Systemic evaluation and Meta analysis on clinical efficacy of Jinhuang Powder for treatment of acute mastitis
2021-07-01PuZhangShuoZhangZhenlinChenWenjingMaTiantianGaoLuWang
Pu Zhang, Shuo Zhang, Zhen-lin Chen*, Wen-jing Ma, Tian-tian Gao, Lu Wang
1 Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xianyang 712046, Shaanxi Province, China
2 Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
Funding: National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81974584)
Abstract Objective: To systematically evaluate the efficacy of Jinhuang Powder in the treatment of acute mastitis. Methods: Literature published in Chinese and English on the treatment of acute mastitis with external use of Jinhuang Powder were retrieved from the construction of databases until November 25, 2020 in Chinese Journal CNKI, Wanfang, VIP, PubMed and Web of Science. The literature containing the included trials were screened and the related data were extracted in the Note Express 3.2.0, and Cochrane collaboration tools were used to assess the risk of bias in the trials and Rev Man 5.3 was used to evaluate the efficacy. Results: Finally 6 documents were included, involving 504 patients with acute mastitis. Meta analysis showed that, the clinical efficacy of Jinhuang Powder alone or combined with antibiotics in the treatment of acute mastitis was 1.16 times [RR=1.16, 95% CI [0.98, 1.38], Z=1.68, P=0.09] and 1.19 times [RR=1.19, 95% CI [1.10, 1.30],Z=4.13, P < 0.0001] than that of antibiotics alone, respectively. The clinical efficacy of Jinhuang Powder combined with Mirabilite (Glauber salt) on acute mastitis was 1.10 times than that of Mirabilite (Glauber salt) alone [RR=1.10, 95% CI [0.94, 1.29], Z=1.18, P=0.24]. Jinhuang Powder can not only improve the clinical efficacy in treatment of acute mastitis, but also shorten the time of pain relief, redness and swelling dissipation, as well as body temperature drop. Conclusion: The external use of Jinhuang Powder can improve the clinical efficacy of acute mastitis, shorten the time of pain relief, redness and swelling dissipation, as well as body temperature drop. Because of the limited sample size collected in some randomized controlled trials and the low methodological quality, more high-quality randomized controlled trials with reasonable design are need in future to provide stronger support.
Key words: Jinhuang Powder; Acute mastitis; Randomized controlled trial; Systems assessment; Meta analysis
Introduction
Acute mastitis is an acute suppurative disease occurring in the breast[1], which mostly occurs in lactating women who have initial childbirth, usually in 3-4 weeks after delivery, it is a common and frequent disease of the breast during lactation. Studies have shown that 33% of breastfeeding women have ever suffered from acute mastitis,and the prevalence rate in some areas is even up to 50%[2].The main clinical manifestations are fever, breast lump,pain, local skin redness, breast-feeding disorders and other symptoms[3], which belongs to the category of “acute mastitis” in the field of traditional Chinese medicine.According to the theory of traditional Chinese medicine,the external cause of this disease includes nipple breakage and rhagades during lactation, leading to wind-toxicity invading breast collaterals; the internal cause of this disease includes the intermingling of liver depression and stomach heat, leading to the obstruction of breast collaterals, the accumulation of breast milk and the stasis of Qi and blood for a long time, which transform into heat and produce toxins[4]. The treatments are divided into external treatment and internal treatment,the external treatment includes breast massage, external application of Chinese medicine for clearing heat and dispersing stagnation, acupuncture and other methods;the internal treatment follows the principle of dispersing the depressed liver-energy and clearing heat[16], and detumescence and eliminating stagnation, and selects Gualou Niubang Decoction with modifications. Modern medicine believes that the occurrence of acute mastitis is mostly related to bacterial infection caused by breast milk deposition or breast trauma, and the main pathogenic bacteria are Staphylococcus aureus[5]. The treatment mainly aims to stop breast-feeding, empty breast milk,and anti-infection. In recent years, it has been found that Jinhuang Powder has a definite effect on early acute mastitis, which can reduce the effect of antibiotics on breast milk and restore lactation as soon as possible[6].Ruyi Jinhuang Powder derives from
Clinical Data and Methods
Literature search
