Retina stem cells, hopes and obstacles
2021-11-02OlgaGermanHarmonieValleseMauriziTamaraSotoNoraRotsteinLuisEnriquePoliti
Olga L German, Harmonie Vallese-Maurizi, Tamara B Soto, Nora P Rotstein, Luis Enrique Politi
Olga L German, Harmonie Vallese-Maurizi, Nora P Rotstein, Department of Biology,Biochemistry and Pharmacy, Universidad Nacional del Sur, Bahia blanca 8000, Buenos Aires,Argentina
Olga L German, Harmonie Vallese-Maurizi, Tamara B Soto, Nora P Rotstein, Luis Enrique Politi,Department of Biology, Biochemistry and Pharmacy, Universidad Nacional del Sur, and Neurobiology Department, Instituto de Investigaciones Bioquímicas de Bahía Blanca(INIBIBB) Conicet, Bahía Blanca 8000, Buenos Aires, Argentina
Abstract Retinal degeneration is a major contributor to visual dysfunction worldwide.Although it comprises several eye diseases, loss of retinal pigment epithelial(RPE) and photoreceptor cells are the major contributors to their pathogenesis.Early therapies included diverse treatments, such as provision of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor and many survival and trophic factors that, in some cases, slow down the progression of the degeneration, but do not effectively prevent it. The finding of stem cells (SC) in the eye has led to the proposal of cell replacement strategies for retina degeneration. Therapies using different types of SC, such as retinal progenitor cells (RPCs), embryonic SC, pluripotent SCs (PSCs),induced PSCs (iPSCs), and mesenchymal stromal cells, capable of self-renewal and of differentiating into multiple cell types, have gained ample support.Numerous preclinical studies have assessed transplantation of SC in animal models, with encouraging results. The aim of this work is to revise the different preclinical and clinical approaches, analyzing the SC type used, their efficacy,safety, cell attachment and integration, absence of tumor formation and immunorejection, in order to establish which were the most relevant and successful. In addition, we examine the questions and concerns still open in the field. The data demonstrate the existence of two main approaches, aimed at replacing either RPE cells or photoreceptors. Emerging evidence suggests that RPCs and iPSC are the best candidates, presenting no ethical concerns and a low risk of immunorejection. Clinical trials have already supported the safety and efficacy of SC treatments. Serious concerns are pending, such as the risk of tumor formation, lack of attachment or integration of transplanted cells into host retinas,immunorejection, cell death, and also ethical. However, the amazing progress in the field in the last few years makes it possible to envisage safe and effective treatments to restore vision loss in a near future.
Key Words: Retina regeneration; Stem cells; Retina stem cell transplantation; Cancer stem cells; Photoreceptor replacement
INTRODUCTION
Stem cells (SC) are rather undifferentiated cells present in most tissues of nearly all multicellular organisms, from humans[1-3],to plants[4-6], having the amazing capacity to either activate self-renewal or differentiate into specific cell types[7].Hence, they are potentially capable of regenerating whole tissues or organs subjected to ablations or damages. This capacity varies between species. It is particularly remarkable in Platyhelminthes, such as the planarian worms, which when beheaded can regenerate their entire bodies in just a few days[8-10]. Many cold-blooded species retain a considerable regenerative capacity; some teleosts, like zebrafish, can regenerate their limbs, spinal cord, retina, heart and brain. By contrary, regenerative capacity in mammals is quite restricted[11,12].
SC have attracted great attention due to their potential for regeneration and knowledge about them has increased enormously in the last few years. Most SC have a rather simple morphology, resembling undifferentiated cells, and essentially, they have the same organelles and molecular machinery present in most eukaryotic cells.However, embryonic pluripotent SCs (PSCs) are capable during development of an extraordinary feat, to give rise to nearly all the cell types present in the body. In addition, after ablations or injuries to a given tissue, they activate a complex response leading to their reentry into the cell cycle and, eventually, to the activation of a differentiation pathway, acquiring the morphology and functions of the cells of the damaged tissue, thus being able to replace lost cells.
Based on their capacity for differentiation, SC can be classified either as unipotent,multipotent, pluripotent or totipotent. Whereas unipotent SC, such as epidermal or muscle SC, are able to generate only one type of cells upon differentiation[13,14],multipotent SC can generate a very limited amount of cell types, belonging to a closely related cell family[14], as usually is the case of adult SC. Müller glial SC in the retina belong to this group, as they potentially differentiate into just one or two retinal neuronal cell types and Müller glial cells (MGCs). PSCs, such as embryonic SC (ESCs)in the inner cell mass of the blastula, may differentiate into nearly all the cell types,while totipotent SC, like the zygote and the first few cells derived from it during zygote segmentation, have the highest capacity for differentiation and can give rise to all the cell types of an organism (Figure 1).
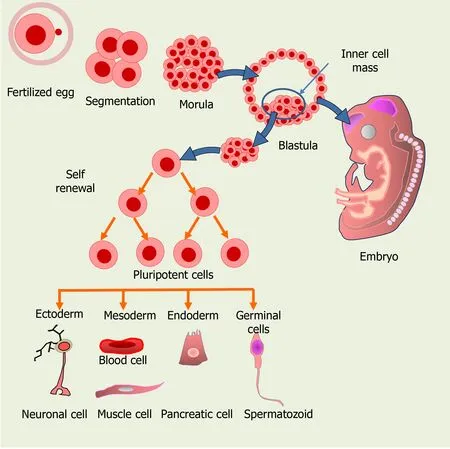
Figure 1 Origin of the different cell types from embryonic stem cells (ESCs) in the developing embryo. ESCs from the inner cell mass of a preimplantation embryo can give rise to all the cell types and to an entire organism.
Based on their source, there are two main types of SC, ESC and adult (mature) SC.ESCs are included in a family of Stem/progenitor cells found in 3-5 d old embryos,which includes retinal progenitor cells (RPCs) and mesenchymal stromal cells. ESCs are pluripotent cells that can give rise to cells of the three embryonic germ layers:ectoderm, endoderm or mesoderm, and can generate all tissues in the body.
A major breakthrough in SC research was achieved less than a decade ago; the introduction of a few SC specific genes, such asMyc,Sox2, Oct3/4andKlf4, induced somatic cells to acquire the morphology, characteristics, and markers of SC, thus being defined as induced PSCs (iPSCs). Their transplantation in nude mice generates tumors exhibiting tissues from the three germ layers[15], suggesting they may be used for cell replacement therapies.
Mature SC are present in small amounts in adult, differentiated tissues; these multipotent cells can give rise to a few types of specialized cells[2]. Mature SC are also found in the umbilical cord and placenta after birth. They also include hematopoietic SC (HSC) from bone marrow (BM), peripheral blood or umbilical cord blood, and are commonly used for transplantation, one of their advantages being that they rarely generate unwanted cell types.
The most relevant features of SC are their ability for self-renewal and for giving rise to multiple cell types. A very active SC self-renewal occurs during the first stages of development, both in the morula and in the inner mass of the blastula to generate the new cells required for the developing organism (Figure 1). Later, SC can activate in damaged tissues, proliferating and then differentiating to replace lost cells. In addition to the “ready to use” pool of undifferentiated SC, some differentiated cells may eventually undergo a dedifferentiation process, reentering the cell cycle and becoming“active” SC. To regain the proliferating capacity, they repress genes required for cell differentiation, activating those required for a proliferative, undifferentiated state[16].
Noteworthy, SC are similar to cancer SC in their ability to self-renew and generate large populations of more differentiated descendants; they also share the phenotypic plasticity that allows them to enter or exit the cell cycle, an ability closely associated with the stemness properties and invasiveness of cancer cells[17]. These morphological and functional similarities compromise current therapeutic efforts, as SC transplantation very frequently leads to deregulation of the mitotic cell cycle and tumor formation[18,19].
The ability of SC to repair damaged tissues and regenerate lost cells has encouraged scientists and clinicians to explore their use to treat or cure different diseases.However, many issues have still to be unraveled before using SC safely in humans.The aim of this review is to analyze the characteristics and potential advantages of using SC for treating retina neurodegenerative diseases, and the risks that remain to be addressed before using these cells in the clinic.
RETINAL DEGENERATIONS AND TREATMENTS
Contrary to early beliefs, nerve tissues in many animals, including mammals, have SC able to give rise to new neurons[20-23], sparking the hope for regenerative approaches to neurodegenerative diseases. However, at least presently, it seems nearly impossible to regenerate the brain as a whole. Humans have about 1011neurons with different morphologies and multiple functions[24], which added to the complex interactions among the different neuronal types, and between neurons and other cell types (i.e.,glial cells), imposes tremendous limitations for brain regeneration.
Retinal degeneration (RD) represents one of the most common causes of irreversible vision impairment leading to blindness worldwide. It comprises several eye diseases,including age-related macular degeneration (AMD), diabetic retinopathy, Stargardt’s disease and retinitis pigmentosa (RP). Among them, AMD is the leading cause of severe vision loss in people over 60 years old, with a global prevalence of 8.7 %, and it currently affects about 200 million persons in western world countries[25]. In spite of the numerous differences between these diseases, dysfunctions of RPE and photoreceptors (PHRs) are the major contributors to their pathogenesis[26].
The retina is part of the central nervous system (CNS); fortunately, its structure is simpler than that of the brain, making its regeneration more feasible. The retina is responsible for receiving light and transforming it into electrical signals that travel to the brain, where visual images are generated. It is a thin tissue of easy access, located in the back of the eye, with an ordered layered organization and a limited number of cells. These features make it possible to use SC to develop strategies for alleviating or,eventually curing, retinal neurodegenerative diseases.
