Investigation of the effectiveness of LI4,LI10,LR3 and ST36 acupoints electroacupuncture in radialis and ulnaris nervus injuries
2021-07-21ErenPolatCihanGunayAhmetKavakl
Eren Polat,Cihan Gunay,Ahmet Kavaklı
1Department of Surgery,Faculty of Veterinary Medicine,Fırat University,Elazıg,Turkey;2Department of Anatomy,Faculty of Medicine,Fırat University,Elazıg,Turkey.
Abstract Background:Radial and ulnar nervus injuries are among the most common peripheral nerve injuries in veterinary medicine.In this study,it was aimed to evaluate electroacupuncture applications in radialis and ulnaris nervus injuries. Methods:New Zealand rabbits were used in the study.Rabbits were divided into treatment groups and control groups.The treatment groups included the acute nerve injury group and the chronic nerve injury group.The control groups included the positive control group (damaged but no treatment),and the negative control group (no damage but with electroacupuncture).Hegu(LI4),Shousanli(LI10),Taichong(LR3)and Zusanli(ST36)acupoints were used for electroacupuncture applications.During the treatment period,clinical examinations of the rabbits were performed. Results:The deep pain sensation and resistance to the applied pulling force in the legs of the rabbits in the treatment groups(both acute nerve injury group and the chronic nerve injury group)were statistically significantly increased (P <0.001 for all).Again,the rabbits in the treatment groups were found to be in a better condition than the positive control group in terms of using their legs while walking and using their claws,and there was a statistically significant difference (P <0.001 for all).Electroacupuncture is an effective treatment for both acute and chronic nerve injuries,as well as being more effective in acute cases than in chronic cases. Conclusion:Electroacupuncture based on LI4,LI10,LR3 and ST36 acupoints is an effective treatment in rabbits’radial and ulnar nervus injuries.
Key words:Electroacupuncture,Rabbit,Radial nerve,Ulnar nerve,Injury
Background
Radialis and ulnaris nervus injuries are very common in veterinary medicine.It is mostly seen with severe soft tissue damage or bone fractures in the front legs[1−4].In radial nerve injuries,the leg hangs down from the elbow joint of animals.Hyperflexion occurs in the carpophalangeal joint.Carpal hyperextension is formed in the nervus ulnaris injuries that innervate the flexor muscles of the carpal joint [2,3,5].Medical treatment options and operative treatment options are used in the treatment of peripheral nerve injuries [2,5,6].Although modern medical techniques are effective in nerve regeneration,they are insufficient to prevent muscles atrophy[3].
Acupuncture (faradization,diathermy,acupuncture,etc.) is an effective treatment method especially used in skeletal and muscular system diseases,neurological diseases [9,10],which could improve the functions of neurons,by promting neural stem cells differentiation and inhibiting neuronal apoptosis [11−13].In the last half a century,physicians have use alternative treatment methods for peripheral nerve injuries[6−8].
Hegu(LI4)and Shousanli(LI10)acupuncture points are important acupoints used in radial nerve injuries[14,15].LI4 acupoint is located between the first and second metacarpal bone,at the level of the second phalanx of the first finger.LI4 is the most commonly used acupoint,which could activate collaterals and alleviate pains[14,15];The LI10 acupoint is located at the medial edge of the extensor carpi radialis muscle.Needling LI10 could alleviate shoulder pain and improve upper limb paralysis [14,15].The Taichong(LR3)acupoint is located between the second and third finger bones in the hind paws,just under half the length of the metatarsal bone.The LR3 acupoint was preferred because it is located in a meridian that encourages the LI meridian.Zusanli (ST36) point is also one of the generally effective acupuncture points,which is important in stroke treatment [14].The ST36 acupoint is located three Cun(10cm)distal to the Dubi(ST35) point,which is lateral to the distal junction of the patellar ligament[15].In this study,it was aimed to investigate the effect of (LI4,LI10,LR3 and ST36)acupoints acupuncture on acute and chronic peripheral nerve injuries.