A randomized controlled trial using Jinhuang Powder for the treatment of acute mastitis was retrieved from 8 electronic databases from construction of the database to November 25, 2020. The databases included: CNKI,Wanfang, VIP, SinoMed, PubMed, Cochrane Library,Elservier, and Web of Science. The search terms in Chinese database was “Jinhuang Powder” or “Ruyi Jinhuang Powder” AND “acute mastitis” or “mastitis” or“breast carbuncle”. According to the characteristics of each database, the theme/abstract/full text retrieval method was adopted. The search terms in English database was“Jinhuang Powder” “Ruyijinhuang Powder” “Jinhuang San”“Ruyijinhuang San” “jin huang san”) AND (“mastadenitis”“mastitis” “mammitis” “acute mastitis”). Finally six randomized controlled trials[10-15]were included, involving 504 patients with acute mastitis, systematic review and Meta analysis were used to evaluate the clinical efficacy of Jinhuang Powder in treating acute mastitis. Methods of treatment in the included trials included Jinhuang Powder vs. antibiotics, Jinhuang Powder and antibiotics vs.antibiotics, and Jinhuang Powder combined with glauber salt vs. glauber salt. Meta analysis showed that both Jinhuang Powder alone and combined with other therapies can significantly improve the clinical efficacy of acute mastitis.
Criteria for literature
Inclusion criteria
(1) Design type of literature was a randomized controlled trial published in professional journals in China and abroad, and the number of cases included in the literature was >10 cases; (2) The balance between groups was good,both the experiment group and control group had a clear course of treatment; (3) The subjects were a patient with“mastitis”, “acute mastitis” or “breast carbuncle” diagnosed by the clinicians according to the symptoms and signs of the patient combined with B ultrasound, molybdenum target, infrared ray and other auxiliary examinations;The course of disease was 3-7 days, regardless of age and race; (4) Intervention measures in the experiment group included external application of Jinhuang Powder, while other treatment methods were adopted in the control group; (5) There were definite criteria for evaluating the efficacy.
Exclusion criteria
(1) No control group was set in the original literature; (2)Animal experiments; (3) Theoretical and comprehensive literature; (4) Trials with non-rigorous design or unreasonable statistical method; (5) Trials in which effective analytical data were not available; (6) Repeated published literature.
Intervention measures
The treatment method of the experimental group was Jinhuang Powder alone or combined with the treatment of the control group, and the treatment method of the control group was other therapies, including glauber salt external application and intravenous antibiotics.
Outcome measures
The primary outcome measures were clinical efficacy,while secondary outcome measures included the time of redness and swelling dissipation, pain relief, and body temperature drop.
Literature screening and data extraction
After the retrieval, two researchers independently screened the literature according to the commonly established criteria for the inclusion and exclusion, read the title and abstract, removed the documents that obviously did not meet the criteria, downloaded and read the full text of the literature that initially met the criteria, determined whether the literature can be included in the trials,and then extracted the literature information. Both the screening and extraction process of the literature were carried out in the Note Express 3.2.0 and followed the principle of cross-discussion check. Any difference should be discussed, and if they cannot reach an agreement, a third party’s opinion is inquired. The data extraction table mainly included: the basic information of the study (author name, research topic, year of publication, country/region),the characteristics of the study (sample size, case source,age, diagnostic criteria, inclusion criteria and exclusion criteria), evaluation index for quality of literature (random sequence generation, allocation concealment, blind method, incomplete outcome data, selective reporting,other bias, loss of follow-up), and the measurement data of outcome measures. The assessment indicators in this study included clinical efficacy, time of redness and swelling dissipation, pain relief, and body temperature drop.
Evaluation of literature quality
Methodological quality of each included trial was assessed using the Cochrane Collaboration tool[8,25]. The evaluation criteria of literature quality bias risk included seven respects: random sequence generation method, allocation concealment, blind method, incomplete outcome data,selective reporting and other bias. The quality evaluation results of each item can be divided into three grades: “low risk”, “high risk” and “unclear risk”. The more rigorous design of each trial and the higher quality of the method were associated with the lower risk coefficient. In the process of evaluating the risk of literature quality bias, if two researchers had different opinions, they will agree through discussion or be evaluated by a third party.