Moreover, and in contrast to other organs of the body, the eye is a relatively immune privileged organ, which supports the likelihood of retina transplantation[27-29].The ocular immune privilege, which is intended to limit local immune and inflammatory responses, can also contribute to avoid the rejection of grafts placed in the anterior chamber of the eye and protect the eye from inflammatory insults[30,31].However, this protection is not absolute and this must be taken into account in cell replacement strategies. Treatments using iPSCs may activate immune rejection, as they can upregulate genes that induce a T cell response, and thus lead to the rejection of transplanted cells. Since the molecular mechanisms involved in these processes are incompletely understood[32], many studies resort to immunosuppression to reduce the risk of rejection[33]. Increasing our knowledge of the molecular processes that inhibit immune rejection of transplants would contribute to elaborate new strategies to facilitate the acceptance of tissue allografts during retinal transplantation.
SC therapy and neural regeneration
The initial efforts to treat RD were oriented to halt degenerative processes of the retina.The proposed therapies included a variety of medical compounds and treatments,including several neurotrophic factors, aimed at controlling oxidative stress and cell death[34,35] or anti-vascular endothelial growth factor agents, to prevent the formation of leaky blood vessels, mainly used to treat wet AMD[36].However, these strategies pose diverse difficulties. In wet AMD, treatments to avoid or minimize choroidal neovascularization, very frequently cause complications, such as uveitis and vitreous hemorrhages, which compromise their effectiveness. On the other hand, the clinical efficacy of the neuroprotective strategies has not been firmly established.Furthermore, surgical interventions like laser therapies may not prevent the progression of the disease in patients with AMD or other RD and can cause inflammatory-related damages[37-39].
The finding of SC in the retina has provided additional tools to develop strategies for repairing the damaged retinas. Therapies using different types of SC, such as stem/progenitor cells, RPCs, PSCs, ESCs, iPSCs, and mesenchymal SCs (MSCs),capable of self-renewal and of differentiating into multiple cell types, have now gained ample consensus. Numerous preclinical studies using SC in several animal models of RD have been performed and their results are encouraging. Emerging evidence suggests that RPCs are among the best candidates for RD treatment; they do not present ethical concerns and they have a relatively low risk of tumorigenesis and immunorejection[40]. Moreover, increasing evidence suggests that the combination of SC therapies with the provision of survival molecules might provide the best strategy to treat RD.
Regeneration following retina damages might require the recapitulation of developmental specification/differentiation programs. Following PHR damage, zebrafish retina evidences an increase in the expression of several developmental competence factors, required for generating ganglion, amacrine, and PHR cells[41]. Retinal injury might turn on cell specification programs in neuronal progenitor cells, which recapitulate the temporal expression sequence occurring during retina development and hence provide precursors suitable for replacing lost cells. A critical question is,which are the features that characterize and distinguish SC from other cells present in the organism? Cumulative evidence indicates that their extraordinary capacities depend, in part, on complex interactions between cell surface proteins and a variety of external and internal signals that activate signaling pathways to regulate pluripotency.These external signals include LIF/STAT3, Wnt/β-catenin, FGF/ERK, TGF/SMAD,bone morphogenetic protein (BMPs), Sonic Hedgehog, and the Wnts and Notch proteins[42].
The internal regulatory system comprises many transcription factors, such as Oct4,Sox2 and Nanog, which interact with specific target genes that regulate self-renewal and pluripotency[43,44] (Figure 2).Oct4(also known asOct3oPou5f1) controls the Sox2 transcription factor, involved not only in self-renewal of SC, but also in embryo development. Sox2 maintains SC in an undifferentiated state, after concluding embryo development[45,46], being important also for regulating proliferation and differentiation of neuronal SC progenitors[47,48]. In addition, both Sox2 and Oct4 interact upstream with the promoter of Nanog, another transcription factor, activating different genes that inhibit differentiation[49,50] (Figure 2). Nanog is involved in the self-renewal of ESC and is critical for maintaining pluripotent cells in an undifferentiated state[51]. Interestingly, genetic deletion of Nanog in ESCs does not abolish pluripotency, although it reduces cell self-renewal activity. As a general rule, Nanog prevents SC differentiation, so it is considered a guardian of pluripotency[50].
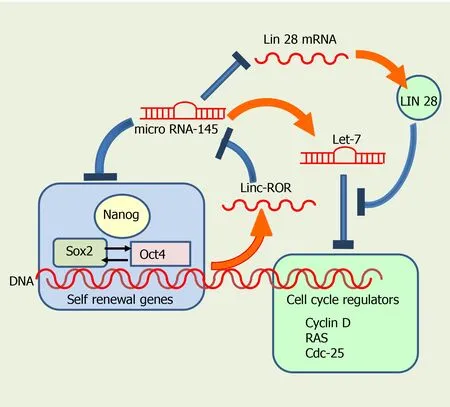
Figure 2 Regulatory control of self-renewal and differentiation by transcription factors and microRNAs. Oct4, Sox2 and Nanog prevent microRNA-145 from blocking the self-renewal of SC. Conversely, microRNA-145 promotes cell differentiation by inhibiting expression of Oct4, Sox2 and Nanog. Let-7, another microRNA, promotes differentiation by interfering with cell cycle regulators, and is regulated in turn by microRNA-145 and Lin 28.
In addition, epigenetical regulation of global changes in genetic expression control SC rate of mitosis, along with other morphological and physiological changes.Acetylation or methylation of H3 and H4 histones regulate the distribution of active and inactive forms of chromatin, and consequently genetic transcription in mouse pluripotent cells. Noteworthy, mouse ESCs have poised (bivalent) domains containing both active and inactive forms of chromatin; hence, poised chromatin has histone modifications associated with both gene activation and repression[52]. Most bivalent domains are associated with the so called, highly conserved noncoding elements,found in clusters around different genes, including many transcription factors implicated in the regulation of cell differentiation during development[53]. Some of these transcription factors are members of the Sox, Fox, Pax, Irx and Pou families.Bivalent domains in SC are thought to maintain stemness by equilibrating the expression of relevant genes involved in differentiation, whereas signals released during development give way to an irreversible differentiation process[54].
Sox2 binds to bivalently marked promoters of poised proneural genes in neural progenitor cells and a subset of other genes, to maintain the bivalent chromatin state,and prevent excessive polycomb repressive complex 2 activities. It decreases the trimethylation of H3 on lysine 27 (H3K27me3) through histone methyl transferase activity. H3K27me3 often interacts in bivalent domains with H3K4me3, another epigenetic modification to H3, which plays a significant role in SC fate determination and early embryo development. Thus,Sox2maintains a permissive epigenetic state,enabling proper activation of the neuronal differentiation program under suitable neurogenic cues[55]. Therefore,Sox2plays an essential role in preserving pluripotency of SC and its interplay withOct4andNanoggenerates a network that preserves the pluripotent state of SC.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are also major regulators of self-renewal and differentiation,modulating the expression of genes involved in cell cycle progression and pluripotential state. Several miRNAs have been proposed to target transcripts that, directly or indirectly, coordinate cell cycle progression in embryonic, somatic and cancer SC.Among these miRNAs, miRNA (MiR)-290-295, miR-302, miR-17-92, miR-106-b25 and miR-106a-363, together with members of the let-7 family, regulate ESC cell cycle,mostly by facilitating the G1/S transition[56,57].
MiRNAs also participate in regulating and promoting SC differentiation (Figure 3).miR-145 is important during hESCs differentiation, having the pluripotency factors Oct4, Sox2, and Klf4 as direct targets (Figure 3). Overexpression of miR-145 Leads to repression of the 3' untranslated regions ofOct4, Sox2, and Klf4, thus inhibiting selfrenewal and promoting differentiation. Interestingly, Oct4 binds to miR-145 promoter and inhibits its transcription in hESCs, acting as a negative loop[58].

Figure 3 microRNA-145 and transcription factors Sox2, Oct4 and Nanog regulate cell renewal and differentiation. Sox2, Oct4 and Nanog interact with microRNA-145 to regulate cell cycle and differentiation of stem cells.
MiR-145 promotes neuronal differentiation and regulates neural SC by repressing the expression of sex determining regionY-box2, andSox2(Figure 2), along with that of Lin28, a well-characterized RNA binding protein and a pluripotency promoter,which suppresses the biogenesis of let-7 miRNA. MiR-145 also upregulates let-7a and let-7b during neurogenesis[59]. In turn, the let-7 family inhibits proliferation by interfering with cell cycle regulators such as RAS, Cyclin D, and CDC25. Pos-transcriptional regulation of let-7 by Lin28 appears to be required for normal development.Moreover, let-7 might have a central role in the regulation of ‘stemness’, by repressing self-renewal and promoting differentiation, not only during normal development, but also in cancer cells[60,61].
Exogenous LIN28 expression has been shown to suppress Let-7 activity, thus reverting inhibition of cell proliferation in human neural progenitor cells[61-65](Figure 2). Moreover, Sox2 is required for preserving the expression of physiological levels of Lin28 in the developing neural tube[61]. Sox2 binds to a promoter region of LIN28, and promotes acetylation, by interacting with the histone acetyltransferase complex[61]. Collectively, these data imply that miRNAs and several transcription factors regulate self-renewal in SC, interacting very precisely to decide whether they continue in the cell cycle or start their differentiation.