Materials and methods
Study design and creation of groups
28 New Zealand rabbits (8-12 months old,14 females,14 males) were used in the study.The study started after the official approval of Firat University Animal Experiments and Ethics Committee (2016/43-Decision no:65).The rabbits were randomly divided into four equal groups.These are the acute nerve injury (ANI),chronic nerve injury (CNI),positive control (PC) and negative control (NC) groups.Electroacupuncture was applied to the rabbits in the ANI and CNI groups after the nerve radial and nervus ulnaris were damaged.The radial and ulnar nerves of rabbits in the PC group were damaged,but electroacupuncture was not performed.No radial and ulnar nerve damages were created in rabbits in the NC group,but electroacupuncture was performed.
Damage to the radial and ulnar nerve
Before inducing nerve damage in the ANI,CNI and PC groups,xylazine hydrochloride (Rompun® 23.32 mg/mL,Bayer,Istanbul,Turkey) at a dose of 5 mg/kg and ketamine hydrochloride (Ketalar® 50 mg/mL,Eczacıbaşı,Istanbul,Turkey) at a dose of 35 mg/kg were administered intramuscularly for anesthesia.Asepsis procedure was performed after anesthesia.Using standard surgical procedures,the nerve radialis and nervus ulnaris were exposed by approaching from the part of the leg.Pressure was applied to the nerves for 60 seconds with the help of hemostatic forceps,1 cm below the point where the nerve radialis and nervus ulnaris separated from the plexus brachialis (Figure 1)[16,17].The operation line was closed following the surgical principles after the hemostatic forceps were removed.Cephalexin (Bavet Cephalexin;150 mg/mL;Bavet,Istanbul,Turkey) (15 mg/kg) was administered intramuscularly for five days postoperatively.
Electroacupuncture application
The first electroacupuncture was applied to the rabbits in the ANI group on the same day after nerve damage was induced.In the CNI group,the first electroacupuncture application was performed on the 30th day after nerve damage was induced.Electroacupuncture was applied to the rabbits in the ANI,CNI and NC groups once in two days.