桃AAAP基因家族的鉴定与分析
2021-07-29杨阳刘媛媛付鸿博申成丞
杨阳,刘媛媛,付鸿博,申成丞
桃基因家族的鉴定与分析
杨阳1*,刘媛媛2,付鸿博2,申成丞2
1. 吕梁学院生命科学系, 山西 吕梁 033000 2. 山西农业大学园艺学院, 晋中 太谷 030801
为了解桃基因家族成员的特征和功能,基于桃基因组,对桃基因家族成员进行理化性质、系统进化树、基因结构和保守基序以及染色体定位和共线性分析。结果表明,桃中共鉴定到家族成员101个,氨基酸序列范围在166~593个范围内,亚细胞定位表明成员全部定位在细胞内膜上;系统进化树分析显示桃成员被分为8个亚家族;基因结构和保守基序分析显示,桃基因家族成员之间基因结构和保守基序存在差异性,但亚家族成员内基因结构和保守基序存在相似性;染色体定位分析显示桃家族成员不均匀的分布的8条染色体上,有53对基因存在串联重复,有3对基因存在共线性。本研究初步了解了桃家族成员的特征和功能,为后期在桃中该基因的功能研究在分子水平上提供了理论支撑。
桃;基因家族; 生物信息学
氨基酸主要以有机氮[1]元素的形式参与植物体内蛋白质合成、代谢过程、激素调控等多种生命过程[2],是多细胞生物体内细胞和组织之间的通讯纽带[3]。这些功能的实现需要氨基酸运输系统,(Amino acid/suxin permease)家族是最大的氨基酸转运蛋白家族之一[1],可以转运生长素(吲哚-3-乙酸)、C氨基丁酸和单L-氨基酸以及多个氨基酸。根据序列间相似性和保守结构域的特点可以将分为八个分支,即AAP(氨基酸渗透酶)、LHT(赖氨酸和组氨酸转运体)、GAT(γ-氨基丁酸转运体)、ProT(脯氨酸转运体)、AUX)生长素转运体)和ANT(芳香性以及中性氨基酸转运体)以及ATLa、ATLb(类氨基酸转运体)[4-6]。不同亚家族成员序列间相似性较低,但所有的AAAP蛋白都具有相同的保守结构域,Aa_trans结构域(PF01490)。
自从第一个AAAP蛋白在哺乳动物中被发现鉴定后,家族基因逐渐延伸到植物领域,如拟南芥中,参与赖氨酸、苯丙氨酸、天冬氨酸以及亮氨酸的转运[7],和将氨基酸从木质部向韧皮部运输[8,9],参与孢子细胞的氨基酸运输来调控花粉的发育[10];在烟草中,参与天冬酰胺、天冬氨酸和谷氨酰胺以及谷氨酸的转运[11];在杨树中,参与木质部脯氨酸的转运[12];在水稻中,会影响种子发育早期阶段氨基酸的分布情况[13]。
桃((L.) Batsch)蔷薇科(Rosaceae)桃属(),多年生木本植物,是世界上重要的经济果树。桃基因组测序的完成和释放[14]为桃重要基因功能的挖掘提供了可行性。本研究利用生物信息学方法对桃基因家族成员进行了鉴定,并对其成员进行理化性质预测,基因结构,染色体定位和串联重复以及系统进化树分析,以期进一步对桃家族基因的功能研究提供基础信息。
1 材料与方法
1.1 桃AAAP基因家族的鉴定及生物信息学分析
