Clinical significance of serum miR-129-5p in patients with diabetes mellitus presenting macrovascular complications
2021-08-25XiaoYunHeChunLinOu
Xiao-Yun He,Chun-Lin Ou
Xiao-Yun He,Chun-Lin Ou,Department of Pathology,Xiangya Hospital,Central South University,Changsha 410008,Hunan Province,China
Xiao-Yun He,Department of Endocrinology,Affiliated Hospital of Guilin Medical University,Guilin 541001,Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region,China
Abstract BACKGROUND Diabetic macrovascular complications (DMCs) are the most common complications encountered during the course of diabetes mellitus (DM) with extremely high mortality rates.Therefore,there is an urgent need to identify specific and sensitive biomarkers for the early diagnosis of DMCs.AIM To investigate the expression and significance of serum miR-129-5p in patients with DM and macrovascular complications.METHODS Serum samples were collected from 36 healthy controls,58 patients with DM presenting no macrovascular complications,and 62 patients with DMCs.The expression of miR-129-5p was detected using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction.Pearson’s correlation assay was performed to analyze the correlation between serum miR-129-5p levels and clinical indicators.Receiver operator characteristic (ROC) analysis was conducted to analyze the diagnostic value of serum miR-129-5p in patients with DM or DMCs.RESULTS There was a 4.378-fold and 7.369-fold increase in serum miR-129-5p expression in the DM (5.346 ± 0.405) and DMCs (8.998 ± 0.631) groups,respectively (P < 0.001),compared with the control group (1.221±0.090).In addition,the expression of serum miR-129-5p in patients with DMCs was higher than that in patients with DM,revealing a 1.683-fold increase (P < 0.001).Additionally,serum miR-129-5p expression significantly correlated with smoking history,disease duration,and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) in patients with DMCs (P < 0.001).The area under the ROC curve (AUC) of miR-129-5p as a serum marker was 0.964 (95%confidence interval [CI]:0.930-0.997,P < 0.001) in distinguishing between patients with DM and healthy controls,whereas the AUC of miR-129-5p as a serum marker was 0.979 (95%CI:0.959-0.999,P < 0.001) in distinguishing between patients with DMCs and healthy controls.CONCLUSION Elevated serum miR-129-5p expression levels correlate with the development of DMCs and can be utilized as a novel early diagnostic biomarker for DM combined with macrovascular complications.
Key Words:Diabetes mellitus;Diabetic macrovascular complications;MircoRNA;Diagnosis;Therapy
INTRODUCTION
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by chronic hyperglycemia and is considered one of the most common human diseases worldwide[1,2].Longterm hyperglycemia may cause systemic vascular damage following the occurrence and development of DM,thereby inducing diabetic macrovascular complications(DMCs)[3-5].DMCs are among the most critical factors related to DM-associated deaths,accounting for approximately 70% of mortalities[6,7].Therefore,there is an urgent need to identify effective biomarkers for early diagnosis,monitoring progression,and targeted therapy of DMCs[8].
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) with a length of approximately 22 nucleotides,which are known to inhibit the expression of crucial molecules by binding to the untranslated region of target mRNA[2,9],thereby affecting the process of human metabolic diseases,including DM[10].Moreover,miRNAs have been detected in tissues as well as in various body fluids,including blood,urine,saliva,and milk,especially in serum.Recently,accumulating evidence has revealed that serum miRNAs are closely associated with DM as well as DMassociated complications,such as DMCs.For example,Baruttaet al[11] have demonstrated that serum miR-126 levels can be associated with vascular complications in DM.However,the patterns and role of a large number of serum miRNAs remain unclear.
In the present study,we aimed to detect changes in the serum expression of miR-129-5p in DM combined with DMCs and analyze the relationship between miR-129-5p expression and the clinical characteristics of DMCs,thus evaluating its potential as a novel biomarker for predicting the prognosis of DMCs.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Subjects and serum collection
In total,156 serum samples,including samples from 36 healthy controls,58 patients with DM without DMCs,and 62 patients with DM presenting DMCs,were collected between March 2017 and January 2019 at the Affiliated Hospital of Guilin Medical University (Guilin,China).We used the most common clinical non-invasive examination,B-mode ultrasound,to diagnose patients with DM presenting macrovascular disease.If patients with DM presented carotid intimal thickening and atherosclerotic plaques on B-ultrasound examination,DM with a macrovascular disease was established.No patient presented with psychiatric disorders or other severe diseases.In addition,patient information,including patient's name,age,body mass index(BMI),duration of disease,systolic and diastolic pressures,oral glucose tolerance test(OGTT),glycated hemoglobin (hemoglobin A1c,HbA1c),and comprehensive metabolic indicators [e.g.,triglyceride (TG),total cholesterol (TCHO),high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-c),and low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-c)]were collected.Written informed consent was obtained from all patients and healthy controls.
