Network pharmacology-based approach to investigate the mechanism of Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Decoction for treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus
2021-07-07HuiLingLiChenChenChaoChen
Hui-Ling Li,Chen Chen,Chao Chen,,3*
1School of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Guangdong Pharmaceutical University,Guangzhou 510006,China;2The Key Unit of Chinese Medicine Digitalization Quality Evaluation of SATCM,Guangzhou 510006,China;3The Research Center for Quality Engineering Technology of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Guangdong Universities,Guangzhou 510006,China.
Abstract Background:Although the benefits of Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Decoction(HLJDD)on type 2 diabetes mellitus are noted,the material base and action mechanism remain unknown.This paper aim is to reveal the material base and action mechanism of HLJDD against type 2 diabetes mellitus in a system pharmacology framework.Methods:The compounds in HLJDD were first retrieved from the Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology database and analysis platform.Once retrieved,they were fed into the SwissTargetPrediction database to predict the interacting targets.Meanwhile,a human expression profile dataset was analyzed in the Gene Expression Omnibus database,and subsequently,the differentially expressed genes were compared to the HLJDD-related targets.We conducted a protein-protein interaction analysis,Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway analysis,and Gene Ontology analysis to identify the potential active compounds and targets.Lastly,to verify the binding affinities of those compounds and targets,we performed molecular docking.Results:We obtained 15 key compounds,such as quercetin,epiberberine,and berberine,and 10 hub genes,such as IκB kinase-β and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit alpha.The top 10 enriched pathways were also found to be tightly related to type 2 diabetes mellitus,including insulin resistance and FoxO signaling pathway.Moreover,all the key compounds were found to bind well to the hub genes.Particularly for the target of IκB kinase-β,11 out of 15 compounds bound to it with energies of<-9.0 kcal/mol.Conclusion:In summary,15 key compounds of HLJDD may affect type 2 diabetes mellitus development by multiple genes such as IκB kinase-β and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit alpha and signaling pathways such as insulin resistance and FoxO signaling pathway.
Keywords:Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Decoction,Type 2 diabetes mellitus,Gene expression profile,GEO database,Network analysis,Molecular docking
Background
Type 2 diabetes mellitus(T2DM)is a complex endocrine and metabolic disorder,which accounts for 90%-95% of all diabetes mellitus cases[1].It has already become a global epidemic,and the population affected by diabetes is expected to rise from 451 million in 2017 to 693 million in 2045[2].T2DM is characterized by insulin resistance,decreased insulin secretion,glycosuria,and chronic inflammation[3].In patients with T2DM,blood glucose levels may rise progressively over time without adequate treatment for increasing insulin sensitivity and lowering blood glucose[4].
Today,there are about nine classes of antidiabetic medicines,including alpha-glucosidase inhibitors,sulfonylureas, biguanides, meglitinides,thiazolidinediones,glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists, dipeptidylpeptidase-4 inhibitors,sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors,and insulin[5].However,metformin is still the first-line medicine for diabetes[6],and there are just a few medicines that are truly effective in treating T2DM due to toxic side effects.For this reason,looking for potential medicine for T2DM treatment including traditional Chinese medicine(TCM)is still challenging.
Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Decoction(HLJDD)was first mentioned inHandbook of Prescriptions for Emergency,written by Ge Hong(284 C.E.-364 C.E.)in the Eastern Jin Dynasty of China[7].HLJDD is composed of four individual herbs,that is,Huanglian(Rhizoma Coptidis),Huangqin(Radix Scutellariae),Huangbai(Cortex Phellodendri),and Zhizi(Fructus Gardeniae)in a ratio of 3:2:2:3 proportion[8].This prescription is a representative prescription for clearing“heat”and“poison”and has the effect of removing“body fire”(in Chinese medicine theory,“heat”,“poison”and“body fire”mean the pathological product of the human body).Nowadays,as a classic TCM prescription,HLJDD has been widely studied as the probe with a purpose in the pharmacological and clinical investigations[9,10].Other than inflammation[11],gastrointestinal disorders,cardiovascular diseases[12],and Alzheimer’s disease[13],existing researches have shown that HLJDD is effective in treating T2DM.Diabetes is a common disease marked by frequent drinking and urinating and dryness-heat due to Yin deficiency is its basic pathogenesis in the clinic.As stated inJingyue’s Complete Workswritten by Zhang Jing-Yue(1563 C.E.-1642 C.E.)in the Ming Dynasty of China,body fluid generates and frequent drinking and urinating stop only when removing body fire,which indicates that clearing heat and removing fire are possible ways for the treatment of frequent drinking and urinating.It was reported[14,15]that rats with T2DM given HLJDD could have lower levels of fasting blood glucose,triglyceride,total cholesterol,and glutathione,which were shown to be increased in the diabetic rats.Although a few reports[8]focused on the bioactive components of HLJDD,there is a lack of data describing the potential benefits of HLJDD in T2DM.
Network pharmacology,as a system biology-based methodology,offers an effective approach to assess the pharmacological effects of drug combinations,especially TCM,at the molecular level by predicting the complex interactions of small molecules and proteins in a biological system.Network pharmacology describes complexities among biological systems,drugs,and diseases from a network perspective and shares a similar holistic philosophy as TCM theory.Thus,recently,it has been successfully used to explain the characteristics of multicomponents,multitargets,and multipathways of TCM[16].For example,Liu et al.revealed the pharmacological mechanism of pharmacokinetic target components of the San-Ye-Tang-Zhi-Qing formula,an empirical formula of Chinese medicine for treating T2DM by a network pharmacology strategy[17].Yue et al.reported the dissection of the synergistic mechanism of Huangqi(Astragali Radix)andRhizoma Coptidisfor diabetes mellitus based on a system pharmacology method[18].Gao et al.addressed that the empirical formula Qijian mixture alleviated T2DM through TP53,Protein kinase B(AKT)1,and PPARA proteins by a system pharmacology paradigm[19].Furthermore,the multiomics analysis combined with network pharmacology showed unique advantages in exploring the material base and the molecular mechanism of TCM in treating various diseases[16].Among the omics techniques,gene expression profile analysis is a useful tool for screening the differentially expressed genes(DEGs)and the underlying mechanism[20].
In our study,we employed network pharmacology combined with gene profile analysis to reveal the material base and action mechanism of HLJDD for the treatment of T2DM.The framework is shown in Figure 1.As a result,we finally obtained 15 key compounds,top 10 interacting genes,and top 10 modulated pathways,and the molecular docking results confirmed that all these compounds bound well to the genes.
