Thoughts on Present Situation of Development of Rural Animal Husbandry and Its Relationship with Construction of Ecological Agriculture and Revitalization of Rural Industry
2021-09-24DejunTANGuoguiWANGYunfenZHUXiaofeiCHENJinMARongLIJunhuiXIE
Dejun TAN, Guogui WANG, Yunfen ZHU, Xiaofei CHEN, Jin MA, Rong LI, Junhui XIE
Enshi Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Enshi 445000, China
Abstract After several rounds of phased ups and downs of development, rural animal husbandry finally presents a shrinking and depressed development situation under the comprehensive action of the failure of transformation and upgrading and the increasing production costs and breeding risks. Actively exploring and guiding the healthy and sound development of rural animal husbandry is not only an important measure to promote the construction of ecological agriculture, but also the main starting point to realize the revitalization of rural industry. This paper analyzes the present situation of the development of rural animal husbandry in recent years, the influence of animal husbandry on the construction of ecological agriculture and the revitalization of rural industry, and puts forward the corresponding measures, in order to promote the steady and efficient development of animal husbandry in the grand strategy of revitalizing rural industry.
Key words Present situation of the development of rural animal husbandry, Construction of ecological agriculture, Revitalization of rural industry
1 Introduction
Animal husbandry is an important part of large-scale agriculture, it plays an important role in improving the quality and efficiency of agricultural production, and is an important pillar industry for farmers to increase their economic income and improve their quality of life. However, in the past 10 to 15 years, due to the constraints of shrinking profits, epidemic risk, shortage of funds, lag of deep processing and low scale, the rural livestock and poultry breeding industry has shrunk year by year. Taking the number of pigs raised in a natural village (300 households) as an example, the total number of pigs in the village 15 years ago could reach 2 500 to 3 000, and the breeding capacity of sows could reach 150 to 200. At present, the breeding capacity of one village (as above) is less than 1 000, and the stock of breeding sows is less than 50. Rural animal husbandry shows a depressed and shrinking development trend under the comprehensive influence of various unfavorable factors. The decline of the development of rural animal husbandry will seriously affect the construction of ecological agriculture. How to promote the healthy development of animal husbandry is an important measure and main starting point to realize the revitalization of rural industry.
2 Present situation of the development of rural animal husbandry (taking pig breeding as an example)
In the past 15 years, the rural pig farming industry has mainly experienced four major development fluctuations, namely: the first cycle 2001-2004, the second cycle 2005-2008, the third cycle 2009-2012, and the fourth cycle 2013-2016. Rural free-range farmers and large-scale farmers lost almost all their money in the process of four rounds of short-term rise and continuous decline in pig prices. The free-range farmers gradually give up the breeding industry or only raise pigs to feed themselves, and most of the large-scale households change careers or only a small number of farms (households) are mainly engaged in restricted breeding. After the cruel market screening, farmers’ breeding passion returns to normal, and the momentum of breeding industry shrinks year by year.
