基于表示学习的高维光谱离群数据挖掘
2021-09-14李林睿常舒予乔一鸣
李林睿 常舒予 乔一鸣


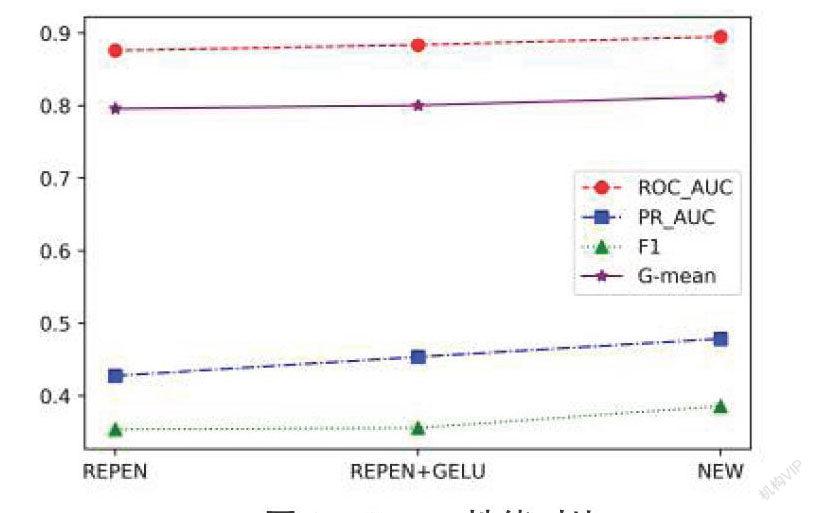
摘要:LAMOST(郭守敬望远镜)提供了大量的天文光谱数据,而天体分类是天文学中得到广泛关注的问题,由于天体数量大,数据维度高,如何使用机器学习的方法对光谱进行处理,成为近些年的热点。针对天体分类问题,提出了HSODM(High-dimensional Spectral with Outlier Data Mining),这是一种改进的高维离群数据识别方法,其采用无监督学習方式,基于随机距离将大量高维光谱数据中的极少数未知天体或离群数据识别出来,便于后续天体分类、离群数据挖掘等相关处理。项目中运用数据预处理、主成分分析降维、长短期记忆神经网络模型建立与训练、参数调优、结果预测与分析,最终通过评估方法和数据可视化等手段对模型进行评价与展示。研究中提出的改进方法和优化的神经网络可以缩短训练时间,提高模型预测准确度。经过实验发现,改进方法对ROC (receiver operating characteristic) 曲线面积、P-R曲线面积、F1分数和G-mean分数都有相应的提高。
关键词: 表示学习;高维光谱;离群点检测;数据挖掘; 分类
Abstract: LAMOST (Large Sky Area Multi-Object Fiber Spectroscopy Telescope) Telescope provides a large amount of astronomical spectral data, and astronomical classification is a problem that has received widespread attention in astronomy. Due to the large number of celestial bodies and the high dimensionality of data, how to use machine learning methods to process spectra has become a problem in recent years. Hot spot. Aiming at the problem of celestial body classification, HSODM (High-dimensional Spectral with Outlier Data Mining) is proposed, which is an improved method for identifying high-dimensional outlier data. It uses an unsupervised learning method and combines a large number of high-dimensional spectral data based on random distance. A very small number of unknown celestial bodies or outlier data can be identified to facilitate subsequent celestial body classification, outlier data mining and other related processing. In the project, data preprocessing, principal component analysis and dimensionality reduction, long and short-term memory neural network model establishment and training, parameter tuning, result prediction and analysis are used in the project, and the model is finally evaluated and displayed by means of evaluation methods and data visualization. The improved method and optimized neural network proposed in the research can shorten the training time and improve the accuracy of model prediction. After experimentation, it is found that the improved method has corresponding improvement on ROC curve area, P-R curve area, F1 score and G-mean score.
Key words: representation learning; high-dimensional spectral; outlier detection; data mining; classification
天文学随着科学技术的发展,先进的观测设备使我们能够望向宇宙更深处,同时也带来了天文数据爆炸式的增长[1]。郭守敬望远镜(LAMOST)作为世界上光谱获取率最高的望远镜,LAMOST每个观测夜晚能采集万余条光谱,这将为一些天文和天体物理学家在星系红移巡天、宇宙学模型、宇宙大尺度结构、星系形成和演化以及结合各类射线的光谱观测等研究工作[2]上提供大量素材,对天文学领域的发展起到推动和完善作用。LAMOST数据集中的每一条光谱提供了3690-9100埃的波长范围内的一系列辐射强度值。光谱分类就是要从上千维的光谱数据中选择和提取对分类识别最有效的特征来构建特征空间,例如选择特定波长或波段上的光谱流量值等作为特征,并运用算法对各种天体进行区分 。