Wanget al[66] established an additional mechanism for regulation of pluripotency,involving a large intergenic noncoding RNA (lincRNA), the linc-regulator of reprogramming, or linc-ROR, which belongs to a larger group of non-coding RNA(ncRNA). While the vast majority of the mammalian genomic DNA is transcribed, the largest fraction are ncRNAs, as only a small fraction are protein-coding genes. In addition to the well-known transfer RNAs, ribosomal RNAs, and miRNAs, these ncRNAs include long ncRNAs (lncRNAs), which are longer than 200 nucleotides.
LincRNAs are transcribed from both strands of DNA in intergenic regions[67], and have both exons and introns. LncRNAs are shorter than lincRNAs, and they both have single-stranded sequences, able to form secondary structures[67]. LincRNA transcripts are generally found in the mammalian nucleus, while lncRNA transcripts are usually in the cytoplasmic region. LincRNAs regulate the transcription of neighboring genes by increasing or repressing transcriptional activation, and are believed to be involved in several pathologies. In contrast, the exact functions of lncRNAs are not fully established. Linc-ROR was the first identified linc-RNA; it promotes reprogramming of differentiated cells into iPSCs and maintains ESCs[68]. Noteworthy, linc-ROR interacts with several miRNAs and has been reported to be controlled byOct4,Sox2andNanogin iPSCs. The presence of binding sites for these pluripotency transcription factors in linc-ROR indicates they regulate its expression, and hence that of human ESC (hESC)[68]. In turn, linc-ROR has been shown to maintain hESC self-renewal by functioning as a “sponge”, trapping miR-145 and preventing miRNA-mediated suppression of the pluripotency factors Oct4, Nanog, and Sox2[66] (Figure 2).
Linc-ROR has also been proposed to modulate the reprogramming of human iPSCs[69]. LINC-ROR may also be oncogenic, having as a target the EF-hand calcium binding protein tescalcin, an oncogene significantly upregulated in ocular melanoma cell lines and animal models[70].
Most of the above described regulatory signals and mechanisms are operative in the retina. Our knowledge on the mechanisms regulating SC function in this tissue has enormously increased during the last two decades. Growth factors and signaling pathways, such as fibroblast growth factor (FGF2), epidermal growth factor (EGF),insulin growth factor (IGF), ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF), Wnt/β-catenin,Notch-Delta, and others, regulate the regenerative response in the retina, supporting and maintaining the status of endogenous SC by activating proliferation and reprogramming cells to replace injured or dead retinal neurons. Some inhibitory extracellular matrix or cell adhesion molecules, along with Bmp4 and other signaling pathways, often have the opposite effect[71]. Other systemic factors such as hormones,growth factors, cells of the immune system and blood, are regulators of the regenerative behavior of endogenous retinal SC[72].
Substantial evidence underscores the role of trophic factors in regulating SC activity.Early work evidenced the relevance of trophic factors in activating SC after injuries;several trophic factors and other molecules, including FGF2, EGF, SC factor,erythropoietin, and brain derived trophic factor (BDNF) increase adult neurogenesis by stimulating generation of new neuronal cells or improving their survival[73].Trophic factors usually contribute to improve the milieu in which SC proliferate;provision of an enriched environment to neural stem/progenitor cells promotes neurogenesis in the brain subventricular zone after inducing a cortical stroke[74].Furthermore, SC appear to contribute to enrich their own environment by releasing trophic and survival molecules. MSC secrete many survival factors such as EGF, IGF-1,FGF2, BMP-7, TGF-b1, and interleukin-6 (IL-6), among other factors, which protect injured cells[75-77]. These factors might regulate SC proliferation, migration, differentiation, and interactions after injuries. Interestingly, enriched environment has a neuroprotective effect in the retina in diverse animal models of pathological situations,such as glaucoma and ischemia reperfusion, preserving or increasing BDNF levels[78,79]; whether it also impacts on SC regulation is a pending question that demands further research.
Retina SC have profiles similar to those of RPCs at early stages of eye development.They respond to many well-known intracellular factors, including the transcription factors Pax6, Chx, Rx, Six, Sox, Prox, Pitx, and others[80-82]. Their regenerative potential is epigenetically regulated[83-85], and they are also influenced by trophic and survival factors. MGCs have been proposed as retina SC and our research group has established that trophic factors as glial-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), FGF2,insulin and IGF-1 increase their proliferation and expression of SC markers such as Pax6 and nestin. This implies that the intrinsic, but dormant proliferative capacity of these cells can be regulated by trophic factors and other environmental molecular cues[86] (Figure 4).
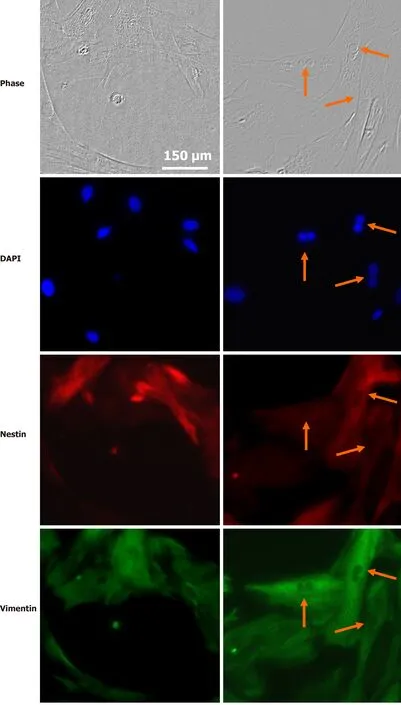
Figure 4 Stem cell properties of Müller glial cells. Photomicrographs of Müller glial cell cultures from rat retina in interphase (left) or mitosis (self-renewal)(right), showing nuclei labeled with the DNA probe DAPI, expression of the stem cell marker nestin (red) and of vimentin (green). Arrows indicate mitotic anaphases.The bar indicates 150 µm.
Interestingly, dental pulp SC, which originate from the neural crest, are able to differentiate into neurons when supplemented with EGF, FGF2, and retinoic acid[87].When transplanted intravitreally, they have been shown to secrete significant amounts of nerve growth factor, BDNF, neurotrophin-3, and GDNF, promoting neuroprotection and axon regeneration in retinal ganglion cells after axon injury[88-90]. Further research is required to identify the trophic factors required for preserving multipotentiality and proliferation in retina SC.
Transcription factors and miRNAs have been shown to control the formation of new retinal neurons derived from endogenous SC. Particularly, miRNAs are involved in controlling the ability of MGCs in non-mammalian and mammalian vertebrates to generate new RPCs[91]. In zebrafish, which, as mentioned before, effectively regenerates the retina after injury[92], miR-216a regulates reprogramming in MGCs,maintaining them in a quiescent state in undamaged retina. miR-216a suppression is necessary and sufficient for MGC dedifferentiation and proliferation, having the disruptor of telomeric silencing-1-like (Dot1 L) as a target; this miR-216a/Dot1 L regulatory axis mediates the initiation of retina regeneration through the Wnt/βcatenin pathway[93]. In addition, miR-9 has been recently identified in zebrafish MGC as a critical factor controlling retinal NSCs proliferation and fate[94], its depletion increasing the number of neural progenitors and neurons. miR-9 has different targets,including lin-28, which is necessary to promote the proliferation of retinal NSCs after injury[95], TLX and ONECUT mRNAs, which promote NSCs differentiation into neurons in both zebrafish and humans[94]. miR-9 might act as a negative regulator of the Sox2-Ascl1a/Atoh7-Lin-28 pathway to prevent MGC proliferation and as an activator of the TLX-ONECUT pathway for reprogramming endogenous MGC into functional retinal neurons[96]. Furthermore, miR-9 is involved in regulating mouse RSC differentiation through repression of polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 1(PTBP1) expression, which is a repressor for polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 2(PTBP2), during neuronal differentiation. Both proteins are highly expressed in the fetal stage and show lower transcript levels in the mature brain, retaining PTBT1 expression in glial cells and that of PTBP2 mostly in neurons[97]. miR-9 promotes the differentiation of neuronal cells from mouse RSCs, reducing the expression of PTBP1 and consequently increasing the expression of PTBP2[98]. Moreover, over-expression of miR-25 and miR-124, or let-7 antagonism induces the expression of proneural transcription factor Ascl1, a crucial regulator in retinal regeneration[99], and promotes the conversion of mature MGC into a neuronal/RPC phenotype[100].
In contrast to miRNA, most biological functions of lncRNAs are still poorly understood. They are believed to control key biological processes, including cell proliferation, apoptosis, differentiation, oxidative stress and inflammation, and have been shown to regulate SC maintenance and neural SCs proliferation[101,102]. In the eye,lncRNAs also appear to regulate SC maintenance, cell lineage commitment, and cellular phenotype differentiation[103] and have been involved in several ocular pathological conditions, such as glaucoma, proliferative vitreoretinopathy, diabetic retinopathy, and ocular tumors[104-107]. Interestingly, a retina-specific lncRNA,Vax2os, is involved in cell cycle progression in PHR progenitor cells during development of the mammalian retina[108,109]. Other lncRNAs, such as RNCR2[110],MIAT[111], and Gomafu have been found in the developing retina[112]. MIAT plays a critical role in regulating mammalian retinal cell specification and is involved in several diseases leading to visual impairment as well[113]. Expression levels of the lncRNA MALAT1 are significantly upregulated in diabetic retinas and it has been suggested to regulate retinal neurodegeneration in several rodent models[114].MALAT1 expression is upregulated in cultured MGCs and retinal ganglion cells following stress, while its suppression decreases reactive gliosis, suggesting that MALAT1 dysregulation leads to neurodegenerative processes[115].