2.1 Several stages of the development of pig farming in recent years
2.1.1
First development cycle (2001-2004). This period can be called the "budding period". Affected by the stimulation of price and the relative improvement of feeding technology, the traditional pig breeding industry began to show a momentum of rapid development. Pig farming has always been an important pillar industry in rural areas, accounting for about 50% of the income of traditional agriculture. However, when the price of live pigs rose from 3.0-4.4 yuan/kg in 2001 to 7-8 yuan/kg in 2004, the number of live pigs and the stock of breeding sows increased at an annual rate of 50% to 100%, the construction of breeding facilities continued to expand and improve, and the whole industry developed rapidly. The budding period gives hope to traditional pig farmers, but it also lays a hidden danger for future losses.2.1.2
Second development cycle (2005-2008). This period can be called "transition period" or "swarming period". When farmers rapidly expand production, what is ushered in is the sustained downturn in pig prices from 2005 to 2006 and the outbreak of epidemic disease (reproductive and respiratory syndrome and various mixed infections) from 2007 to 2008, which made farmers feel panic, but the epidemic situation was quickly brought under control, and a prevention and control vaccine was developed. The development of pigs was very stable. As pig prices rose from 5 yuan/kg in 2005 to 1920 yuan/kg in 2008, farmers’ worries were quickly watered down by 100% returns. Under the alternating influence of endogenous and exogenous forces, farmers became fanatical, the development momentum of the rush spread rapidly, and the breeding model changed from free farming and small-scale farming in the past to large-scale and standardized farming. Large-scale and standardized pig farming not only expands the production scale, but also increases capital construction and capital investment, which becomes a hidden danger of operation on borrowings and capital chain breaking in the later stage.2.1.3
Third development cycle (2009-2012). This period can be called "scale period and debt period". The number of free-range farmers gradually decreased or withdrew, and the number of large-scale farmers increased year by year. During this period, feed prices rose as a whole. The interaction of factors such as the expansion of the scale of infrastructure construction, the sharp increase of capital investment, the frequent occurrence of mixed epidemic diseases and the continuous fluctuation of prices led to meagre profits or even losses, and most large-scale farms were in the stage of operation on debt and production reduction. Pig prices returned to normal after briefly rising at the end of 2011 and early 2012, and farmers’ early large capital investment did not get a generous return. The sustained large amount of capital investment led to a high debt in rural scale farming where financing was difficult.2.1.4
Fourth development cycle (2013-2016). This period can be called "empty stock period and atrophy period". Due to the influence of factors such as continued weak prices and capital preservation operation, rising production costs and shrinking profits of the industry, many farmers withdrew from the industry, and the few remaining farmers kept going by painstaking effort. The number of live pigs decreased significantly, by 50% to 70% compared with the peak period, and sows were reduced by 70% to 80%. There were a large number of empty farms. Although pig prices increased at the end of 2016, the enthusiasm for pig farming completely faded, and the momentum of overall shrinkage loomed large.2.2 Analysis on the causes of the shrinkage of animal husbandry in rural areas
2.2.1
