Research progress on the regulation of androgen receptor signaling pathway in the treatment of prostate cancer by traditional Chinese medicine monomers
2021-07-21ShanQiGuoYaoTangJinMingSongXiaoJiangLiYingJieJia
Shan-Qi Guo,Yao Tang,Jin-Ming Song,Xiao-Jiang Li,Ying-Jie Jia*
1Department of Oncology,First Teaching Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Tianjin,300381,China;
2Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Tianjin 301617,China.
Abstract The prevalence of prostate cancer in males worldwide is increasing every year.Androgen and androgen receptor drive the development of prostate cancer and are important targets for the treatment of prostate cancer.A growing number of reports indicate that the traditional Chinese medicine has a clear advantage in the prevention and treatment of prostate cancer.This article provides an overview of the in vitro and in vivo studies of different traditional Chinese medicine monomers acting on the androgen receptor-signaling pathway in prostate cancer.
Key words:Prostate cancer,Traditional Chinese medicine monomers,Monomer of Chinese traditional herbs,Androgen receptor signaling pathway
Background
Prostate cancer is the most common malignancy tumor in the male urinary system,with the second highest incidence (14.1%) in males worldwide,which is a common reason of cancer death in male [1].The growth and survival of prostate cancer cells depend on androgen,and surgical or pharmacological androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) is now the basic treatment for prostate cancer patients.However,the median time to ADT sensitivity is 18-24 months in most patients,after which almost patients will progress to castration resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) [2].Poor prognosis and survival in patients with CRPC,and the median survival time is about 14-26 months [3].In addition,ADT has been controversial for causing adverse events such as erectile dysfunction,hot flushes,anaemia and depression [4].Surgery and radiotherapy are ineffective for metastatic prostate cancer,and the side effects of chemotherapy severely compromise patients quality of life.Therefore,the search for new,safe and effective drugs is currently an important research direction in the treatment of prostate cancer.In recent years,the AR signaling pathway plays a significant role in the development of prostate cancer,and traditional Chinese medicine monomers has attracted more and more attention for its good curative effect and less side effects.
Androgen and androgen receptor signalling pathway
Androgen in the circulating blood is mainly testosterone produced by the testis (the vast majority)and adrenal glands.Free testosterone enters the prostate cells and is converted to 5α-hihydrotestosterone (DHT) by the action of 5α-reductase;DHT has an extremely strong AR affinity.The AR has four different functional structural domains: (1).the N-terminal domain;(2).the DNA binding domain;(3).followed by the Hinge domain;(4).the C-terminal ligand-binding domain.As well as other members of the nuclear receptor molecules,AR binds to heat shock proteins (e.g.HSP70,HSP90) and other proteins,stabilizing their conformation and localizing them in the cytoplasm.Upon binding to DHT,the AR undergoes a series of conformational changes leading to separation from the heat shock protein and phosphorylation by protein phosphatase A.In addition,AR dimerized in the presence of ligands and binds to androgen response elements in the promoter region of the target genes.Activated dimers are able to recruit co-regulator proteins (e.g.steroid receptor co-activator-1,SRC-1),co-activator proteins(e.g.CREB binding protein,CBP),co-repressor proteins (e.g.SMRT and HDAC) to form an AR complex.The complex transcriptionally activates or transcriptionally represses the expression of target genes,for instance,prostate specific antigen (PSA),TMPRSS2,NKX3.1 etc,and thereby regulating prostate cancer cells growth and survival [5,6].(Figure 1)

Figure 1 Androgen receptor signaling pathway.