通过GDR(http://www.rosaceae.org)下载桃基因组(genome.v2.2.a1),通过TAIR(http://arabidopsis.org)下载拟南芥基因家族氨基酸序列。通过Pfam(http://pfam.xfam.org)搜索隐马尔可夫模型(PF01490),利用Hmmer3.0构建本地蛋白数据库并进行候选基因筛选。将所有候选基因在NCBI上对其保守结构域进行进一步确认。利用ExPASy(https://www.expasy.org)对家族成员进行理化性质分析,利用CELLO(http://cello.life.nctu.edu.tw/)进行亚细胞定位预测。
1.2 桃AAAP基因家族的系统进化树分析
利用拟南芥AAAP氨基酸序列和桃AAAP氨基酸序列构建系统进化树:将所有氨基酸序列导入MEGA中,以Cluster W进行序列比对,以Maxumum Likelihood构建系统进化树。参数设置如下:Bootstrap Replications为1000,Mode/Method为Poisson model,Gaps/Missing Data Treatment为Partial deletion,Site Coverage Cutoff(%)为50,利用iTOL(https://itol.embl.de/)对进化树进行优化处理。
1.3 桃AAAP家族基因结构与保守基序分析
利用GSDS(http://gsds.gao-lab.org/)对桃进行基因结构分析,利用MEME(http://meme-suite.org/)和TBtools对桃进行保守基序分析。
1.4 桃AAAP基因家族染色体定位和共线性分析
根据桃的位置信息,利用TBtools中MCScanX对桃基因进行染色体定位及串联重复事件和共线性。
2 结果与分析
2.1 桃AAAP基因家族的鉴定及生物信息学分析
根据HEMMER筛选和NCBI中保守结构域的鉴定,共确认桃中有101个基因家族成员,根据染色体位置将其命名为-(表1),对得到的所有家族成员进行氨基酸长度、分子量、等电点、亲水性、脂肪族氨基酸指数和亚细胞定位(表1)表明,氨基酸序列长度从166到593,编码蛋白长度最小的是,由166个氨基酸组成,编码蛋白最大的是,由593个氨基酸组成;分子量在19.17 kDa()~49.54 kDa()范围内;等电点在5.41()~9.99();不稳定系数在21.60()~61.56()范围内;脂肪族氨基酸指数在86.22()~130.89()范围内;亲水性在0.240()~-0.942()范围内;亚细胞定位表明,所有家族成员均定位在细胞内膜上。
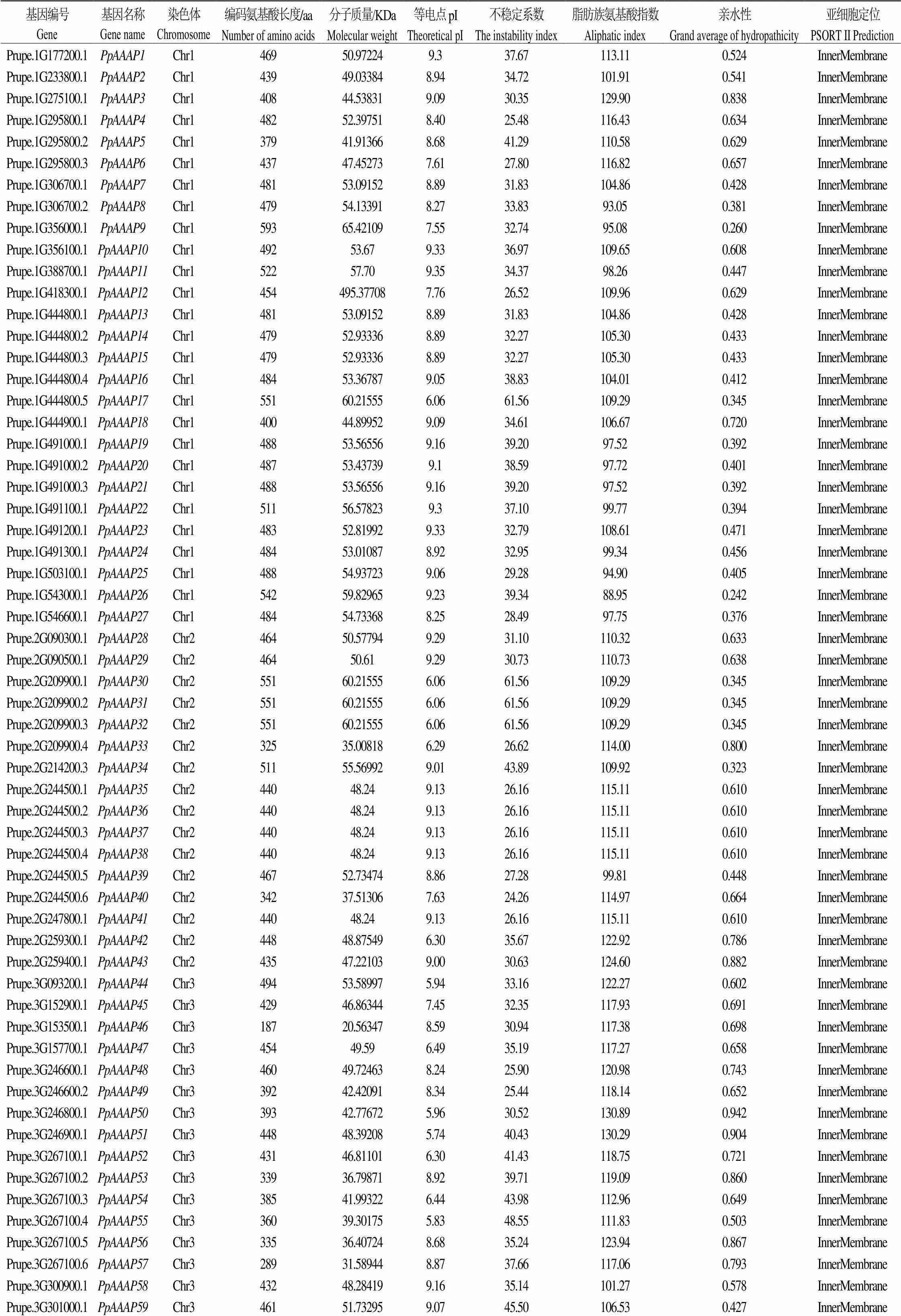
表1 桃PpAAAP家族成员生物信息学分析
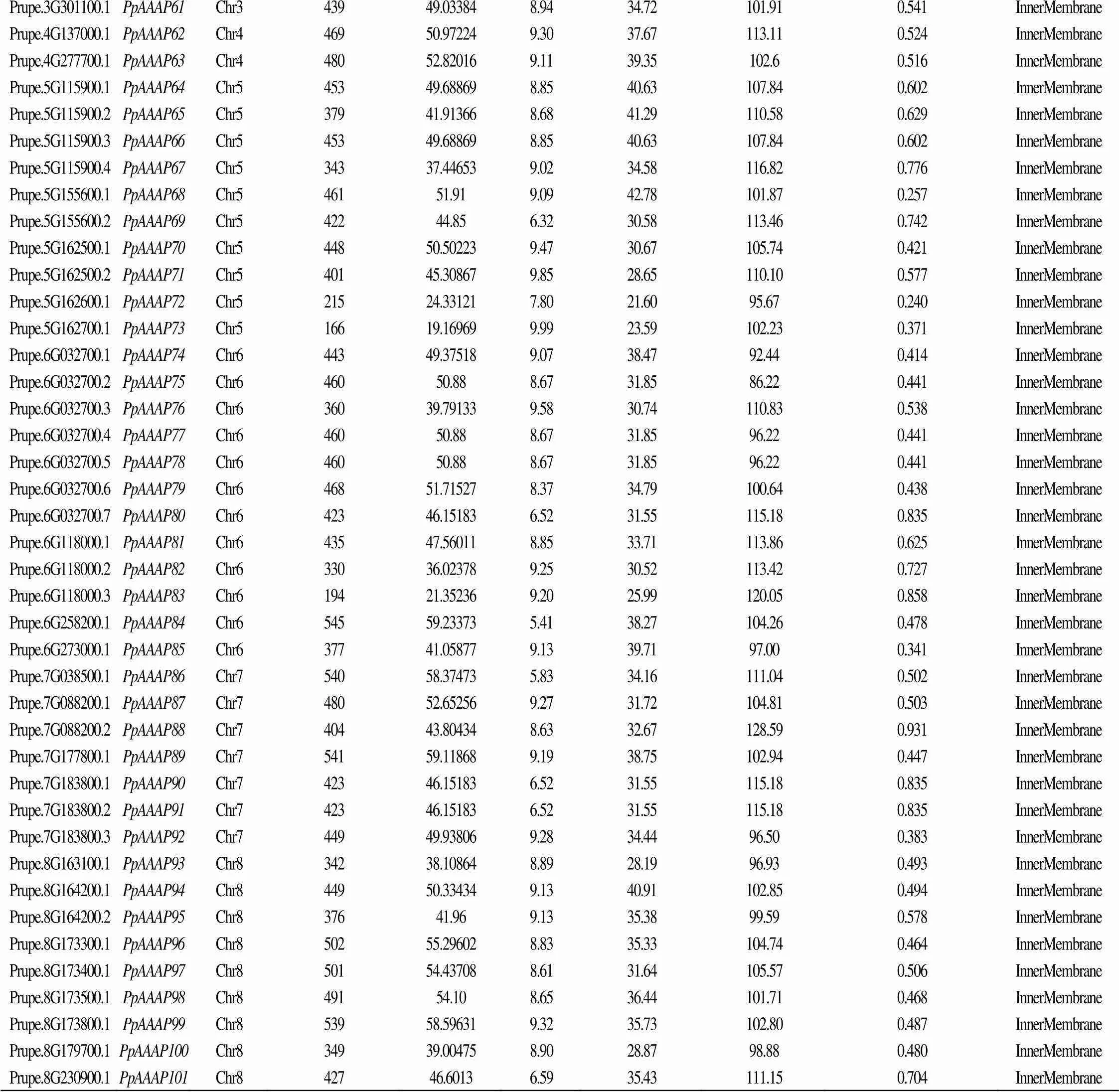
Prupe.3G301100.1PpAAAP61Chr343949.033848.9434.72101.910.541InnerMembrane Prupe.4G137000.1PpAAAP62Chr446950.972249.3037.67113.110.524InnerMembrane Prupe.4G277700.1PpAAAP63Chr448052.820169.1139.35102.60.516InnerMembrane