C17-fengycin B,produced by deep-sea-derived B acillus subtilis,possessing a strong antifungal activity against Fusarium solani*
2021-10-12WeixiangLIUChaominSUN
Weixiang LIU ,Chaomin SUN ,
1 CAS and Shandong Province Key Laboratory of Experimental Marine Biology, Institute of Oceanology, Center for Ocean Mega-Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao 266071, China
2 Laboratory for Marine Biology and Biotechnology, Pilot National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology (Qingdao),Qingdao 266237, China
Abstract Root rot disease caused by Fusarium solani is the most devastating disease of the tomato and legume crops in China.The metabolites of Bacillus species can inhibit many fungal diseases.In this study,the metabolites of deep-sea-derived bacterium Bacillus subtilis 2H11 can significantly inhibit the growth of F.solani.The metabolite C17-fengycin B,one of the cyclic lipopeptides,was identified by the combination of silica column chromatography,high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC),high-energy collision induced dissociation mass spectrometry (HCD-MS) and tandem mass spectrometry (HCD-MS/MS).The results of scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) showed that C17-fengycin B could destroy the structure of the hyphae and spores of F.solani.The antifungal activities of C17-fengycin B against F.solani were tested at concentrations ranging from 0.05 mg/mL to 0.20 mg/mL.The results indicated that C17-fengycin B inhibited the growth of F.solani with antifungal index of 89.80%at 0.20 mg/mL,and the antifungal activity of C17-fengycin B was further verified by the pot experiment.In addition,the cytotoxicity experiment showed that C17-fengycin B had good biocompatibility and was a potential candidate for the development of biocontrol pesticide in the future.
Keyword:Bacillus species;lipopeptide;fengycin;antifungal;pesticide
1 INTRODUCTION
Root rot is a kind of soil-borne disease which is common in the global economic crop production area(Egamberdieva et al.,2017).The first research on root rot was reported by von Schrenk in 1902 when he was studying apple tree diseases (Von Schrenk and Spaulding,1902).Since then,root rot infections have been found in potato (Al-Mughrabi et al.,2013),soybean (Cui et al.,2016),cucumber (Wiggell and Simpson,1969) and other crops.At present,root rot has become one of the main diseases of economic crops,which can reduce the yield by 25%–60% in serious cases (Coetzee et al.,2018).Root rot can be caused by a variety of soil microorganisms,among whichFusariumspp.is the main group (Egamberdieva et al.,2017;Chang et al.,2018).Fusariumspp.has a wide range of distribution,andFusariumsolaniis the main pathogen of root rot because of its high isolation frequency and strong pathogenicity (Chittem et al.,2015;Schroers et al.,2016).At present,the control strategies ofFusariummainly include chemical control and biological control (Patzke et al.,2017;D’Agostino et al.,2018).Among them,chemical control method has the advantages of low cost,good effect,quick effect and easy to use,which has been wildly used (Bonilla-Landa et al.,2018).However,excessive use of chemical pesticides will lead to soil pollution,food pesticide residues,and other problems,which brings a huge threat to environment and food safety (Lewis et al.,2016;Shugart,2017;Nile et al.,2019).At the same time,long-term use of chemical pesticides will lead to drug resistance of pathogenic microorganisms (Sav et al.,2018;da Rosa et al.,2019).Therefore,it is an urgent task to find new effective and green biological pesticides to control root rot (Azizbekyan,2019).
For decades,researchers have been studying marine natural products and found a series of compounds with significant biological activities(Blunt et al.,2018).Marine bacteria are an important branch of natural product research.It can be cultured by large-scale fermentation,which solves the problem of limited production of separated compounds and the sustainability of marine microbial resources(Kobayashi,2016).In 2018 alone,1 554 new marine derived compounds were reported,many of which have antibacterial,insecticidal,or antitumor activities(Carroll et al.,2020).
