Acupoint rules of acupuncture for functional dyspepsia treatment based on complex network analysis
2021-10-31XinYuanZhangYiHuaFanGuoXingLingHaiHangDongXinZhaoXinJuLiXuWang
Xin-Yuan Zhang,Yi-Hua Fan,Guo-Xing Ling,Hai-Hang Dong,Xin Zhao,Xin-Ju Li*,Xu Wang
1College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 301617, China.2Department of rheumatology and immunology,First Teaching Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Tianjin 300193,China.3National Clinical Research Center for Chinese Medicine Acupuncture and Moxibustion, Tianjin 300381, China.4School of Acupunture-moxibustion and Tuina, Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 301617, China.5Department of Acupuncture,Tianjin Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine Affiliated Hospital,Tianjin 300120,China.
Abstract Objective:To analyze the acupoints selection rules in the treatment of functional dyspepsia using complex network technology. Method: This paper uses "functional dyspepsia" and "acupuncture" as searching terms, searches the Chinese and English literature included in the five major databases of Pubmed, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, Sino Med, VIP and Wanfang databases until August 2021, and performs data mining and visualization of prescriptions so as to analyze the pattern of acupoints. Results: 128 papers involving 40 acupoints were selected.The top three acupoints in terms of frequency of acupuncture are Zusanli (ST 36), Neiguan (PC 6)and Zhongwan(RN 12);these three acupuncture points have the highest support for alliance.The core prescriptions for acupuncture in the treatment of functional dyspepsia can be divided into four following categories.The first category is ST 36, PC 6, Gongsun (SP 4), Neiting (ST 44),and Yinlingquan (SP 9); the second category is RN 12,Tianshu(ST 25),Guangyuan (RN 4),Qihai(RN 6),and Xiawan (RN 10);the third category is Zhangmen (IR 10),Liangmen (ST 21), Qimen (IR 14), Taichong (IR 3), and Sanyinjiao (SP 6); and the fourth category includes Weishu (BL 21), Pishu (BL 20), and Ganshu (BL18). Conclusion: The top three meridians with the highest frequency of acupuncture for functional dyspepsia are the Stomach Meridian of Foot-Yangming, the Conception Vessel and the Bladder Meridian of Foot-Taiyang.This paper analyses the prescription of acupuncture for functional dyspepsia through a complex network,which can more effectively summarize the pattern of acupuncture point selection from various aspects.
Key words:Acupuncture,Functional dyspepsia,Complex network
Background
Functional dyspepsia (FD) is a common abnormal gastrointestinal disorder characterised by recurrent or persistent epigastric pain or burning sensation,postprandial epigastric fullness or early satiety, and may be associated with loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting [1].The clinical manifestations of FD cannot be explained by organic, systemic or metabolic diseases [2].Functional dyspepsia is diagnosed in 79.5% of patients with dyspepsia [3].FD has a slow onset and is stable.However, FD can cause considerable distress as it is closely linked to emotions[4].Furthermore,FD has a serious impact on the health status of our population,due to its high prevalence.
Western medicine treats FD mainly with mucosal protectors, gastroprokinetic agents, acid neutralizers,H2-receptor antagonists and proton pump inhibitors[5].However, studies have found [6−7] those gastroprokinetic agents such as domperidone can cause adverse effects mainly in the form of endocrine system damage, which can be seen in lactation, menstrual irregularities, amenorrhea, gynecomastia, etc.; while proton pump inhibitors can cause antibody-dependent enhancement involving a wide range of organ systems.FD belongs to the category of"Weiwan pain"(the pain in the upper abdomen) and "Pi man" (abdominal flatulence)in traditional Chinese medicine[8],and is a dominant disease in Chinese medicine.Acupuncture treatment is often used for FD [9].However, the acupoints lack of uniform/regular rules.Based on the data mining and information visualization techniques,we wanted to discover the pattern of acupoints rules for the treatment of FD.
Data and methods
Data sources
Using the computer to search the Chinese and English literature included in five major databases, namely Pubmed, China National Knowledge Base, VIP,Wanfang and Sino Med, from the establishment of the database to August 2021, and identifies the search terms "functional dyspepsia", "acupuncture", and searches the databases with a combination of subject terms and free terms.
Data screening
Inclusion criteria.① The literature belongs to the category of clinical research literature, including randomized controlled trials and randomized self-control clinical study; ②All included cases meet the Roman Ⅳdiagnostic criteria for FD [9]; ③ The intervention method is based on acupuncture but combine with other Chinese and Western medicine therapies.
