改良式阴腹联合子宫骶骨固定术治疗子宫脱垂的效果评价
2021-10-26周爱龙万玉珍
周爱龙 万玉珍
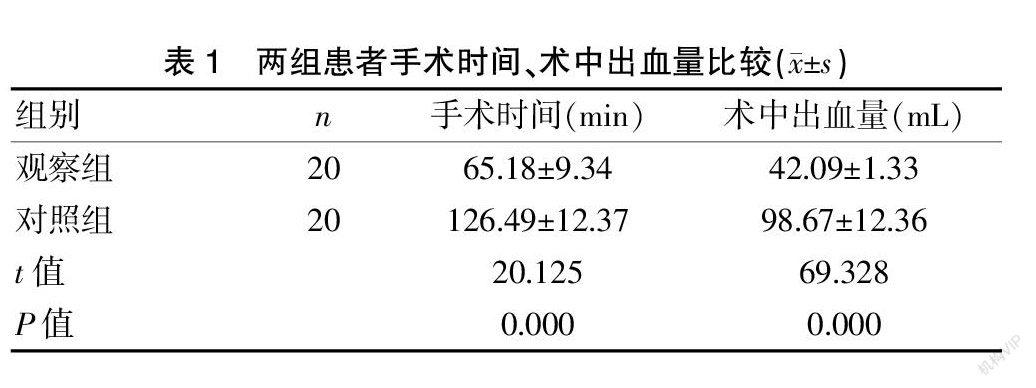

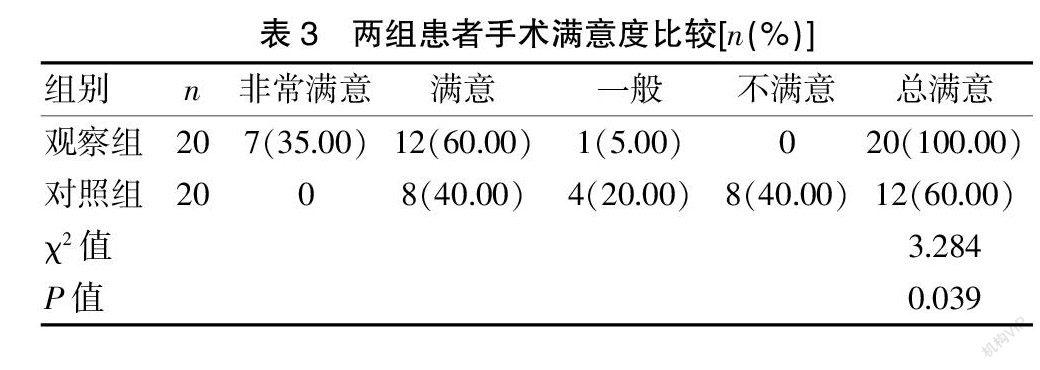
[摘要] 目的 探討改良式阴腹联合子宫骶骨固定术治疗子宫脱垂的效果。 方法 选择2019年1月至2020年5月江西省妇幼保健院进行治疗的40例患者纳入本研究。按照抽取法随机分为两组,每组各20例。对照组采用腹腔镜下子宫骶骨固定术,观察组采用改良式阴腹联合子宫骶骨固定术。观察两组手术时间、术中出血量、并发症、手术满意度、盆底功能症状评分、性生活满意度评分。 结果 与对照组相比,观察组手术时间较短,术中出血量较少,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);观察组并发症总发生率明显低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);观察组手术满意度明显高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预前两组PFDI-20、POP、排便症状、排尿症状评分比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);干预后观察组PFDI-20、POP、排便症状、排尿症状评分高于干预前和对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);对照组干预后PFDI-20、POP、排便症状、排尿症状评分高于干预前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预前两组PISQ-12、PGI-C评分比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);干预后观察组PISQ-12、PGI-C评分高于干预前和对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预后对照组PISQ-12、PGI-C评分高于干预前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。 结论 改良式阴腹联合子宫骶骨固定术治疗子宫脱垂效果较好,可以缩短手术时间、减少术中出血量,降低并发症的发生,提高手术满意度,改善盆底功能症状评分、性生活满意度评分,应用价值较高。
[关键词] 改良式;腹腔镜;子宫;骶骨固定;子宫脱垂;效果
[中图分类号] R711.74 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2021)24-0086-04
Evaluation of the effect of modified vaginal abdomen combined with uterosacral fixation in the treatment of uterine prolapse
ZHOU Ailong WAN Yuzhen
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Jiangxi Maternity and Child Health Hospital, Nanchang 330006, China
[Abstract] Objective To explore the effect of modified vaginal abdomen combined with uterosacral fixation in the treatment of uterine prolapse. Methods A total of 40 patients who were treated in Jiangxi Maternity and Child Health Hospital from January 2019 to May 2020 were selected for this study. According to the extraction method, they were randomly divided into two groups, with 20 cases in each group. The control group underwent laparoscopic uterosacral fixation. The observation group underwent a modified vaginal abdomen combined with uterosacral fixation. The operation time, intraoperative blood loss, complications, surgical satisfaction, pelvic floor function symptom score, and sexual satisfaction score were observed. Results Compared with the control group, the operation time in the observation group was shorter, and intraoperative blood loss was less, and the difference between the groups was significant (P<0.05). The total complication rate in the observation group was lower than that in the control group, and the difference between the groups was significant (P<0.05). The surgical satisfaction in the observation group was higher than that in the control group, and the difference between the groups was significant (P<0.05). There was no significant difference in the scores of PFDI-20, POP, bowel symptoms, and urination symptoms between the observation group and the control group before intervention(P>0.05). The scores of PFDI-20, POP, bowel symptoms, and urination symptoms in the observation group after intervention were higher than those before the intervention and the control group, and the differences were significant(P<0.05). The scores of PFDI-20, POP, bowel symptoms, and urination symptoms in the control group were significantly higher than those before the intervention, and the differences were significant(P<0.05). There was no significant difference in PISQ-12 and PGI-C scores between the observation group and the control group before intervention(P>0.05). The PISQ-12 and PGI-C scores in the observation group after the intervention were higher than those before the intervention and the control group, and the differences were significant(P<0.05). The PISQ-12 and PGI-C scores in the control group after the intervention were higher than those before the intervention, and the difference was significant(P<0.05). Conclusion Modified vaginal abdomen combined with uterosacral fixation is effective in treating uterine prolapse, which can shorten the operation time, reduce intraoperative blood loss, reduce complications, increase surgical satisfaction, improve pelvic floor function symptom score, and sexual life satisfaction degree score. It has a high application value.