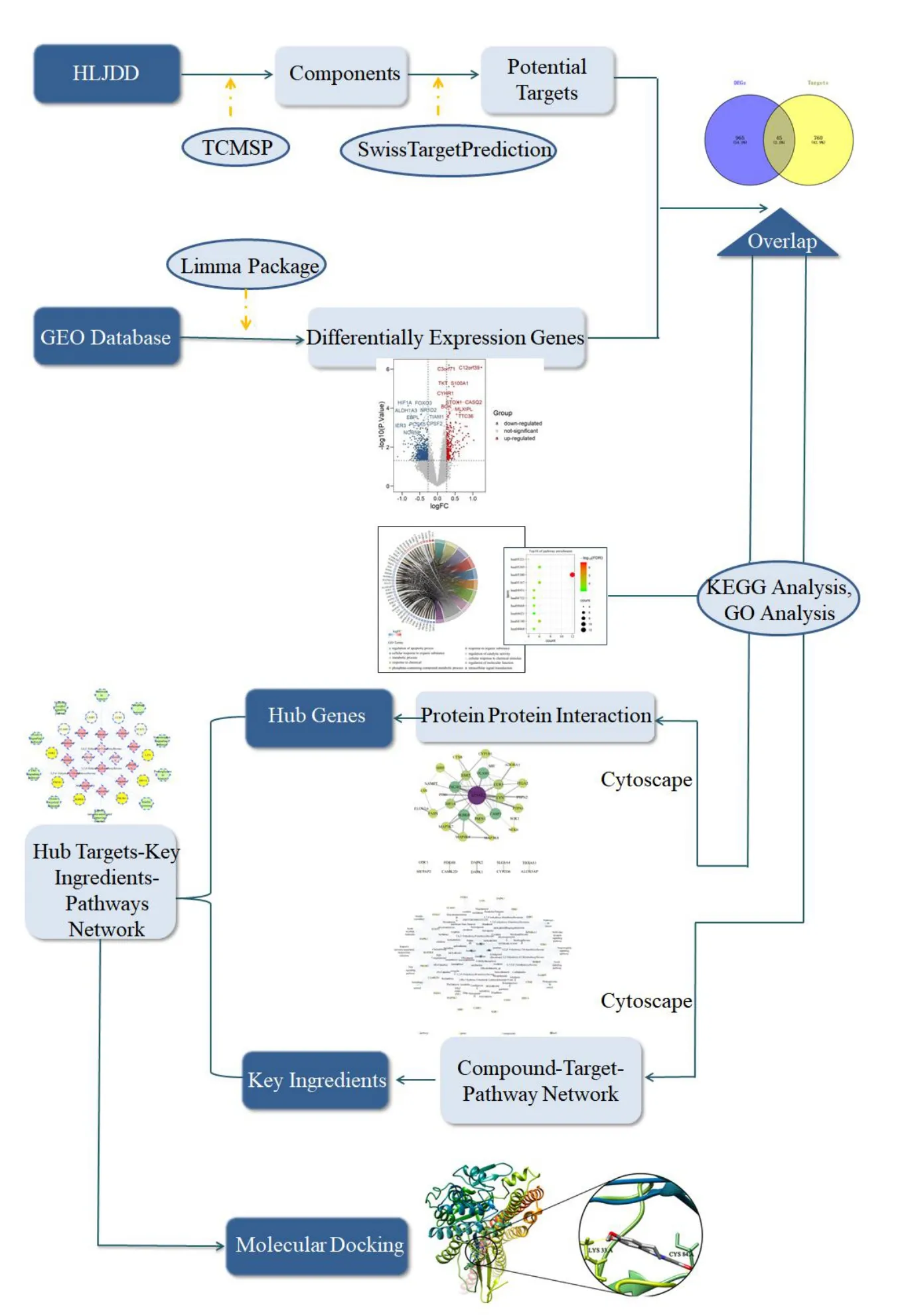
Figure 1 Framework of the present study.HLJDD,Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Decoction;TCMSP,Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology;GO,Gene Oncology;KEGG,Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
Methods
By retrieving the Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology(TCMSP)database and analysis platform,a free public platform designed for herbal medicines,which provides pharmacokinetic characteristics including oral bioavailability(OB)and drug likeness(DL),we obtained the chemical compounds of each herbal medicine in HLJDD[21].These two ADMET features were used to identify the candidate compounds[22].Here we set OB≥30%and DL≥0.18 as the criteria for screening the potential active compounds.
Afterward,those compounds were fed into the SwissTargetPrediction database(http://www.swisstargetprediction.ch/)to predict their interacting targets.As a freely accessible database,the SwissTargetPrediction is based on chemical similarities and pharmacophore models to perform target prediction for any bioactive small molecule[23].
Analysis of gene expression profiles
Affymetrix human gene expression array dataset(GSE78721),retrieved from the Gene Expression Omnibus(GEO)database[24],was based on the GPL15207 platform and contained 62 control and 68 diabetic samples.The data were of adipocytes and infiltration macrophages obtained from abdominal and peripheral adipose depots from normal glucose tolerant and type 2 diabetics Asian Indians[25].
To process and normalize the raw files to ensure comparability of gene expression datasets,robust multichip average(RMA)[26]in the affy package(https://www.bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/h tml/affy.html)was used.The linear models for microarray data(LIMMA)method was used to identify the differentially expressed genes(DEGs:P<0.05 and fold change>1.2)between the control group and the diabetic group[27].Additionally,the R platform(version 3.5.3,https://www.r-project.org/)was used to accomplish the statistical analysis in this study.
Gene Ontology(GO)annotation and pathway enrichment analysis
GO annotation and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes(KEGG)pathway analysis were performed using the STRING database(https://string-db.org/)to investigate the functions of the DEGs at the cellular level.Compared to other enrichment tools,STRING displays every functional pathway/term that can be associated with at least one protein in the network by making full use of the latest protein network information[28].It tests a number of functional annotation spaces including KEGG,GO,the protein families database,and the InterPro database.Furthermore,in the GO and KEGG analysis,theP-values are corrected for multiple testing using the method of Benjamini and Hochberg for controlling the false discovery rate(FDR).
Construction of network and identification of hub nodes
A protein-protein interaction(PPI)network was obtained using the STRING database(https://string.embl.de/)to clarify the interactions of all DEGs. On the other hand, the compound-target-pathway network(CTPNet)was also constructed and visualized by the Cytoscape software(version 3.7)(https://cytoscape.org)to understand the mechanism of HLJDD for the treatment of T2DM.
The key topological parameters that characterize the most influential nodes in a network are the average shortest path length,closeness centrality,and degree.In our study,the topological properties of nodes in the network were analyzed using the network analyzer plugin of Cytoscape to filter out the hub nodes.To reliably identify the key compounds and targets in HLJDD,the medians of the three topological parameters of all nodes were considered the principles for screening core nodes.