Bacillusis a kind of Gram-positive bacteria,which can adapt to a variety of extreme environments,even in the deep sea (Shafi et al.,2017).Research on the secondary metabolites ofBacillusfrom marine environment has been always a hot spot in the research of natural products (Zeigler and Nicholson,2017).Many types of compounds,such as ester peptide,polypeptide,polyketone,and fatty acid,have been isolated from their metabolites.Meanwhile,these compounds also have antibacterial,antitumor,and other biological activities (Li et al.,2011;Xing et al.,2018).In this study,we purified C17-fengycin B from the metabolites ofB.subtilis2H11 (BS2H11) isolated from the sediment of deep-sea cold seep.The structure was analyzed by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) and tandem mass spectrometry(ESI-MS/MS).The antifungal property of C17-fengycin B againstF.solaniwas evaluated.In addition,we also studied the effects of C17-fengycin B on spores and hyphae ofF.solaniby electron microscopy.The ester peptide derivative may be developed as an agricultural antifungal agent.
2 MATERIAL AND METHOD
2.1 Isolation,identification,and culture conditions of bacterial strains
Marine sediment was collected by RVKexue(Sciencein Chinese) from the cold seep in the South China Sea (119°17ʹ04.956ʺE,22°06ʹ58.384ʺN) at a depth of approximately 1 143 m in September 2017.The marine bacterial strain used in this study was isolated from the above-described samples by dilution method and cultured in the improved ZoBell 2216E broth (5-g/L tryptone,1-g/L yeast extract,1-L filtered seawater,pH adjusted to 7.4 to 7.6),with the temperature of 28 °C (Schut et al.,1993).To determine the phylogenetic position of the bacterial strain,universal primers 27F (5ʹ-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3ʹ) and 1492R (5ʹ-TACGGCTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3ʹ) specific for bacterial 16S rRNA genes were used to amplify the corresponding gene.Then,NCBI-BLAST (see http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST) and the phylogenetic analysis program MEGA6 were used to compare the 16S rRNA gene sequence with related sequence in public databases(Tamura et al.,2013).
2.2 Screening of bacteria inhibiting the growth of F.solani
In this study,F.solani,the main pathogen of root rot,was taken as the target fungus.To determine the antifungal activity of the bacteria strain,the surface plating method was used.The test method was as previously described in Zhang and Sun (2018).The bacterial suspension was incubated overnight and adjusted to 0.2 at 600 nm (OD600).F.solaniwas placed on potato glucose agar (PDA) plate and cultured at 28 °C for 5 d.The hyphal plug (0.5 cm in diameter)removed from the edge of theF.solaniculture was placed in the center of the new plate.Ten microliters of different bacteria were inoculated 3 cm from the plug edge ofF.solani.Plates containing onlyF.solani,or plates containing different bacteria andF.solani,were incubated at 28 °C for another 3 days,and then the growth area of fungi was measured.Then,the results were obtained by observing the presence (growth) or absence (non-growth) of fungi.
2.3 Isolation,purification,and identification of antifungal compound from B.subtilis 2H11
The single colony ofB.subtilis2H11 strain was inoculated into a 250-mL flask containing 100-mL of Luria-Bertani (LB) medium and cultured at 180 r/min for 24 h at 28 °C.Then 10 mL of this seed culture was inoculated into a 3-L flask containing 1 L of LB medium and cultured at 180 r/min for another 24 h at 28 °C.The supernatant was obtained by centrifuging the fermentation broth (8 000×g,4 °C,10 min).The pH of the supernatant was adjusted to 2.5 with 6 mol/L HCl at 4 ℃.When the solution turned clear,the precipitate was obtained by centrifugation (8 000×g,4 °C,10 min),washed with 0.1 mol/L HCl and then extracted with methanol filtered through a 0.22-μm membrane and concentrated under reduced pressure.The supernatant was then passed through a Sephadex LH-20 column for fractionation and eluted with methanol as the mobile phase (Ramos and Prohaska,1981).The eluted fraction was concentrated with a vacuum rotary evaporator and determined for antifungal activity using the paper disc method(Kordali et al.,2008).The eluted fraction with antifungal activity was filtered through a 0.22-μm membrane filter and further purified by reversedphase high performance liquid chromatography (RPHPLC) (Agilent 1260) equipped with an Eclipse XDB-C18 column (5 μm,9.4×250 mm).The mobile phase A consisting of water and methanol (20∶80,v/v)and the mobile phase B was methanol.The eluting strategy was as follows:0–20 min,0% B;20–60 min,0% B to 100% B and 60–80 min,100% B.The flow rate was 2 mL/min and the elution was monitored using a UV detector set at 210 nm.Each elution peak was collected and the antifungal activity was determined.The stability of the active compound(s)was determined by HPLC column twice.
