Surface Topography Assessments of Spine Shape Change within the Day in Healthy Male Adults
2021-08-25JianmingLuLiangliangXiangandHuwWiltshire
Jianming Lu,Liangliang Xiang and Huw Wiltshire
1College of Science&Technology,Ningbo University,Ningbo,315300,China
2Auckland Bioengineering Institute,University of Auckland,Auckland,1010,New Zealand
3Cardiff School of Sport&Health Sciences,Cardiff Metropolitan University,Cardiff,CF5 2YB,UK
ABSTRACT Surface topography is a no-invasive,radiation-free method that can measure sufficient surface spine parameters by the structured back surface scan and a precise anatomical landmarks recognition.The purpose of the present study was to measure the spine shape parameter changes within the day via the DIERS Formetric 4D analysis system.Ten male healthy volunteers were recruited to participate in the experiment.All participants were sedentary people with the average sitting time during study or work t ≥8 h and without any back disease in the past six months.Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA,which set time points within the day as variable and shape results as the dependent variable.The significant difference could be found for the trunk length VP-DM with a one-way ANOVA test of p=0.011.There was a significant difference(p=0.024)between time slots of 9 am and 7 pm with 95%CI(–15.83,–1.01)and MD–8.42.No significant difference statistically for the scoliosis angle and the p-value of the one-way ANOVA test is 0.715.There was no significant difference for trunk inclination VP-DM with a one-way ANOVA test of p=0.284.Statistical analysis depicted no significant difference for the trunk imbalance VP-DM with a one-way ANOVA test of p=0.730.Trunk length VP-DM was significantly decreased in the afternoon and evening.This may be a potential back pain risk for sedentary individuals.Regular physical activity and mild to moderate exercise are recommended to improve spinal stability and maintain spinal shape.
KEYWORDS Surface topography;DIERS Formetric 4D;spine shape;postural assessment
1 Introduction
Abnormal spine posture may cause several symptoms,for instance low back pain,scoliosis,kyphosis and lordosis.Low back pain,as a common spine disorder,may affect around 70% of residents in the western world and has caused a fairly economic burden in the last decade[1].According to the study by Negrini et al.[2],adolescent idiopathic scoliosis(AIS)is a common spinal disorder with an incidence of 2%–3%.Prior to any intervention or treatment is implemented,the anatomical situation of the spine must be assessed[3].
Surface topography is a no-invasive,radiation-free method that can measure sufficient surface spine parameters by the structured back surface scan and a precise anatomical landmarks recognition.Diagnostic investigation of the spine and trunk could be conducted by surface topography technique,which can threedimensionally re-build the surface and vertebral column and stimulate spine shape[4].It is cost-saving,convenient and can reduce ionizing radiation exposure,comparing to traditional radiograph methods[5].
DIERS 4D Formetric system based on moiré principle and reconstructs the anatomy of the spine virtually from the back surface with a frequency of up to 24 Hz[6,7].The spine posture data measuring from it has shown high validity from previous studies[8–11].However,it is argued that Formetric 4D raster stereography is validated but only reliable[12].Bassani et al.[13]recommended that the rasterstereography method cannot be considered as a valid alternative to radiographic evaluation,but it can be utilized for early spine disorder screening and it is cost-benefit comparing to other traditional approaches.
The evidence has shown that the DIERS 4D Formetric system can quantify the deformity of AIS[14].Lason et al.[7]found a significant difference between the angulations of the spine.Several studies have proven that spinal shape parameters are reliable in healthy participants and in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis through within a day[15,16]and over several days[7,17,18]of data collection.Girdler et al.[5]illustrated that the DIERS formetric scanner can contribute to AIS diagnosis and monitor without radiation exposure.Through measuring spine posture difference,it was found that DIERS 4D Formetric system can evaluate the differences of trunk inclination and kyphotic angle between barefoot and shod runners[19].Spine morphology is also a crucial index for acute and chronic low back pain evaluation[1].
Spine morphology presents a high degree of plasticity[20].Postural changes contribute to the alternations of the intrinsic shape of the spine as well[21].Low physical activity may reduce spine bone mineral density and muscle strength[22–24].Thus,physical activities or sedentary behaviors may potentially influence spine shape.The purpose of the current study was to investigate the spine shape parameter changes within the day via the DIERS Formetric 4D analysis system.It was hypothesized that healthy participants from the sedentary cohort would demonstrate a deteriorated spine morphology reversibly within the day.