Prupe.5G115900.1PpAAAP64Chr545349.688698.8540.63107.840.602InnerMembrane Prupe.5G115900.2PpAAAP65Chr537941.913668.6841.29110.580.629InnerMembrane Prupe.5G115900.3PpAAAP66Chr545349.688698.8540.63107.840.602InnerMembrane Prupe.5G115900.4PpAAAP67Chr534337.446539.0234.58116.820.776InnerMembrane Prupe.5G155600.1PpAAAP68Chr546151.919.0942.78101.870.257InnerMembrane Prupe.5G155600.2PpAAAP69Chr542244.856.3230.58113.460.742InnerMembrane Prupe.5G162500.1PpAAAP70Chr544850.502239.4730.67105.740.421InnerMembrane Prupe.5G162500.2PpAAAP71Chr540145.308679.8528.65110.100.577InnerMembrane Prupe.5G162600.1PpAAAP72Chr521524.331217.8021.6095.670.240InnerMembrane Prupe.5G162700.1PpAAAP73Chr516619.169699.9923.59102.230.371InnerMembrane Prupe.6G032700.1PpAAAP74Chr644349.375189.0738.4792.440.414InnerMembrane Prupe.6G032700.2PpAAAP75Chr646050.888.6731.8586.220.441InnerMembrane Prupe.6G032700.3PpAAAP76Chr636039.791339.5830.74110.830.538InnerMembrane Prupe.6G032700.4PpAAAP77Chr646050.888.6731.8596.220.441InnerMembrane Prupe.6G032700.5PpAAAP78Chr646050.888.6731.8596.220.441InnerMembrane Prupe.6G032700.6PpAAAP79Chr646851.715278.3734.79100.640.438InnerMembrane Prupe.6G032700.7PpAAAP80Chr642346.151836.5231.55115.180.835InnerMembrane Prupe.6G118000.1PpAAAP81Chr643547.560118.8533.71113.860.625InnerMembrane Prupe.6G118000.2PpAAAP82Chr633036.023789.2530.52113.420.727InnerMembrane