The impact of unstable livestock and poultry prices. The price of livestock and poultry rises and falls greatly. Take live pigs as an example, farmers generally lose money for three years and make money for one year, while free-range farmers and large-scale households lose almost all their money. The loss and withdrawal of free-range farmers and the loss and debt of large-scale households make it difficult to resume production, and the interaction between them leads to a sharp reduction in the number of live pigs and the shrinkage of traditional farming industry.2.2.2
The impact of failure in transformation and upgrade. In the process of the transformation of livestock and poultry breeding from scattered breeding to large-scale and standardization, due to the shortage of funds and backward technology, the scale of livestock and poultry breeding is not high, the degree of standardization is not high or the transformation fails, and the ability to resist market risks is weak. In addition, due to the difficulty of industry financing and the discontinuity of policy support, many farms are already in debt and unable to develop production, resulting in a waste of resources, funds and projects.2.2.3
The impact of insufficient deep processing of products. The sale of livestock and poultry breeding industry is mainly based on the direct sale of live animals, and the cold chain segmentation and insufficient brand building and deep processing development of livestock and poultry slaughtering have seriously affected the market competitiveness of the breeding industry and the economic added value of the products. The farmers at the bottom of the industrial chain make meagre profits after the stripping of their profits, which seriously dampens their enthusiasm and restricts the development of the industry, thus forming a vicious circle and leading to the shrinkage of the breeding industry.2.2.4
Adverse effects of resource allocation. The rural livestock and poultry breeding industry must rely on the support of land, forest, water conservancy, transportation, electric power, funds, projects and other related resources, but the rural resources are scattered and difficult to integrate, which hinders the development of the whole industry. Often, those who are willing to develop do not have the resources and do not have the financial support for the project. Those who have no willingness to develop have the resources, get the financial support of the project, but do not develop the industry, leaving only an empty shelf, which affects the healthy development of the animal husbandry industry.2.2.5
The impact of inadequate funding, technology and backward ideas. Due to the lack of funds in the rural livestock and poultry breeding industry, it restricts the development and innovation of the industry. The lack of technology and backward management lead to the increase of feeding cost and the decrease of breeding benefit. The intertwined influence of the above factors makes livestock farmers lose the best period of development and investment opportunities, miss the opportunities for development and growth, and restrict the development of the whole industry.2.2.6
The impact of risk of animal disease prevention and control. The risk of disease prevention and control in rural livestock and poultry breeding is high. Due to the lack of awareness of animal disease prevention and control in rural areas and the backwardness of prevention and control measures, livestock and poultry breeding will be completely paralyzed and failed due to the impact of an epidemic, and there is a lack of response and remedial measures. Many farms (households) withdraw from the breeding industry because of the failure of epidemic prevention and control and fear of epidemic infection, resulting in the shrinkage of livestock and poultry breeding industry.2.3 Comprehensive impact