2 Methods
2.1 Participants
Recruitment information was spread through the internet and posters.Sample size was calculated in power analysis(pwr package,R)with significance level=0.05,groups=3,power=0.8,effect size=0.5.Fifteen symptom-free,healthy male volunteers(Age:25.8 ± 2.06 years,Heights:1.77 ±0.06 m,Weight:69.75 ± 6.95 kg,BMI:22.21 ± 0.72 kg/m2)were recruited to participate in the experiment.All enrolled participants were sedentary people with the average sitting time during study or work t ≥8 h and without any back disease in the past six months.Participants with scars and tattoos on their back surface were excluded.Informed consent was obtained from all subjects who informed the study objective,requirements and experimental protocol.The procedure of this experiment was approved by the local Ethics Committee,which was in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
2.2 Apparatus and Experience Protocol
The surface topography of the spine was scanned utilizing a video raster stereography,DIERS Formetric 4D(Formetric®-System,DIERS International Gmbh,Schlangenbad,Germany)(Fig.1).Before the experiment,closing the curtains,lights and doors in the laboratory in order to avoid stripes covered by surrounding light.Each participant should take off their shirt and shoes,and remove jewelry if they wore.The sacrum point should be uncovered by the underpants.During the experiment,subjects were standing still,look slightly down and relaxing arms for 5–10 s,till the instructor told participants that scanning was finished.
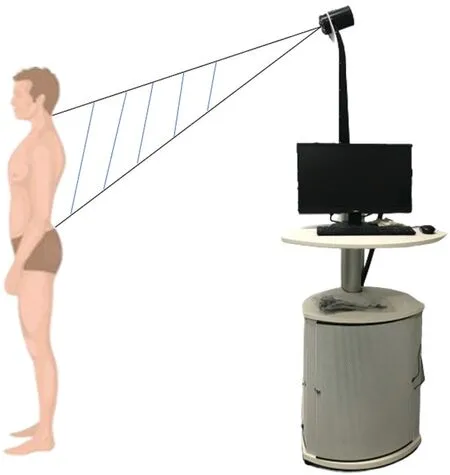
Figure 1:DIERS Formetric 4D system using in the experiment
Prior to scanning,the static 3D measure was chosen in DICAM 2.5.12 software(DIERS International Gmbh,Germany),and by adjusting the height of the camera to identify the angulus inferior of the scapula.Stripe projection needs appropriate reflection on the subject’s back during the scanning(Fig.2).Manual landmark correction was adopted if dimple points(DL and DR)were not detected correctly[25].
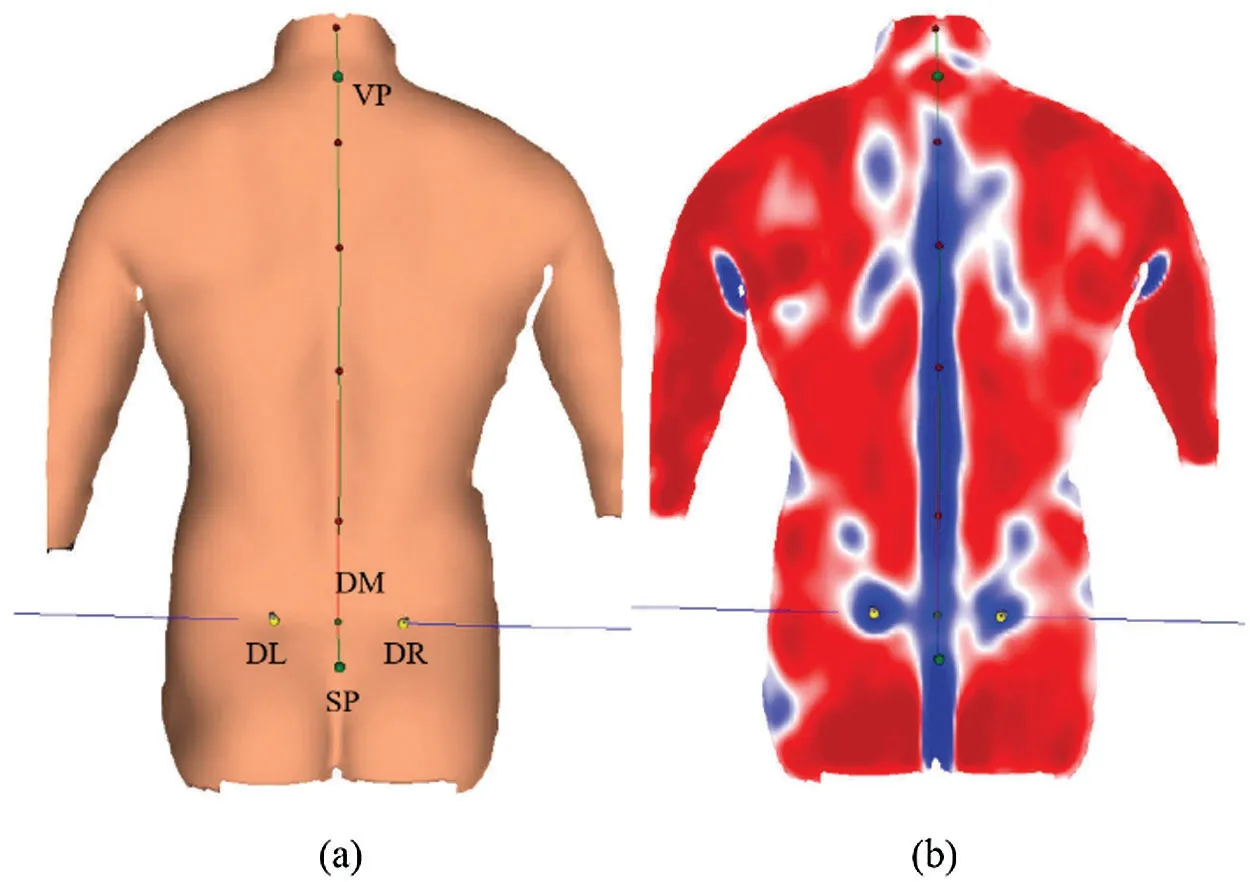