(15 sessions).For the application,LI4,LI10,LR3,and ST36 acupoints were used.While choosing acupuncture points,points used in the treatment of radial nerve injuries and peripheral nerve damage and points that encourage these points according to Traditional Chinese medicine were preferred (The locations of acupuncture points in rabbits were determined according to the Xie's Rabbit Acupoints Chart in Chi University Bookstore) [15].Electroacupuncture was performed at 50 Hz mA and 400 µs constant current for 30 minutes (Figure 2).Rabbits were given 5 mg/kg xylazine hydrochloride intramuscularly for each session[18].
Clinical evaluation
Deep pain sensation,degree of foot use,foot pulling strength,hypotonia/atrophy status in foreleg muscles and degree of paw use were evaluated.Scales were created to evaluate these clinical parameters (Table 1,Table 2,Table 3 and Table 4).
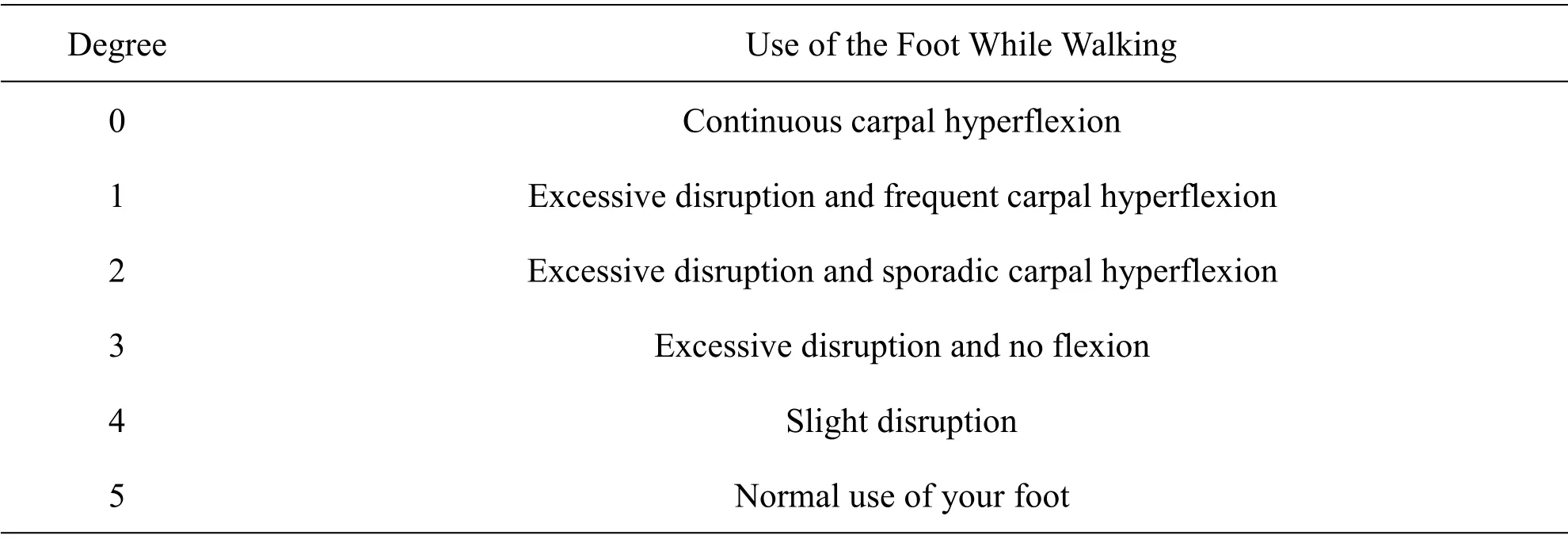
Table 2 Evaluation scale of the usage status of the foot with nerve damage during walking

Table 3 The scale of evaluation of the response of the foot with nerve damage to the pull
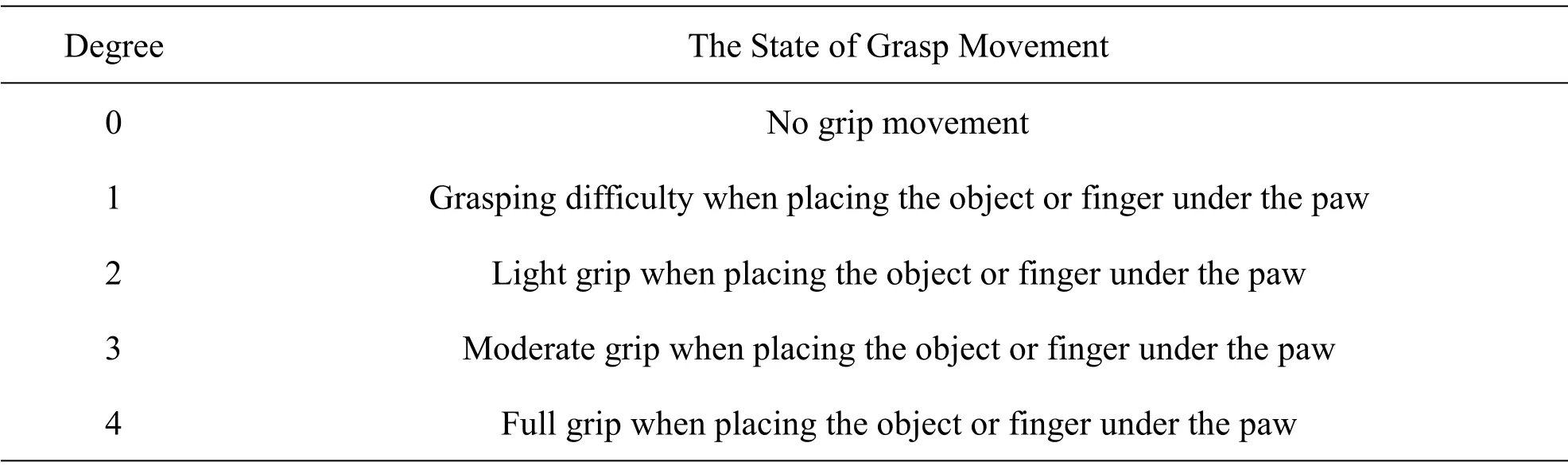
Table 4 Grip movement status evaluation scale of nerve-damaged foot
Statistical analysis
SPSS Ms Windows Release 21.0 program was used in statistical analysis.While evaluating clinical findings,one-way analysis of variance was used for differences between groups.Binary comparisons between groups were determined by the Tukey post hoc test.In terms of clinical findings,differences between groups according to measurement times were determined by Friedman test.Binary comparisons between groups were determined by Wilcoxon test.
Results
Evaluation of Deep Pain Sensation
During the treatment period,it was determined that the deep pain sensation of the rabbits in the ANI and CNI groups increased day by day and this increase was statistically significant compared to the PC group (P<0.001).However,a statistically significant increase was found in the rabbits in the ANI and CNI groups in terms of deep pain sensation between days(P<0.001).The scale in Table 1 was used to evaluate deep pain sensation.Statistical analysis of the effects of electroacupuncture on deep pain sensation is presented in Table 5.