Exclusion criteria.① Duplicate publications were not included, only the earliest studies were included;② Reviews, empirical summaries, Meta-analyses,animal studies,etc.
Data processing
Database establishment.Using the above-mentioned subject terms as keywords,325 papers on the treatment of functional dyspepsia with acupuncture are obtained;and after screening them according to the data nesting criteria, 128 valid papers are finally obtained.This paper uses Microsoft Excel 2010 to create a database of acupuncture prescriptions for functional dyspepsia,and then enters the 128 validated papers after filtering by the fields of "publication date", "literature name","author"and"acupuncture prescription".
Data preprocessing.This paper uses the International Standard of the People's Republic of China: Name and Positioning of Acupoints (GB/T12346-2006) as the main reference, and the Chinese Dictionary of Acupuncture and Moxibustion and the seventh edition of the textbook Meridian and Acupuncture Points as supplementary references, regulates the naming of acupoints entered into the database, and establishes a"Table of Acupoint Naming Specifications".
Statistical processing.Using the Apriori algorithm model in the information visualisation software IBM SPSS Modeler 14.1, this paper analyses the frequency and association rules of the acupoints and their affiliated meridians entered in the database.Using the software Gephi, this paper constructs prescription complex networks and analyses their network properties, node properties, association divisions and k-core acupoint composition.
Result
Frequency analysis
A total of 40 acupoints are involved in the 128 prescriptions included.The top 10 most frequently used acupoints were Zusanli (ST 36), Zhongwan (RN 12), Neiguan (PC 6), Tianshu (ST 25), Pishu (BL 20),Taichong (IR 3), Weishu (BL 21), Qihai (RN 6),Sanyinjiao (SP 6) and Xiawan (RN 10), which are shown in Table 1,and the top three of them are located as shown in Figure 1.The top three acupoints in terms of frequency of attribution to the meridians were the Stomach Meridian of Foot-yangming, Conception Vessel and Bladder Meridian of Foot-Taiyang, as shown in Table 2.