Fasting venous blood samples (5 mL) were collected from all participants.After standing for 2 h,samples were centrifuged at 3500 rpm for 20 min at 4 °C;the obtained serum samples were transferred to freshly sterilized tubes and immediately stored at -80 °C.
RNA extraction and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction
Total RNA was extracted from serum specimens using a miRNA Serum/Plasma Isolation Kit (Qiagen,Hilden,Germany) according to the manufacturer's protocol.Reverse transcription was performed using Mir-XTM miRNA First-Strand Synthesis Kit (Clontech,United States),and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction(qRT-PCR) assays were performed as described previously[12].The relative expression of miR-129-5p was normalized to the expression of U6 and calculated using the comparative threshold cycle (Ct) method using the formula 2-ΔΔCt.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism 5.0 (GraphPad Software,Inc.,San Diego,CA,United States) and SPSS 18.0 (IBM Corp.,Chicago,IL,United States).Student’st-test and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) were employed to evaluate the differential expression of serum miR-129-5p between patient groups and the healthy control group.Pearson’s correlation coefficient was utilized to analyze the correlation between two indicators.The relationship between clinical factors and miR-129-5p expression was estimated using the Chi-square test.Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was performed using the SigmaPlot suite 13.0 software.Results withP <0.05,P <0.01,orP <0.001 were deemed statistically significant.
RESULTS
Comparison of general data
Overall,no significant differences in age,sex,BMI,TCHO,or HDL-c were observed among the three groups.Data values for systolic pressure,diastolic pressure,OGTT,HbA1c,TG,and LDL-c in the DM and DMC groups were significantly higher than those in the control group (P <0.05).Moreover,there was a 1.964-fold (P <0.001)increase in the disease duration in the DMC group (10.560 ± 1.230 years),compared to that in the control group (5.376 ± 0.716 years);this finding was consistent with a previous study indicating that a DM duration of more than 5 years might induce DMCs more often[13].
Serum miR-129-5p levels in patients with DM and DMCs and healthy controls
Next,we used qRT-PCR to detect the differential expression of serum miR-129-5p in patients with DM presenting no DMCs,patients with DMCs,and healthy controls.There was a 4.378-fold and 7.369-fold increase in serum miR-129-5p expression in the DM (5.346 ± 0.405) and DMC (8.998 ± 0.631) groups,respectively,compared to the control group (1.221 ± 0.090;P <0.001;Figure 1).Further analysis showed that serum miR-129-5p expression level in patients with DMCs was significantly higher than that in patients with DM,demonstrated as a 1.683-fold increase (P< 0.001,Figure 1).
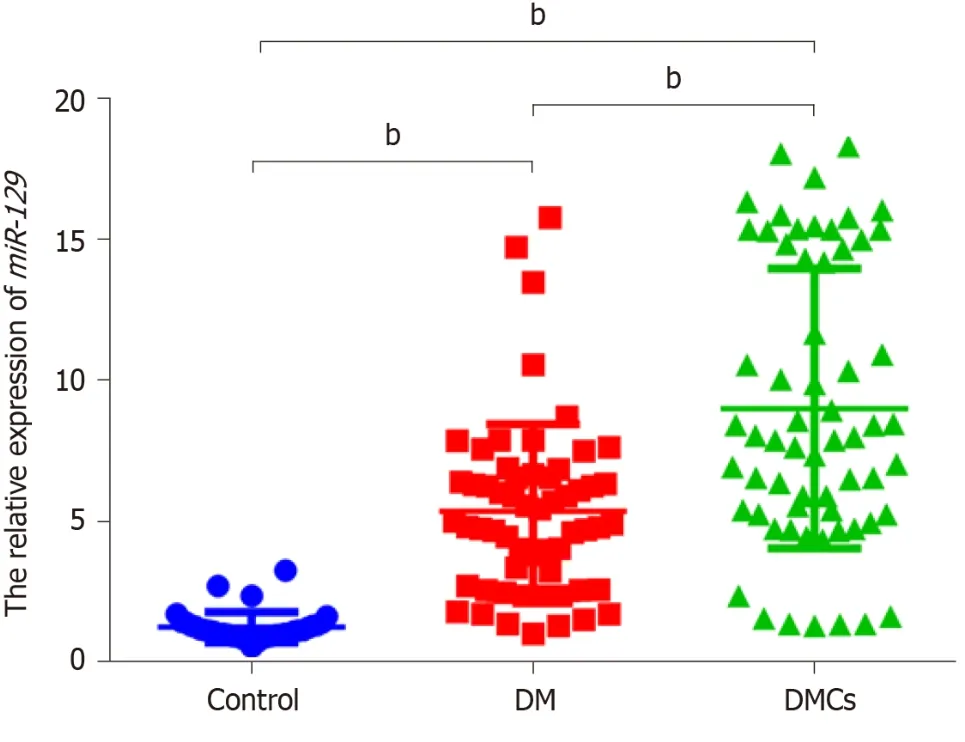
Figure 1 The expression levels of serum miR-129-5p in healthy controls and in patients with diabetes mellitus and diabetic macrovascular complications.