Molecular docking
Molecular docking was applied to predict the binding affinities of key components to hub targets and explore the binding modes.The structures of target proteins were downloaded from the RCSB Protein Data Bank database(PDB,https://www.rcsb.org/),while the structures of key compounds were obtained from the PubChem database(https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/).
The 3D structures of the compounds were constructed using the UCSF Chimera software(version 1.14)[29].Before docking,hydrogen atoms and charge were added by Dock Prep module in Chimera.The binding pocket of a protein is defined by its eutectic ligand,while the binding site of protein without ligand was predicted by POCASA based on an algorithm named Roll[30].AutoDock Vina[31]in Chimera was run to dock,and the value of the binding energy<-5.0 kcal/mol indicates a great binding activity[32].Besides,three antidiabetes drugs including glyburide,acarbose,and pioglitazone were also docked,the results of which were considered a positive control.
The eutectic ligand is docked into the protein from which it was extracted,namely,self-docking,to evaluate the accuracy and reliability of docking methods.The root-mean-square deviation(RMSD)is calculated by comparing the coordinates of the ligand,which is expected to be smaller than 2.0Å(Åmeans angstrom.One angstrom is equal to 0.1 nm.)and indicates the accuracy of the docking procedure[33].
Results
Compounds and targets in HLJDD
Out of the four individual herbs in HLJDD,95 compounds(with OB≥30% and DL≥0.18)were retrieved from the TCMSP database.After the removal of the duplicates,78 compounds were left,14 of which originated fromRhizoma Coptidis,29 fromRadix Scutellariae,21 fromCortex Phellodendri,and 14 fromFructus Gardeniae,respectively.By searching the SwissTargetPrediction database,7,604 potential targets interacting with the bioactive small molecules were predicted,of which 805 unique targets were left after deleting the duplicates.
DGEs in T2DM
By the analysis of gene expression profiles,the DEGs associated with diabetics were identified,and 1,010 genes met the screening criteria.All the genes were depicted by the volcano plot in Figure 2a,where the top 10 upregulated and top 10 downregulated genes were also shown.Moreover,the Venn diagram was bgdrawn to show the relationship between the HLJDD interacting genes and the DEGs.As can be seen from Figure 2b,45 identical genes were obtained,including 12 upregulated genes and 33 downregulated genes(see Table 1S in the supplementary materials).
GO annotation and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis
To investigate the functions of these genes,the above 45 DEGs were subject to the STRING database.As a website database,STRING provides functional annotation tools for identifying the enriched GO terms,including biological processes,cellular components,and the pathways associated with the genes.Figure 3 shows the top 10 GO enrichment analysis results with low FDRs.
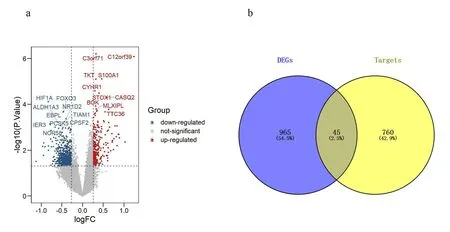
Figure 2 The volcano plot of 1,010 DEGs(a),and the Venn diagram of HLJDD interacting genes and DEGs(b).Top 10 up-regulated genes include C3orf71,C12orf39,S100A1,TKT,CYHR1,STOX1,CASQ2,BOK,MLXIPL,TTC36 and top 10 down-regulated genes are HIF1A,FOXO3,EBPL,NR1D2,TIAM1,ALDH1A3,IER3,PCSK5,NOP58,CPSF2.DEGs,differentially expressed genes;HLJDD,Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Decoction.
Based on the biological process analysis results,the 45 DEGs were primarily enriched in regulation of the apoptotic process,cellular response to chemical stimulus,regulation of molecular function,and metabolic process(Figure 3a).The results showed that the DEGs have strong associations with these biological processes,and HLJDD may have antidiabetic effect by modulating apoptotic process or metabolic process,which leads to the pathogenesis of T2DM.Based on the cellular component analysis,most of the DEGs were located in the cytoplasm part and cytoplasmic and endomembrane system such as endoplasmic reticulum(Figure 3b).Furthermore,the molecular function annotation indicated that the DEGs were mainly enriched in catalytic activity,protein serine/threonine kinase activity,protein kinase activity,phosphotransferase activity,and protein binding(Figure 3c).
Additionally,the significantly enriched pathways were identified in the KEGG pathway enrichment analysis.Figure 3d shows the top 10 enrichment pathways including insulin resistance,TNF signaling pathway,FoxO signaling pathway,and pathways in cancer.As listed in Table 1,these pathways were roughly divided into four categories,that is,metabolic disease,signal transduction,immune system,and cancer and others.