Statistical analysis
Rev Man 5.3 software was used for Meta analysis of the included literature. Relative risk (RR) and 95% confidence interval (95% CI) were used as efficacy statistics for dichotomous variables. The continuous variables were the mean difference (MD) and 95% confidence interval (95% CI). According to the I2 test results, the heterogeneity of the test was determined, a level of I2 <50% indicated low heterogeneity among tests, and fixed effect model was adopted. In addition, when I2 > 50%,random effect model[9]was adopted. The literature was analyzed in subgroups according to the presence/absence of other treatments used in the experiment group and the difference between other treatments. The potential publication bias was analyzed using an inverted funnel plot (α=0.05).
Results
Retrieval results
According to the retrieval strategy, 181 documents were retrieved in 8 electronic databases, after deletion of duplicate documents, 105 literature were remained.According to the inclusion and exclusion criteria, 70 literature were deleted by reading the title and abstract,and 29 literature that did not conform to the inclusion and exclusion criteria were deleted after further reading the full text, eventually 6 randomized controlled trials[10-15]were included. Literature retrieval flow chart was shown in Figure 1.
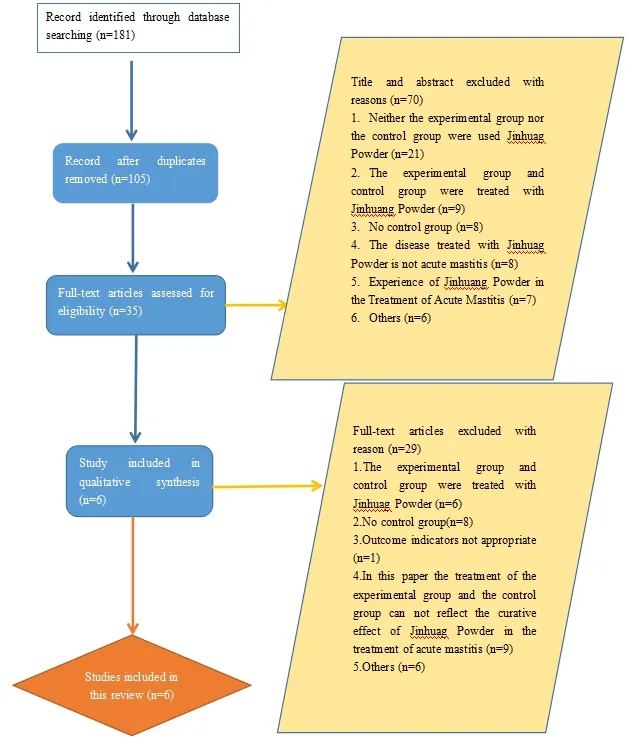
Figure 1 Literature retrieval flow chart
Basic features of the included literature
Table 1 summarized the basic characteristics of the included 6 trials[10-15], all of which were conducted in China. A total of 504 patients with acute mastitis were involved in the included trials, the sample size ranged from 23 to 80 samples, and the course of treatment was 5-7 days. Four[10,11,12,15]trials were conducted using Jinhuang Powder combined with antibiotics vs. antibiotics, while one[14]trial using Jinhuang Powder vs. antibiotics, one[13]trial using Jinhuang Powder combined with Glauber salt vs. Glauber salt. All trials[10-15]reported clinical efficacy,with three trials[10,11,12]reporting pain relief time, two trials[10,11]reporting body temperature drop time, and two trials[11,12]reporting the time of redness and swelling dissipation.
