at different time points.
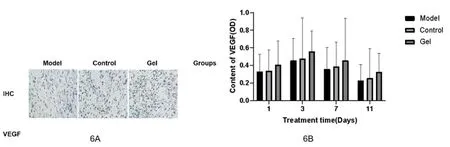
Figure 6.Expression content of rat wound tissue VEGFA at different time points.
Discussion
In traumatic diseases, the repair of blood vessels has a very important significance for the prognosis of trauma.Considering the existing database analysis, VEGF is the most important factor of vascular repair in trauma.Existing treatments are focused on the development of exogenous growth factors, and we believe that some components of Chinese herbal medicine can promote the secretion of endogenous growth factors and promote the repair of vascular damage.
Huangqi and Danshen is a common combination of traditional Chinese medicine prescriptions.In their studies of these two herbs, researchers have confirmed that some components of Huangqi and Danshen can promote the formation of growth factors and cytokines in human body.Especially for vascular repair factors such as VEGF, TNF, IL-6, FGF, EGF and so on [14-17].The potential compounds in herbal medicines play a further cytological role, and the extracts of both herbs or herbs often appear in prescriptions for cardiovascular diseases, cerebrovascular diseases and microcirculation disorders [18, 19].At present, there are no reports of Huangqi and Danshen in the treatment of chronic refractory wound.Our clinical experience suggests that some components of these two drugs may contribute to wound vascular healing.Reviewing the results of network pharmacology, we have predicted and screened 5 compounds that may act directly on VEGFA and promote wound healing (Table 3).
The GO annotation analysis of the network pharmacology of Huangqi and Danshen suggests that compounds may be involved in positive regulation of cell migration; response to oxidative stress; blood vessel development etc.In cells, these compounds are involved in the isobiological process such as cytokine receptor binding; phosphatase binding; transcription factor binding; protease bindin etc.Therefore, the action of these compounds is multi-pathway.Although our later results verified that these compounds can promote the expression of VEGFA, they cannot be regarded as a single target.The mechanism of action is multi-pathway, multi-target, multi-effect, and the final comprehensive manifestation is to promote the healing of blood vessels in the wound.For the final KEGG analysis, the pathway in which these compounds act most like AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications; MAPK signaling pathway; Pathways in cancer; human cytomegalovirus infection; Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis etc.These pathways provide a possible basis for the mechanism of action of compounds in Huangqi and Danshen, but because of our limited work funds, it is not possible to verify and analyze all these pathways through experiments.
As one of the targets of the compounds in Huangqi and Danshen, VEGFA is of great significance for the repair of vascular injury in the wound, especially for those chronic refractory wounds.The compounds in these herbs can provide possible solutions for the treatment of such diseases.Huangqi and Danshen are often used as an oral drug in clinic, but these two herbs are used as external drugs in this study, so the fatsoluble components are chosen as far as possible in the screening of related compounds.On the preparation of drugs, we comminuted the root tissue of Huangqi and Danshen into particles < 3μm in diameter.At the same time, we used gel preparation to mix with particles.The active components in the gel are more easily diffused on the wound surface and absorbed through the wound tissue.This study showed that VEGFA is one of the main targets for the repair of blood vessels in the wound, but the significance of other targets remains to be further verified.
Additionally, in network pharmacology, like VEGFA, we note that many growth factors are enriched as targets of compounds.As the main binding body of receptor protein tyrosine kinase, RPTKs, growth factor has some specific biological significance and has an important effect on cell migration and the expression of various proteins in cells [20, 21].The pathway of RPTKs/cofilin proteins, growth factor binding binds to their respective RTKs and activates PI3K, transforming PIP2 into an activity that deprives the PIP2 of binding Cofilin [22].Because of this mechanism, Cofilin can induce the formation of cell membrane protrusions by aggregating around the cell membrane, thus mediating cell movement, which also provides the basis for cell movement in angiogenesis [23, 24].Therefore, the potential of these compounds can be involved in the treatment of various human injury diseases, there is also a lot of research space in the proliferation and differentiation of tumor cells [25].We will pay more attention to this mechanism in the future and further study the effect of compounds in Huangqi and Danshen on human trauma diseases.
Although due to the limitations of the experiment, we only selected VEGF related to vascular repair as the verification index.In fact, in the process of vascular repair, Huangqi and Danshen are carried out through multi-target and multi-channel.For example, the targets, we screened, include IL6, AKT1, INS, VEGFA, TNF, EGF, CASP3, mapk1, TP53, etc.Recent studies have pointed out that IL6/STAT3/VEGFA pathway is of great significance to angiogenesis, so drug development often looks for important targets in this pathway.In addition, it also has a similar effect on angiogenesis by promoting the expression of EGF [26, 27].Chronic inflammation is also unfavorable to vascular regeneration.The increased expression of TNF and IL6 can inhibit vascular tissue regeneration, such as TNF-α.It can promote the expression of endothelial cell adhesion factor and the excessive synthesis and release of vasoactive substances, resulting in vascular endothelial injury and increased permeability [28].The deactivation of AKT1 in vascular tissue is also of great significance for vascular remodeling.It often acts together with Nitric oxide synthase, eNOS to reconstruct vascular endothelial cells [29].Based on our results, the active components of Huangqi and Danshen have targeted effects on many factors in wound healing, including coagulation stage, inflammation stage, granulation tissue formation stage and tissue remodeling stage.Experimental verification also confirmed that VEGF, an important factor throughout vascular repair, is the target of Huangqi and Danshen, which is also the main reason for Huangqi and Danshen gel to promote vascular healing.In addition, our study also confirmed that Huangqi and Danshen have potential to repair many traumatic diseases.
Conclusion
A total of 115 active components and 297 target genes were selected from Huangqi and Danshen, and 123 target genes were intersected with vascular injury, among which IL6, AKT1, INS, VEGFA, TNF, EGF, CASP3, MAPK1, TP53 were the active genes with the highest intersection value.The pathways involved are mainly related to AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications, MAPK signaling pathway, Pathways in cancer, human cytomegalovirus infection, Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis, Endocrine resistance, foxo signaling pathway etc.We experimentally validated VEGFA based on the primary target of vascular regeneration, the experimental results showed that there was different expression of VEGFA proteins in wound vascular healing process, and the quercetin, daidzein, luteolin, apigenin, tanshinone i of 115 active components were selected as the main compounds acting on the VEGFA.Huangqi and Danshen can be used as a new natural drug for traumatic vascular diseases and has certain potential.
Data Availability Statements
Participants of this study did not agree for their data to be shared publicly.
杂志排行
TMR Modern Herbal Medicine的其它文章
- Guizhi-Fuling formula inhibits ovarian cancer progression by targeting STAT3 signaling network
- Differential expression of exosomal circRNAs and regulatory framework genes in myocardial infarction patients with cardiac remodeling in response to Tongguan Capsules
- Application of Chinese Herbal Medicine in the lnhibition of Salmonella and its virulence
- Network pharmacology-based analysis on bioactive compounds and mechanisms in Yiqifumai formula in the treatment of heart failure
- The clinical efficacy of traditional Chinese medicine in the auxiliary treatment of grade 1 hypertension: A systematic review and metaanalysis
- lncreased macrophage inflammation response in pancreatic cancer patients with a diagnosis of Shi-Re