Under the long-term mutual influence of the above factors, the development desire of livestock farmers turns to rationality after many setbacks, and the blind and impulsive development is curbed. Large-scale farms (households) are deeply in debt in the failure of transformation, and are unable to resume production in a short time. The reduction of the above two major types of farmers has led to the overall shrinkage of the livestock and poultry breeding industry. Table 1 shows the changes of pig production and price in a village from 2001 to 2016. As can be seen from Table 1, the pig farming in this village is completely consistent with the four stages of pig farming development. During the breeding peak, the stock of pigs could reach 2 500-3 000, the stock of breeding sows could reach 150-200, while in 2016, the stock of live pigs was only 850, and the stock of breeding sows was only 40.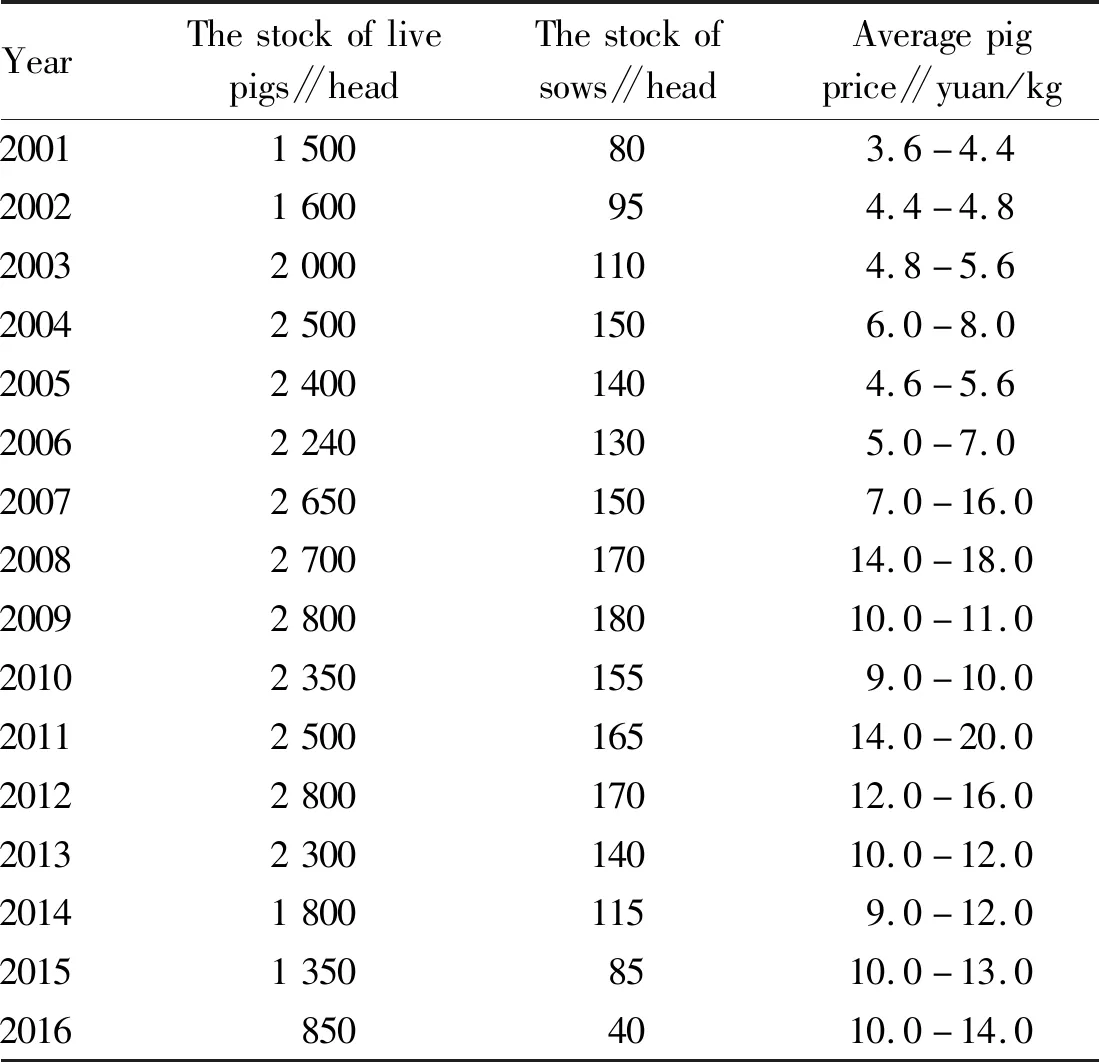
Table 1 Changes of pig production and price in a village from 2001 to 2016
3 Impacts of the development of livestock and poultry breeding on ecological agriculture
3.1 The development of animal husbandry can improve the efficiency of agricultural production
Ecological agriculture is a circular and efficient agricultural production mode. The primary products, inferior products and processed by-products in agricultural production are high-quality feed for livestock and poultry, which can be transformed into high-quality animal husbandry products on the spot and increase the efficiency of agricultural production. At the same time, it also improves the quality of livestock and poultry products.3.2 The development of animal husbandry can provide high quality organic fertilizer for ecological agriculture
After fermentation, precipitation and processing, the manure produced in the process of animal husbandry production is a high-quality organic fertilizer used in agricultural production. Take pig and sheep as an example: one pig can produce 547 kg manure and 1 095 kg urine in the whole year, and one sheep can produce 547 kg manure and 274 kg urine in the whole year. The fertilizer produced by 2-3 pigs or 3-4 sheep can be used in 667 mfarmland.3.3 The development of animal husbandry can improve the quality of agricultural and sideline products
Due to the extensive use of organic fertilizer in agricultural production, the use of chemical fertilizer is reduced, the agrochemical residues of agricultural products are reduced, the quality of agricultural products is improved, and the competitiveness of agricultural products is enhanced.3.4 The development of animal husbandry can improve soil fertility structure
The organic fertilizer produced in animal husbandry production can be used in farmland, which can loosen soil, increase soil water holding capacity and permeability, improve the quantity and structure of soil microflora, promote the decomposition and absorption of soil nutrient factors, and thus increase soil fertility.3.5 The development of animal husbandry can adjust the agricultural production structure and optimize the allocation of resources
The development of animal husbandry can optimize the agricultural production structure, expand the agricultural production chain, and make rational use of all kinds of resources. The development of animal husbandry can make full use of rural grasslands, grassy slopes and crop straws. It is recommended to raise livestock, improve the utilization rate of resources and increase economic benefits. We can change the agricultural production and management mode based on single grain production, realize multi-channel production and operation, and enhance the ability to resist market risks and natural disaster risks.4 Impacts of the development of livestock and poultry breeding industry on the revitalization of rural industry
4.1 Animal husbandry is a traditional pillar industry in rural areas
, with solid foundation and rapid development
Rural animal husbandry has relatively perfect infrastructure construction, high-quality and diverse livestock and poultry germplasm resources, rich and cheap feed sources, relatively mature feeding and management technology, relatively good foundation, and is easy to develop, so it is a pillar industry that is easy to support for the revitalization of the rural industry.
