2 型糖尿病周围神经病变患者血清维生素D水平变化及意义
2021-09-28徐清田周群燕朱晓巍徐湘
徐清田 周群燕 朱晓巍 徐湘

[關键词] 血清25羟维生素D3;2型糖尿病;糖尿病周围神经病变
[中图分类号] R587.1 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-9701(2021)22-0024-04
Changes and significance of serum vitamin D level in patients with type 2 diabetic peripheral neuropathy
XU Qingtian1 ZHOU Qunyan1 ZHU Xiaowei2 XU Xiang2
1.Department of Clinical Nutrition, Wuxi People′s Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Wuxi 214023, China; 2.Department of Endocrinology, Wuxi People′s Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Wuxi 214023, China
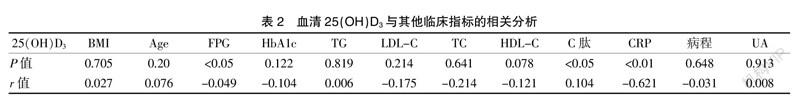
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the change and clinical significance of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 [25(OH)D3] level in peripheral neuropathy with type 2 diabetes mellitus(T2DM) and provides the diagnosis basis for early prevention and traetment of DPN. Methods A total of 214 patients with T2DM were admitted to The People Hospital of Wuxi City from April 2016 to February 2019 were geted into this study. Through clinical retrospective study, 214 subjects were divided into 109 DPN group and 105 NDPN group according to the diagnostic criteria of DPN. The serum levels of 25(OH)D3 which were determined by ELISA. Fasting blood-glucose(FPG), Fasting C-peptide,blood lipids, glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), and C-Reactive Protein(CRP), Biochemical indicators such as blood lipid and uric acid were detected in all objects of the study. The pearson correlation between 25(OH)D3 and each indicator was analyzed. The vitamin D deficiency is currently recommended to be less than 20 ng/mL, the subjects were splited into vitamin D deficiency and non-vitamin D deficiency groups on the basis of the criteria. To compare the morbidity of DPN between the two groups and multiple linear stepwise regression analysis was performed to observe independent risk elements for DPN. Results The standard of serum 25(OH)D3 was obviously higher in the NDPN group (36.47±11.01 ng/mL) than that in the DPN group (26.64±7.41ng/mL) (P<0.01), and the difference was statistically significant. The serum standard of 25(OH)D3 was positively correlated with Fasting C-peptide in T2DM, but negatively correlated with FPG、CRP(r=0.104, P<0.05; r=-0.049, P<0.05, r=-0.621, P<0.01); Multivariate regression analysis indicated that the 25(OH)D3 and CRP were the independent influencing elements of DPN. (β=-0.093, P<0.01,β=0.354, P<0.05). T2DM patients in the vitamin D deficiency groups had 1.54 times the risk of promoting DPN compared with those in the non-vitamin D deficiency groups(OR=1.54). Conclusion To reduce the standard of serum vitamin D may promote the risk of DPN. The serum vitamin D is involved in glucose and lipid metabolism and inflammatory response in T2DM patients which may promote the occurrence of DPN. Monitoring the standard of 25(OH)D3 is beneficial to the early diagnoisis and treatment of DPN.