SC IN RD: CURRENT APPROACHES
An advantage of SC therapies in the eye is that they may provide a tool for achieving cellular regeneration in diseases leading to the loss of particular cell types, as retinal ganglion cells are to be replaced in glaucoma, and PHRs or RPE cells in AMD or RP.Noteworthy, the recovery of a particular cell type might also have a trophic role,restoring the provision of trophic factors released by that cell type. As stated above,the fact that the vitreous cavity is a relatively immune-privileged site also contributes to the feasibility of SC transplantation.
These advantages have prompted researchers to establish the most suitable sources of SC and define which protocols to apply for each particular situation. Two main approaches can be described; one of them takes into account the cell type contributing to the degeneration; thus, many studies focus in RPE cells, when their damage plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of the disease, such as AMD; a second approach aims to directly replace the retinal neurons affected in each disease.
In the first approach, the efforts have been directed mainly to transplanting SCderived RPE cells into the eye, either as a monolayer or as a cell suspension.Numerous protocols have been assayed, with different advantages and disadvantages;establishing the most suitable therapeutic strategy demands a careful analysis of all of them. A successful treatment would allow the replacement of the damaged RPE cells,thus preventing the progression of diseases such as AMD. A potential disadvantage is that in these diseases the initial degeneration of RPE cells is usually followed by the degeneration of neurons, mainly PHRs. Since most of the SC used are unipotent and will only generate new RPE cells, this approach has the limitation that it can only be useful at early stages of the disease, as no replacement of lost PHRs or other neuronal cells will be achieved when used at advanced stages.
Using SC to replace retina neurons faces several obstacles. The first is the difficulty to achieve their differentiation into the required neuronal cell type. Even if this is surpassed, the integration of the newly generated cells into the host retina confronts numerous critical complications such as their engrafting onto Bruch’s membrane,achievement of their adequate polarization, reestablishing an adequate circuitry, and finally avoiding immune rejection[116,117].
PHR death is the cause of most RDs, excluding glaucoma. Hence, a second approach to treat most RDs is to directly replace PHRs. With this aim, several strategies have been evaluated. Early work showed that transplants of embryonic murine retinas into the anterior chamber of adult eyes survive and develop, resulting in the differentiation of both neurons and MGC, with few cases of graft rejection[118,119]. Subsequent strategies involve the reactivation of the dormant potential for regeneration of endogenous populations of cells within the retina to generate new PHRs or also to attempt retinal repair by transplantation of healthy PHRs into the vitreous or the subretinal space[120,121].
Therapeutic efficacy of different retina SC
Since the expectation of recovering visual function by using SC emerged, there has been an active search to establish the most adequate SC sources. As occurs with other tissues in the body, the retina has several cell types that display properties of SC. This is evident in fish and amphibians during development and regeneration. During embryogenesis, most of the retina originates from the ciliary marginal zone, a ring of cells found at the periphery of the retina. In contrast, different sources might provide new neurons during regenerative responses. In the amphibian retina of urodeles, RPE cells play a critical role during retina regeneration; these cells dedifferentiate into retinal progenitors that have to recapitulate the normal development of the retina, first proliferating, and then differentiating into the different retinal cell types[122].In zebrafish, MGCs are recruited following damage of the retina, and transiently dedifferentiate, express SC markers, and re-enter the cell cycle, to generate retinal progenitors that migrate to replace the lost neurons[92].
Consequently, cumulative evidence has shown that the ciliary margin zone, the RPE cells, the iris, and MGCs are the major sources of SC in the eye[71,120,123-125]. Some of these cells are represented by stem and low-differentiated cells and others by latent,differentiated progenitors[71,120,123-125].In spite of their different origin, all of them share the essential requisites of SC, namely, the capacity for unlimited self-renewal and the ability to differentiate into different cell lineages. These traits turn them into ideal sources for recovering the different cell types lost in diverse retina degenerative diseases, thus repairing the retina and restoring vision. The feasibility of reprogramming resident, non-neuronal cell types into neuronsin vivo[126] has led to include them as well among the SC types apt to contribute to neuronal regeneration in the retina.
We will now describe briefly the most explored candidates for cell replacement in the retina and the research, including clinical trials, that support their use.
RPCs are among the most promising SC type for treating RDs (Table 1). All cells in the retina derive from them, making these cells, obtained from human fetal retinas, an attractive source of SC for retina repairing. The evolutionary conserved, temporal organization of the genesis of each cell type, and even of particular subtypes, during development of the retina is well established[127]. RPCs proliferate actively, are generally multipotent and have been shown to produce a specific repertoire of cell types at defined developmental stages, suggesting they exhibit intrinsic changes in their state of competence along development[128]. Noteworthy, RPCs are very heterogeneous regarding their gene expression[129]. Although intrinsic cues play a central role in defining cell fate, this fate is not strictly determined and the context, i.e.,regulatory and transcription factors, miRNAs, active/inactive signaling pathways,influences the cell response to a certain perturbation[127]. In addition, extrinsic cues may contribute to modulating the temporal progression of cell fate acquisition; soluble factors released by ganglion or amacrine cells can limit the generation of the respective cell type[129,130], implying their involvement in feedback inhibition.
SC-derived RPCs (SC-RPCs) obtained from embryos are a possible source of cells for retina cell replacement strategies[131]. These multipotent cells display markers indicative of retinal SC fate, such asPax6,Vsx2,Lhx2,Six3,Rax, and can differentiate into MGCs and the six types of retinal neurons[132-136]. Establishing the strategies required for achieving the differentiation of SC-RPCs into the multiple cell types that constitute the retina and drawing a more precise roadmap of the cues involved is crucial for their successful use in regeneration schemes.
Initially, the feasibility of expanding these cells in order to achieve a sufficient amount for transplantation, while simultaneously preserving their multipotency was a limiting factor for using RPCs isolated from the fetal neural retina. Promisingin vitroandin vivostudies have shown that SC isolated from embryonic or fetal retina can be expandedin vitro[12], under particular conditions, such as low-oxygen culture conditions[137], paving the way for their use.
The ability of human or mouse fetal RPCs to repair retinal damages has been analyzed in multiple sub-retinal transplantation studies, which have evidenced they can rescue PHRs, preserving rhodopsin expression and visual function[18,138-141].
Human RPCs are able to differentiate into specific retinal cell types, including PHRs, preserving vision in rats[132,137,142-144]. RPCs isolated from retinas of postnatal day 1 mice, expanded in culture and grafted in the degenerating retina of RD or rho-/-mice differentiate and express PHR markers; in rho-/-mice, RPCs integrate in different retina layers, increasing outer nuclear layer thickness and improving lightmediated behavior[12]. Transplantation of RPCs in the subretinal space has been proved feasible; mice retinal progenitors obtained from postnatal day 1 retinas and injected into the subretinal space of different adult mouse models of retina degeneration can integrate, differentiate as PHRs and improve visual function[132,145]. Transplantation of human RPCs into Royal College of Surgeons (RCS) rats, an animal model in which a mutation in RPE cells leads to PHR degeneration, preserves the outer nuclear layer thickness and cell count and prevents visual loss[138].Preclinical studies have also used RPCs obtained from human fetal retinas, between 14 wk and 20 wk of gestation, a time point at which PHR progenitors are exiting the cell cycle and initiating their differentiation[146]. Delivery of human RPCs by intravitreal transplantation has also been proved effective; injecting human RPCs, obtained from retinas of 16 wk to 18 wk’ gestational age, in the vitreal cavity of RCS rats has no adverse effects, and preserves PHR cell nuclei in the outer nuclear layer and visual function for 8 wk, decreasing afterwards[40]. However, the low efficiency of integration of RPCs in these studies, usually restricted to areas near the injection site,with few cells achieving differentiation are significant drawbacks still to be overcome.
Fetal RPCs have been used to repair atrophied retina areas in patients with RP or AMD[147-149] (Table 1). Intravitreal and subretinal delivery of allogeneic RPCs for RP treatment are still under evaluation in clinical trials. A sole intravitreal injection of human RPCs has been associated to an improvement in visual acuity in treatedvsnontreated eyes, after a 12-month follow-up in phase I/IIa RP patients[151] and a phase IIa trial has been initiated[152] to evaluate safety.