Mass spectra of active antifungal substances was analyzed by linear ion trap Orbitrap spectrometer(LTQ Orbitrap XL,Thermo fisher) using highenergy collision induced dissociation (HCD),which was a new mass spectrometry pyrolysis technology and could provide abundant fragmentation information.Data from HCD-MS/MS were acquired under the following conditions:electrospray ion source (ESI),spray voltage 3 kV,ion transfer capillary temperature 275 °C;the dry gas was nitrogen gas,and the pressure was 0.05 MPa;HCD collision gas was helium,anion pattern detection;the collision energy of HCD is 45–60 eV.And then the results were analyzed by Xcalibur 2.1 (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc,Waltham,MA).
2.4 Antifungal assay (in vitro)
The antifungal activity was evaluated in-vitro againstF.solaniby a mycelium growth rate test.Data were collected as previously described in literature(de Rodríguez et al.,2005).The antifungal activity was detected at the concentrations of 0.05,0.10,and 0.20 mg/mL,respectively.The plates inoculated with mycelia ofF.solaniwas cultured at 27 °C.When the mycelium reached the edge of the negative control plate (no sample was added),the antifungal index was calculated by the following formula:
Antifungal index (%)=(1–Da/Db)×100.
DaandDbare the diameter of hyphae in the test plate and negative control plate respectively.Each test was repeated three times,and the results were averaged.
2.5 Protective and curative Activity (in vivo)
In this study,in-vivo antifungal activity was measured by pot experiment,and the protective and curative activity of the samples were measured.Because of the large amount of samples needed in the pot experiment,the crude extract was used.Data were collected as previously described in Benaouali et al.(2014).The experiment was carried out when tomato seedlings were cultured to at least 8 true leaves.For protective activity,the seedlings were treated with 10-mL test reagents of 0.40 and 0.80 mg/mL,respectively.24 hours later,the spore suspension was adjusted to 3.5×103spores/mL,and 2 mL of spore suspension was used to irrigate the seedlings.For curative activity,the sample treatment and spore suspension treatment time were exchanged.Tomato seedlings were treated with spore suspension at first,and then treated with sample after 24 h.Then the seedlings were cultured at 25±3 °C and 85% humidity.Each treatment was repeated in 3 groups.Seven days later,the disease index and control effi cacy were calculated.
2.6 Morphology changes of F.solani hyphae following C17-fengycin B treatment
Scanning electron microscope (SEM) was used to determine the effects of C17-fengycin B on hyphae ofF.solaniat the ultrastructural level.C17-fengycin B was spotted on a small sterilized filter paper and placed 2 cm away from the edge of the margin of freshly grownF.solani.The hyphae with or without C17-fengycin B treatment was prefixed with 2.5%glutaraldehyde.Fixed cells were rinsed three times for 10 min with 10 mmol/L Phosphate buffer solution(PBS) (pH 7.2 to 7.4).The samples were dehydrated through an ethanol gradient and coated with gold.Hitachi S-3400N scanning electron microscope was used for analysis (Hitachi,Tokyo,Japan).
2.7 Morphology changes of F.solani spores following C17-fengycin B treatment
To induce the formation of sporangium,six hyphal plugs were cut from a 1–2 week culture dish,covered with sterile distilled water and placed in a growth chamber for 48 h at 25 °C,and the light intensity was 1 400 lx (Matheron and Porchas,2000).Then the culture dish was placed at 4 °C for 1 h to promote the release of spores.The spores were washed with distilled water and the concentration of spores was checked under microscope.After spores were collected,C17-fengycin B was added into spore suspension (1×105spores/mL) of equal volume.The final concentration was 0,0.10,and 0.20 mg/mL,respectively.The spores were incubated at 25 °C in dark for 1 h.The germination of spores was examined by transmission electron microscopy.The germination of spores was examined by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) (HT7700 Hitachi).