Association rule analysis
Using the Apriori algorithm model in IBM SPSS Modeler 14.1, we further analyse the association rules for each of the acupoints entered into the prescription and the meridians to which they belong, and sets the support level to 10, the confidence level to 80, and the maximum number of antecedents to 3.The higher support means the more frequently it is used.And the higher the confidence, the more reliable it is.In this paper, the data are ranked in descending order of support, and the top 10 combinations in terms of support are shown in Table 3.It can be seen that the combination of the two acupoints RN 12 and ST 36 has the highest support; when the confidence level is 100%,the combination of the two acupoints ST 36 and PC 6 has the highest support;when the three acupoints are combined,the combination of RN 12,PC 6 and ST 36 has the highest support.
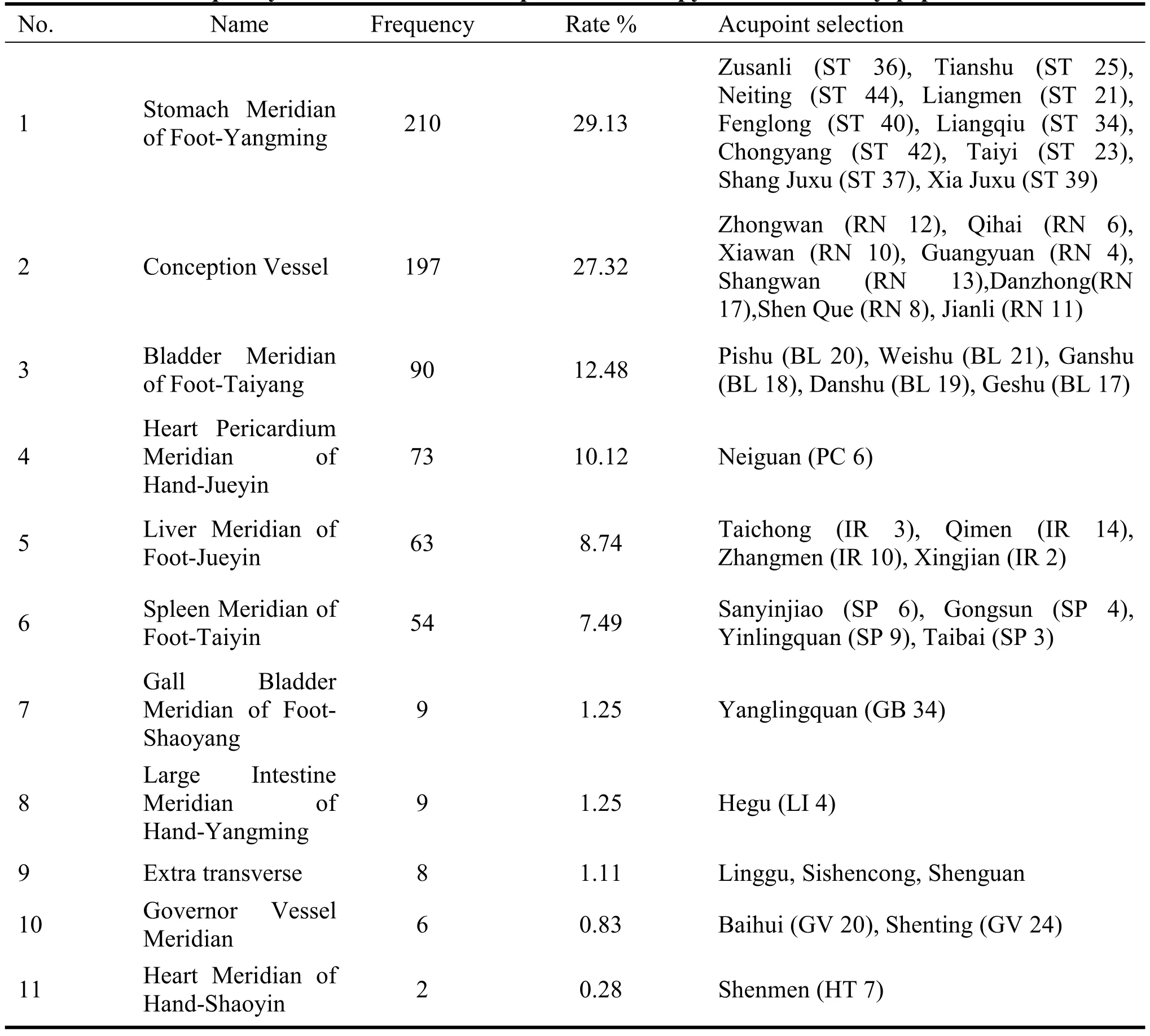
Table 2 Frequency of meridian use of acupuncture therapy for functional dyspepsia literature
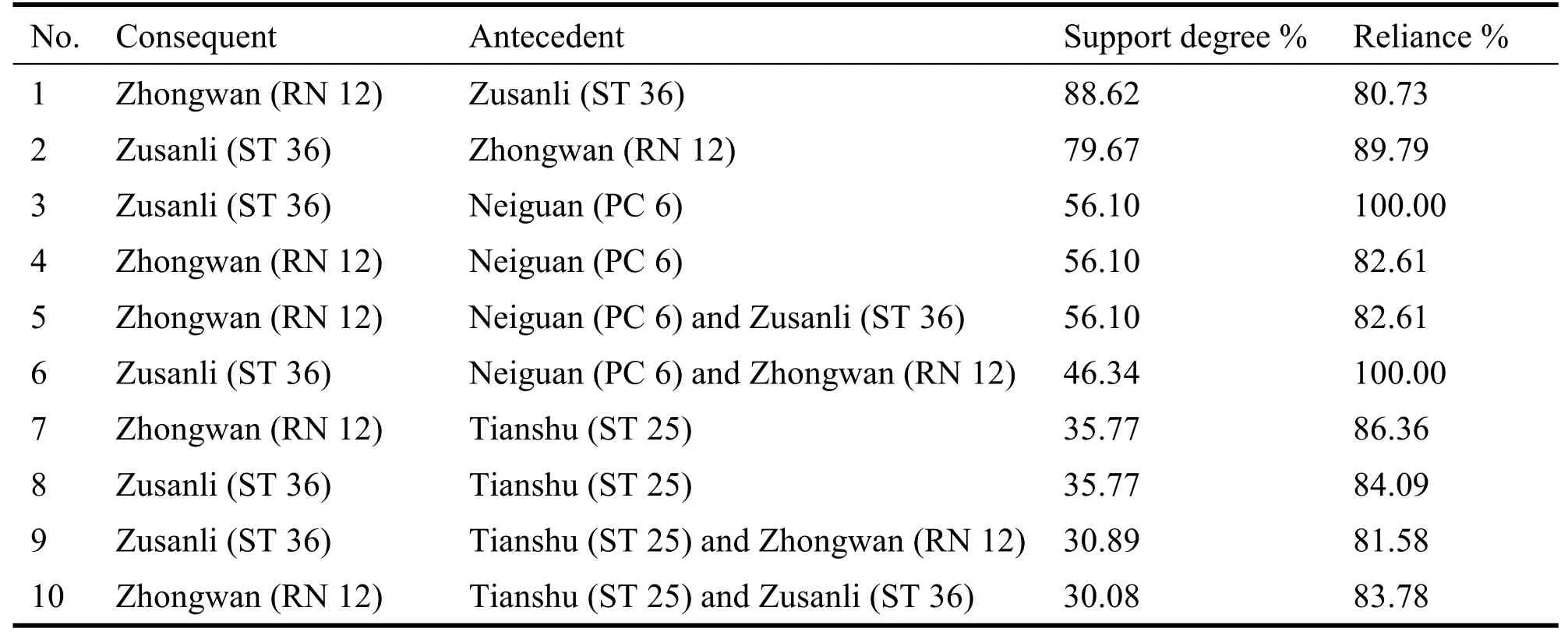
Table 3 High-frequency acupuncture association rules for acupuncture and treatment of functional dyspepsia
Complex network analysis
We construct a complex network of prescriptions with Gephi software [10] and Fruchterman-Reingold algorithm for force-guided layout; the warmer the color of the node is set, the greater the node degree of that node;and the node size is proportional to the node degree,and the width of the edge is proportional to the weight of the edge.This paper presents a complex network diagram of all the incorporated prescriptions for acupuncture for functional dyspepsia, as shown in Figure 2.