4.2 The development of animal husbandry can promote the development of many industries
The industrial chain of animal husbandry extends back and forth, which can promote the development of agriculture and feed processing industry, and the development of slaughtering and processing industry, animal food processing industry, catering industry, product marketing industry, transportation and logistics industry,etc.
It can stretch the industrial chain, expand intensive processing, increase industrial income and make the rural economy prosper.4.3 The development of animal husbandry industry is conducive to promoting the virtuous circle of rural agriculture
Animal husbandry industry is a consumptive industry, which can consume agricultural primary products and produce green and healthy animal husbandry products; it can also produce a large amount of organic fertilizer to return to the field, reduce agricultural residues and improve the quality of agricultural products; promote the virtuous circle of agricultural production and ensure food security.
4.4 The development of animal husbandry is conducive to promoting the development of rural tourism and contract agriculture and animal husbandry
There are many varieties in animal husbandry, and the rational planning and layout of rural livestock and poultry breeding can increase the vitality of peaceful mountain villages, promote the development of rural tourism, allow tourists to visit farms and green planting bases in person, and increase tourists’ understanding of green and healthy agricultural and animal husbandry products, so as to develop order and experience agriculture and animal husbandry, and increase the income of agriculture and animal husbandry production. The revitalization of rural industry is the basis of the revitalization of rural industry. The revitalization of rural industry is to make full use of high-quality resources in rural areas, including forest and fruit, vegetables, grain and oil, medicine, livestock and poultry, environment,etc.
, to gather talents from all walks of life, develop intensive processing, and build famous and high-quality brands, expand industrial chains, broaden marketing channels, increase farmers’ income, and build a beautiful countryside.5 Recommendations for promoting the healthy and stable development of rural livestock and poultry
In view of the current situation of the shrinkage of the rural livestock and poultry industry, it is necessary to explore long-term, pragmatic and practical solutions to promote the healthy and stable development of the rural livestock and poultry industry.
5.1 Making rational layout planning according to the reality of the countryside
According to the reality of the countryside, it is necessary to reasonably plan the long-term development of the leading breeds of pigs, cattle, sheep and chickens. In areas dominated by grain production and areas with better infrastructure for breeding, emphasis should be placed on the development of livestock and poultry varieties such as pigs and chickens. In areas with more grassy hills, grassy slopes and sloping farmland, it is necessary to return farmland to grassland and improve pastures, and strive to develop grain-saving herbivorous livestock, cattle and sheep.5.2 Creating one product per village and promote the development with characteristics
The whole county or the whole town should make an overall layout, create a characteristic breeding mode of one product for one township, form continuous development, and create a development model with the integration of production, processing and sale. According to the county and township environment and climate, cultural habits, industrial advantages, internal and external resources,etc.