Prupe.6G118000.3PpAAAP83Chr619421.352369.2025.99120.050.858InnerMembrane Prupe.6G258200.1PpAAAP84Chr654559.233735.4138.27104.260.478InnerMembrane Prupe.6G273000.1PpAAAP85Chr637741.058779.1339.7197.000.341InnerMembrane Prupe.7G038500.1PpAAAP86Chr754058.374735.8334.16111.040.502InnerMembrane Prupe.7G088200.1PpAAAP87Chr748052.652569.2731.72104.810.503InnerMembrane Prupe.7G088200.2PpAAAP88Chr740443.804348.6332.67128.590.931InnerMembrane Prupe.7G177800.1PpAAAP89Chr754159.118689.1938.75102.940.447InnerMembrane Prupe.7G183800.1PpAAAP90Chr742346.151836.5231.55115.180.835InnerMembrane Prupe.7G183800.2PpAAAP91Chr742346.151836.5231.55115.180.835InnerMembrane Prupe.7G183800.3PpAAAP92Chr744949.938069.2834.4496.500.383InnerMembrane Prupe.8G163100.1PpAAAP93Chr834238.108648.8928.1996.930.493InnerMembrane Prupe.8G164200.1PpAAAP94Chr844950.334349.1340.91102.850.494InnerMembrane Prupe.8G164200.2PpAAAP95Chr837641.969.1335.3899.590.578InnerMembrane Prupe.8G173300.1PpAAAP96Chr850255.296028.8335.33104.740.464InnerMembrane Prupe.8G173400.1PpAAAP97Chr850154.437088.6131.64105.570.506InnerMembrane Prupe.8G173500.1PpAAAP98Chr849154.108.6536.44101.710.468InnerMembrane Prupe.8G173800.1PpAAAP99Chr853958.596319.3235.73102.800.487InnerMembrane Prupe.8G179700.1PpAAAP100Chr834939.004758.9028.8798.880.480InnerMembrane Prupe.8G230900.1PpAAAP101Chr842746.60136.5935.43111.150.704InnerMembrane