Network basic properties.This complex network has 40 nodes and 243 edges;the network diameter is 2;the average path length is 1.666; and the average clustering coefficient was 0.825, between 0 and 1,which indicates that the network has a high degree of connectivity.
Nodal analysis.Nodal degree is the number of edges associated with the node; the greater the nodal degree,the more acupoints can be paired and the more important of the node in the network.The closeness centrality reflects the average distance from a node to other nodes; the betweenness centrality reflects the number of edges of all shortest paths passing through a node.This paper ranks the nodal degrees of the top 20 nodes in descending order, and all values are retained to two decimal places; the nodal degrees, closeness centrality and betweenness centrality of the top 20 nodes are shown in Table 4.Six nodes have the best the nodal degrees, closeness centrality and betweenness centrality, which makes them important acupoints for the FD treatment.These were ST 36,RN 12,PC 6,ST 25,IR 3 and BL 21,the ST 36 is the most crucial acupoint.
K-core analysis.This paper performs k-core operation on the complex network of acupuncture for functional dyspepsia; when an acupoint node belongs to k-core but not to (k+1)-core, k is the kernel degree of the complex network [11].When the maximum value of k is taken as 12, we obtain 18 acupoints account for the largest proportion.They were ST 36, RN 12, BL 20,BL 21, PC 6, ST 25, IR 3, Ganshu (BL18),Yinlingquan (SP 9), Liangmen (ST 21), Gongsun (SP 4), Zhangmen (IR 10), Neiting (ST 44), Guangyuan(RN 4),RN 6,RN 10,SP 6 and Qimen(IR 14);among them, the ST 36, RN 12, BL 21, PC 6, ST 25 and BL 20.RN 12,BL 21,PC 6,ST 25 and BL 20 encircle the ST 36.Therefore, these six acupoints are the core prescription for acupuncture in the treatment of functional dyspepsia,as shown in Figure 3.
Association division analysis.We further divided the core network into modules,setting the resolution to 0.7 and the modularity to 0.001.The core acupoints can be divided into four categories (Figure 4).The first category nodes were set in red; the second category of nodes is set in yellow;the third category of nodes is set in blue;the fourth category of nodes is set in grey.