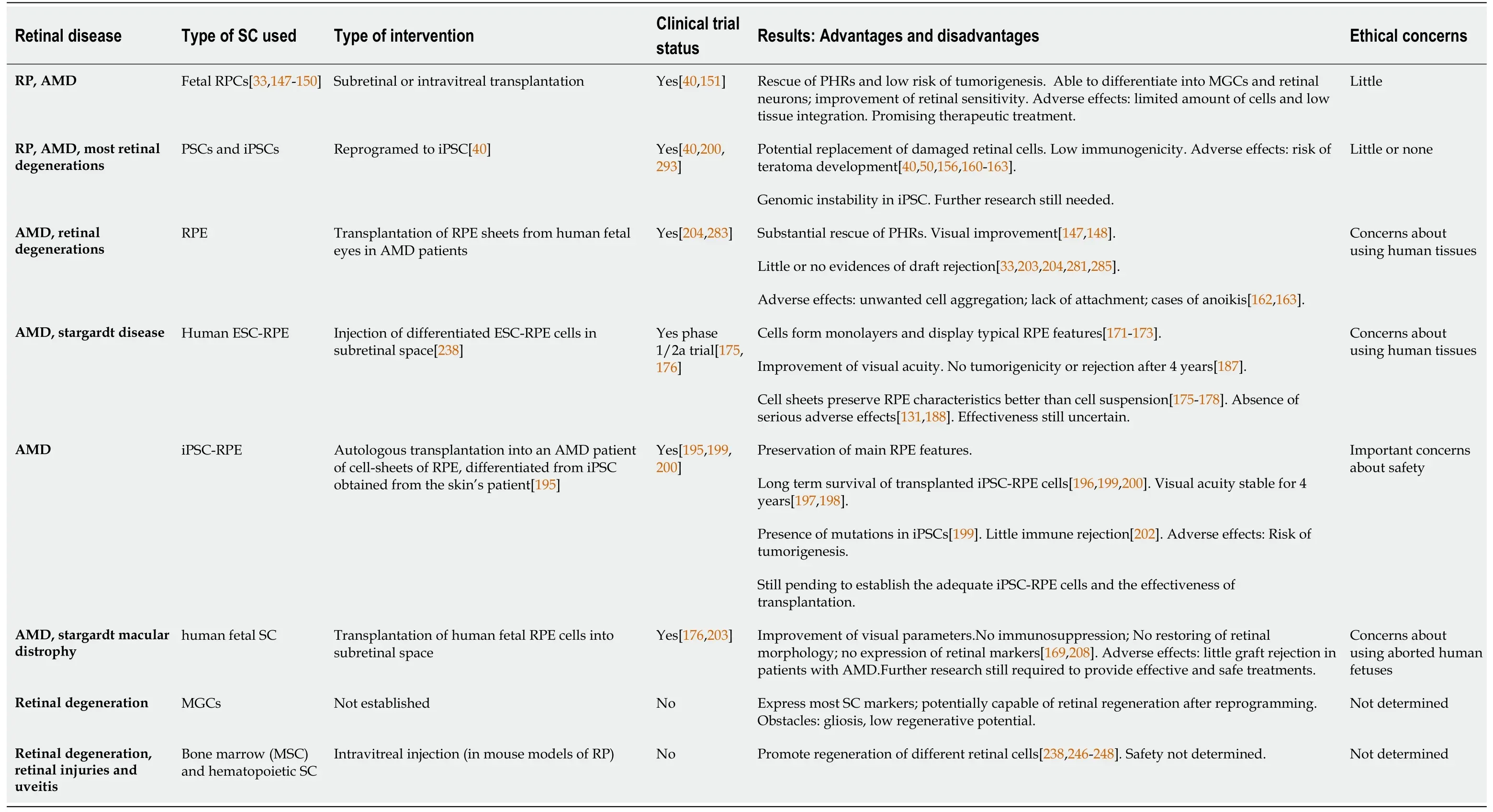
Table 1 Stem cells in retinal diseases
Although RPCs emerge as a promising source of SC to achieve PHRs and retina regeneration, further knowledge is necessary to improve the efficiency of their integration, and control their differentiation into the required cell type, the extent of their reparative effect and, when allogeneic conditions are used, the magnitude of potential immune-derived damage.
PSCs are another potential source of cells to treat RDs. These cells were initially restricted to ESCs deriving from the inner cell mass of preimplantation embryos, and can be indefinitely maintained in the pluripotent state (Figure 1). This pluripotent state
is preserved by a complex and coordinated gene network, along with several signaling pathways activated by environmental cues that start in blastocysts (in the blastula stage) and persist until gastrulation; at this time point, levels ofOct4andNanogdecrease, and pluripotency can no longer be preserved[152-155]. However, a major step forward for SC-based therapies came from thein vitrotechnology developed by Takahashi and Yamanaka[15], and Takahashiet al[156], that allowed to obtain PSCs by inducing dedifferentiation of adult somatic cells through their reprogramming to a pluripotent state, thus generating iPSCs. As ESCs, iPSCs cells can be expanded indefinitely, preserving an undifferentiated state and, eventually, can differentiate into cells of the three germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm[157].
Numerousin vitrostudies have now evaluated the capacity of IPSCs for retina cell replacement. Addition of low molecular-mass compounds to iPSC cultures leads to their differentiation into retinal progenitors, RPE cells and PHRs[158]. In a recent work, Fligoret al[159] demonstrated that three-dimensional retinal organoids derived from human iPSCs can recapitulate retina differentiation and are useful models to investigate guidance of developing neurites toward their targets.
The ability of human iPSCs to differentiate into a wide range of cell types turns them into a suitable and attractive alternative to ESCs, avoiding the ethical issues associated to the later. Hence, human iPSCs appear as likely candidates to be successfully used in the near future, providing better models for studying, treating,and eventually curing retinal degenerative diseases. Nonetheless, a crucial problem precluding their use is that they have been shown to give rise to teratomas when injected into immune-deficient mice[160,156,161-163].
Further research on the mechanisms underlying self-renewal properties, and safety of human PSCs are still needed to solve the pending questions associated with their therapeutic possibilities[164] (Table 1).
Ciliary-derived cells and RPE cells have also been reported as a potential source of progenitor cells that can be mobilized to the injured retina[165]. RPE cells form a monolayer between the PHRs and the choroidal vasculature. They transport ions,water and metabolic end products from the subretinal space to the blood, they represent the only blood supply for the outer retina and have the critical function of constantly clearing shed PHR outer segments by phagocytosis. Their interactions with the Bruch’s membrane and the choriocapillaris constitute a barrier that regulates exchange of substances between the neural retina and the circulation. To perform these functions adequately, RPE cells must maintain a polarized structure, which is crucial for the homeostasis of the outer retina, the disruption of which leads to degenerative retinopathies[166].
Transplantation of SC-derived RPE cells has been in the spotlight for over 10 years as a cell replacement strategy, particularly for patients with macular disorders, in which the early loss of RPE cells leads to the subsequent death of PHRs. A huge amount of information has been accumulated regarding their efficacy and safety, and clinical trials are already on course.
RPE cells were among the first candidates evaluated for subretinal transplantation since they can be easily obtained from patients, for autologous replacement therapies,or even from corpses, and can be maintainedin vitrofor long periods. Autologous RPE cells have been used in patients with RP or AMD, transplanting patches of RPE cells into the damaged areas of the retina[147-149]. A weakness to the therapeutic possibilities of adult RPE cells is that the normal functions of RPE cells are not fully reestablished after these procedures, and they may retain some aging features[117].
Transplantation of RPE cells has many advantages, appearing as a suitable strategy to treat inherited diseases, such as AMD. The possibility of differentiating RPE cells from hESC (hESC-RPE) and from iPSC (iPSC-RPE) has paved the way for their use,since it provides a potentially unlimited source for the replacement of affected or dead RPE cells[167]. hESC-RPE cells can be obtained by culturing ESC colonies, in which cells spontaneously differentiate into RPE cells after removal of FGF. Sheets of RPE cells can be obtained from cultures of either ESCs, or iPSCs, and they can form confluent monolayers, reproducing many of the functions of RPE cells[168-170]. They not only form monolayers, but also display the typical RPE microvilli and pigmentcontaining melanosome granules, and express RPE markers, such as Na+K+ATPase,Pax6, and RPE65, together with proteins associated with tight junctions and involved in retinol cycling[163-171]. hESC-RPE cells have also been shown to express and release pigment epithelial derived factor from their apical surface[174]. Following their transplantation into RCS dystrophic rats, hESC-RPE cells survive in the subretinal space, expressing low levels of RPE65 and downregulating the cell cycle and Pax6 expression, while maintaining expression of other markers[172].
The efficacy of transplanting these cells as either a cell suspension or as sheets is a matter of extensive analysis. ESC-derived RPE cell suspensions were safely used in a phase I/IIa trial for treating AMD and Stargardt disease patients[175,176] (Table 1).However, the effectiveness of this strategy is still uncertain as these suspension are unable to form the typical RPE monolayers and to survive long periods of time[177,178]. Animal studies evidence the feasibility of subretinal transplantation of a hESCRPE monolayer re-grown in a biocompatible membrane, which shows a normal implantation[179,180]. Current evidence suggests that cell sheets, rather than cell suspensions, might be more effective for preserving morphology, polarization,survival and physiology of RPE cells[177].
Different materials have been used to support RPE monolayers, with or without artificial scaffolds, as these materials may influence inflammation, adequate insertion and interaction of RPE cells with other cell types in the retina[181]. These patches allow the formation of tight junctions, required to acquire a fully polarized morphology, which, as stated above, is critical for RPE cells functions and for their interaction with PHR segments[182]. However, the survival of these patches after transplantation is a significant problem to deal with (Table 1).
The transplantation site is also still subject of considerable research. The subretinal space, a frequent transplantation site, is a relatively immune privileged site, and RPE cells located in this space have immunosuppressive functions. However, transplanted RPE grafts can be eventually rejected, as they can be attacked by immune cells due to their immunogenicity[181,183] (Table 1). Initial studies to evaluate the efficacy and safety of RPE cells for retina regeneration therapies were performed in animals, and most of them involved immunosuppression. Transplantation of RPE sheets prepared from human fetal eyes in RCS rat eyes indicates a substantial rescue of PHRs in the area of the RPE patches, with no evidence of draft rejection[33]. Later work evidenced that subretinal transplantation of hESC-RPE in RCS rat eyes leads to PHR rescue and improvement in visual performance; donor hESC-RPE localized adjacent to the RPE layer show no uncontrolled proliferation or evidence of tumor formation[171].Similarly, long-term functional rescue is observed after subretinal injection of ESC-RPE in animal models of AMD and Stargardt disease, diseases in which RPE degeneration leads to PHR loss and visual deficiency; the retinas preserve PHR integrity and function, without evidence of teratomas or pathological changes[184].
Some problems still remain. Cell transplantations of RPE in the retina frequently causes unwanted cell aggregation or lack of attachment onto the Bruch´s membrane[185], with RPE cells tending to form aggregates (rosettes) instead of functional monolayers[172] or undergoing anoikis when dissociated from their usual extracellular matrix[186] (Table 1).