2.2 桃AAAP基因家族的系统进化树分析
为分析桃基因在植物中的进化模式,选取拟南芥和桃的AAAP蛋白的氨基酸序列使用MEGA构建系统进化树(图1),结果表明,该基因家族可以分为八个亚族,即为AAP(氨基酸渗透酶)、LHT(赖氨酸和组氨酸转运体)、GAT(γ-氨基丁酸转运体)、ProT(脯氨酸转运体)、AUX)生长素转运体)和ANT(芳香性以及中性氨基酸转运体)以及ATLa、ATLb(类氨基酸转运体)。亚族内成员数量最多的为AAP亚族,含有23个成员;其次亚族成员数量加多的为ATLb、LHT、ATLa数量分别为18、18和12;亚族成员数量最少的是AUX亚族和ANT亚族,仅含有4个和6个。
2.3 桃AAAP基因结构与保守基序分析
对桃基因家族101个成员进行基因结构和保守基序分析(图2、图3、图4),结果表明,桃基因家族成员内皆因结构相似性较低,家族成员内部含有的外显子个数不等。对桃家族中的10个保守基序进行鉴定,发现在桃成员内保守基序间存在差异,motif9高度保守,motif4、5相对保守。每个亚族内成员具有相似的保守基序组成。
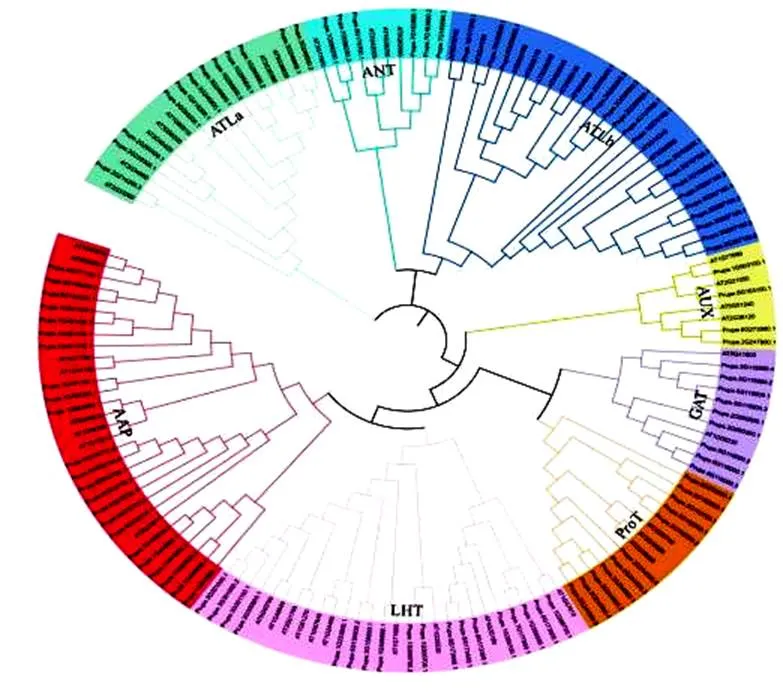
图1 桃AAAP和拟南芥AAAP系统进化树

图2 桃AAAP基因结构

图3 保守基序示例

图4 桃AAAP保守基序分析
2.4 桃AAAP基因家族染色体定位和共线性分析
为了了解桃基因在染色体上的分布,利用TBtools将桃基因定位在染色体上,同时展示基因串联重复事件和共线性分析。结果表明(图5)桃基因不均匀的分布在桃8条染色体上。其中,1号染色体上含有桃基因数量最多,为27个,其次是2号和3号染色体,数量分别为16和18,而4号染色体上仅有两个基因。基因的串联重复事件是指位于同一条染色体上的基因物理距离在200 kb内且相似性大于70%的基因。由图6可以看出,桃基因共有53对基因存在串联重复,其中,在1号染色体上有13对基因存在串联重复,2号染色体上9对基因存在串联重复,3号染色体上有13对基因存在串联重复,5号染色体上有5对基因基因存在串联重重复,6号染色体上有6对基因存在串联重复,7号染色体上存在3对基因有串联重复,8号染色体上存在4对基因有串联重复,而在4号染色体上未发现基因串联重复事件。通过TBtools中MCScanX功能展示桃基因在染色体上共线性(图6)发现,在桃基因内存在3对基因Prupe.8G173300.1)~(Prupe.1G356000.1)、(Prupe.1G233800.1)~(Prupe.3G300900.1)和(Prupe.1G275100.1)~(Prupe.3G267100.1)具有共线性,由此推测这3对基因可能是由于染色体的大片段复制而形成的。

图5 桃AAAP基因在染色体上的分布
注:):代表串联重复基因。
Note: ) Representative tandem repeat gene

图6 桃AAAP基因在染色体上分布及共线性分布
3 讨论