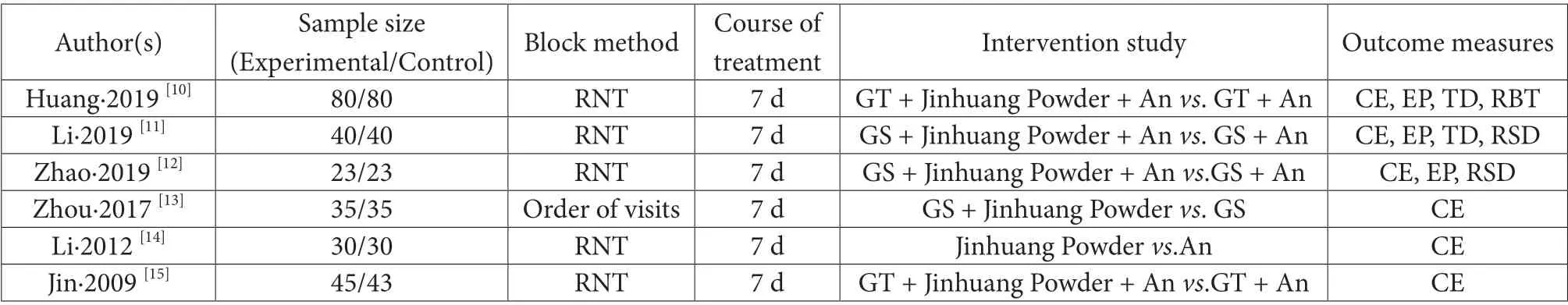
Table 1 Literature features included in the randomized controlled trials of external application of Jinhuang Powder for treatment of acute mastitis
Results of risk bias of included literature
In six literatures[10-15], five papers[10,11,12,14,15]were grouped according to the random number table, in which the risk of bias was judged as low risk, and one paper[13]was randomly divided into groups according to the order of visits, the risk of bias was high. All documents did not describe the allocation concealment and blind method,and the risk of bias was judged as unclear. There were no drop-out cases, no intention-to-treat analysis, no description of follow-up and side effects in all literatures,therefore, its bias risk was low. Taking the RR values of six papers[10-15]as the abscissa and the SE (log [RR]) as the ordinate, a funnel plot was drawn. The distribution map showed that the literature samples were roughly distributed around the total effect and symmetrically arranged around the center line, a small part was tilted,which indicated that the included literatures had a low bias (Figure 2). The percentage results for each bias risk of the included trial were shown in Figure 3. The results of methodological quality assessment of the included study were shown in Figure 4. In the figures, red, green, and yellow represented the high risk, low risk and unclear risk of bias, respectively.

Figure 2 Inverted funnel plot of clinical efficacy in the included trial
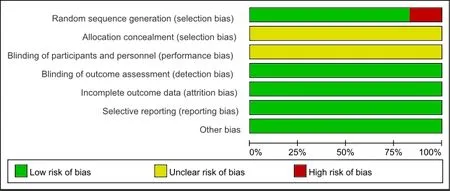
Figure 3 Results of percentage risk of bias for each of the included trials
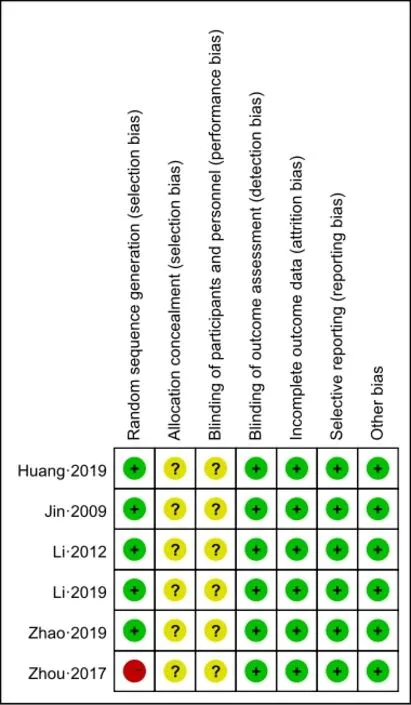
Figure 4 Results of methodological quality assessment for all included trials
Research results
Clinical efficacy
The clinical efficacy was reported in all trials[10-15], and the heterogeneity between literatures was low, so the fixed effect model was used (P=0.97, I2=0%) [RR=1.17,95% CI [1.10, 1.26], Z=4.59,P< 0.00001], the results showed that Jinhuang Powder alone or in combination with other therapies could significantly improve the clinical efficacy of acute mastitis, and the difference was statistically significant. The six trials[10-15]were classified into subgroups according to their different intervention measures, among them there are four trials[10,11,12,15]studied Jinhuang Powder combined with antibiotics vs. antibiotics in the treatment of acute mastitis, the heterogeneity among literatures was low, hence fixed effect model was adopted (P=0.98, I2=0%) [RR=1.19, 95% CI[1.10, 1.30], Z=4.13,P< 0.0001]. Meta analysis showed that the clinical efficacy of Jinhuang Powder combined with antibiotics in the treatment of acute mastitis was 1.10 times than that of antibiotics alone, with statistically significant difference. However, compared with the use of Glauber salt alone[13], the clinical efficacy of combined with Jinhuang Powder in the treatment of acute mastitis did not show obvious advantages [RR=1.10, 95% CI [0.94,1.29], Z=1.18,P=0.24][14]. Compared with intravenous antibiotics[14], the clinical efficacy of external application of Jinhuang Powder in the treatment of acute mastitis also did not show obvious advantages [RR=1.16, 95% CI [0.98,1.38], Z=1.68,P=0.09], as shown in Figure 5.