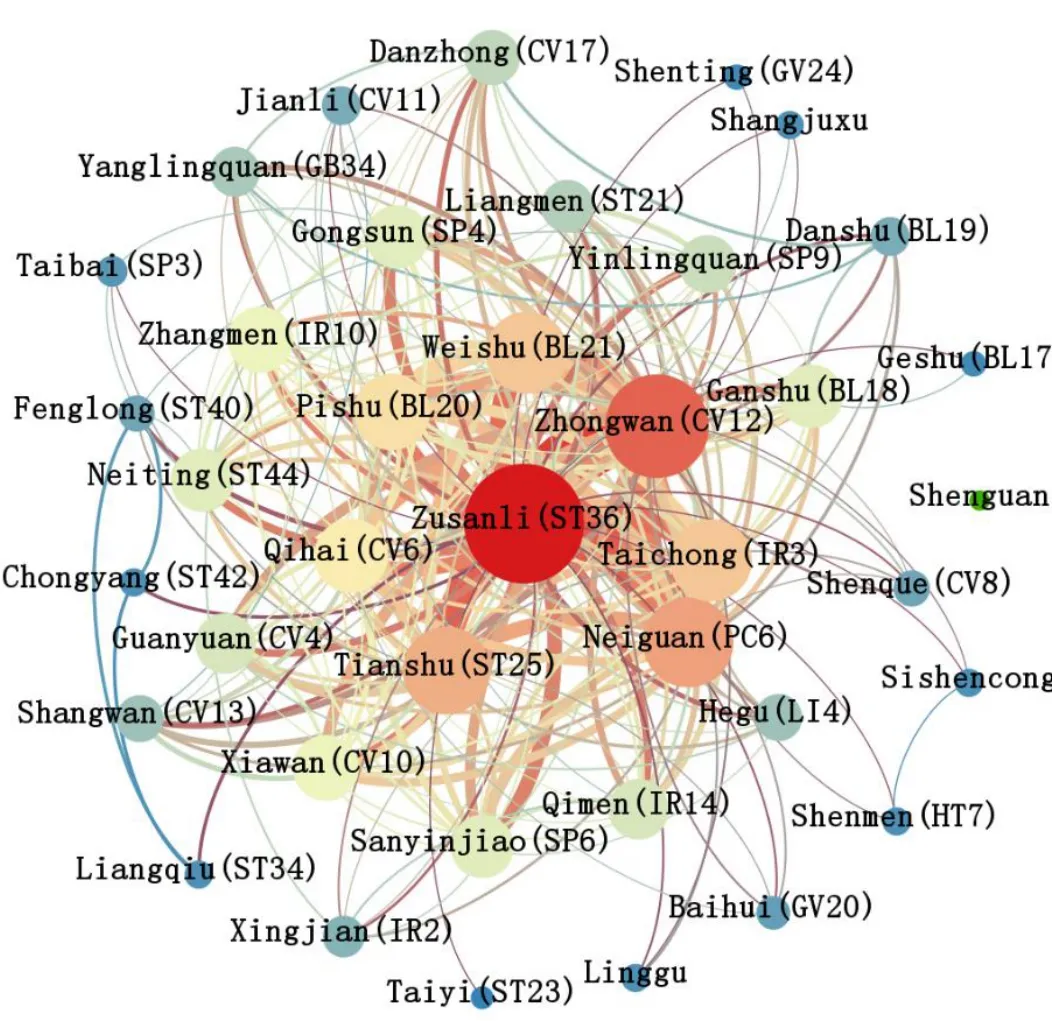
Figure 2 the complex network of acupoints for functional dyspepsia
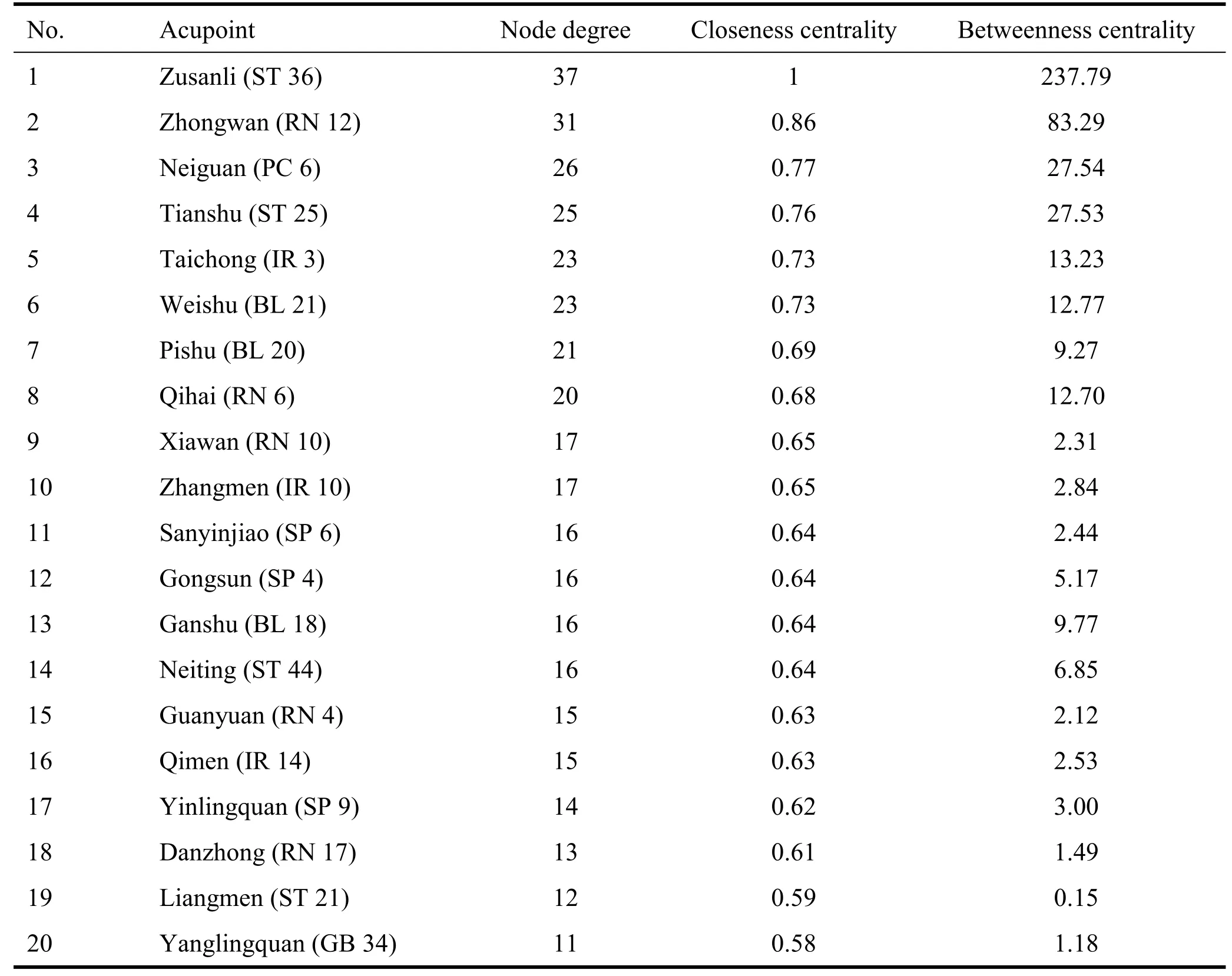
Table 4 Parameters of top 20 functional dyspepsia with acupuncture
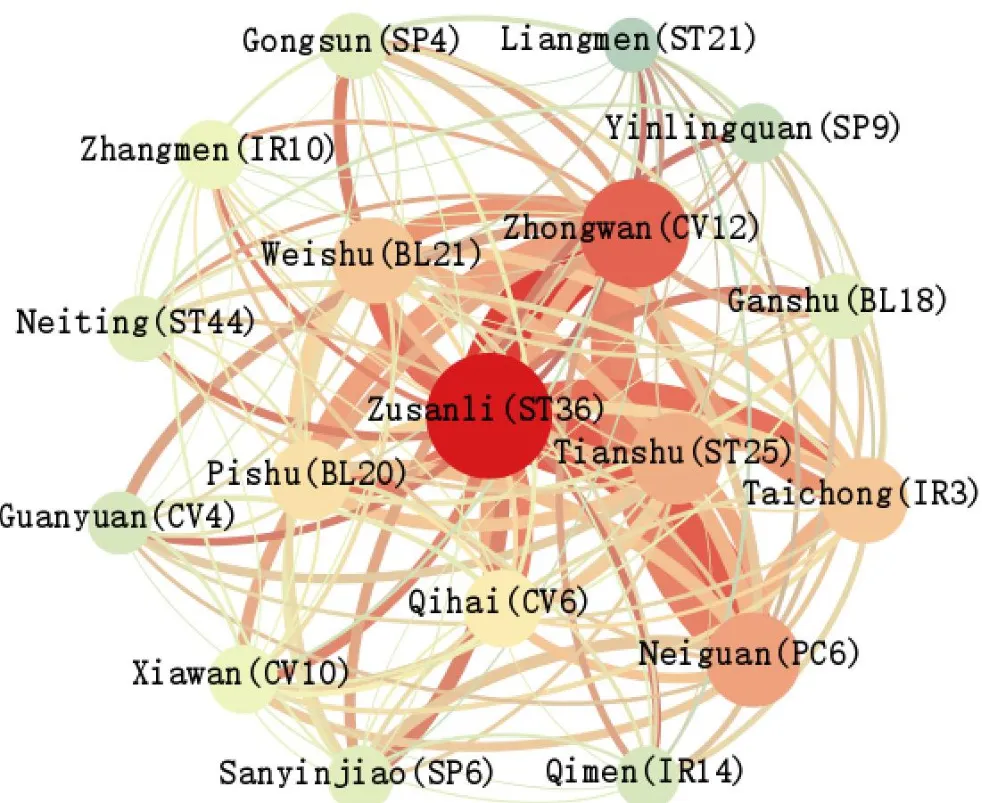
Figure 3 The k-core network of acupoints for functional dyspepsia
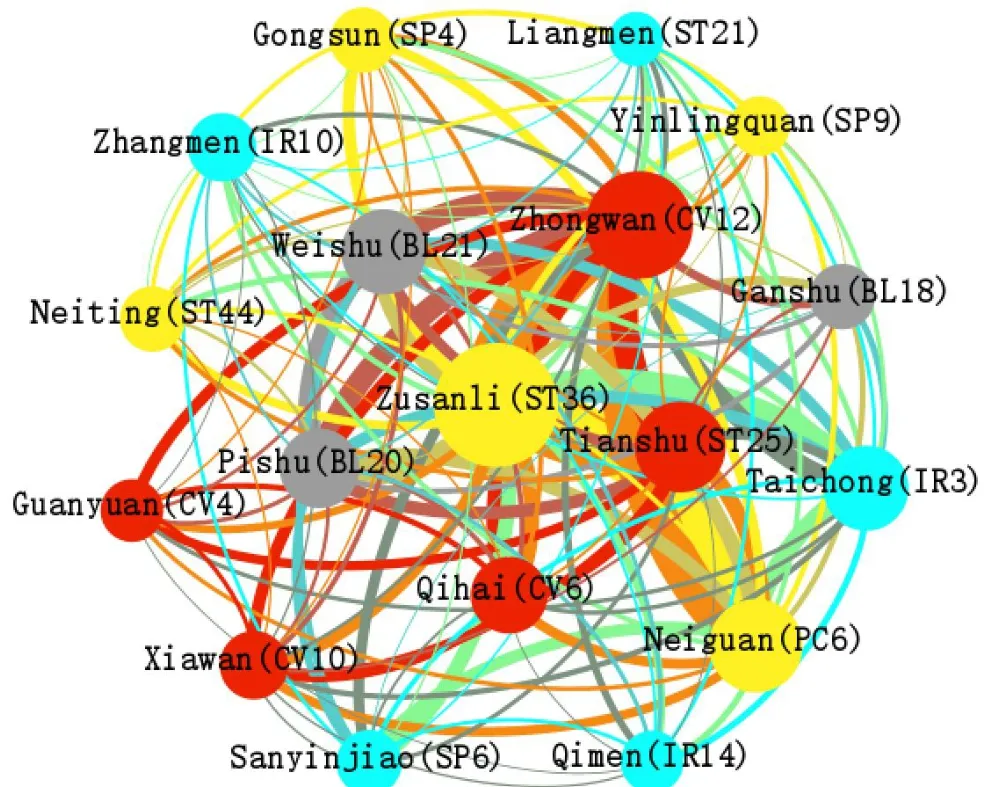
Figure 4 Association division of core acupoints for functional dyspepsia
Discussion
This paper analyses the prescription of acupuncture for FD based on a complex network to further clarify the rules and principles of acupuncture.The three acupoints most frequently used and with the highest degree of support by the rules of association are ST 36,PC 6 and RN 12.The ST 36 is a joint point of the Stomach meridian of Foot-Yangming, which is located below the stomach and has the function of strengthening the spleen, benefiting the stomach and eliminating food.It has found that ST 36 has no significant effect on digestive system function in normal subjects, but significantly shortens