大量跨膜氨基转运蛋白在生理和基因层面上都有鉴定[15,16],作为一个重要的基因家族,基因在植物生长发育的各个方面发挥着重要作用,在玉米[17]、油菜[18]和模式植物拟南芥中均被鉴定到,Yong等[19]曾报道拟南芥中AAP1将氨基酸转运到拟南芥根部和Grallath等[20]曾报道过拟南芥ProT家族具有相似底物特异性,但表达模式不相同。
系统进化树根据蛋白序列的相似性以及保守结构域可以揭示物种之间的亲缘关系,进而推测基因的功能。通过对桃和拟南芥基因构建系统进化树发现,桃中含有植物家族的所有亚族(共八个亚族)。AAP亚族的成员能运输中性条件下带有正电荷以及碱性氨基酸,在拟南芥中AAP家族还能参与调控植物对根结线虫的抵抗过程[21],由此推测桃AAP亚家族内成员具有类似的功能,而此亚族也是桃家族最大的亚族;AUX亚族主要负责转运生长素物质,在拟南芥中主要转运吲哚-3-乙酸来促进侧根形成[22]由此推测桃AUX亚家族中的成员具有相同的功能;在拟南芥中可以调控根的表皮组织和皮层细胞β-葡萄糖醛酸酶的活性[19],由此推测桃ProT亚家族内成员具有类似的功能,同样地,其他亚家族内的成员基因功能也与进化树上亚家族的拟南芥功能类似。
Motif是蛋白质分子内具有特定空间构象、特定蛋白质功能的结构成分,是结构域的亚单位,与特定功能联系在一起[23],推测具有不同motif的家族成员在进化和功能上存在差异。
文献[24]曾报道,基因部分重复和串联重复是植物中基因家族扩增的两个重要因素,根据桃基因家族内的比对,我们检索到53对基因存在串联重复和3对基因存在共线性关系。这些研究结果表明桃基因间存在基因串联重复和部分重复,对桃家族基因的扩张发挥了重要作用。
4 结论
本研究通过对桃基因组内基因家族的筛选,我们共确认鉴定101个家族成员,氨基酸序列长度为166~593范围内,跨度范围较广;等电点和其他理化性质同样跨度范围较广,说明桃基因成员相似性较低,同样系统进化树发现,将桃家族分为把八个亚族,与前人[18]研究结果一致。通过对桃家族成员进行基因结构和保守基序分析发现,在桃家族成员内基因结构和保守基序存在差异性,但亚家族成员内基因结构和保守基序分布相对一致。染色体定位和串联重复事件显示,桃基因不均匀的分布在桃8条染色体上,同时可以发现桃基因以片段重复和串联重复的方式扩增。本文在分子水平上为桃基因的功能挖掘提供了一定的理论支持。
[1] Fischer WN, Kwart M, Hummel S,. Substrate specificity and expression profile of amino acid transporters (AAPs) in[J]. Biol Chem. 1995,270(27):16315-20
[2] 曲越.蒺藜苜蓿与鹰嘴豆基因家族的全基因组分析[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨师范大学,2019
[3] Clark JA, Amara SG. Amino acid neurotransmitter transporters: structure, function, and molecular diversity [J]. Bioessays, 1993,15(5):323-332