Figure 5 Comparison of clinical efficacy of Jinhuang Powder combined with other therapies vs. other therapies in treatment of acute mastitis
Pain relief time
Three trials[10-12]reported pain relief time before and after treatment. Meta analysis results showed that, antibiotics combined with Jinhuang Powder could significantly reduce pain relief time in patients with acute mastitis compared with antibiotic therapy alone, and the heterogeneity between literatures was low (P=0.29 > 0.05, I2=19%), and the fixed effect model was adopted [MD=-2.50, 95% CI[-2.80, -2.20], Z=16.48,P<0.00001], as shown in Figure 6.
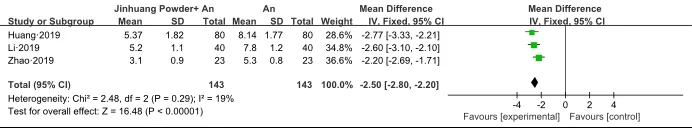
Figure 6 Comparison of pain relief time of study subjects
Redness and swelling dissipation time
Two trials[11,12]reported the time of redness and swelling dissipation before and after treatment. Meta analysis results showed that, Jinhuang Powder combined with antibiotics could improve the redness and swelling symptoms in a shorter time than the use of antibiotics alone [MD=-2.34,95% CI [-2.80, -1.88], Z=10.04,P<0.00001], as shown in Figure 7.

Figure 7 Comparison of redness and swelling dissipation time of study subjects
Body temperature drop time
Two trials[10,11]reported the time of body temperature drop before and after treatment. Meta analysis results showed that, Jinhuang Powder combined with antibiotics was better than antibiotics alone on reducing body temperature in the treatment of acute mastitis [MD=-2.53,95% CI [-2.92, -2.14], Z=12.71,P<0.00001], as shown in Figure 8.

Figure 8 Comparison of body temperature drop time of study subjects
Discussion
Six randomized controlled trials[10-15]involving 504 patients with acute mastitis are finally included in this study, the treatment methods of the included trials consist of Jinhuang Powder vs. antibiotics, Jinhuang Powder combined with antibiotics vs. antibiotics, and Jinhuang Powder combined with Glauber salt vs. Glauber salt. Meta analysis shows that Jinhuang Powder alone or combined with other therapies can significantly improve the clinical efficacy of acute mastitis. In the subgroup analysis, two trials use Jinhuang Powder vs. antibiotics and Jinhuang Powder combined with Glauber salt vs. Glauber salt.Meta analysis results of these two subgroups show that,the treatment methods of the experimental group and the control group have no significant difference in the clinical efficacy of acute mastitis. The reasons may be: (1) Only one document is included in the two subgroups, which lacks the support from a great quantity of clinical sample data;(2) Glauber salt for local use has the effect of clearing heatfire and detumescence. Modern pharmacological studies have proven that external use of Glauber salt can eliminate swelling, and external application of Jinhuang Powder can inhibit inflammation, produce bacteriostasis and analgesia effects. Therefore, compared with external use of Glauber salt alone, the combined treatment can reduce swelling,inhibit inflammation, produce bacteriostasis and analgesia effect in treatment of acute mastitis, but this conclusion still needs a support from more clinical sample data; (3) A meta analysis of Jinhuang Powder vs. antibiotics in treating acute mastitis shows that, there is no significant difference in the clinical efficacy of Jinhuang Powder and antibiotics in treating acute mastitis. The combination of the two treatments for acute mastitis produces a more significant effect than single treatment.