Correlation between serum expression of miR-129-5p and clinical factors in DM and DMCs
Pearson’s correlation coefficient was employed to analyze the correlation between the expression of serum miR-129-5p and clinical variables in DM and DMCs.The results demonstrated that the expression of serum miR-129-5p positively correlated with OGTT (glucose 2 h after dinner) in patients with DM (P <0.05,Table 1);however,inpatients with DMCs,serum miR-129-5p expression positively correlated with the disease duration,smoking history,DM family history,fasting glucose (OGTT),and HbA1c (P <0.05,Table 2).Our findings revealed that the serum expression of miR-129-5p was more closely related to the clinical factors of DMCs than those of DM,suggesting that serum miR-129-5p can serve as a potential molecular marker for detecting the development of DMCs.
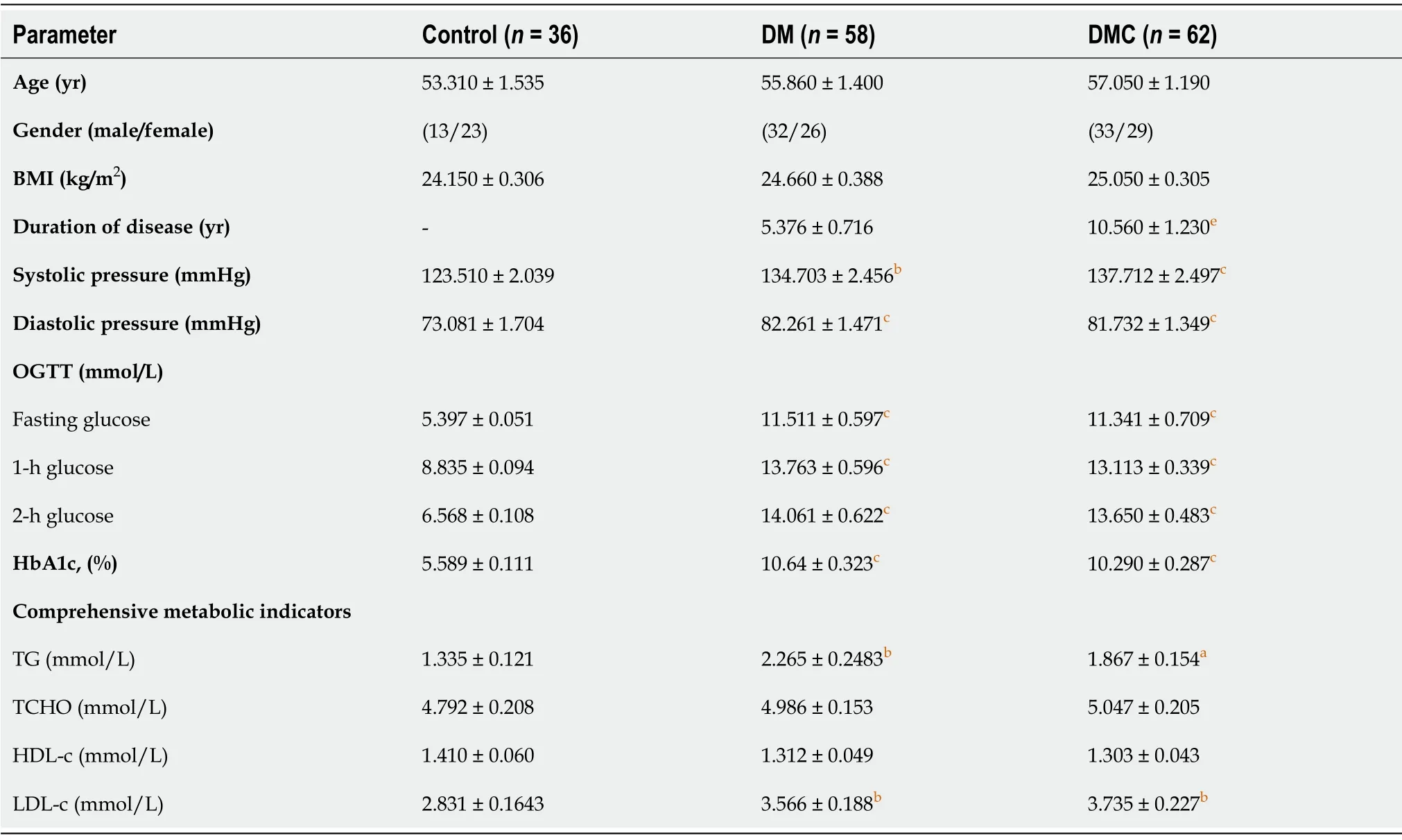
Table 1 Baseline characteristics of all participants
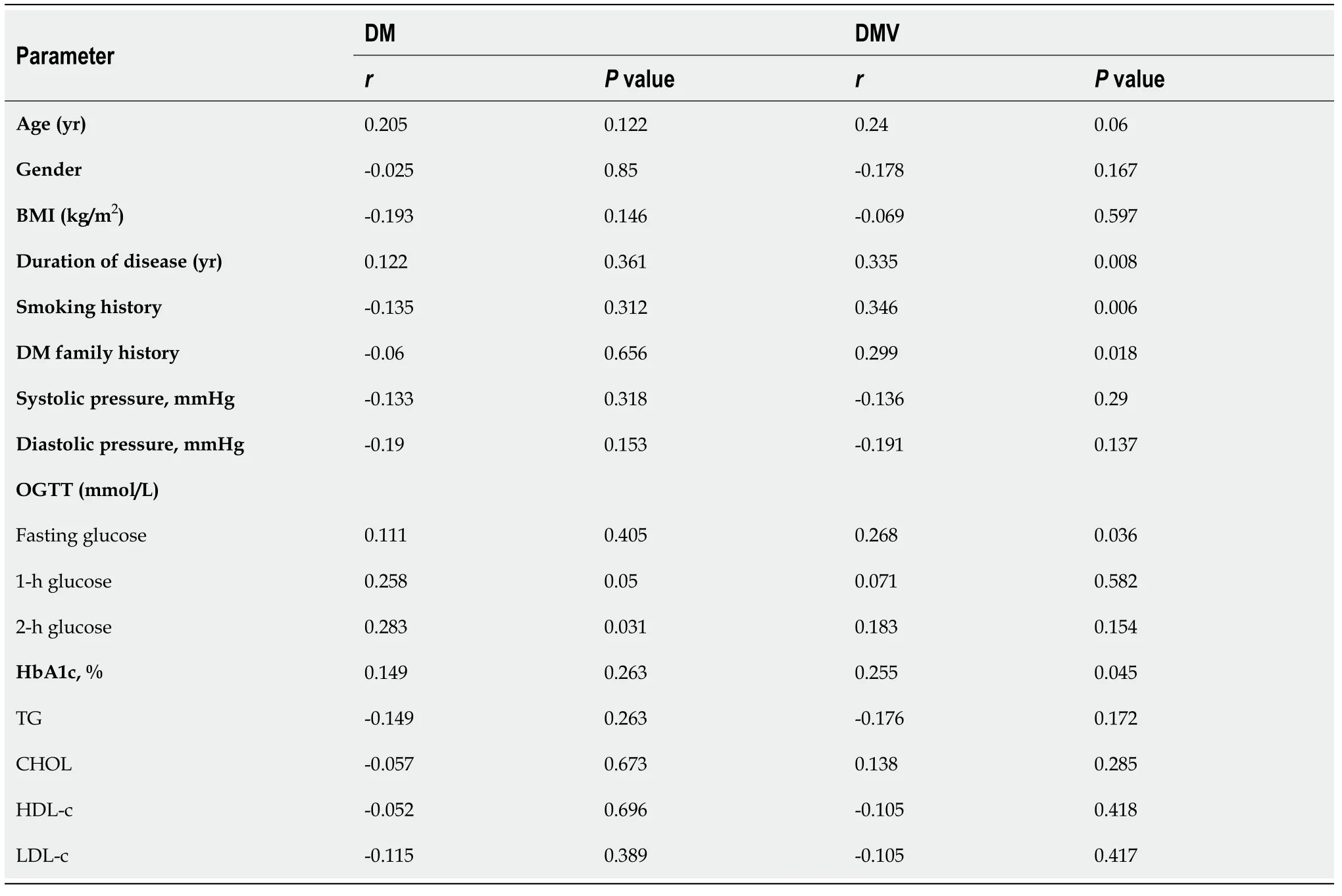
Table 2 Correlation between the expression of serum miR-129-5p and clinical factors in diabetes mellitus and diabetic macrovascular complications
Clinical associations of serum miR-129-5p in patients with DMCs
Based on the median serum level of miR-129-5p,patients with DM presenting DMCs were divided into high- and low-level groups.The relationship between the expression levels of serum miR-129-5p and clinical factors in DMCs was analyzed using the Chi-square test.As shown in Table 3,the