Further studies are required to solve these pending issues; nevertheless, cumulative information support ESC-RPE as a potentially useful and inexhaustible source of SC for treating retina degeneration.
The first clinical study evaluating the feasibility of transplantation of hESC-RPE cells to human patients was reported by Schwartz and colleagues in 2012[175]. These researchers injected differentiated hESC-RPE cells in the subretinal space of patients having macular degeneration. The cells integrated in the host RPE layer, forming monolayers, and improved visual acuity in over half of the patients, with no visible hyperproliferation, tumorigenicity or rejection-related inflammation even after 4 years[187]. A similar study evidenced an improvement in visual acuity and the absence of serious adverse effects[188]. In a Phase I trial, hESC-RPE cells on a coated, synthetic basement membrane transplanted in two patients with severe exudative AMD successfully survived for a year and increased visual acuity[189]. Therefore, retinal implants of ESC-RPE cells appear as a promising therapeutic tool to treat retinal diseases (Table 1).
iPSC-RPE are also a promising source of RPE cells for transplantation as they provide a virtually unlimited number of RPE cells, in a non-invasive manner (Table 1).iPSC-RPE cells have the same genetic background, and display morphological and functional characteristics of mature RPE cells, which they retain after their transplantation in the rodent retina[190-193]. iPSC-RPE cells have been established from mouse, monkey and human, using different methods to obtain the iPSCs and then induce their differentiation into RPE cells[194-196]. These cells preserve key RPE features; Carret al[191] showed that following their transplantation into the RCS dystrophic rat, iPSC-RPE phagocyte PHR material, bothin vitroandin vivo.
Several studies have reported that human iPSC-RPE cells also exhibit native RPE features, such as gene expression and cellular functions, and have immunosuppressive properties, suppressing T-cell activationin vitro[181].
Ensuring safety and efficacy are major concerns for their clinical applications.Tumorigenesis is a major risk, due to the reprogramming methods used and their possible contamination with iPSCs, which might contribute to formation of teratomas[181].
The potential use of iPSC-RPE cells has been tested in fewer clinical trials than ESCRPE cells. The first human pilot trial was conducted by Mandaiet al[197] and generated great public attention. iPSCs were induced from the patient´s skin cells by introducing reprogramming factors and then differentiated into RPE cells; an autologous RPE sheet was then prepared and transplanted into a patient with neovascular AMD[197]. The graft remained stable, with no signs of rejection or increased proliferation, and the patient´s visual acuity remained constant for four years[197,198]. A further trial was suspended due to the presence of mutations in iPSCs from another subject[199]. Takahashi´s group is currently evaluating the use of allogeneic iPSC-RPE cell grafts, which would be faster to prepare and easier to control genomic stability; their use requires to take into account the different factors leading to a higher risk of immune rejection.
In an early clinical study, Sugitaet al[200] used iPSC-RPE cells derived from major histocompatibility complex (MHC) homozygous donors; after being transplanted into patients with exudative AMD having a matched MHC, the graft cells remained stable for one year, showing no abnormal growth. Although the patients experienced many moderate adverse events, such as corneal damages, retinal edema, elevated intraocular pressure, endophthalmitis, and mild immune rejection in the eye, this trial demonstrates long term survival and safety of transplanted iPSC-RPE cells[196,200,201]. Ongoing clinical studies in five patients with neovascular AMD have safety as their main concern and report the survival of the transplanted grafts and only one case of immune rejection[202]. Once the safety of their use is established, further clinical trials will be required to determine which iPSC-RPE cells are the most adequate and whether their transplantation is effective to improve visual function. Of note,treatments with iPSC-derived RPE cells are limited to early stages of RDs; they may be ineffective in patients with an irreversible PHR loss.
Fetal RPE cells provide another source of RPE cells for transplantation. In an early work, Algvereet al[203] transplanted human fetal RPE cells into the subretinal space in AMD patients, with no immunosuppression; although patients with exudative lesions showed graft rejection, patients with geographic atrophy of dry AMD presented little evidence of rejection (Table 1). Even when alerting about the risk of rejection, they concluded that it is feasible to transplant human RPE into the submacular space of nonexudative AMD patients without adversely affecting visual function. Further clinical trials show that subretinal human RPE allografts transplanted into eyes of AMD patients, without immunosuppression, exhibit high rejection rates after 2 years,probably through a disruption in the blood retinal barrier; on the other hand, small extrafoveal transplants remain essentially unchanged for over 2 years in nonexudative AMD without immunosuppression[204]. Interestingly, transplants of fetal retinal tissues as intact sheets, or even as aggregates, in the sub retinal space in rats have been shown to survive, adhered to the host RPE sheets[116,205,206].In these cases, the occurrence of a pre-existing RPE sheet in the transplanted recipient provides paracrine trophic support for the grafted tissue, preventing cell death[205,206].
Human fetal neural SC are another possible source of SC. These cells, obtained from aborted fetuses, were identified by the expression of the cell-surface marker CD133,and cultured under conditions that induce rosette formation. After injection into the subretinal space in RCS rats, these cells survived away from the injection site and improved visual parameters, even when they neither restored retinal morphology, nor expressed retinal markers[207,208] (Table 1).
Taken as a whole, the above findings imply that transplantation of fetal cells is a promising approach, still requiring further research to provide an effective and safe treatment.
MGCs emerge as a further promising source of SC for retina regeneration. MGCs are the principal glial cells in the retina and play crucial roles in the preservation of retinal structure and function[209]. They provide the main trophic and metabolic support for retinal neurons, playing a major role in the preservation of homeostasis,the regulation of nerve signal transduction, and the formation of synaptic structures in the retina. Emerging evidences suggest that MGCs are dormant stem-like cells present throughout the retina that serve as a source of progenitor cells to regenerate retinal neurons after injury[209,210]. In teleost fish, MGCs are a major source of progenitors for retina regeneration after injury. In the damaged zebrafish retina, the activation of a reprogramming process in MGCs leads to their de-differentiation to generate neuronal progenitor cells, which proliferate and finally differentiate into all the cell types forming the retina[92]. This remarkable regeneration capacity is much diminished in vertebrates; although vertebrate MGCs have been established as retina SC, they have a very limited capacity to achieve retina regeneration upon damage. In spite of this limitation, MGCs would provide an intrinsic source of SC, in contrast to ESCs, iPSCs,or embryonic fetal RPCs, for regenerative purposes. A further complication is that injuries to the mammalian retina turn on a reactive process in MGCs, termed “gliosis”,through which MGCs initially orchestrate a neuroprotective response and then, if the injury persists, turn on a pro-inflammatory response that further impairs neuronal function and tissue repair (Figure 5). This gliotic process is common to other glial SC in the CNS; following injuries to nerve tissues, astrocyte-like cells with SC properties activate a reactive gliotic response that interferes with neurogenesis, turning gliosis into a considerable obstacle for regenerative processes[211] (Table 1).
During this gliotic response MGCs up-regulate the expression of intermediate filaments and recruit macrophages. Reactive gliosis following transplantation also occurs in response to many other donor cell types, including neuronal cells, iPSCs, and PHR precursors, when transplanted either into the vitreous or in the subretinal space.This suggests gliosis is independent of the type and origin of transplanted SC. Intravitreally transplanted cells secrete CNTF and IL-6, among other factors, that activate the JAK2/STAT3 cascade, and STAT3 mediates glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP)upregulation (Figure 5). Noteworthy, pharmacological inhibition of STAT3 in BM MSC reduces GFAP expression and improves their retinal engraftment[212]. Moreover,activation of JAK/STAT signaling cascades is required for increasing proliferation of MGC-derived progenitors in NMDA-injured chicken retinas[213].
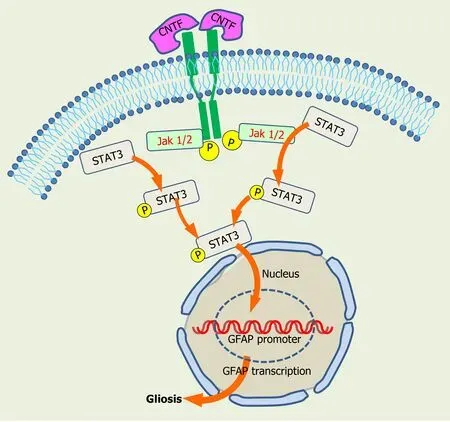
Figure 5 Activation of gliosis by the JAK2/STAT3 signaling cascade. Jak/Stat signaling cascade is activated by ciliary neurotrophic factor and other factors, generating phosphorylated STAT3 intermediates, which turn on glial fibrillary acidic protein promoter gene to induce gliosis. CNTF: Cliary neurotrophic factor;GFAP: Glial fibrillary acidic protein.
In spite of eliciting gliotic responses and scar formation in damaged retinas, that prevent neurite elongation and cell migration, MGCs still retain regenerative capabilities. Several studies have shown that a reduced amount of vertebrate MGC dedifferentiates and re-enters the cell cycle, after different injuries, and eventually differentiate as retinal neurons[214].
MGCs have been shown to replace some or all retinal cell types in various species[215].In response to damage, or when exposed to a combination of insulin and FGF2,MGCs in the chick retina can de-differentiate into proliferating progenitor cells, reenter the cell cycle and express neuronal transcription factors such as CASH-1, PAX6 and CHX10[210,216]. However, their neurogenic competence is limited and they can only generate a few amacrine and bipolar cells[216-218].