[4] Wolf N F, Bruno A, Doris R,. Amino acid transport in plants [J]. Trends in plant science, 1998,5(3):188-195
[5] Tegeder M, Ward JM. Molecular evolution of plantP andAmino Acid transporters [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2012,3:1-21
[6] Saier MH, Reddy VS, Tsu BV,The transporter classification database (TCDB): recent advances [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2016;44(D1):D372-D379
[7] Hunt E, Gattolin S, Newbury HJ,. A mutation in amino acid permeasereduces the amino acid content of the Arabidopsis sieve elements but leaves aphid herbivores unaffected [J]. J Exp Bot. 2010,61(1):55-64
[8] Sakiko O, Roberto S, Mechthild T,High affinity Amino Acid transporters specifically expressed in xylem parenchyma and developing seeds of[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2002,227(47):45338-45346
[9] Zhang L, Tan Q, Lee R,. Altered xylem-phloem transfer of amino acids affects metabolism and leads to increased seed yield and oil content in[J]. Plant Cell, 2010,22(11):3603-3620
[10] Hirner A, Ladwig F, Stransky H,. Arabidopsisis a high-affinity transporter for cellular amino acid uptake in both root epidermis and leaf mesophyll [J]. Plant Cell, 2006,18(8):1931-1946
[11] Zhao YY, Xu YL, Wang Z,. Genome-wide identification and characterization of an amino acid permease gene family in[J]. RSC Advances, 2017,7:38081-38090.