expression levels of serum miR-129-5p showed no significant correlation with patient gender,age,family history of DM,high blood pressure,or fasting blood glucose (P> 0.05).However,serum miR-129-5p levels significantly correlated with smoking history,disease duration,and HbA1c in patients with DMCs (P <0.05).
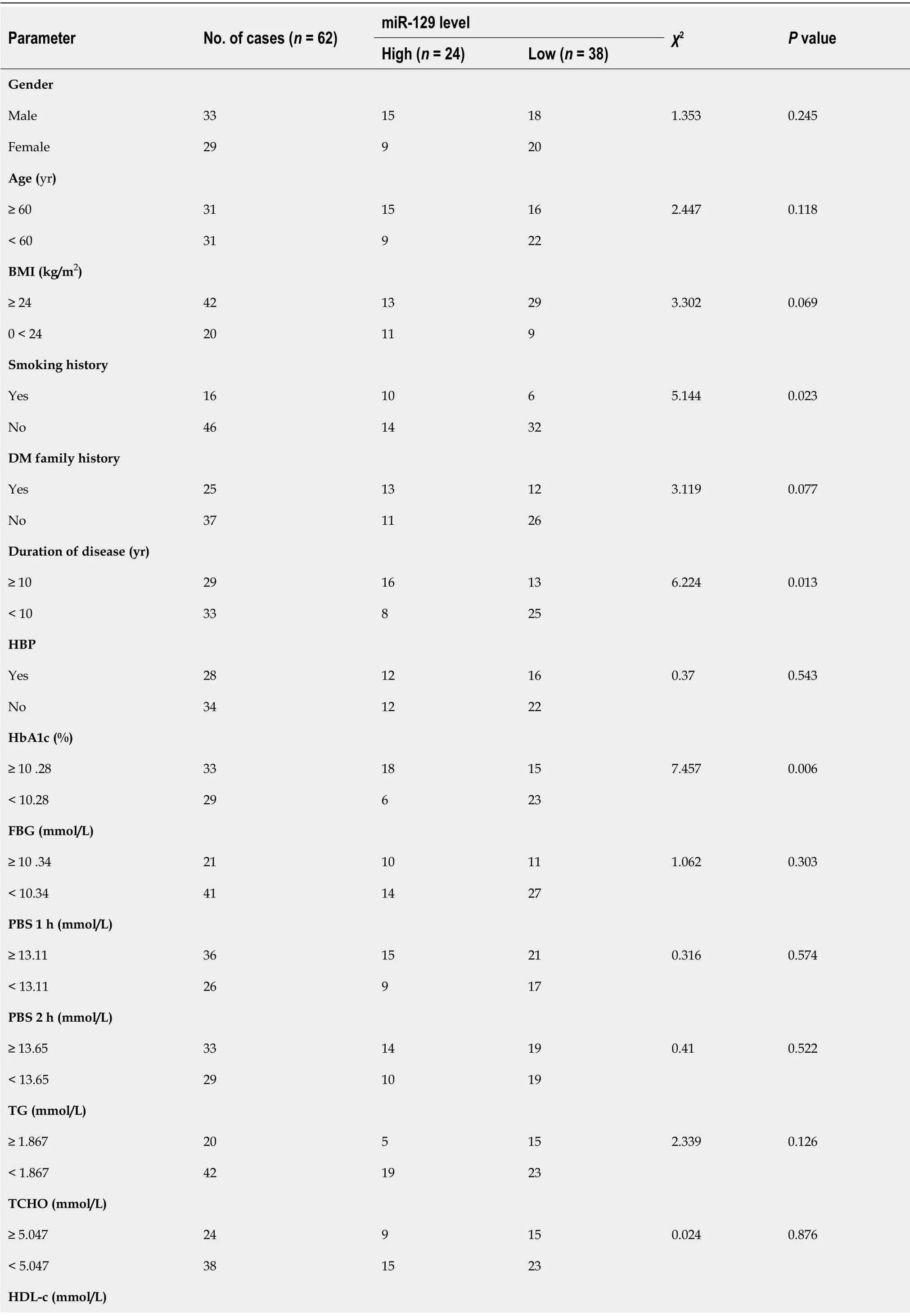
Table 3 Relationship between the expression of serum miR-129-5p and clinical factors in diabetic macrovascular complications
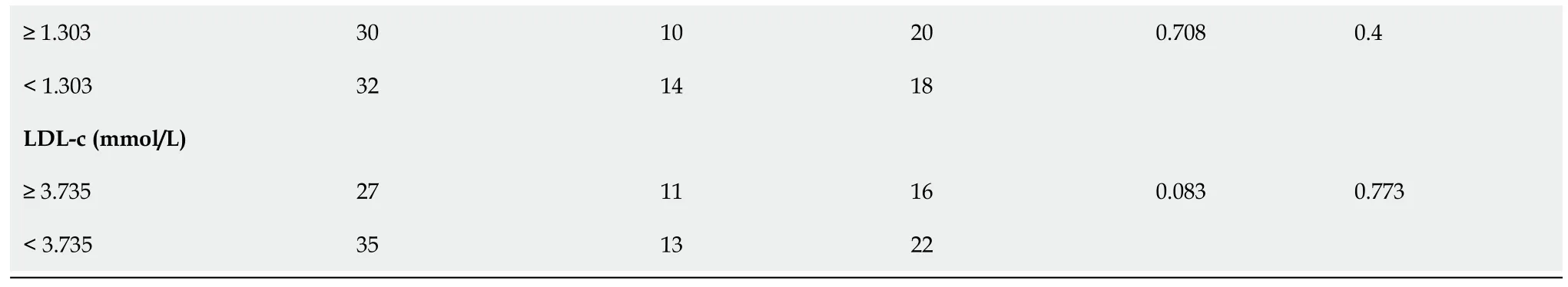
BMI:Body mass index;DM:Diabetes mellitus;OGTT:Oral glucose tolerance test;HbA1c:Hemoglobin A1c;TG:Triglyceride;TCHO:Total cholesterol;HDL-c:High-density lipoprotein-cholesterol;LDL-c:Low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol.
Diagnostic value of serum miR-129-5p in patients with DMCs
Furthermore,we performed ROC curve analysis to evaluate the diagnostic value of serum miR-129-5p as a serum marker in patients with DM lacking DMCs and patients with DMCs.The results revealed that the area under the ROC curve (AUC) of miR-129-5p as a serum marker was 0.964 (95%CI:0.930-0.997,P <0.001,Figure 2A) in distinguishing between patients with DM and healthy controls;the AUC of miR-129-5p as a marker was 0.979 (95%CI:0.959-0.999,P <0.001,Figure 2B) in distinguishing between patients with DMC and healthy controls.This result implied that the diagnostic value of serum miR-129-5p in patients with DMCs was higher than that in patients with DM.