Zhou Cong-he[19]has performed in vitro culture experiments and found that Jinhuang Powder has certain inhibitory effects on common pathogenic bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa,and could effectively regulate the expression and release of inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α and IFN-α when inflammatory response occurs, so as to control the development of inflammation and inhibit the infection of subcutaneous soft tissue. Wang Xi-yun et al[20,21]have demonstrated that Jinhuang Ointment can obviously increase the content of lysozyme in purulent secretion and serum, thus improve the body’s defense ability. Therefore,the anti-inflammatory, bacteriostatic and analgesic effects of Jinhuang Powder have been confirmed by modern pharmacological studies. In the treatment of acute mastitis,it can not only improve the curative effect, but also shorten the cure time[7].
Acute mastitis often occurs in lactating women, which seriously affects the lactation and quality of life of patients. Therefore, we should not only pay attention to the treatment of acute mastitis, but also emphasize on the prevention. Methods to avoid acute mastitis include:(1) Early lactation: After delivery, the suckling of infants can increase the secretion of prolactin, promote milk production and secretion, and colostrum is rich in immunoglobulin, can provide immunity for newborns;(2) Breast-feeding breast hygiene: during suckling period,nipples should be cleaned using warm water or soapy water to keep the opening of the lactiferous duct; (3)To prevent galactostasis: the milk stasis site is kneaded,squeezed, pushed and repeatedly massaged using the hand palm in the direction from external site to the nipples, and also the breast milk can be aspirated with the aid of breast pump; (4) Correction of nipple deformity: for the nipple retraction, the nipples should be often repeatedly pulled and squeezed in the early pregnancy to lift the retracted nipples; (5) Develop good lactation habits: regular lactation, feeding on alternating nipples, suck the milk as much as possible; when too much milk cannot be sucked out, massaging the breast is performed to squeeze out the milk or suck out with a sucker; (6) Taking light and nutrient diet, prohibiting raw, cold, spicy and greasy food.Keeping in a good mood, avoiding mental tension, actively cooperating with treatment[22].Limitations of this study: (1) Most of the included literatures are small-sample single-center studies, and more large-sample, multi-center randomized controlled trials are needed; (2) Different diagnostic criteria,exclusion criteria, and definitions of treatment effect are used in the included literature, which will increase the heterogeneity; (3) Some included literatures fail to describe the randomization method and blind method in detail, and the methodological quality is fair; (4) The included literature is only published papers, excluding gray literature, which may cause literature selection bias.To sum up, external application of Jinhuang Powder has significant advantages in the treatment of acute mastitis,which can not only improve the clinical efficacy, but also reduce the time of pain relief, redness and swelling dissipation and body temperature drop. It is recommended that patients who have a poor efficacy using antibiotics alone can received the combined treatment using external Jinhuang Powder. Combined with the results and limitations of this study, it is suggested that future clinical studies should pay attention to the design of the study protocol, for multi-center, randomized, prospective,large-sample studies with more rigorous design, and the control of bias risk factors should be strengthened during implementation, randomized controlled trials should be written in strict accordance with the
杂志排行
Global Traditional Chinese Medicine的其它文章
- Exploration on YE Tianshi’s thinking of medication in the treatment of metrorrhagia and metrostaxis based on data mining
- A systematic review and meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of Coix Seed Decoction in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
- Analysis of the medication for impotence based on data mining
- Etiology, pathogenesis and treatment of granulomatous mastitis
- Etiology analysis and treatment progress of diminished ovarian reserve function in traditional Chinese and Western medicine
- Traditional Chinese Medicine syndrome and treatment of brucellosis in chronic stage