2.8 Cytotoxicity assay
In-vitro cytotoxicity of C17-fengycin B on LO2 cell line was evaluated by methyl thiazolyl tetrazolium(MTT) assay (Hu et al.,2014).LO2 cells (1×105cells/well) were inoculated in 96-well flat-bottom culture plate and cultured in incubator for 24 h,and then introduced C17-fengycin B,the concentrations were 0.05,0.10,and 0.20 mg/mL,individually.24 hours later,the supernatants were removed,and 100-μL MTT working solution were added into each well.After incubation for 4 h,the formazan crystals were dissolved by MTT stopping buffer for 18 h and determined spectrophotometrically at 550 nm by a microplate reader (Infinite M1000 Pro,TECAN,Mannedorf,Switzerland).
2.9 Statistical analysis
Repeat each test three times and take the average result.All the data were expressed by the mean±SD of four independent measurements,and ANOVA was performed by SPSS software (version 18.0 for windows,SPSS,Inc.,Chicago,IL,USA).The mean comparison was performed by Duncan’s multiple comparison test.Statistical differences were significant atP<0.05.
2.10 Accession number
The GenBank accession number for the 16S rRNA gene ofB.subtilis2H11 is MT211278.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Antifungal activity of marine bacterium B.subtilis 2H11 against F.solani
In this study,more than 100 marine cold seep bacteria were screened through antagonistic experiments,and their ability to inhibit the growth ofF.solaniwas evaluated in an order to obtain metabolites with antifungal activity.According to the plate assays,strain 2H11 was proved to significantly inhibit the growth ofF.solani(Fig.1).In addition,the expansion of the edge ofF.solanicolony was inhibited even whenB.subtilis2H11 was not contacted,which indicated that the metabolites produced byB.subtilis2H11 could inhibit the growth ofF.solanihyphae.By comparing the 16S rRNA sequence with relevant sequences in NCBI website,it was found that the strain had the highest homology withB.subtilisstrain JCM1465 (Supplementary Fig.S1),and the sequence similarity reached 99%.Therefore,the marine bacterial strain 2H11 was designated asB.subtilis2H11.

Fig.1 Antifungal assay of B.subtilis 2H11 (b) against F.solani (a)
3.2 Isolation,purification,and identification of antifungal compounds from B.subtilis 2H11
To obtain compound(s) with antifungal activity fromB.subtilis2H11,purification was performed as described in the Materials and Methods.UsingF.solanias the indicator fungus,the paper disc method was used to trace the bioactive compound(s).In the RP-HPLC chromatogram (Fig.2a),we found a single peak related to antifungal activity,indicating that the compound here has inhibitory effect on the growth ofF.solani.Then we tested the activity of the compound obtained by RP-HPLC by the filter paper disk test,and found that they had strong antifungal activity againstF.solani(Fig.2b).The chemical structure of the compound was further analyzed and elucidated by mass spectrometry.
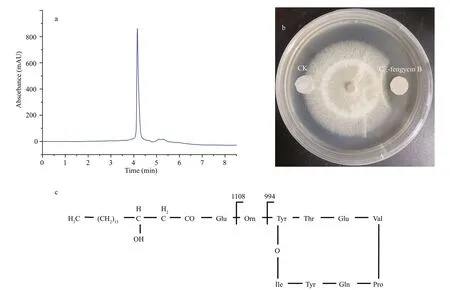
Fig.2 Purification and characterization of the active compounds from B.subtilis 2H11 inhibiting the growth of F.solani
In the results of HCD-MS and HCD-MS/MS,we found the singly-and doubly-protonated molecular ions atm/z1 505.85 [M+H]+andm/z753.43[M+2H]2+,respectively (Fig.3a).Therefore,the molecular weight of the purified active compound was 1 505 Da.It should be noted that the result is consistent with the MS data of fengycin cyclic lipopeptide (CLP) previously reported (Zhang and Sun,2018).The typical fragmentation ionsm/z994 and 1 108 in the secondary mass spectrometry were caused by the loss of fatty acid-Glu (-398 Da) and fatty acid-Glu-Orn (-512 Da) from the N-terminal segment with a Val residue at position 6 in C17-fengycin B cyclic decapeptide,respectively (Fig.3b)(Chen et al.,2010;Pecci et al.,2010).The loss of fatty acid-Glu and fatty acid-Glu-Orn usually results in the simultaneous emergence of nine peptide (Orn-Tyr-Thr-Glu-Val-Pro-Glu-Tyr-Ile,m/z1 108) and octapeptide (Tyr-Thr-Glu-Val-Pro-Glu-Tyr-Ile,m/z994) as integral fragmentation ions.In conclusion,HCD-MS and HCD-MS/MS spectral data are consistent with the corresponding information of C17-fengycin B (Fig.2c) (Pecci et al.,2010).Therefore,the antifungal metabolite produced byB.subtilis2H11 was demonstrated as C17-fengycin B.