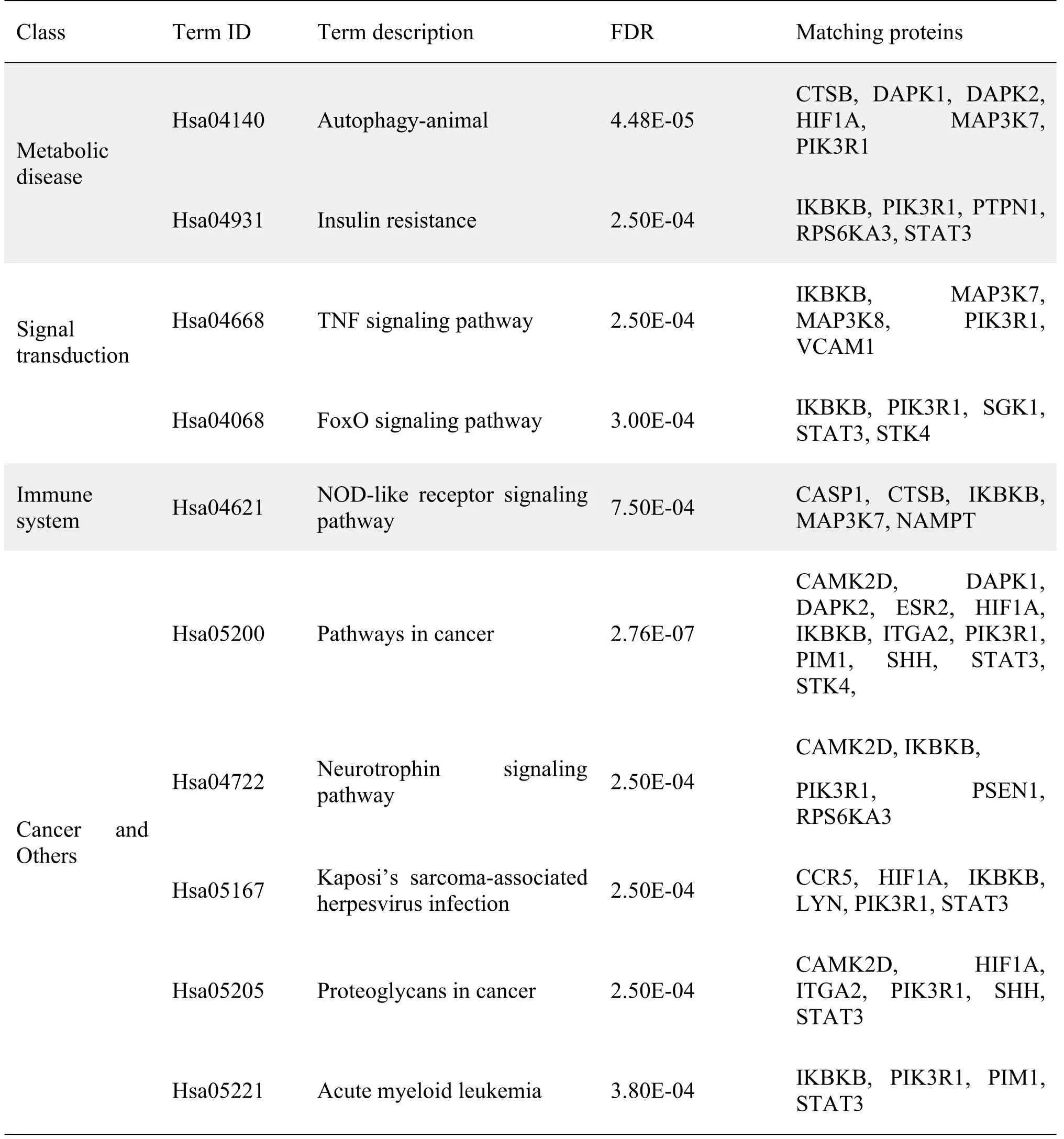
Table 1 Results of top 10 KEGG pathways
PPI network and CTPNet construction and analysis
By the STRING database,the PPI network was built using the 45 DEGs.It contained 53 interactions connecting 38 potential target genes related to HLJDD(Figure 4).Subsequently,10 hub genes with a degree value≥4 were identified,indicating that they might have similar molecular functions and be closely related to the mechanism of T2DM.The CTPNet of HLJDD was constructed to elucidate the relationship among the compounds,potential gene targets,and top 10 pathways.As shown in Figure 5,the CTPNet contained 108 nodes(4 herbs,70 candidate compounds,24 unique genes,and 10 pathways)and 849 edges.To filter out the key compounds,three topological parameters including the average shortest path length,closeness centrality,and degree were analyzed.As a result,15 key compounds were identified,whose parameters(closeness centrality and degree)were bigger than the medians,and the average shortest path length was shorter than the medians.These compounds are listed in Table 2,which were speculated to form the material base of HLJDD against T2DM.
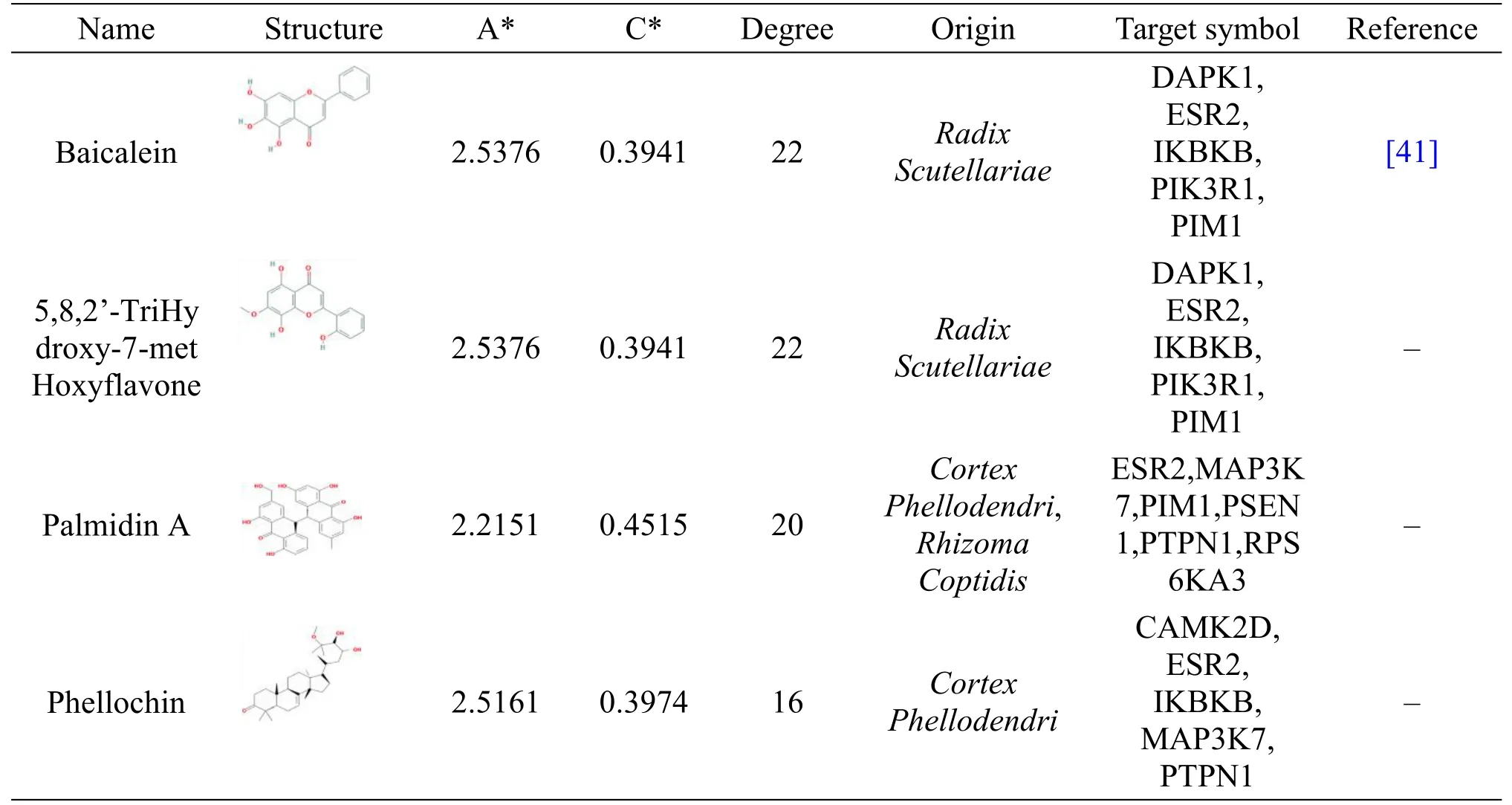
Table 2 Details of 15 key compounds and the literature evidences of them in relation to T2DM.(Continued)
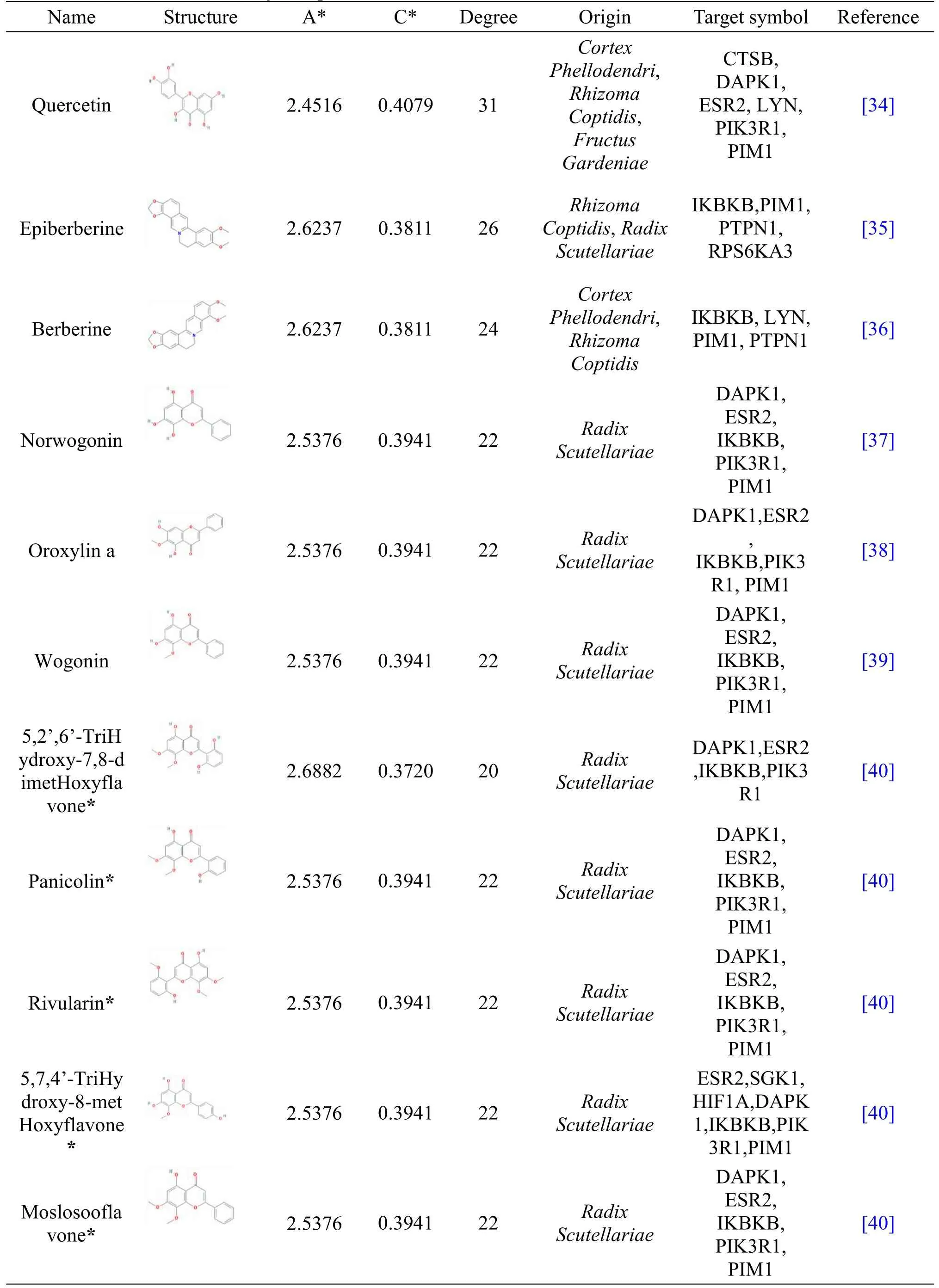