In the mouse retina, neurotoxic injury activates proliferation and the expression of progenitor markers in MGCs[219], which can then differentiate into specific neuronal types[220,221]. Our work has shown that oxidative stress induces the de-differentiation and increases the proliferation of rat cultured MGCs[222]. Moreover, in mixed neuro-glial cultures, MGCs preserve the proliferative potential and SC characteristics of retina progenitor cells, even after successive reseedings, and also stimulate their differentiation as PHRs, increasing opsin expression and markers of PHR function,such as glutamate uptake and light-dependent cGMP degradation[223]. Interestingly,MGCs from therd1mice retina fail to preserve their proliferative capacity and the expression of SC markers, such as Sox2 and Nestin, in mixedrd1neuron-glial cultures.Nestin expression is recovered whenrd1MGCs are co-cultured with wild type neurons and, conversely, it decreases in wild type MGCs co-cultured withrd1neurons; this suggests that an active crosstalk between MGCs and PHRs is essential for the preservation of the regenerative potential of MGCs[224].
A recent work shows that culturing of human surgical retinal explants obtained from the equatorial retina reveals spontaneously migrating cells that express ESC markers, as Pax6,Sox2, Nestin and also MGC markers, such as GFAP and glutamine synthetase. This implies that following injury, this area of the retina might provide a source of RPCs, since it generates cells that possess the potential for regeneration, with markers consistent with Müller cell lineage[225].
As a whole, these findings imply that although with a restricted capacity, MGCs have the potential for neuronal regeneration. Understanding the mechanisms that limit this regenerative capacity and how to unleash it would allow reprogramming of MGCs as a source of progenitors for retina regeneration. Furthermore, given the undesired long-term effects of reactive gliosis, a better comprehension of the mechanisms of gliosis is essential before considering the use of MGCs for transplantation therapies.
A recent promising strategy has been successfully applied to unleash SC features in MGCs, through the transfer of cytoplasmic materials between transplanted and recipient cells. This transfer, by membrane fusion, exosome delivery or other methods of intercellular trafficking has been shown as an efficient tool for reprogramming cells[226,228]. Endogenous hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells transplanted into retinas of genetic and drug-induced mouse models of retina degeneration efficiently fuse with retinal MGCsin vivo, reprogramming them back to a neural progenitor-like state, to finally differentiate into PHRs, improving the electrophysiological response and the regeneration of the retina[228]. This supports transfer of intracellular material from SC as a new tool for turning on regenerative programs in MGCs.
Although this transfer appears as a promising strategy, understanding the molecular mechanisms involved is crucial for improving effectiveness of MGCs reprogramming. Extensive research has been devoted to uncover the diverse signaling pathways and the genetic network leading to MGCs reprogramming[229]. In zebrafish, this reprogramming involves the activation of different injury-induced genes that regulate neurogenic competence; among them, the proneural transcription factor ascl1a emerges as a crucial regulator in retinal regeneration[99]. OverexpressingAscl1and modifying MGCs epigenome, with a histone deacetylase inhibitor, promotes the generation of inner retina neurons from MGCs in adult mice after retinal damage[230]; this impliesAscl1activation and epigenetic regulation are required for MGCs reprogramming. In contrast, the Hippo pathway repression of the transcription cofactor YAP blocks the ability of MGCs to adopt a proliferative, progenitor-like identity[231]. Exciting new data uncovers the genetic networks that control the regenerative capacity of MGCs in zebrafish and mice[232]. Retina injury triggers a reactive state in MGCs in zebrafish and mouse; however, while most zebrafish MGCs then adopt a progenitor fate, a dedicated gene regulatory network, which includes upregulation of nuclear factors I (NFI) factors, restore reactive mice MGCs to quiescence. Deletion of NFI factors in mice MGCs allows the generation of MGCderived inner retina neurons, implying these factors are crucial to suppress neurogenesis from MGCs[232]. Although many questions remain to be answered,these findings suggest MGC reprogramming is a promising tool to unleash the SC potential of MGCs, which would contribute to human retina regeneration (Table 1).
As regardless of their source, most SC have the capacity to differentiate into nearly all of the cell types occurring in the human body, SC types like those from umbilical or placental tissues, have been evaluated in animal studies and in clinical trials for their therapeutic use in the eye. Umbilical tissues contain adult MSC, and other non-ocular cell types, such as placental cells and bone-marrow derived MSCs are also available[117,233-235]. An early study compared the efficacy of these three human-derived types of SC injected at early stages of RD in the subretinal space in RCS rats. Cells obtained from human umbilical cords were the most effective, rescuing larger areas of PHRs and preserving visual function, with no sign of tumor formation[236]. These cells were found to rescue phagocytic dysfunction in RCS-derived RPE cells in culture,by releasing trophic factors such as BDNF, GDNF, hepatocyte growth factor, and bridge molecules that bind to PHR outer segments and facilitate RPE phagocytosis[237] (Table 1). Adipose, BM and umbilical MSCs have been shown to secrete multifunctional exosomes with low risk of toxicity and immunological rejection[238].In a clinical trial evaluating the safety and tolerability of the subretinal injection of human umbilical cord tissue-derived cells in patients with visual impairment due to geographic atrophy[239], patients showed a variable and consistent increase in visual acuity after 12 months, with no rejection or tumor formation[240]. Umbilical cord cells might thus provide a potential source of SC, able to contribute to PHR survival and function.
The use of BM SC has also gained relevance, given the evidences that these cells can rescue degenerating and ischemic retina[238]. Studies injecting BM SC subretinally in mouse models of RP show improvements in visual parameters and in the structure and function of RPE cells and PHRs[241,242] (Table 1).
BM SCs comprise MSC and HSC. MSC are easily accessible primary cells, with various biological functions and properties such as multi-lineage differentiation, antiinflammation, immune suppression, and neuroprotection. They express specific cell surface markers including CD105, CD73, CD44, CD90, CD166, CD146 CD54, and CD49. HSC are capable of self-renewal, and can be identified by cell surface markers,like CD34+ in humans[243]. They have been used for transplantation treatments in retinal diseases, as in mice models of diabetic retinopathy or in ischemia-reperfusion injury[244].
BM SCs have generated great expectations for treating several RDs, including retinal injury, and autoimmune uveitis. Their intravenous injection reduces laserinduced damage in the retina, by inhibiting apoptosis and inflammatory responses,even when they do not migrate to the injured retina[245]. These cells release many soluble factors and exosomes; interestingly, exosome administration prevents the potential risks caused by MSC transplantation, mainly allogeneic and xenogeneic immunological rejection, and malignant transformation. MSCs can also be incorporated intravitreally into the damaged retinas, releasing molecules that activate the cell cycle, thus promoting regeneration of different retinal cells[238,246-248].Although promising, the safety of these treatments remains to be established.
ESCs are pluripotent cells, with the ability to differentiate into any cell type in the body; hence, in addition to giving rise to ESC-RPE cells they represent an attractive source for replacement of retinal neurons. ESCs have been cultured with Wnt and nodal antagonists, involved in patterning the embryo and in the maintenance of pluripotency and carcinogenesis[249], and then with activin to induce retinal fate, thus generating cells with a PHR phenotype, expressing Rhodopsin and recoverin[250].Using a combination of noggin, Dickkopf (dkk1), an inhibitor of Wnt signaling pathway, and IGF-1, Lambaet al[251] generated retinal progenitors from human ESCs,which integrate into degenerating retinas, increasing PHR differentiation.
ESCs emerge as a promising source of cells for retinal replacement. Nevertheless,extensive research is still necessary to identify the signals that promote retinal fate,allowing ESC differentiation into particular neuronal types, and to establish whether neurons derived from ESCs can be functionally integrated in human host retinas.
Moreover, taking advantage of the ability of ESCs for differentiating into multiple cell types is challenged by ethical questions, since human embryos have to be used as donors to obtain them. In contrast, as discussed for RPE cells, iPSCs represent a source to generate ESC-like cells that do not require a human embryonic cell donor, posing no ethical objections. However, transforming donor cells into iPSCs still has the potential risk of developing tumors or cancer cells[116,252] (Table 1).
iPSCs are similar to human ESCs in their morphology, proliferation, surface antigens, gene expression, epigenetic status of pluripotent cell-specific genes, and telomerase activity. The successful reprogramming of adult somatic cells (i.e., skin, or blood cells) into iPSCs by introducing the so called Yamanaka´s factors (Oct3/4, Sox2,Klf4 and c-Myc)[15], allows the generation of essentially all kind of tissues, including human dermal fibroblasts[15,156,253-255],as these iPSCs can differentiate into cell types from the three germinal layersin vitro[256].One of the main difficulties of this approach is the requirement forc-Myc, a proto-oncogene capable of transforming iPSCs into cancer cells; to avoid it, a combination ofOct4, Sox2, NanogandLin28has been used[257]. Human iPSCs have been shown to generate several types of neurons and even brain organoids, showing both excitatory and inhibitory synapses and exhibiting functional synaptic activity[258] and demonstrating an extraordinary capacity to emulate human fetal synapses[259]. An amazing finding was that cultured human iPSCs release intrinsic cues that allow them to recapitulate the main steps of retinal development, leading to the formation of three-dimensional retinal tissue exhibiting rather differentiated, photosensitive PHRs.Thus, iPSCs cells have proved to be very effective in developing organoids of three-dimensional tissues, containing mini optic vesicles, with characteristics similar to those of tissues and organs developedin vivo[18,260,261]. These organoids are useful to investigate the pathophysiology of various diseases and to evaluate therapeutic strategies[262].