The situation of using the foot with nerve damage during walking
At the end of the study,it was determined that the rabbits in the ANI and CNI groups used their feet better during walking compared to the PC group,and there was a statistically significant difference (P<0.001).In addition,the difference between days in the use of their feet during walking during the treatment period of the rabbits in the ANI and CNI groups was found to be statistically significant (P<0.001).The scale in Table 2 was used to evaluate the use of the feet of the rabbits during walking.Statistical analysis of the effects of electroacupuncture on foot use during walking is presented in Table 6.
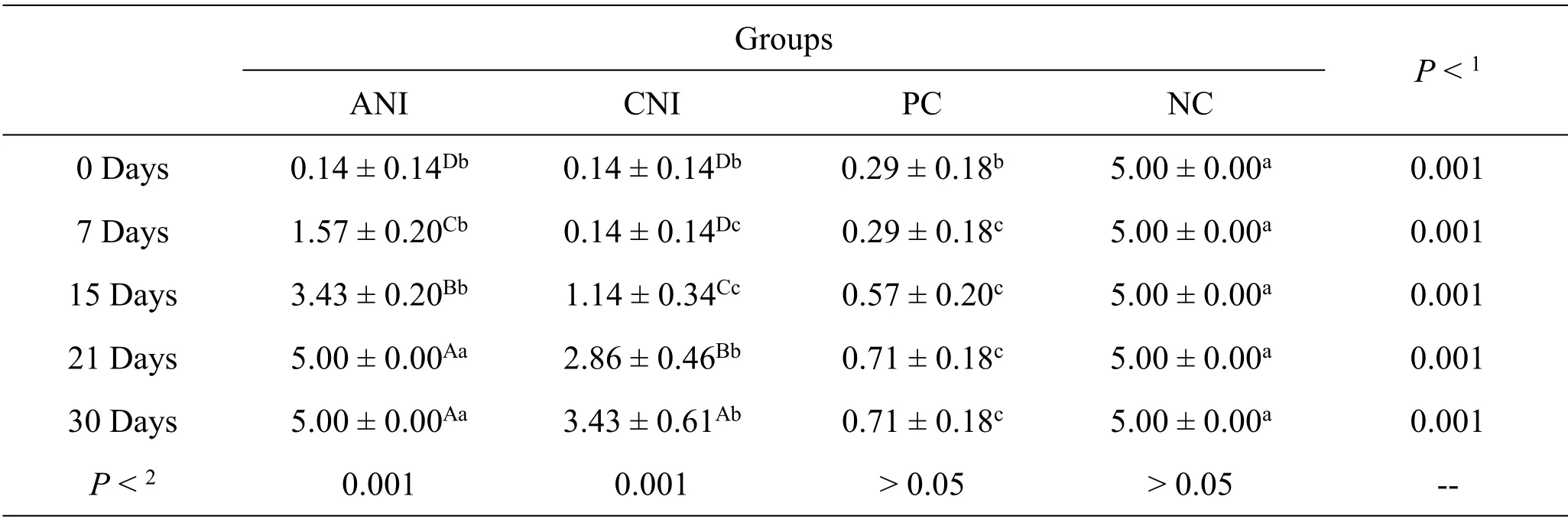
Table 5 Statistically evaluation chart of deep pain sense
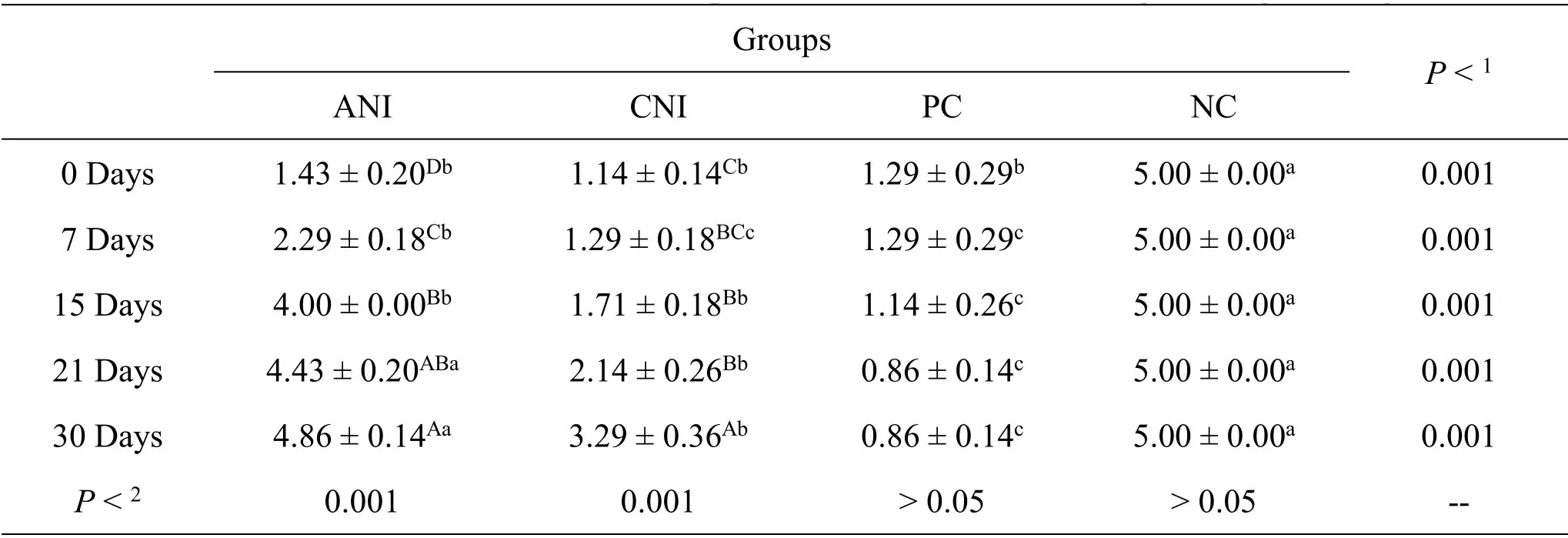
Table 6 Assessment chart of foot compression status of nerve damage during walking
Evaluation of the response of the foot with nerve damage to the pull
When pulling force was applied to the foot with nerve damage,it was found that the resistance to withstand was statistically significantly increased in the ANI and CNI groups compared to the PC group (P<0.001).In addition,during the treatment process,it was determined that there was a statistically significant difference in the within-group change by days in the ANI and CNI groups(P<0.001).The scale in Table 3 was used to evaluate the foot pulling force.Statistical analysis of the effects of electroacupuncture on foot pulling force is presented in Table 7.
Assessment of hypotonia in legs with nerve damage
In this study,while evaluating the effectiveness of electroacupuncture,hypotonia conditions in the foreleg muscles were evaluated.During the evaluation,the muscles in the healthy left front leg were considered as reference.There was no evidence of hypotonia in the leg muscles of the rabbits in the ANI,CNI and PC groups the day after the nerve damage was created.The number of rabbits in which hypotonia was detected in the legs in all groups during the treatment is presented in Table 8.

Table 7 Evaluation schedule of response conditions to footing

Table 8 Number of rabbits with leg muscle hypotonia during treatment in groups
Evaluation of grasping ability of claw
In the evaluation of the ability of rabbits to use and grip their paws,it was determined that ANI and CNI groups improved significantly compared to the PC group (P<0.001).The scale in Table 4 was used to evaluate the degree of rabbits' paw use (Figure 3).Statistical analysis of the effects of electroacupuncture on the degree of use of paws is presented in Table 9.