Table 2 Details of 15 key compounds and the literature evidences of them in relation to T2DM.
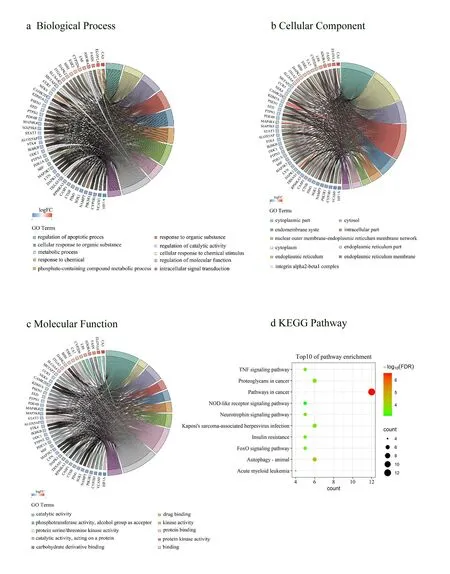
Figure 3 Top 10 function enrichment analysis results.The GO function enrichment analysis results(a,b,c),and logFC was the log value of fold change.And top 10 enrichment pathways(d).The color changes from green to red to indicate that the-log10(FDR)values change from low to high.The bubble size was decided by the number of enriched genes.FDR:false discovery rate.FC,fold change;GO,Gene Oncology;KEGG,Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
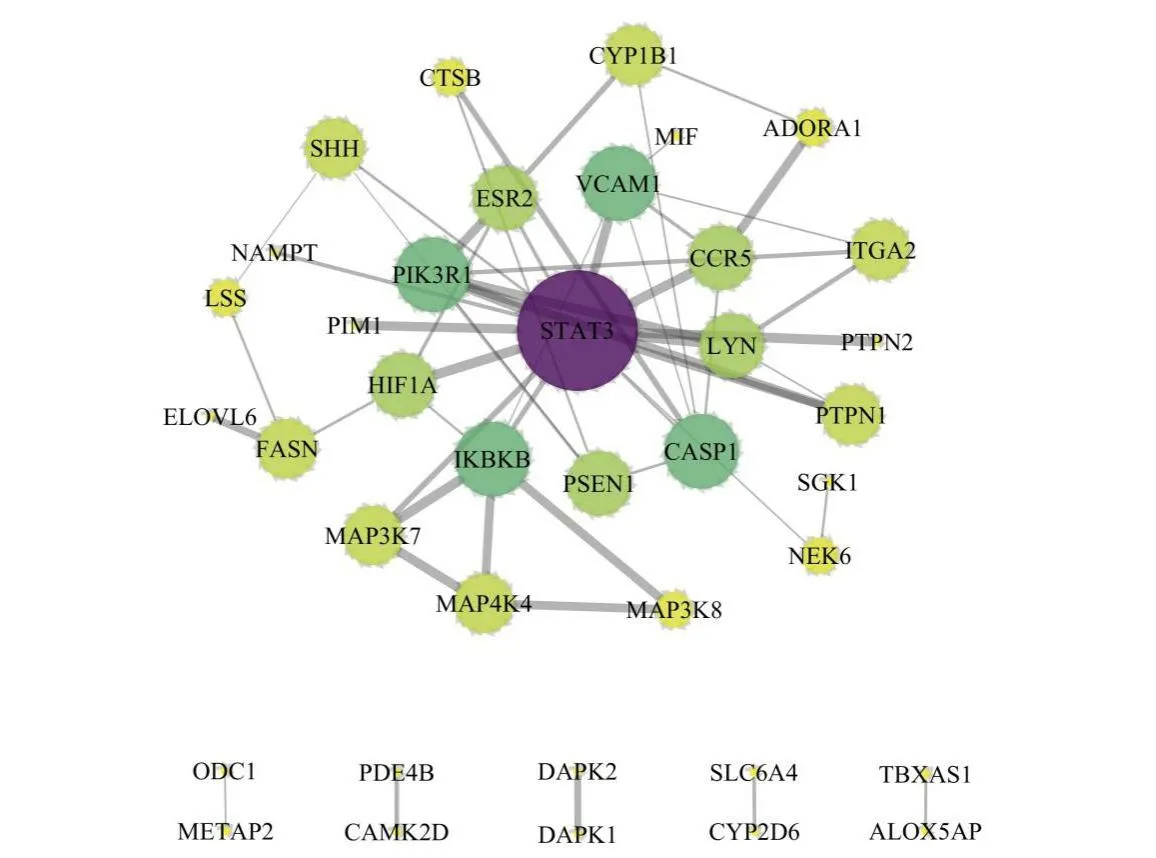
Figure 4 PPI network of the 45 DEGs.The nodes size is proportional to the degree(connectivity).The nodes color changes from light green to dark purple to indicate that the degree values change from low to high.The edge size represents the combined score from low to high.PPI,protein-protein interaction;DEGs,differentially expressed genes.
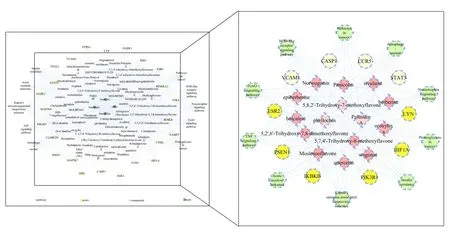
Figure 5 CTPNet of HLJDD on treating T2DM.Circle nodes represent target genes;diamond nodes,HLJDD compounds;quadrangle nodes,four herbs in HLJDD;hexagon nodes,signaling pathway.The dark red diamonds are the key compounds that have been verified for T2DM treatment,while the pink diamonds are not yet.The dark yellow circle nodes represent the hub genes that interact with key compounds,while the light