Figure 2:3D modeling scanned from DIERS Formetric 4D system.Abbreviations:VP:vertebra prominent;DL:dimple left;DR:dimple right;DM:center between DL and DR(dimple middle);SP:sacrum point
Spine postural assessment within the day was measured including 3 time slots 9:00,14:00,and 19:00.A three days test protocol was applied for all subjects.For each test,two trials were collected and each participant attends the experiment with a session of three days within a week.All data collection was conducted by the same instructor.
2.3 Data Process and Statistical Analysis
Through system algorithms,a set of spine shape parameter values were obtained after scanning for postural assessment[26].Surface topography data collected in this experiment including trunk length VP-DM,sagittal imbalance VP-DM(trunk inclination VP-DM),coronal imbalance VP-DM(trunk imbalance VP-DM),and scoliosis angle.Data were described as means ± SD,and normality distribution of data was examined and confirmed with the Shapiro-Wilk test.Homogeneity of variance was tested using Brown-Forsythe was used to test for homogeneity of variance for all vertebral column parameters prior to analysis of variance.The relevant data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA,which set time points within the day as variable and shape results as the dependent variable.Tukey HSD test was used for posthoc analysis.All statistical tests were conducted in R(version 3.6.1).The significant threshold for all statistical tests was set atp<0.05.
3 Results
The spine shape parameters altered within the day(9 am in the morning,2 pm in the afternoon and 7 pm in the evening)as shown in Tab.1.The significant difference could be found for the trunk length VP-DM with a one-way ANOVA test ofp=0.011.The mean difference(MD)between 9 am and 2 pm was 8.04,95%CI(0.63,15.45)with a statistical difference ofp=0.032.Thepost hoctest of trunk length VP-DM between 2 pm and 7 pm showed apvalue of 0.993.There was a significant difference(p=0.024)between time slots of 9 am and 7 pm with 95%CI(–15.83,–1.01)and MD–8.42.