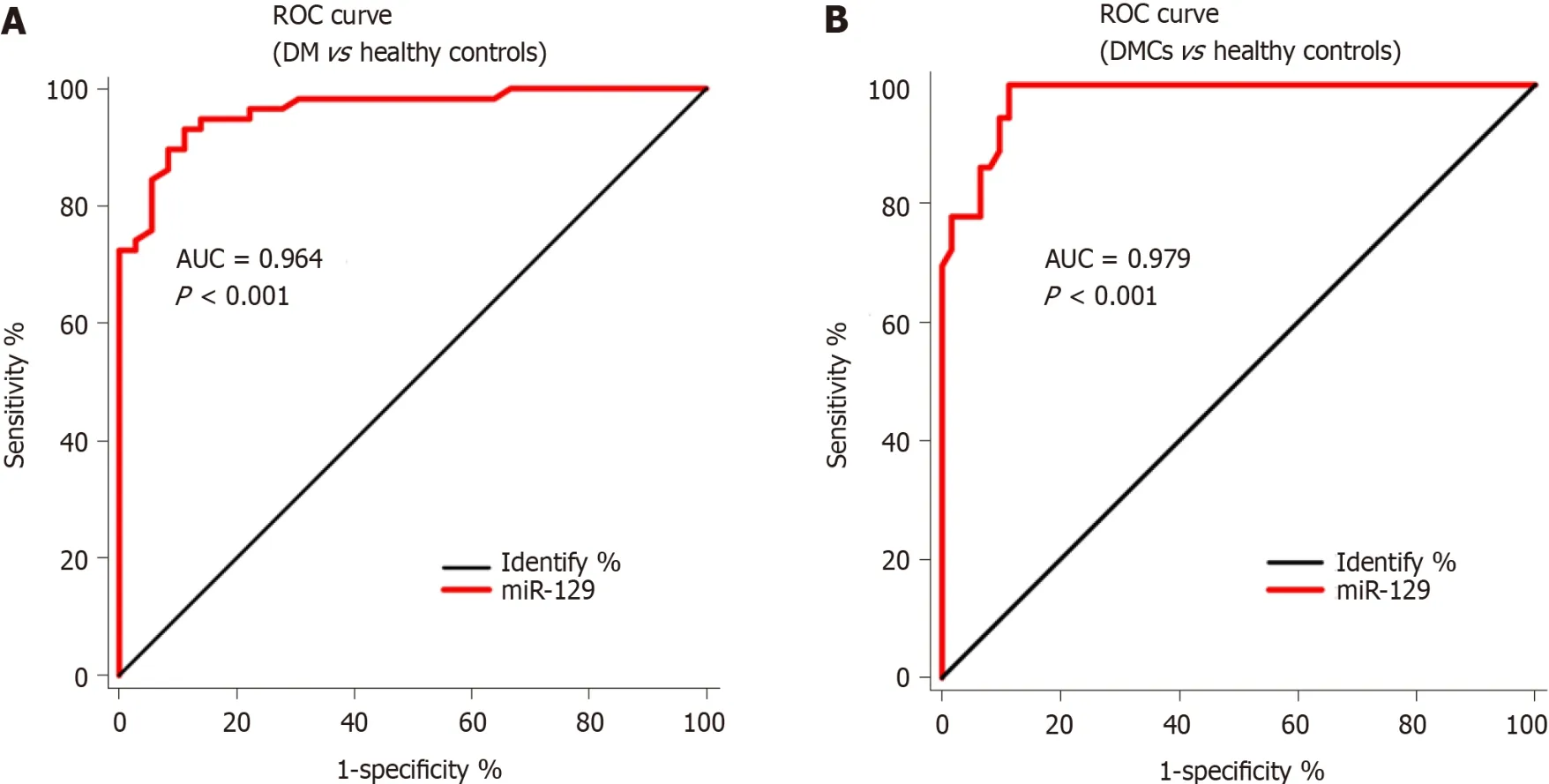
Figure 2 Receiver-operating characteristic curve analysis to analyze the potential of miR-129-5p as a serum marker for patients with diabetes mellitus or patients with diabetic macrovascular complications.
DISCUSSION
DMCs are the most common complications associated with DM and are typically accompanied by pathological changes in endothelial cells,cardiomyocytes,vascular cells,and stem cells.The occurrence and development of DMCs involve various underlying mechanisms,including autophagy[14],oxidative stress[15],inflammatory response,and immune response[16].In the present study,we revealed that the disease duration in the DMC group was significantly prolonged when compared with the DM group (P <0.001),indicating that vascular complications are important factors in DMrelated deaths.Therefore,there is considerable urgency in the search for early diagnostic markers and drug targets for DMCs.