yellow ones have no interactions with those key compounds.CTPNet,compound-target-pathway network;HLJDD,Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Decoction;T2DM,type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Results of molecular docking
The eutectic ligands were docked into the proteins and the RMSD values were calculated to evaluate the accuracy and reliability of the docking procedures.As shown in Table 3,the RMSD values were all<2.0Å,indicating that the docking methods were reliable and can be applied to the HLJDD compounds.The results are illustrated in Figure 6,where it can be clearly seen that all the 15 key HLJDD compounds showed good binding activities to the hub genes.Some of them even yielded the binding energies of far smaller than-5.0 kcal/mol.Particularly for the target of IκB kinase-β(IKBKB),11 out of 15 key compounds bound to it with energies of<-9.0 kcal/mol.The docking poses of some of them are shown in Figure 7.Meanwhile,compared to the three drugs,the 15 HLJDD compounds yielded comparable or better docking results,which confirmed that these compounds might serve as the material base of HLJDD against T2DM.
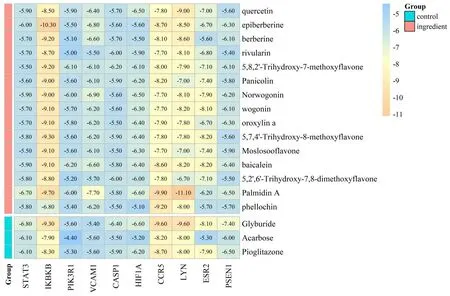
Figure 6 Binding energies of 15 key HLJDD compounds and three drugs to 10 hub genes.HLJDD,Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Decoction;T2DM,type 2 diabetes mellitus.