[12] Jérémy CE, Michael FD, Damien BM., a high affinity amino acid transporter specifically expressed in differentiating xylem cells of poplar [J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2010,61(6):1671–1682
[13] Peng B, Kong H, Li Y,.functions as an important regulator of grain protein content and nutritional quality in rice [J]. Natural Communications, 2014,11(5):484
[14] Ignazio V, Albert G, Francesco S,. The high quality draft genome of peach () identifies unique patterns of genetic diversity, domestication and genome evolution [J]. Nature Genetics, 2013,45(5):487-194
[15] Gregory B, Young DL, Jack DW,. The amino acid/auxin:proton symport permease family [J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1999,1415:306-322
[16] Daniel W, Uwe L, Mechthild T,Conservation of amino acid transporters in fungi, plants and animals [J]. Trends in Biocheminical Science, 2002,27(3):139-147
[17] Lei S, Lin D, Han WY,. A genome-wide analysis of thegene family in Maize [J]. Journal of Proteomics & Bioinformatics, 2014,7(1):023-033
[18] Hu L, Yin W, Chen Y,. Functional divergence and evolutionary dynamics of the putativegene family in[J]. Plant Mol Biol Rep., 2014,32:517-530
[19] Yong HL, Justin F, Janet C,transports uncharged amino acids into roots of[J]. Plant Journal, 2007,50:305-319
[20] Grallath S, Weimar T, Meyer A,. Thefamily. Compatible solute transporters with similar substrate specificity but differential expression patterns [J]. Plant Physiol., 2005,137(1):117-126
[21] Marella HH, Nielsen E, Schachtman DP,. The amino acid permeasesandare involved in root-knot nematode parasitism of[J]. Mol Plant Microbe Interact., 2013,26(1):44-54
[22] Marchant A, Bhalerao R, Casimiro I,. AUX1 promotes lateral root formation by facilitating indole-3-acetic acid distribution between sink and source tissues in theseedling [J]. Plant Cell, 2002,14(3):589-597
[23] 赵晶,李旭彤,梁学忠,等.陆地棉漆酶基因家族鉴定及在黄萎病菌胁迫下的表达分析[J].作物学报,2019,45(12):1784-1795
[24] Cannon SB, Mitra A, Baumgarten A,. The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene family in[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2004,4(10):1-21
Identification and Analysis ofgene family in(L.) Batsch
YANG Yang1, LIU Yuan-yuan2, FU Hong-bo2, SHEN Cheng-cheng2
1.033000,2.030801,
In order to understand the characteristics and functions offamily members inpeach, based on the peach genome, the physicochemical properties, phylogenetic tree, gene structure and conservative motifs, chromosome location and collinearity analysis ofgene family members were carried out. The results showed that there were 101 members of thefamily identified in(L.) Batsch, with amino acid sequences ranging from 166 to 593. The subcellular location indicated that allmembers were located on the cell membrane; phylogenetic tree analysis showed that the members of thewere divided into 8 Analysis of gene structure and conservative motifs shows that there are differences in gene structure and conservative motifs among members of thefamily in(L.) Batsch, but there are similarities in gene structure and conservative motifs among members of the subfamily; chromosome mapping analysis shows thaton the 8 chromosomes with uneven distribution of family members, 53 pairs of genes have tandem duplication, and 3 pairs of genes have collinearity. This study has a preliminary understanding of the characteristics and functions of the members of thefamily in(L.) Batsch, which provides theoretical support at the molecular level for the later functional research of this gene in(L.) Batsch.
(L.) Batsch;gene family; bioinformatics
A
1000-2324(2021)03-0408-08
2020-10-18
2020-11-25
杨阳(1983-),女,博士研究生,讲师,主要从事园艺作物种质资源开发及生物技术应用. E-mail:147414658@ qq.com