Traditional Chinese medicine monomers
Phenolic compounds
Curcumin is an active ingredient extracted from the plant medicine curcuma longa,has the capability to inhibit AR at the level of protein and gene transcription in prostate cancer(PCa)cells,and can regulate AR signaling pathway in a variety of ways.Curcumin obviously suppress PCa cells proliferation and growth in dose-dependent manner [7].In prostate cells,AKR1C2 acts as a 3‐ketosteroid reductase to reduce DHT level and prevent androgen receptor activation.Curcumin increased AKR1C2 expression and decreased prostate testosterone levels in LNCaP cells and TRAMP mouse prostate tissue,and curcumin decreased androgen synthesis by down-regulating the expression of steroidogenic acute regulatory protein,CYP11A1 and HSD3B2[8].Curcumin down-regulates transcription and expression of AR,activator protein-1,nuclear factor-kappa B,and CREB binding protein,and also suppressed the transforming activitiy of PCa cell lines [9].In addition,curcumin treatment PC-3 cells also altered the overexpression of heat shock protein,resulting in the reduced AR utilization [10].Curcumin analogues have been found to enhance the degradation activity of androgen receptor[11].Another study reported that curcumin inhibited the expression of R1881- and IL-6-mediated PSA gene expression in LNCaP cells through decrease the expression and activity of androgen receptor [12].Curcumin has also shown positive results in animal models,retarding tumours growth and inhibiting AR expression in LNCaP xenograft model [13].In the clinical randomized controlled trial of curcumin and soy isoflavones in the treatment of prostate cancer patients,the androgen receptor and PSA level of the experimental group were significantly decreased [14].These results demonstrate that curcumin has a significant inhibitory effect on PCa cells and may be a potential drug for the treatment of prostate cancer.
Neoisoliquiritin,is a flavone from licorice(Glycyrrhiza),can regulate several critical steps in the AR signaling pathway.It can reduce AR activity by blocking DHT-induced AR nuclear translocation;it also modulate the DNA binding activity of AR androgen response element,inhibiting the expression and transcription activity of AR,and suppressing downstream AR signaling transduction,thereby inhibiting the proliferation of LNCaP cells [15].Carnosol can decrease the expression of AR protein in LNCaP and 22Rv1 PCa cells,inhibits tumorigenesis rate and reduce serum PSA in 22Rv1 prostate cancer tumor transplantation mouse model[16].
Sesquiterpenoids
ST1 and ST2 were obtained from Myrrh,which inhibited the proliferation of LNCaP cells.Subsequent studies found that ST1 and ST2 significantly reduced the expression of AR in LNCaP cells,inhibited AR translocation into the nucleus,reduced the expression of the androgen receptor cofactor and the steroid receptor co-activator-1 of AR in LNCaP cells.It interfered with the interaction between AR and ARA70 and SRC-1 to mediate the inhibition of AR translocation receptor co-activator,thereby inhibiting the trans-activation of AR to mediate the suppression of AR transcription[17].
Hinokitiol (β-thujaplicin) interfere with AR signaling and inhibits the growth of PCa cell lines.The mechanism is hinokitiol with a dose and time-dependent manner suppress androgen/AR-mediated cell growth and androgen-stimulated DNA synthesis by[(3)H]thymidine incorporation.In addition,hinokitiol obviously repress the mRNA and protein expression level of AR,which result in the decrease of PSA secretion[18].
Triptolide (TPL),a ciretical active ingredient obtained from the Chinese herb Thunder God Vine,possesses anti-cancer activity in human PCa cells.Triptolide inhibited mRNA and protein expression of AR in LN-CaP cells,as well as the expression of AR target genes PART1 and PSA,and down regulated the expression of PI3K/AKT/NF-κB pathway proteins associated with AR promoter activity,thereby reducing androgen receptor activity [19].It was demonstrated that TPL at low concentration (6.25 nm) inhibited the ligand-dependent and ligand-independent trans-activation activities of AR-FL and AR variants,without affecting their protein level.TPL also attenuated AR activity by inhibiting XPB/CDK7-mediated phosphorylation of AR at Ser515.In addition,TPL combined with enzalutamide displayed synergistic and highly effective anti-CRPC effects in vitro and in vivo,including inhibiting the proliferation and survival of CRPC cells,and without obvious side effects.Thus,the combination of TPL with enzalutamide is a potential therapeutic treatment for CRPC[20].