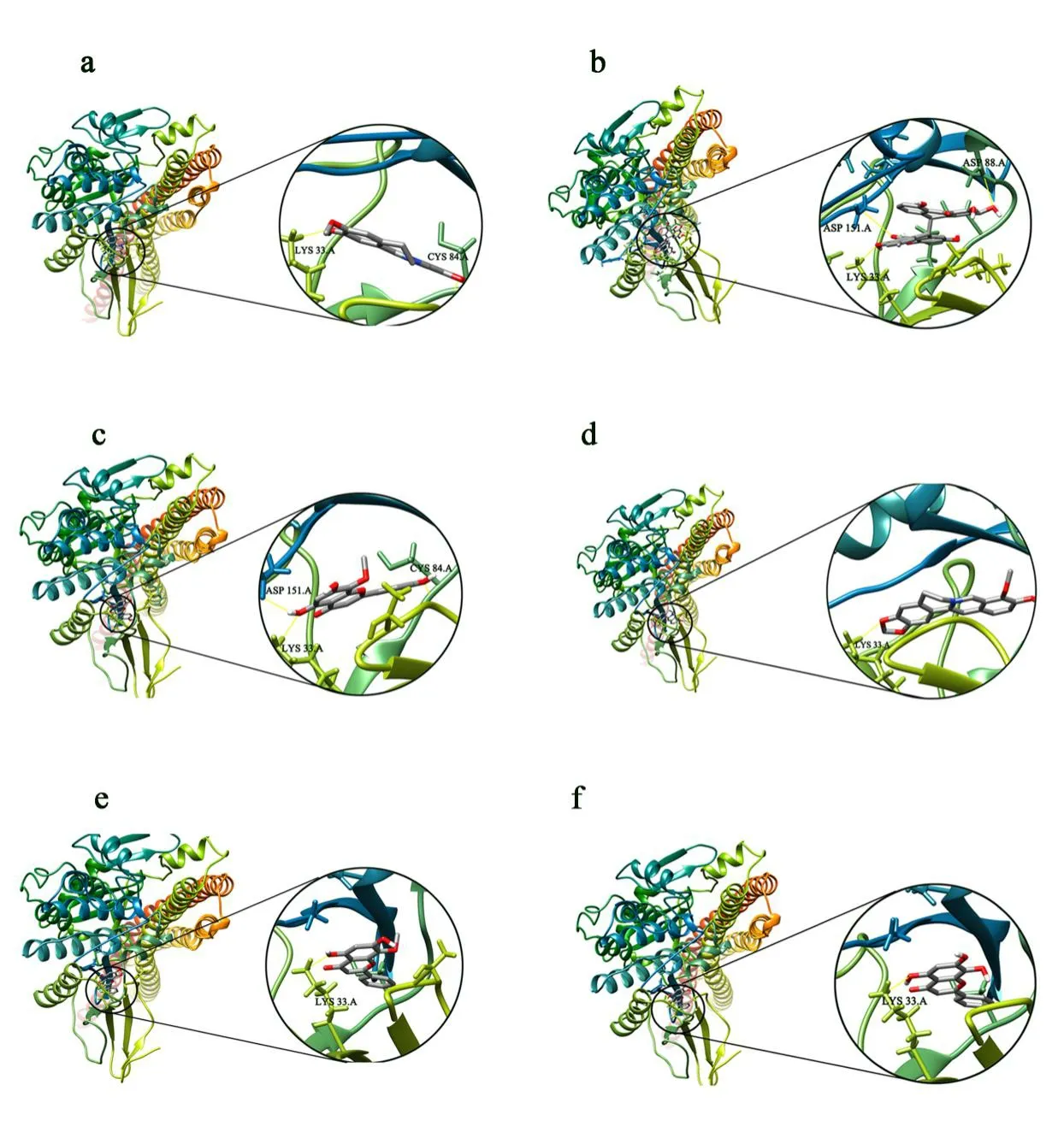
Figure 7 Detailed docking poses.The yellow line represents hydrogen bonding.a,IKBKB-epibererine;b,IKBKB-palmidin A;c,IKBKB-5,7,4’-Trihydroxy-8-methoxyflavone;d,IKBKB-berberine;e,IKBKB-wogonin;f,IKBKB-norwogonin.IKBKB,IκB kinase-β.
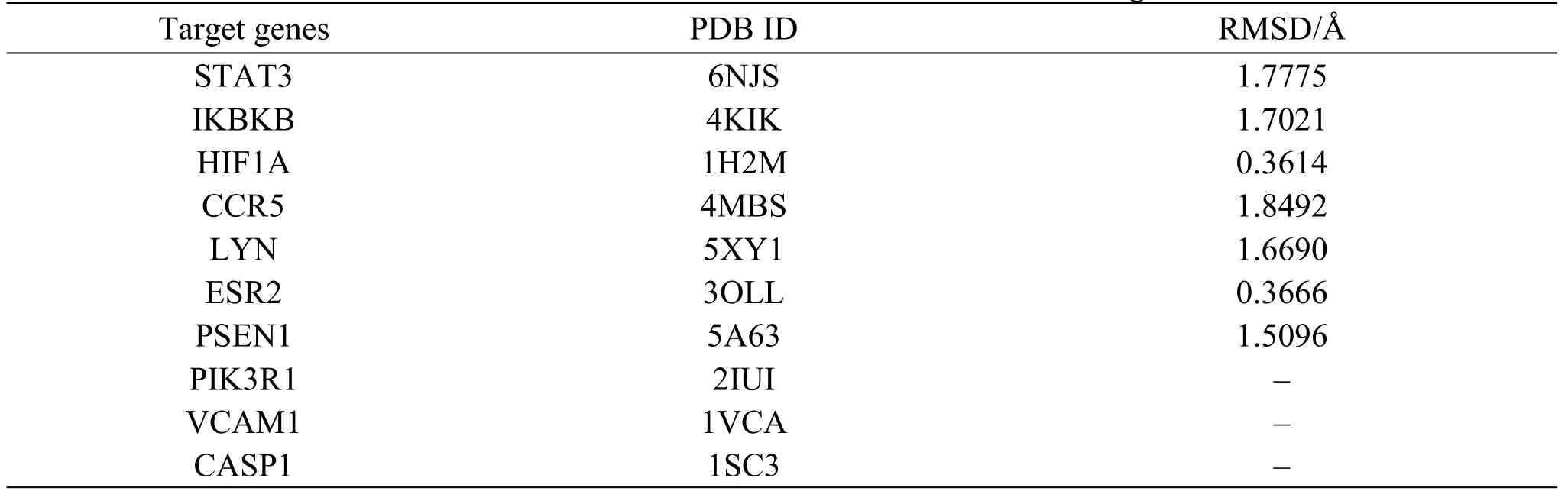
Table 3 Results of RMSD values in the self docking
Discussion
At present,the incidence of T2DM is increasing year by year.According to the statistics,2.5%-15% of medical expenses in many countries are caused by T2DM.For this reason,exploring the hub genes and pathways associated with T2DM is crucial for the diagnosis and treatment of patients with T2DM[42].Given the potential and influence of TCM prescriptions for the treatment of complex diseases,we investigated the link between HLJDD and T2DM.
Pathway analysis
As listed in Table 1,the top 10 enriched pathways were ranked by FDRvalues,which can be roughly divided into four categories.The first was metabolic disease-related pathways,including insulin resistance and autophagy-animal.The second was signal transduction related pathways,including the TNF signaling pathway and FoxO signaling pathway.The third was the immune system-related pathway,including NOD-like receptor signaling pathway.The last was cancer and others,including pathways in cancer,neurotrophin signaling pathway,Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection,proteoglycans in cancer,and acute myeloid leukemia.
Among these pathways,most of them are associated with the development of T2DM.For instance,the relation between insulin resistance and T2DM has been well evidenced for many years.Insulin action involves a series of signaling cascades.The insulin receptor is dephosphorylated and inactivated by protein tyrosine phosphatases,such as tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 1(PTPN1).The phosphorylation of insulin receptors leads to activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase(PI3K),subsequently to recruit signaling proteins including Akt and its downstream mediators.All of them are critical steps for stimulating glucose transport induced by insulin[43,44].Autophagy-animal is a known pathway to influence transport and catabolism,and regulation of autophagy was found to improve hepatic glucose and lipid metabolism in diabetic rats[45].
