床旁心肺超声在心力衰竭合并肺水肿患者中的应用
2021-09-28彭贵平洪涛梁敏徐素音周世云李智惠叶扶于
彭贵平 洪涛 梁敏 徐素音 周世云 李智惠 叶扶于


[关键词] 肺超声;心力衰竭;肺水肿;超声心动图
[中图分类号] R541.6 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2021)22-0136-04
Application of bedside cardiopulmonary ultrasound in patients with heart failure and pulmonary edema
PENG Guiping HONG Tao LIANG Min XU Suyin ZHOU Shiyun LI Zhihui YE Fuyu
Department of Ultrasound, Jiujiang NO.1 People's Hospital in Jiangxi Province, Jiujiang 332000,China
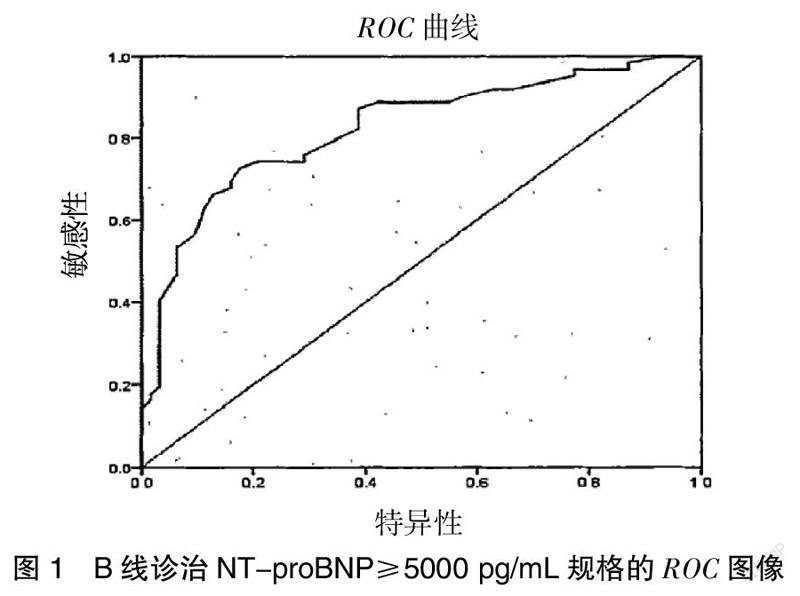
[Abstract] Objective To explore the clinical application of bedside cardiopulmonary ultrasound in patients with heart failure and pulmonary edema. Methods Forty patients with congestive heart failure admitted to the intensive care unit or emergency ward of our hospital between May 2019 and August 2020 were selected. All patients were examined by bedside cardiopulmonary ultrasound. Results The ultrasound pulmonary edema score was tested for patients with heart failure (NYHA) with heart function above grade Ⅱ. All patients were involved in bilateral diffuse B lines. The average examination time for patients was (3.0±0.3)min. The median of the B-line score of the 7-zone method was 11 points. The pulmonary edema score of heart failure (NYHA) patients with heart function above grade Ⅱ was diagnosed by ultrasound. It was found that the diagnostic value was 12.4.The sensitivity under this value could reach 80.78%,and the specificity was 60.24%. Multivariate regression analysis showed that among the risk factors of heart failure patients with pulmonary edema,the independent risk factors included average E/e', SPAP, NT-proBNP. Conclusion Bedside pulmonary ultrasound is currently an effective method for clinical evaluation of patients with heart failure and pulmonary edema. At the same time,it has the advantages of simple operation method and relatively fast evaluation speed. Therefore, pulmonary ultrasound can become an important index for clinical rapid prediction and prognosis assessment of heart failure complicated with pulmonary edema.
[Key words] Lung ultrasound; Heart failure; Pulmonary edema; Echocardiography
急性心力衰竭是临床上较为常见的一种疾病,病情较为严重,会严重影响患者的生命安全,心力衰竭是多种病因导致的患者出现心脏收缩或舒张功能障碍,导致患者肺循环、体循环或者心脏循环出现障碍的综合征[1]。在患者进行肺循环时,由于会出现一系列的障碍,其中较为关键的因素之一是肺水肿,肺水肿在患者的临床诊断或早期的就诊中作為心力衰竭治疗的一个重要依据,如果能早期诊断可以有效的提升患者的预后和生存质量[2]。本文主要用肺部超声对心力衰竭合并肺水肿的患者进行临床研究,旨为患者的临床治疗提供更好的依据,现报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
本研究选取本院重症监护室或急诊病房2019年5月至2020年8月间根据Framingham的标准诊断40例住院的充血性心力衰竭患者,所有患者均有不同程度的呼吸困难,美国纽约心脏病协会(New York heart association,NYHA)心功能分类分为NYHAⅡ,NYHAⅢ和NYHAIV。房颤、二尖瓣狭窄患者被排除在外。排除肺部疾病主要取决于临床症状,胸部X光片和实验室检查。本研究获得本院医学伦理委员会的批准。参与研究的患者及家属均签署知情同意书。