Bakuchiol,one of the main active ingredients of Psoralea corylifolia,was found that bakuchiol exhibit anti-metastasis activity through NF-κB cross talk signaling with AR and ERβ in androgen-independent PCa cells(PC-3)[21].
Flavonoids
Quercetin,a naturally occurring polyphenolic compound,can inhibit the AR expression at the transcriptional level in LNCaP PCa cells,and thereby down-regulate the androgen-inducible genes that can promote prostate cancer,including PSA,hK2,NKX3.1 and ODC [22].Numerous studies demonstrate that splicing factors hnRNPA1 promote the generation of AR-V7,and contributing to enzalutamide resistance in PCa cells.Quercetin can reduce the expression of hnRNPA1,and consequently,that of AR-V7,antagonizes androgen receptor signaling,and resensitizes enzalutamide-resistant PCa cells to enzalutamide treatment in vivo in mouse xenografts[23].Also,quercetin reverse docetaxel resistance in prostate cancer via androgen receptor signaling pathway[24].
Baicalein was effective inhibiting the growth of AR-positive PCa cells at low concentrations,but had no significant effect on AR-negative PCa cells.Mechanism dissection suggest that baicalein suppresses AR N-C dimerization and AR-coactivators interaction and AR target genes (e.g.PSA,TMPRSS2,and TMEPA1) expression in both androgen responsive LNCaP cells and castration resistant CWR22Rv1 cells,and thus inhibits androgen receptor (AR)-mediated prostate cancer progression [25].Another study found that baicalein significantly reduced AR and PSA protein expression in LNCaP cells and inhibited the growth of prostate cancer xenografts in nude mice[26].
Icaritin (ICT) is a natural flavonoid extracted from the traditional Chinese herb Epimedium brevicornu,with potential therapeutic effects against prostate cancer.In a significant proportion of prostate cancer patients,androgen receptor splice variants (ARvs)play a key role in contributing to the resistance against ADT.However,clinically used anti-androgens drugs that target the AR ligand-binding domain,such as bicalutamide and enzalutamide,have failed to inhibit these AR variants,leading to prostate cancer patient's failure to escape the outcome of developing CRPC.Research found that ICT could inhibit transcription of AR-regulated genes,as well as the ARvs-regulated genes UBE2C,and promoted the degradation of both AR and ARvs by binding to arylhydrocarbon-receptor to mediate ubiquitin-proteasomal degradation [27].Thus,ICT may be able to delay the progression to CRPC in prostate cancer patients by reducing the generation of ARvs,but it requires further research.
Fisetin,as AR ligand,through competing with the high-affinity androgen to interact with the ligand-binding domain of AR,resulted in substantial decrease in AR stability and decrease in amino-terminal/carboxyl-terminal (N-C) interaction of AR.This resulted in blunting of AR-mediated transactivation of target genes.In addition,treatment of LNCaP cells with fisetin reduced AR protein level.In vivo experiments in athymic nude mice also showed that fisetin could inhibit tumor growth and reduce serum PSA level[28].
Quinones
Emodin is a natural compound that can inhibits the transactivation of AR by inhibiting androgen-dependent AR nuclear translocation.Emodin reduces AR binding to HSP90 and increases AR binding to MDM2,which in turn induces AR degradation via a proteasome-mediated non-ligand-dependent pathway.Thus,emodin can directly target AR to inhibit PCa cells growth[29].
Cryptotanshinone (CTS) is a natural compound derived from the roots of salvia miltiorrhiza,which has anti-prostate tumor activity.CST has a structure similar to dihydrotestosterone (DHT),modulates AR transactivation,and inhibits the DHT-mediated AR target genes (PSA,TMPRSS2,and TMEPA1)expression in both androgen responsive PCa LNCaP cells and castration-resistant CWR22Rv1 cells.CTS selectively suppress AR without inhibiting the activitiy of other nuclear receptors,such as PR,GR,and ERα.Furthermore,CTS efficiently suppress CWR22Rv1 cells growth and expression of AR target genes in the xenograft animal model[30].