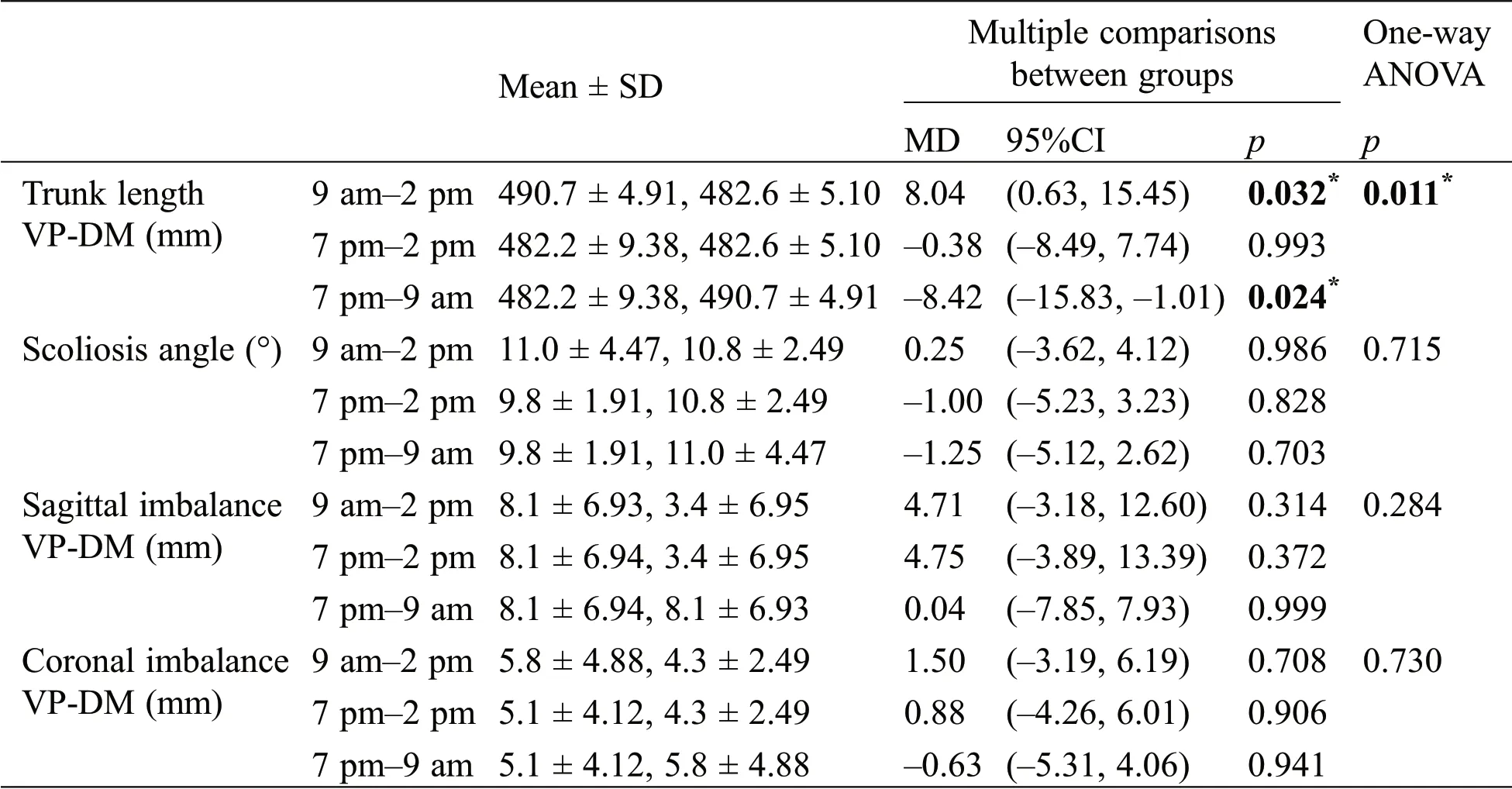
Table 1:One-way ANOVA analyze and paired comparison of spine surface topography parameters
There was no significant difference statistically for the scoliosis angle with a one-way ANOVA test ofp=0.715.The mean difference(MD)between 9 am and 2 pm was 0.25,95%CI(–3.62,4.12)withp=0.986.Thepost hoctest of the scoliosis angle showed apvalue of 0.828 for the comparison of 2 pm and 7 pm.There was no significant difference(p=0.703)between time slots of 9 am and 7 pm with 95%CI(–5.12,2.62)and MD –1.25.