the time to gastric emptying and increases gastric emptying-related hormone levels in patients with functional dyspepsia [12].PC 6 is a ligament point of the Heart Pericardium Meridian of Hand-Jueyin,which can indirectly regulate gastrointestinal function by regulating emotions, and is also connected to the Yin Wei pulse, which has the function of maintaining the internal organs of the body along with the Yin Wei pulse.A study by Wu Yali et al [13] finds that stimulating PC 6 increases gastric acid excretion and serum gastrin, promoting the recovery of gastric digestive function.RN 12 belongs to the Conception vessel, is located in the upper abdomen of the human body,and its deep part is the gastric pylorus.ST 36 is a distal point along the meridian,PC 6 is a special point,and RN 12 is a local point,with the highest association rules for the combination of meridian,local and special points; moreover, the combination of the three acupoints, namely, ST 36, RN 12 and PC 6, can maximize the protection of the gastric mucosa and activate the neurons of the dorsal reticular subnucleus of the medulla oblongata [14−15],enhancing the firing of the same neurons to regulate the output of spinal cord signals to regulate visceral function.
The top three meridians in terms of frequency of acupuncture points are the Stomach Meridian of Foot-Yangming,the Conception vessel and the Bladder Meridian of Foot-Taiyang.The Stomach Meridian of Foot-Yangming passes through the abdomen and stimulating the acupuncture points of the Stomach Meridian can unblock the flow of Qi and blood in this meridian and treat stomach disorders.The Conception vessel passes through the middle of the abdomen,which can lead the Qi of meridians belonged to Yin and regulate all the internal organs of the body.The Bladder Meridian of Foot-Taiyang is the meridian in which the back-shu points (acupoints on back that gather Qi of inside) are located; some studies have found [16] that stimulating the back-shu points can regulate the function of the internal organs through regulateing the autonomic nervous system.