In the case of FoxO signaling,the binding of insulin-like growth factor I(IGF-1)to its receptor called insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor(IGFIR)triggers the activation of several kinases,including PI3K.The subsequent activation of Akt,IKK inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit alpha/beta(IKKα/ẞ),and serine/threonine-protein kinase(SGK)facilitates the phosphorylation by the kinase pyruvate dehydrogenase acetyl-transferring kinase isozyme 1/2(PDK1/2).Then,the activation of PI3K/Akt responded to insulin,which leads to the phosphorylation of FOXO1 by Akt,which is implicated in the regulation of target genes involved in metabolism,such as gluconeogenesis[46].It is commonly agreed that insulin signaling can repress lipolysis.Moreover,several studies have suggested that FOXOs were important regulators in the metabolism of adipocytes.Notably,the inhibition of FOXO1 activity contributes to alleviating insulin resistance and treating T2DM.Furthermore,IKBKB is the critical kinase for the phosphorylation of FOXO3[47].The TNF signaling pathway is linked to the insulin resistance pathway[17],and the ability of TNF-α to induce insulin resistance was reported[48].
As for the NOD-like receptor signaling pathway,Luo Lin et al.[49]reported that the specific DEGs of diabetic peripheral neuropathy were enriched in the NOD-like receptor signaling pathway.NLRP3,a member of the NOD-like receptor family,was found to have increased expression in macrophages from type 2 diabetic patients[50].Additionally,the activation of NLRP3 was linked to the enhancement of interleukin-1 beta(IL-1β),which is a risk factor for T2DM[51].
In the fourth category,several cancer-related pathways were also significantly enriched.Xu et al.[52]explored the mechanism of Sanhuang Xiexin decoction for T2DM based on network pharmacology and also reported the association between T2DM and cancer.An umbrella review of meta-analyses[53]reported that patients with T2DM have increased incidence of cancer,and treatment with metformin for T2DM leads to a reduced risk of cancer[54].Giovannucci et al.speculated that the shared risk factors such as aging,obesity,and diet may in part lead to the association between T2DM and cancer[55].Neurotrophin signaling was also found to be required for insulin secretion.Elevated glucose increased nerve growth factor(NGF)secretion and stimulated neurotrophic receptor tyrosine kinase 1(TrkA)phosphorylation in islets[56].Subsequently,through tyrosine kinase receptors,neurotrophins activated its downstream modulators such as Ras,PI3K,and signaling pathways which were mediated by these proteins,including the MAP kinases signaling[57].It was reported that patients with T2DM had a higher risk of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection[58]and that the high-glucose microenvironment had a positive effect on Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection[59].
Key compounds in HLJDD and T2DM
Four elements,namely,“monarch,minister,assistant,and guide”,are the basic principles for individual therapy in TCM.In HLJDD,Rhizoma Coptidisrepresents the“monarch herb”,Cortex Phellodendriserves as“minister herb”,Radix ScutellariaeandFructus Gardeniaeare usually regarded as“adjuvant”and“guide”herbs.As shown in Table 2,there were 4,4,11,1 key compounds that were identified in“monarch herb”,“minister herb”,“adjuvant herb”,and“guide herb”,respectively.
TakingRhizoma Coptidisas an example,one can see four key compounds,for example,quercetin,epiberberine,berberine,and Palmidin A in Table 2.It is generally accepted that obesity is a disease that increases the risk of T2DM.The two alkaloids of berberine and epiberberine were reported to provide a possible approach for the treatment of obesity and obesity-related disease by inhibiting adipocyte differentiation through a C/EBP-α- and PPAR-γ-mediated mechanism[60].Moreover,it was found that epiberberine was more active than berberine[61].Meanwhile,berberine was reported as a promising therapy in T2DM for its effect in lowering blood glucose,which was evidenced in the treatment of human diabetes and diabetic rat models[36].Another study revealed that berberine could increase insulin sensitivity by inhibiting mitochondrial respiration[62].Additionally,quercetin,as a flavonoid compound,was shown to effectively improve diabetic complications mainly by reducing the inflammation and improving the antioxidant capacity[63].What is more,compared to treatment with sitagliptin alone,treatment with a combination of quercetin and sitagliptin was found to more efficiently reduce the serum levels of glucose in diabetic rat models[64].
By the molecular docking,15 key compounds were confirmed to be able to bind well to the hub targets,where the binding energies were all<-5.0 kcal/mol and were comparable or even better than those of the three antidiabetes drugs.Particularly for the IKBKB,one hub gene at the core of PPI and CTPNet network,the binding energies were even<-9.0 kcal/mol.IKBKB was found to be involved in the etiology of T2DM[65],and it was reported that IKBKB deletion reduced the expression of inflammatory cytokines that caused insulin resistance[66].
Conclusion
As shown in Figure 5,those 15 chemical constituents may play crucial roles against diabetes,12 of which(represented by dark red)have been reported with experimental evidence suggesting their therapeutic effects on diabetes.Those compounds interacted with hub targets,such as IKBKB,phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit alpha(PIK3R1),presenilin-1(PSEN1),estrogen receptor beta(ESR2),and HIF1A.The molecular docking results confirmed the binding affinities.The mediated pathways included insulin resistance and FoxO signaling pathway.
Although the present results are found to be consistent with some reports,indicating the rationality and accuracy of our method,there are still some limitations.For example,the HLJDD compounds were retrieved only from the TCMSP database.In the future,more compounds and their metabolites may be expanded by searching other TCM databases,such as the TCM Database@Taiwan(http://tcm.cmu.edu.tw)and HIT(http://lifecenter.sgst.cn/hit/),or directly detected by modern instrumental analysis methods,such as high performance liquid chromatography,ultra-performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry,and gas chromatography mass spectrometry.Of course,in vitro and in vivo tests are also needed to confirm the potential targets and pathways.
杂志排行
Traditional Medicine Research的其它文章
- Phytochemical composition,therapeutical and pharmacological potential of Nigella sativa:a review
- Network analysis and molecular docking of the mechanism of Shengmai decoction in treating patients with severe novel coronavirus pneumonia
- Study on possible synergistic anticancer cachexia effects of the main active compounds of Radix Sophorae flavescentis
- Traditional Chinese medicine of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge:a review of phytochemistry,pharmacology and pharmacokinetics
- System pharmacology-based dissection of the potential effective material basis and mechanism of Xiaoxianxiong decoction for type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Pharmacological research progress of ursolic acid for the treatment of liver diseases