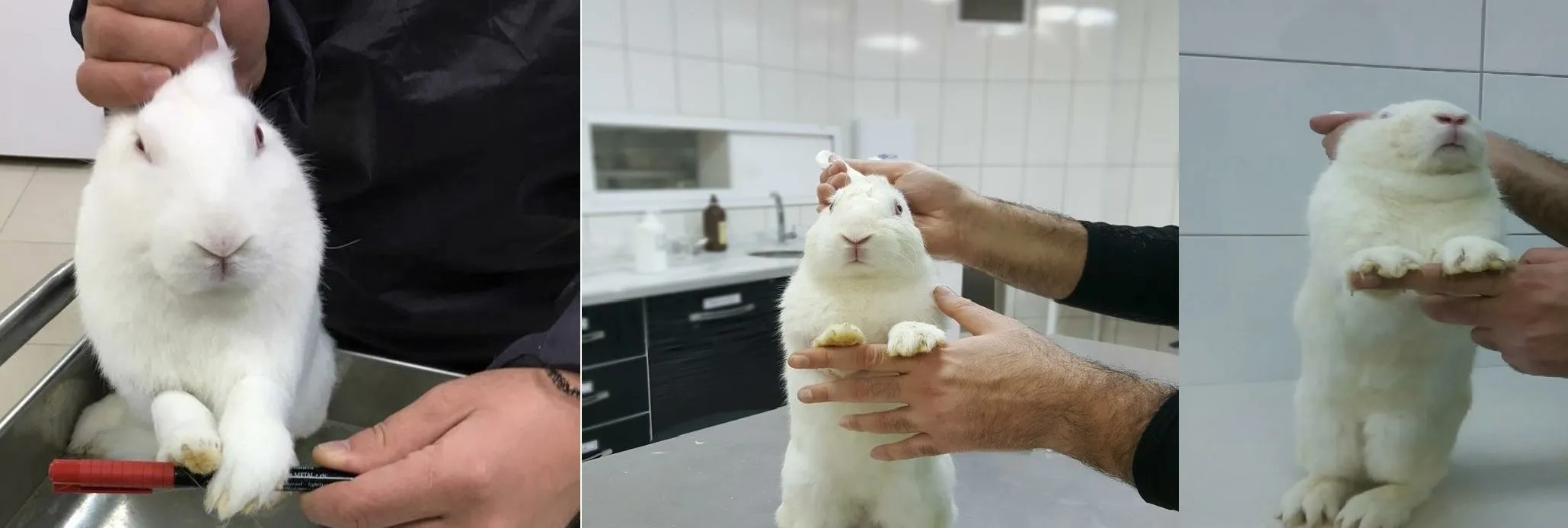

Figure 3 Grip test(Grade 0,Grade 2,Grade 4)
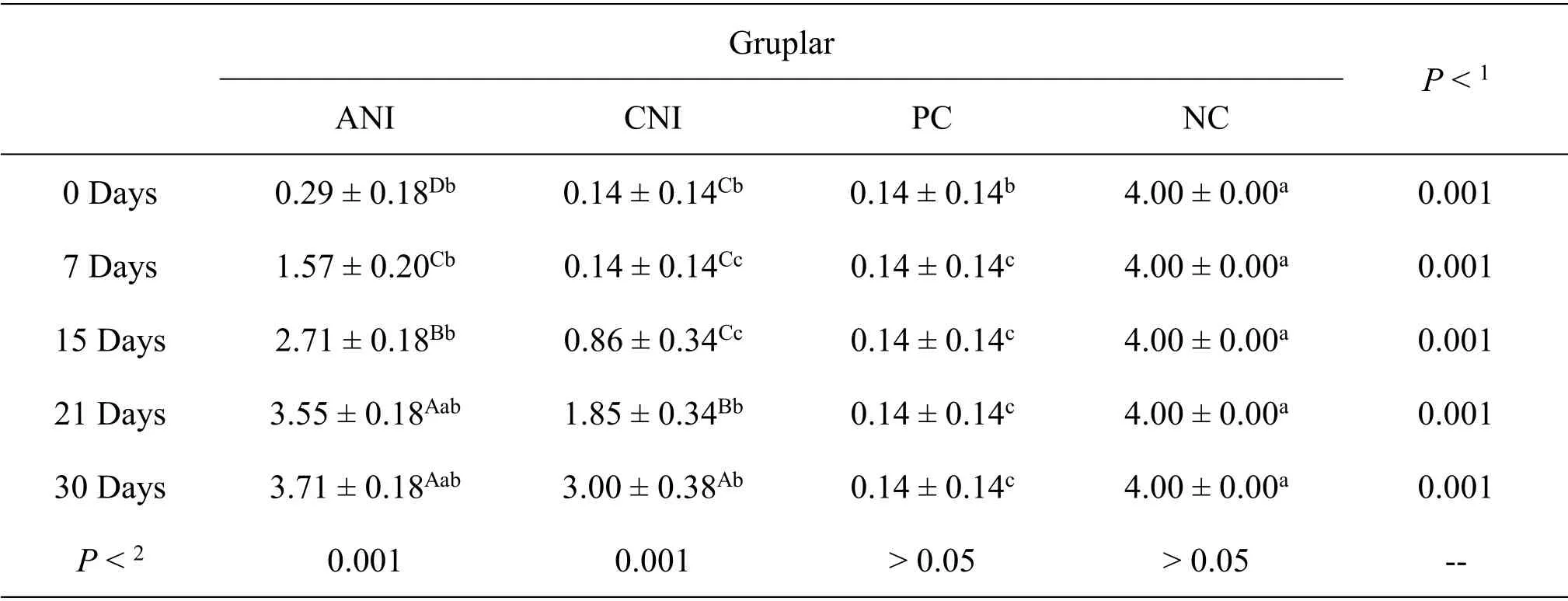
Table 9 Grasping ability assessment chart
Discussion and Conclusion
Radial and ulnar nerve injuries are the most common peripheral nerve injuries in animals.Although there are multiple reasons,severe soft tissue trauma and bone fractures in the front legs can cause radial and ulnar nerve damage [3,5,19,20].Since it is a common problem in veterinary medicine,the subject of this study was determined as radial and ulnar nerve injuries.