The core prescriptions can be divided into four categories via societies.One category is ST 36, PC 6,SP 9, SP 4 and ST 44, all of which are distal points.Among them, ST 36 is the main point for spleen and stomach diseases, and is used to dry and transform spleen dampness and generate stomach Qi; for spleen and stomach disorders, regardless of whether deficiency or excess,cold or hot,ST 36 can be selected.It has found that the vagal pathway is mostly triggered by the lower limb points represented by ST 36, while the sympathetic pathway is mostly triggered by the upper limb points represented by PC 6 [17], so the combination of ST 36 and PC 6 can regulate digestive system in two-way.The combination of SP 4 and PC 6 is an important point for treating the stomach and the heart and chest, and SP 9 is a joint point of the Spleen meridian and is an important point for treating water-dampness.Indigestion is a weakness of Yang energy in traditional Chinese medicine often manifested by Spleen Dampness, and is suitable for acupuncture of SP 9; it has also been shown [18] that the combination of SP 4 and ST 44 has the effect of tonifying the spleen, strengthening the stomach and restoring digestive function.If the spleen and stomach are deficient, they cannot subdue fire and often suffer from toothache, epistaxis and insomnia, so combining them with ST 44 can help to clear heat from the stomach.
The second group is RN 12, RN 10, ST 25,Guanyuan(RN 4)and RN 6,all of which are proximal points.Of these, all except ST 25 are located on the Conception Vessel.RN 12 is the point of the stomach and is the meeting of the internal organs.Similar to the ST 36, RN 12 treats all spleen and stomach disorders,and has a complementary effect of raising the Yang energy of the spleen and stomach together with RN 4 and RN 6; RN 10 is equivalent to the pylorus of the stomach and has a regulating effect on the pylorus, so it has the function of stopping vomiting.ST 25 is the point of the large intestine and is located next to the navel, which enables the Qi of the spleen and stomach unobstructed.Wang Haiping et al.[19]have found that acupuncture of the ST 25 has a two-way regulatory effect on intestinal movements in different segments,which can help speed up gastric emptying in patients with FD.
The third category is IR 10, ST 21, SP 6, IR 3 and IR 14, all of which are points that harmonize the liver and spleen.Patients with dyspepsia often show signs of liver and spleen disharmony.Stabbing IR 10 and ST 21 can both comb the liver qi.Yi Shouxiang, et al[20]have found that stimulating ST 21 can increase blood flowing speed to the gastric mucosa to aid digestion;SP 6 is where the three Yin meridians of foot meet, so stimulating SP 6 can harmonise the Qi of the liver and spleen and nourish the liver and kidneys; IR 3 is the first important point for de-stressing the Qi of the liver;and IR 14 is a point for the liver, which also has the effect of de-stressing the Qi of the liver.It has also been found[21]that after acupuncturing SP 6 and IR 3 together with the ST 36, the expression of smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase and smooth muscle actin in the regulatory mechanism of smooth muscle contraction thick muscle filaments was increased, and gastric motility was restored.
The fourth category is BL 20,BL 21,and BL 18,all of which are back-shu points, that is, points where the Qi of the internal organs is transferred to the back, and they are all points of the Bladder Meridian of Foot-Taiyang.According to Chinese medicine, the back of the body is belong to Yang, and the Bladder Meridian of Foot-Taiyang are connected to the Fengfu(DU 16) and the Governor Vessel, where Yang energy is most vigorous.The spleen,stomach and liver are the core organs of dyspepsia, so acupuncture points on the back can be used to draw Yin from Yang and mobilise Yang energy to invigorate the spleen and stomach.These acupuncture points are in the same nerve segment with the stomach and will produce a benign stimulus to the stomach and intestines through the nerve reflexes of the same segment when stimulated,thereby regulating hormone levels and improving the peristaltic function of the stomach, intestines and oesophagus[22].
In summary, this study selects acupoints from the included literature with a combination of proximal and distal extraction of acupoints, and puts an emphasis on the effect on digestive function caused by stimulation of back-shu points.The core acupoints are mainly the ST 36, RN 12, BL 21, PC 6, ST 25 and BL 20.This study uses complex network technology to analyze and discuss the pattern of acupuncture points in the treatment of FD from several aspects, which may provide a reference for safer clinical therapy for patients with FD.