Fig.3 Structure elucidation of C 17-fengycin B by HCD-MS (a) and HCD-MS/MS (b)
3.3 In-vitro antifungal activity of the purified C17-fengycin B against F.solani
The secondary metabolites of marine-derivedBacillushave been one of the hotspots in natural products research.Many kinds of compounds have been isolated from their metabolites.Among them,fengycin CLPs have attracted much attention due to their antifungal (Chen et al.,2010;Ma et al.,2014;Nam et al.,2015).In this essay,F.solani,the pathogenic fungus of root rot,was selected as the target.C17-fengycin B was dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO).The original concentration was 0.80 mg/mL.The antifungal results of C17-fengycin B are shown in Fig.4.The inhibitory effects of C17-fengycin B were compared with those of polymyxin B that is a polypeptide antibiotic and has a strong inhibitory effect on a variety of microorganisms.It has been widely used in many fields,and is a typical lipopeptide antibiotic.Therefore,we set it as the positive control to facilitate comparative analysis.
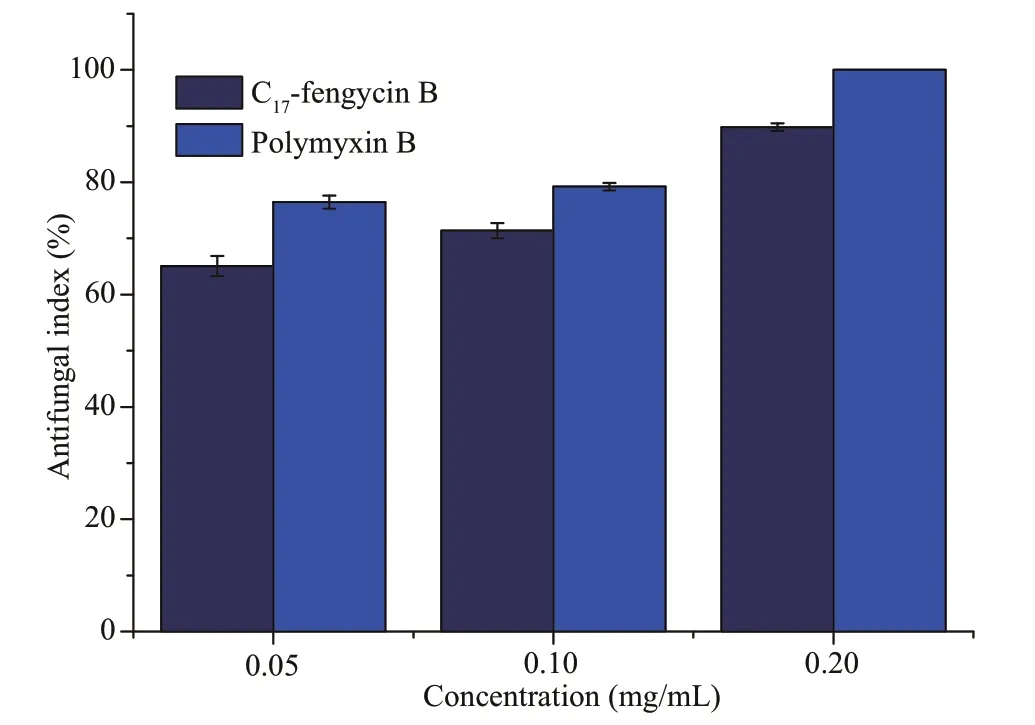
Fig.4 Antifungal activity of C 17-fengycin B and polymyxin B against F.solani
It was observed that C17-fengycin B exhibited relatively high inhibitory effect againstF.solani,and the inhibitory rates were 65.10%,71.37%,and 89.80% at the concentrations of 0.05,0.10,and 0.20 mg/mL,respectively.At the same doses,the inhibition rate of positive control polymyxin B was slightly higher than those of C17-fengycin B,and polymyxin B could inhibit the growth ofF.solani100% at 0.20 mg/mL.Some studies have shown that there is a certain relationship between the antifungal activity of lipopeptide antibiotics and their hydrophobicity (Thiericke and Rohr,1993).Generally,in the RP-HPLC system,the elution time has a positive relationship with the hydrophobicity of molecules,that is,the longer the elution time,the stronger the hydrophobicity performance.Therefore,we conclude that hydrophobic groups in C17-fengycin B may play an important role for the antifungal activity.