PTS33 a new sodium derivative of CTS,has a similar function to CTS that selectively inhibits AR activities and modulate AR transactivation and suppress the AR target genes (e.g.TMEPA1,TMPRSS2,and PSA) expression in both androgen responsive PCa cells (LNCaP) and castration-resistant C4-2 cells[31].
Shikonin,a natural naphthoquinone extracted from the traditional Chinese medicine Zi Cao,inhibited the transcription activity of AR in LNCaP and 22Rv1 PCa cells,and decreased the mRNA and protein expression levels of AR,thereby inhibiting the growth of PCa cells [32].In addition,shikonin reduces growth of docetaxel-resistant prostate cancer cells through necroptosis[33].
Tashinone IIA is one of the main components of tanshinone.In a randomized controlled clinical study of tashinone IIA combined with endocrine therapy in treating advanced-stage prostate cancer.The tashinone IIA trial group not only had a better reduction in PSA levels,but also more effective in improving patients'quality of life,IPSS scores and clinical symptoms,demonstrating that tashinone IIA in combination with conventional endocrine therapy can enhance the clinical efficacy of prostate cancer treatment[34].
Alkaloids
Berberine is an isoquinoline alkaloid with a long history of use in traditional Chinese medicine.Berberine reduced AR transcription activity,decreased the expression of AR-regulated genes,and mediated AR protein degradation via the proteasome pathway in both androgen-dependent and CRPC cells.In addition,animal experiments showed the berberine exerted the growth inhibitory and AR downregulating effects specifically in the tumor tissues [35].Aldo-keto Reductase Family 1 Member C3 (AKR1C3) is involved in steroid synthesis in human PCa cells,which possesses reductase activity for the catalysis of low activity hormone precursors,androstenedione and androsterone,to highly active testosterone (T) and DHT.AKR1C3 is overexpressed in localized,advanced or recurrent prostate cancers and the CRPC,and the expression levels of AKR1C3 were closely correlated with the Gleason grade of prostate cancer progression.Berberine can inhibits AKR1C3 enzyme activity in a dose-dependent manner to reduce intracellular androgen synthesis and inhibit the growth of 22Rv1 cells[36].
Camptothecin,a pentacyclic alkaloid first extracted from the Chinese tree Camptotheca acuminata,is a DNA topoisomerase I inhibitor.Camptothecin can block androgen binding to AR in PCa cells,significantly inhibited AR transcription activity and reduced AR protein expression[37].
Others
Ginsenoside 20(S)-protopanaxadiol-aglycone is derived from ginsenosides,the main active ingredient in ginseng,and induces proteasome-mediated degradation and represses AR gene transcription,thereby effectively down-regulating the expression and activity of full-length AR and AR-Vs.In vivo experiments showed that ginsenoside 20(S)-protopanaxadiol-aglycone inhibited the growth of LNCaP xenograft tumours and the expression and activity of AR,but normal prostate morphology and AR expression were unaffected[38].
Honokiol,one small-molecule extracted from the bark of Magnolia officinalis,inhibits PCa cells growth by suppressing androgen receptor activity through transcriptional repression and proteasomal degradation[39].
Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Overall,as shown in Table 1,in vitro and in vivo studies have shown that herbal monomers have a positive effect on the treatment of prostate cancer by modulating the androgen receptor signaling pathway.However,there are still shortcomings: most of the current studies are about cell experiments,lack of in vivo experiments to further prove its effectiveness;certain herbal monomers have only been reported in single studies;the mechanism of action on prostate cancer cells is not detailed;Lack of accurate knowledge of bioavailability and effective dose.Therefore,experimental studies should be conducted in a combination of in vivo and in vitro approaches,and preclinical and clinical studies should be conducted to better understand the mechanism of action,bioavailability,safety,dose efficacy and stability of different monomers in order to transform them into drug candidate to treat prostate cancer.