While this approach is very promising, several safety concerns should be dealt with before using iPSCs for treating degenerative retina diseases. A troublesome finding is the report that iPSCs retain an epigenetic memory, since the pluripotent cells obtained by these reprogramming methods preserve residual DNA methylation signatures,characteristic of their original donor cell types[263]. Alteration of the genome due toin vitromanipulation, leading to oncogene mutations, is another major concern[18,262,264]. Due to the reprogramming process and their active cell division, iPSCs can accumulate mutations with a high risk of developing cancer cells[265]. This is a shared feature of many SC, which harbor malignant SC in their niches, able to maintain an active self-renewal while generating differentiated cells[266]. Although embryonic and adult iPSCs have the capacity of preventing the accumulation of genetic damages and avoid their propagation to daughter cells, this capacity is hampered by mutations occurred during their life span. Many critical functions of SC, like self-renewal,survival, proliferation, and differentiation are regulated by Jak/STAT kinase,phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/phosphatase, NF-κB, and other signaling pathways, the dysregulation of which could lead to cancer development[267].
Cancer SC are particularly tolerant to DNA damages and fail to undergo senescence or regulated cell death. In spite of the accumulation of genetic lesions, they remain proliferating, contributing to form tumors and resisting chemo- and radio-therapy[266]. Since the risk of different cancer types correlates strongly with the amount of mitotic cycles of the normal self-renewing cells, SC are believed to be particularly prone to generating cancer cells and tumors[268], a feature that threatens their use in regenerative medicine.
The versatility of iPSC-derived organoids described above and their similarity to specific tissues and organs turn them into effective tools to evaluate the progression of multiple diseases and the effectiveness of new drugs. This has become apparent during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. This disease is caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. The respiratory system is the primary infected organ, but several other organs, including the CNS, the eyes and the retina may also be infected[269,270].
The angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is the main host cell receptor for the entry of SARS-CoV-2. The eye expresses ACE2, and this expression is present in its inner part, including the retina[271-273]. Furthermore, SARS-CoV-2 is detected in post mortem retinas of COVID-19 patients[274]. As human iPSC-derived retinal organoids have been used to investigate disease progression, and for drug testing[275], the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic led researchers to use iPSC-derived organoids to investigate both SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis and the effectiveness of antiviral drugs[276]. iPSC-derived human neuronal progenitor cells, neurospheres and brain organoids are permissive to SARS-CoV-2[277], suggesting SARS-CoV-2 can productively infect the brain and might thus be involved in the neurological symptoms observed in the disease. As ACE2 is expressed in human iPSC-derived retinal organoids and monolayer cultures derived from their dissociation and both platforms can be infected by a GFP-expressing lentivirus with a SARS-CoV-2 spike (S)protein[278], these platforms appear as suitable models to investigate SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis and evaluate drug efficacy.
In addition, to using SC for cell replacement strategies, the feasibility of transplanting PHR cells into the damaged retinas has been a subject of extensive study.Using these cells presents particular advantages and difficulties. Their position as a layer in the retina makes their transplantation feasible; however, since PHRs do not divide, how to reach a critical mass of replacement cells, sufficient to lead to vision improvement is a pending, imperative question that remains to be answered[116,169].
On the other hand, regeneration of PHRs faces less complications that of brain neurons. The short single axons of PHRs would allow an easier reestablishment of the appropriate contacts and connections, when compared to the complex neuronal circuitries found in other regions of the CNS. Axonal growth would be further facilitated since the myelin components that bind to the Nogo 66 receptor, inhibiting this growth in the brain, are relatively absent in the retina[116,279].
Early work evidenced that when PHR sheets or dissociated cells are transplanted into the subretinal space ofrd(C3H rd/rd) mice, the transplanted PHRs survive for one month, developing outer segment-like processes, and synaptic terminals[141,280].Transplantation of PHRs as a cell suspension inrd1(C3H/HeNHsdrd1) mice regenerates a functional outer nuclear layer[281,282]. Even if no host rod cells are left in the degenerating retina, the transplanted PHRs reestablish the outer nuclear layer,preserve their appropriate polarization, and adequately reconnect their axons with the host neurons.
In an early clinical trial, subretinal transplantation of a sheet of PHR cells obtained from corpses to two advanced RP patients, without immunosuppression, showed no evidence of rejection. Although no improvement in visual acuity was observed, this trial demonstrated that PHRs can be harvested from human cadaveric eyes and safely transplanted to patients with RP[283]. Subretinal transplantation of human fetal retinal micro-aggregates in patients with RP and neovascular AMD evidences an apparent high tolerance for graft tissue, even when no positive effect on visual function has been observed. Interestingly, the transplantation of retinal micro-aggregate suspensions or retinal sheets from human fetuses in patients with RP and wet AMD leads to a transient improvement of light sensitivity in about 30% of the patients[284].Similarly, subretinal transplantation of fetal retinal sheets in RP and AMD patients improves their visual acuity, supporting the efficacy of these therapies[281,285,286].
Other clinical trials are currently taking place. Many variables occurring during PHR transplants still require to be defined before successfully using these transplants in RD patients.
Regulation of SC death is a further critical problem that most regenerative processes still face. Thus, the initial exacerbation of the cell cycle in ESC, required for replenishing the cell loss occurring during degeneration, leads to a progressive accumulation of DNA damages, to which ESCs are very sensitive[287-289], and leads them to trigger apoptosis even after low damage doses[290].The reason for this sensitivity remains unclear, as, in contrast, adult SC evidence a variable sensitivity to damage.Deregulated proliferation of SC increases the risk of mutations associated with cancer development. Thus, ESCs have to choose between cell death resistance, which may lead to the accumulation of mutations and cancer, or a high sensitivity to DNA damage, which may cause SC depletion, and regeneration failure[290], due to the activation of cell death response to preserve genetic stability[291].
In addition, PHR death is intrinsically generated in several retina degenerative diseases, such as RP, due to genetic causes. These causes will persist, even when allogenic therapies with human iPSCs allow a successful transplantation. Therefore,the combination of cell replacement therapies with new strategies aimed at inhibiting cell death will be essential to prevent the death of the newly generated PHRs.
Finally, it is important to mention the risks regarding the inadequate use of SC therapies. Attracted by the big economic benefits, a growing “stem cell” industry is developing[292]. The excitement regarding the therapeutic possibilities of SC and their potential capacity for regenerating most damaged tissues has led to the emergence of many unauthorized “Stem cell clinics” around the world, proposing treatments that lack carefully tested protocols, thus exposing desperate patients to high risks. Due to the relatively easy anatomic access and physiological monitoring of the retina, SC therapies for many ocular conditions are already being offered for improving or curing eye degenerative diseases without providing solid scientific data. Usually the efficacy of the treatments is exaggerated, and the potentially serious health risks of the untested “stem cell therapies” underestimated. It is important to remark that, up to now, only few SC therapies have been approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration[117]. Our knowledge on SC therapies develops much faster than the regulations supervising the ethical and legal concerns related to their clinical use.Hence, governmental offices around the world have neither approved nor disapproved numerous SC treatments offered in multiple websites. In spite of the warnings regarding the risks of undergoing non-approved stem-cell based, ocular treatments, such as that of the American Academy of Ophthalmology (2016), many vulnerable patients throughout the world have been deceived into believing that they are under safe, legal, which instead have repeatedly resulted in severe vision loss(American Academy of Ophthalmology, 2016. Intraocular Stem Cell Therapy).
CONCLUSION
Degeneration of RPE and PHR are the main pivotal causes of RD, a major cause of blindness around the world. The finding of SC in the retina, potentially able to restore the lost cells and repair this degeneration, has opened a new era toward more effective treatments or eventually cures for these diseases. Most SC types like the iPSCs, RPE,and RPCs, are potentially able to replenish the cell loss. Up to now, RPE and RPCs,derived from multiple sources, emerge as the best candidates for treating RD and several “proof of concept” studies support their use. However, none of the proposed SC fulfill yet all the requirements to successfully restore vision and significant problems remain to be addressed before using them safely in the clinic. The list of difficulties is significantly large; while some SC do not attach adequately to their substrata, others are immune-rejected, only survive for short periods of time, fail to integrate into the host retina or do not improve visual function[116]. How to avoid the risk of tumor development, and to address ethical issues are questions still unanswered and a careful balance of benefits and potential harms is required to choose an effective strategy for transplanting SC in the retina.
Additional pending difficulties are how to control the migration of the new cells in the host retina, their differentiation into the required cell types and their reestablishment of synaptic connectivity. Since our knowledge regarding the mechanisms underlying these processes are in their infancy, clinicians strongly rely in the capacity of the tissues surrounding the implanted grafts to provide the cues for the successful integration and function of the newly generated cells.
In spite of these enormous obstacles, outstanding progress has been made around the world to uncover the molecular mechanisms and understand the pathways that control SC potential. This progress allows us to hope that, in a near future these obstacles will be overcome, thus paving the road toward the treatment or eventual cure of RD by using SC.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We are greatly indebted to Victoria Simon PhD and Ms. Edgardo Buzzi from the Instituto de Investigaciones Bioquímicas of Bahía Blanca, for their generous advices and recommendations in the preparation of figures and pictures.
杂志排行
World Journal of Stem Cells的其它文章
- Translational products of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells: Bench to bedside applications
- Unveiling the morphogenetic code: A new path at the intersection of physical energies and chemical signaling
- Alternative RNA splicing in stem cells and cancer stem cells:Importance of transcript-based expression analysis
- SOX transcription factors and glioma stem cells: Choosing between stemness and differentiation
- Considerations for the clinical use of stem cells in genitourinary regenerative medicine
- Age and genotype dependent erythropoietin protection in COVID-19