3.4 In-vivo protective and curative activities of C17-fengycin B
The protective and curative activities of C17-fengycin B are shown in Table 1 and Supplementary Fig.S2.The disease indexes of tomato irrigated with C17-fengycin B were significantly lower than that of the negative control group irrigated with water.In addition,the control effi cacy of C17-fengycin B increased with its concentrations.At the concentration of 0.8 mg/mL,the protective activity and curative activity of C17-fengycin B were 85.19% and 73.50%,respectively,which were close to those of positive control polymyxin B.There were no obvious pathological changes in the roots of seedlings treated with C17-fengycin B,and the roots were not blackened.Moreover,in contrast to the positive control polymyxin B,the protective activity of C17-fengycin B was higher than that of its curative activity at the same concentration,which indicated that the antifungal activity of C17-fengycin B would not be damaged by the soil and would play a sustainable role in the application.
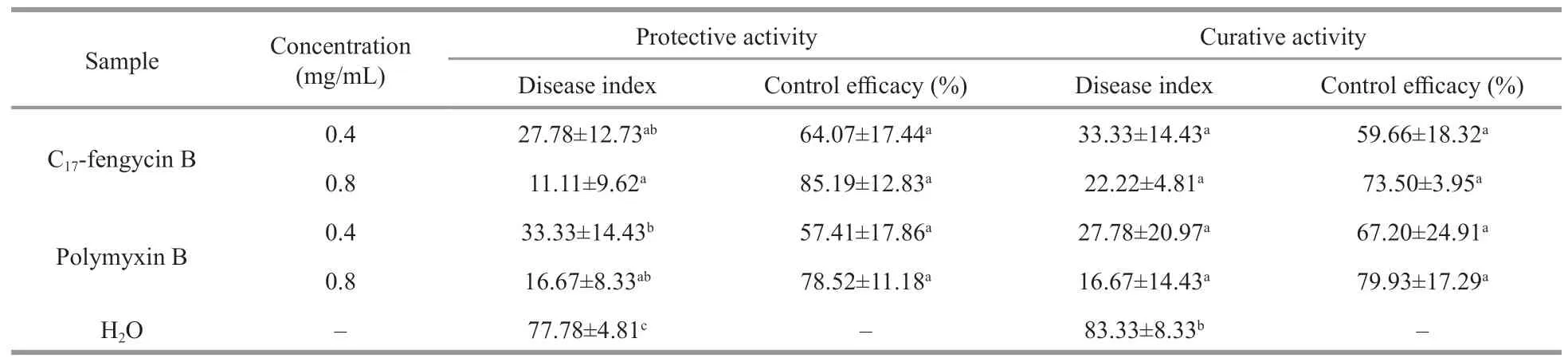
Table 1 Protective and curative activities of C 17-fengycin B against F.solani
3.5 Morphology changes of F.solani hyphae caused by C17-fengycin B
To study the effects of C17-fengycin B on the morphology ofF.solanihyphae,SEM observation was conducted.As shown in Fig.5,the hyphae ofF.solaniin the control group grew normally,with plump and intact trunks.In contrast,the morphology of hyphae treated with C17-fengycin B was significantly different with the control.Compared with the control group,the amount of hyphae treated with C17-fengycin B was significantly reduced,and the hyphae appeared rough and shriveled.