There was no significant difference for trunk inclination VP-DM with a one-way ANOVA test ofp=0.284.The mean difference(MD)between 9 am and 2 pm was 4.71,95%CI(–3.18,12.60)withp=0.314.Thepost hoctest of sagittal imbalance CP-DM showed apvalue of 0.372 for the comparison of 2 pm and 7 pm.There was no significant difference(p=0.999)between time slots of 9 am and 7 pm with 95%CI(–7.85,7.93)and MD 0.04.
Statistical analysis depicted no significant difference for the trunk imbalance VP-DM with a one-way ANOVA test ofp=0.730.The mean difference(MD)between 9 am and 2 pm was 1.50,95%CI(–3.19,6.19)withp=0.708.Thepost hoctest of coronal imbalance VP-DM showed apvalue of 0.906 for the comparison of 2 pm and 7 pm.There was no significant difference(p=0.941)between time slots of 9 am and 7 pm with 95%CI(–5.31,4.06)and MD–0.63.
4 Discussion
The present study aimed to measure and evaluate spine shape parameters change,mainly trunk length VP-DM,trunk inclination VP-DM,trunk imbalance VP-DM,and scoliosis angle by surface topography method.The posture scan was conducted within the day(9 am,2 pm and 7 pm)utilizing the DIERS Formetric 4D system.It was found trunk length VP-DM had a significant decrease in the afternoon and evening,comparing to the value in the morning.
The radiograph technique is used as the standard-of-care for disorder evaluation,but it contains shortages for instance inconvenient and safe-considering[27].In recent years,surface topography technique has been widely used in the spine shape monitoring[13,28,29],and it has been proven for the data validity of the DIERS Formetric 4D spine scan[4,8].
Scoliosis angle,also known as the Cobby angle,is a key parameter for scoliosis evaluation.Cobb angle beyond 10° is defined as scoliosis,10°–20° is mild scoliosis[30].Through the correlation and principal component analysis,Manca et al.[29]found the spine parameters,surface rotation-rms and side deviation-rms,is significantly associated with scoliosis angle.The participants in our study have a risk of scoliosis,the reason may be that only the sedentary white-collar or postgraduate cohort was selected exploring spine shape parameters alteration within the day.However,contrary to our hypothesis,the scoliosis angle in the evening was slightly decreased,compared to data in the morning and afternoon.It implies that further investigation should be conducted in the future to illustrate this finding.
Consistent with our hypothesis,trunk length VP-DM was significantly decreased in the afternoon and evening.This may be a potential back pain risk for sedentary individuals.The spine shape may deteriorate in the future for the sedentary youngsters.Moderate exercise has showed crucial role in spine[31,32].Regular physical activity and mild to moderate exercise are recommended to improve spinal stability and maintain spinal shape[33–35].
There is a deficiency in this work.No dynamic evaluation of spine morphology was performed.So,only stand still parameters were scanned and compared.Further study should explain the sedentary/physical inactivity effect for our spine within the day through investigating the dynamic vertebral column alter.In conclusion,this study conducted a prospective investigation into the spine shape alters within the day for sedentary individuals.The findings implicate that trunk length VP-DM was significantly decreased in the evening comparing to data in the morning,while the scoliosis angle demonstrated no statistical difference.
5 Conclusion
To sum up,this study measured the spine shape parameter changes of the sedentary cohort within the day via the DIERS Formetric 4D analysis system.Spine postural assessment within the day was measured including 3 time slots 9:00,14:00,and 19:00.Spine shape parameter values were obtained after scanning for postural assessment.A significant difference could be found for the trunk length VP-DM between time slots of 9 am and 2 pm,and 9 am and 7 pm.This may be a potential back pain risk for sedentary individuals.Regular physical activity and mild to moderate exercise are recommended to improve spinal stability and maintain spinal shape.
Funding Statement:The authors received no specific funding for this study.
Conflicts of Interest:The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to report regarding the present study.
杂志排行
Molecular&Cellular Biomechanics的其它文章
- Analysis of the Movement Track of Top Spinning Ball and Biomechanics in the Process of Hitting Tennis Ball
- Impact of Coronary Artery Curvature on the Longitudinal Stent Foreshortening:Real-World Observations
- Comparison of Detection and Classification of Hard Exudates Using Artificial Neural System vs. SVM Radial Basis Function in Diabetic Retinopathy
- Study of Hepatocytes Polyploidization Peculiarities in Cholestatic Liver of Adult Rats