With the development of RNA-seq and next-generation sequencing technologies[17,18],an increasing number of miRNAs have been discovered and identified to be strongly associated with the development of DM[19-21].miRNAs are present in human plasma in a stable form,showing a higher specificity and sensitivity of detection than serum proteins.Therefore,serum miRNAs have been widely employed as novel diagnostic biomarkers for DM.To date,numerous serum miRNAs are found to be aberrantly expressed during DMCs,including miR-148[22],miR-342[23],and miR-133a[24],with a few recent studies elaborating the relationship between serum miRNAs and DMCs.
miR-129-5p is a member of the miRNA family and is closely related to the development and progression of human cancers[25,26].Recently,miR-129-5p was found to regulate diabetic wound healing[27],DM-associated inflammatory response[28],and revascularization[29].However,the patterns and role of high serum miR-129-5p expression in DMCs remain unclear.In the present study,we observed that serum expression of miR-129-5p was significantly higher in patients with DM and patients with DMCs than in the control group.Furthermore,the expression of serum miR-129-5p was significantly higher in patients with DMCs than that in patients with DM (P <0.05).Further evaluation revealed that the expression of serum miR-129-5p correlated significantly with smoking history,disease duration,and HbA1c in patients with DMCs (allP <0.001).Additionally,the AUC of miR-129-5p as a serum marker was 0.964 (95%CI:0.930-0.997,P <0.001) in distinguishing between patients with DM and healthy controls,whereas the AUC of miR-129-5p as a serum marker was 0.979(95%CI:0.959-0.999,P <0.001) in distinguishing between patients with DMCs and healthy controls.
CONCLUSION
Collectively,our findings provide convincing evidence demonstrating the upregulation of serum miR-129-5p,which can serve as a novel molecular marker for the early diagnosis of DMCs.In addition,the expression of serum miR-129-5p significantly correlates with smoking history,disease duration,and HbA1c in patients with DMCs.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Diabetic macrovascular complications (DMCs) are the most common complications encountered during the course of diabetes mellitus (DM) with extremely high mortality rates.
Research motivation
There is an urgent need to identify specific and sensitive biomarkers for the early diagnosis of DMCs.
Research objectives
To investigate the expression and significance of serum miR-129-5p in patients with DM and macrovascular complications.
Research methods
Serum samples were collected from 36 healthy controls,58 patients with DM presenting no macrovascular complications,and 62 patients with DMCs.The expression of miR-129-5p was detected using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction.Pearson’s correlation assay was performed to analyze the correlation between serum miR-129-5p levels and clinical indicators.Receiver operator characteristic analysis was conducted to analyze the diagnostic value of serum miR-129-5p in patients with DM or DMCs.
Research results
These finding demonstrated that serum expression of miR-129-5p was significantly higher in patients with DM and patients with DMCs than in the control group.Furthermore,the expression of serum miR-129-5p was significantly higher in patients with DMCs than in patients with DM (P < 0.05).Further evaluation revealed that the expression of serum miR-129-5p correlated significantly with smoking history,disease duration,and HbA1c in patients with DMCs (P < 0.001).Additionally,the AUC of miR-129-5p as a serum marker was 0.964 (95%CI:0.930-0.997,P < 0.001) in distinguishing between patients with DM and healthy controls,whereas the AUC of miR-129-5p as a serum marker was 0.979 (95%CI:0.959-0.999,P < 0.001) in distinguishing between patients with D MCs and healthy controls.
Research conclusions
Elevated serum miR-129-5p expression levels correlate with the development of DMCs and can be utilized as a novel early diagnostic biomarker for DM combined with macrovascular complications.
Research perspectives
The high serum miR-129-5p expression is related to the development of DMCs and can be employed as a novel early diagnostic biomarker for DM combined with macrovascular complications.
杂志排行
World Journal of Diabetes的其它文章
- Clinical effects of antidiabetic drugs on psoriasis:The perspective of evidence-based medicine
- What can we learn from β-cell failure biomarker application in diabetes in childhood? A systematic review
- Which predictors could effect on remission of type 2 diabetes mellitus after the metabolic surgery:A general perspective of current studies?
- Polymorphisms in HIF-1a gene are not associated with diabetic retinopathy in China
- Association of β-cell function and insulin resistance with pediatric type 2 diabetes among Chinese children
- Decabromodiphenyl ether causes insulin resistance and glucose and lipid metabolism disorders in mice