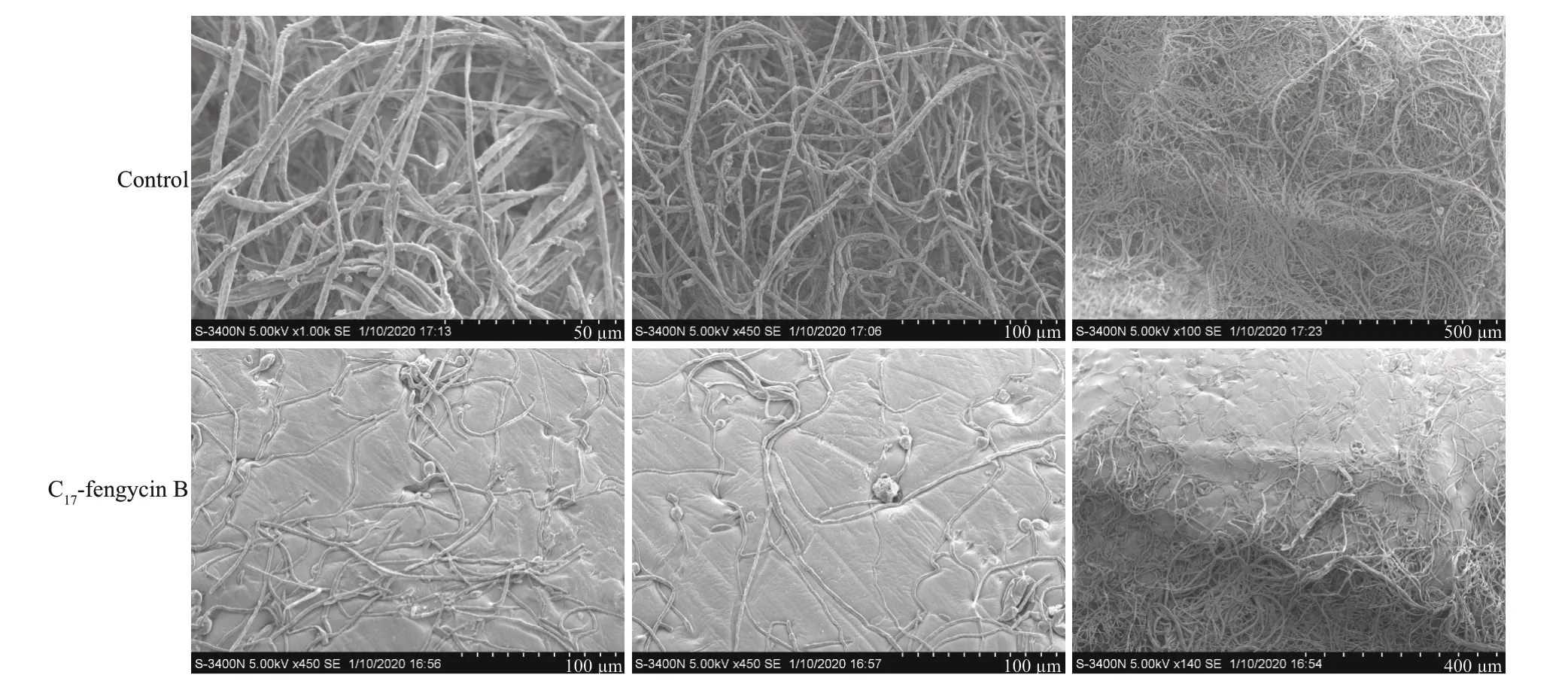
Fig.5 Effects of C 17-fengycin B on the morphology of F.solani hyphae observed by SEM
3.6 Morphology changes of F.solani spores caused by C17-fengycin B
TEM was used to observe the effects of C17-fengycin B on the morphology changes ofF.solanispores (Fig.6).The normal fungal spores have intact and regular cell walls and membranes,with dense cytoplasm and uniform spatial distribution in the intracellular space.However,after C17-fengycin B treatment,the cytoplasm became sparse and light,and the cell membrane became incomplete or even ruptured.At the same time,we also found that higher concentration of C17-fengycin B destroyed spores more seriously,which indicated that the antifungal activity of C17-fengycin B was positively correlated with its concentration.In conclusion,the electron microscopy results showed that C17-fengycin B can damage the cytoplasm and membrane ofF.solaniand destroy the integrity of cells.