Medical treatment options (Vitamin B applications,vesican ointment applications,etc.) and operative treatment options(neuroraphy,tendo transposition,etc.)are used in the treatment of peripheral nerve injuries[2,5,6].In addition to these,medical and operative treatments are supported by physiotherapy techniques[7,8].In the last half a century,physicians have started to frequently use alternative treatment methods(faradization,diathermy,acupuncture,etc.) for peripheral nerve injuries [6].Many scientific sources support the view that electroacupuncture is an effective treatment method in peripheral nerve injuries.Electroacupuncture improves the functions of neurons,provides differentiation and proliferation of neural stem cells.Electroacupuncture also has an inhibitory effect on neuronal apoptosis [11−13].In this study,it was aimed to evaluate the effect of electroacupuncture on acute and chronic peripheral nerve injuries using clinical parameters.
Both this study and other studies have proven that acupuncture is an effective treatment option for healing nerve damage.Rosa et al.(2010) reported that they achieved 46.7% success in their study where they treated their patients with facial palsy with acupuncture[21].Jin-Sheng et al.(2009)reported that their patients with facial palsy recovered 90.9% with acupuncture treatment [22].Hayashi et al.(2007) investigated the efficacy of acupuncture treatment with corticosteroids on 50 dogs with intervertebral disc disease.In their study,the efficiency rate in the acupuncture group was 88.5%,while the efficiency rate in the group without acupuncture was 58.3% [23].Joaquim et al.(2010)investigated the effectiveness of decompressive surgery and electroacupuncture applications on 40 dogs with thoracolumbar intervertebral disc disease and severe neurological disorders.As a result of the applications,they reported that they achieved 40%success in dogs with decompressive surgery,78.94%in dogs with electroacupuncture,and 72% in dogs with electroacupuncture with decompressive surgery [24].Janssens (1985) applied acupuncture in addition to medical treatment on 32 dogs with cervical disc disease.It was reported that 68.75% of the patients recovered completely after the applications [25].In this study,it was determined that 64.3% of the rabbits in the ANI and CNI groups recovered completely.It was also found that 85.7%of the rabbits in both groups recovered completely or significantly.
It has been reported in many studies that acupuncture application reduces the recovery time of nerve injuries [23,26].In this study,a significant improvement was found between 10−12 days in rabbits in the ANI group.It was determined that complete recovery was between 22−24 days.Four of the rabbits in the CNI group recovered completely.Significant recovery times of these rabbits were determined as 18−20 days.Complete recovery time is 28 days.Three rabbits in the CNI group only improved significantly.This development period was found to be 22−24 days in rabbits.This showed that the recovery period of the rabbits in the CNI group was longer than the rabbits in the ANI group.
As a result,considering the clinical evaluations,it was concluded that electroacupuncture is an effective treatment method for peripheral nerve injuries,since the rabbits in the ANI and CNI groups showed positive progress compared to the rabbits in the PC group.Electroacupuncture was more effective in acute cases due to the greater recovery of rabbits in the ANI group than in the CNI group.It was concluded that the effectiveness of electroacupuncture in peripheral nerve injuries were significant,which could be encouraged.However,it will need many more studies before the technique used.