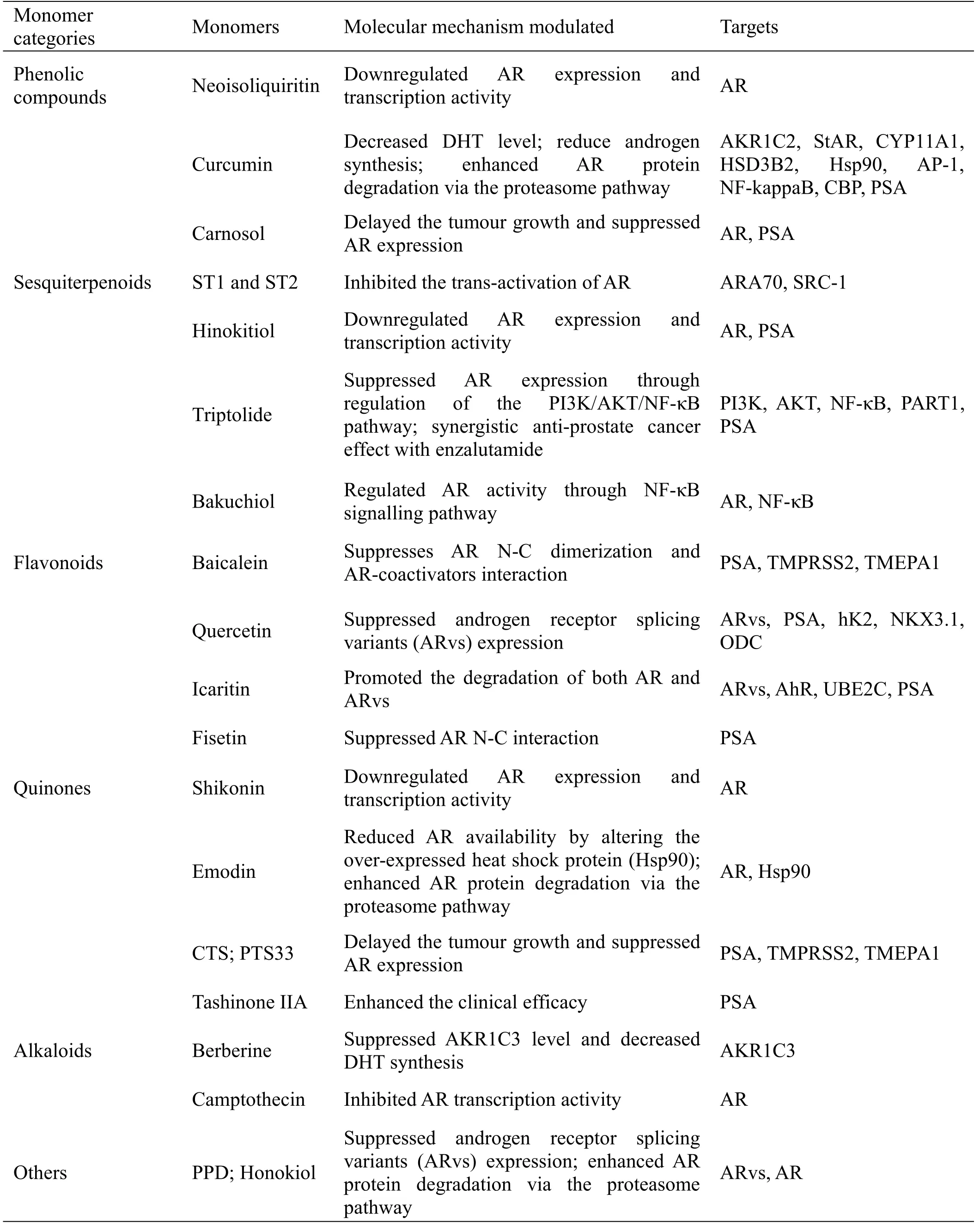
Table 1 Molecular mechanism of Chinese medicine monomers anti-prostate cancer through regulation of AR signaling pathway