, it is necessary to co-ordinate the development of farming with rural characteristics. It is necessary to choose leading breeding varieties, create a complete industrial chain, create a number of famous and high-quality local brands, enhance the market competitiveness of products, and promote the development of animal husbandry industry.5.3 Leading green development and improving product quality
Relying on the good natural environment of the countryside, it is necessary to develop green and healthy breeding. It is necessary to implement the ecological cycle model combining planting and breeding. According to the suitable geographical environment, it is necessary to develop a batch of ecological chicken raising models under the forest, orchard, tea garden and medicine garden or a batch of semi-open pig breeding models, develop pure natural forage and feed, increase the diversity of feed varieties, improve animal welfare, reduce animal stress, adapt to the biological characteristics of livestock and poultry as far as possible, promote the health of livestock and poultry, improve the quality of livestock and poultry, and increase the economic benefits of livestock and poultry breeding.5.4 Promoting intensive processing and continuously improving quality and efficiency
It is necessary to promote the intensive processing of livestock and poultry products and establish modern livestock and poultry products processing enterprises in rural areas that integrate slaughtering, cold chain, segmentation, packaging, and processing of livestock and poultry meat products, so as to increase the added value of livestock and poultry products and increase economic benefits. It is necessary to encourage rural farming enterprises and farming federations to set up livestock and poultry product processing enterprises, increase policy support and financial support, gradually form a complete industrial chain, enhance the ability of farmers to resist market risks, and promote the healthy development of rural breeding industry.5.5 Building a modern sale system
It is necessary to change the traditional sale model of live livestock middlemen, gradually form a point-to-point sale of livestock and poultry products or reach a dedicated service sale model, realize the organic combination of rural green farming with high-end consumption in big cities, and enhance the economic value of green livestock and poultry products, to ensure the hygiene and safety of animal food. It is necessary to actively explore Internet sale, vigorously cultivate consumers, enhance brand reputation, safety reputation, and service reputation, enhance market share, and increase marketing income.5.6 Establishing regional variety protection system and improved variety breeding system
According to the development and reality of local livestock and poultry breeding industry, it is necessary to increase state investment, establish a local livestock and poultry variety protection system and improved breed breeding system, and constantly enhance the regional breed supply capacity of local livestock and poultry breeding farms, so as to meet the needs of livestock and poultry breeding industry, reduce the risk of disease and high cost burden of livestock and poultry breeding, and ensure the healthy and stable development of rural livestock and poultry breeding industry.5.7 Increasing the support of talents, technology and policies for rural livestock and poultry breeding
In rural livestock and poultry breeding, we should constantly improve the technical and management quality of practitioners and enhance the degree of standardization of the whole industry. We should constantly strengthen the functions of township animal husbandry and veterinary service centers, increase human, financial and material security, and build the most solid fortress for the development of animal husbandry. Professional learning, and training institutions covering counties and townships should be established to teach modern breeding concepts, epidemic prevention and control technology and feed nutrition science through the network, classroom and training platform on a regular basis, to constantly improve the practitioners’ professional technology and risk, crisis prevention and control awareness. We should strengthen the regional construction capacity of livestock and poultry medical equipment and biological laboratories, constantly improve the public service capacity, meet the scientific and technological needs of rural livestock and poultry development, and provide a strong guarantee for the revitalization of rural animal husbandry industry.6 Conclusions
In recent years, rural animal husbandry, like other traditional rural industries, is gradually weakening in the tide of modernization. We should actively explore and realize the organic connection between traditional animal husbandry and modern animal husbandry, promote the improvement of quality and efficiency of traditional animal husbandry, and give full play to the green and health advantages of traditional animal husbandry products instead of using simple methods of abandonment, elimination and prohibition to restrict the development of traditional animal husbandry. Only in this way can the construction of rural ecological agriculture be formed, and will the road of rural industry revitalization be wider and wider.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Efficiency Comparison and Influencing Factor Analysis of Dairy Farms over/at Different Scales: Based on the Survey Data of 263 Scale Farms in 22 Provinces of China
- Regional Differences and Optimal Allocation of Cultivated Land Utilization Benefits Based on Improved TOPSIS Method: A Case Study of Guangxi
- Characteristics of Fallen Seed Distribution by Domestic and Imported Aerial Seeding Equipment
- Implementation Path and Development Trend of Green Buildings Based on Life Cycle Management
- Hot Spot Analysis and Development Trend of Intelligent Roof Parking Lot: Bibliometric Analysis Based on CiteSpace Visualization Software
- Biological Evaluation of Water Quality for Benthos in Typical Rivers of Eastern Jilin Province