Fig.6 Effects of C 17-fengycin B on the morphology of F.solani spores observed by TEM
3.7 Cytotoxicity assay
As we all know,most chemical fungicides have strong toxicity.These fungicides are harmful to insects,animals,and human beings.Therefore,the search for new fungicides with low toxicity and high effi ciency has always been an important field of pesticide research.At present,most of the studies on the cytotoxicity of fengycin CLPs focus on their antitumor activity,but few on the cytotoxicity of normal animal cells (Yin et al.,2013;Ramachandran et al.,2017;Rofeal and El-Malek,2020).The results showed that some fengycin CLPs had significant cytotoxicity to human embryonic kidney 293(HEK293),human internalized keratinocyte (HaCaT),human cervical cancer (Hela),and human type II alveolar epithelial (A549) cell lines.In this study,we used LO2 cells as the target to test the cytotoxicity of C17-fengycin B.The effects are listed in Fig.7,showing that at the concentrations of 0.05 and 0.10 mg/mL,the cell viability of LO2 cells treated with C17-fengycin B was 91.54% and 83.46%,respectively.In addition,at the same concentration,the cytotoxicity of C17-fengycin B was significantly lower than that of positive control polymyxin B.These results indicate that C17-fengycin B has good biocompatibility to LO2 cells and has the potential to develop into an environmental friendly biological fungicide.
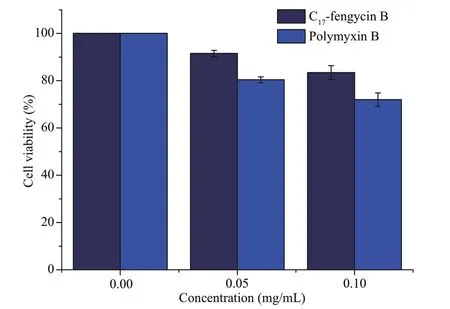
Fig.7 The toxicity of C 17-fengycin B on LO2 cells
In this study,the presence of C17-fengycin B(0.05 mg/mL) appeared to have no effect on LO2 cells.Compared with chemical method,microbial fermentation has the advantages of low cost,environment-friendly,and easily scaled up for large scale synthesis.This study demonstrated that C17-fengycin B can be used as a biofungicide to control root rot caused byF.solani.C17-fengycin B showed strong antifungal activity in vitro and in vivo,and had a low cytotoxicity to LO2 cells.
The results can provide a new idea for the control of root rot in the future.The biosynthesis of C17-fengycin B byB.subtilisis an effi cient,green,and sustainable method.This will greatly reduce the environmental pollution and pesticide residues caused by chemical pesticide production.However,before developing the agricultural application of C17-fengycin B,it is necessary to do more researches on the antifungal mechanism of C17-fengycin B.
4 CONCLUSION
This study was conducted to determine the activity of cyclic lipopeptide C17-fengycin B,produced by deep-sea bacteriumB.subtilis2H11,in the suppression ofF.solani(pathogen of the tomato root rot disease).The structure of C17-fengycin B was confirmed by HCD-MS and HCD-MS/MS.The antifungal effects of C17-fengycin B againstF.solaniwas evaluated invitro and in-vivo.The results show that C17-fengycin B could effectively inhibit the growth ofF.solani.At the same dose,the inhibition rate of C17-fengycin B was slightly lower than that of positive control polymyxin B.In addition,a cytotoxicity assay of C17-fengycin B was also performed,and the results show that the cytotoxicity of C17-fengycin B was significantly lower than that of polymyxin B.Moreover,the hyphae and spores ofF.solanitreated with C17-fengycin B were observed by electron microscope,and the antifungal mechanism of C17-fengycin B was discussed.In conclusion,C17-fengycin B has a good antifungal activity and biocompatibility,it could be a potential candidate for the development of biocontrol pesticide.
5 DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
The data that support the findings are all presented herein.
杂志排行
Journal of Oceanology and Limnology的其它文章
- Screening of stable internal reference genes by quantitative real-time PCR in humpback grouper Cromileptes altivelis*
- Effect of fasting on protein metabolism in muscle tissue of Larimichthys crocea revealed by transcriptome and proteome*
- Comparison of fungal community composition within different intestinal segments of tilapia and bighead carp*
- Mitochondrial phylogenomics reveal the origin and adaptive evolution of the deep-sea caridean shrimps (Decapoda:Caridea)*
- Relationship between morphospecies and microcystinproducing genotypes of Microcystis species in Chinese freshwaters*
- Size-dependent spatio-temporal dynamics of eukaryotic plankton community near nuclear power plant in Beibu Gulf,China*
