Thiophene and naphthalene-based double helix:Synthesis,structures and chirality
2021-04-02ChunmeiZhoZhiyingChunliLiLiXuHuWng
Chunmei Zho,Zhiying M,Chunli Li,Li Xu*,Hu Wng,*
a Engineering Research Center for Nanomaterials, Henan University, Kaifeng 475004, China
b School of Chemical Engineering and Food Science, Zhengzhou Institute of Technology, Zhengzhou 450044, China
c College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Henan University, Kaifeng 475004, China
ABSTRACT Both racemate and enantiomer of a novel double helix, binaphthylcyclooctaterthiophene (BN -COTh),which is a DNA-like molecule constructed by two single helices intertwined with each other via covalent bonds, have been synthesized with two building blocks, cycloocta-tetrathiophene (COTh) and cyclooctadinaphthyldithiophene (CONT) fused together via Negishi coupling reaction.Another homologue, dinaphthylcyclooctaterthiophene (DN-COTh) has been employed together as a model compound.Besides the synthetic work, BN -COTh and DN-COTh have been investigated by studying their crystal structures, spectroscopic behaviors, chiral resolution and chiral characteristics, including circular dichroism(CD)spectra and optical rotations.In addition,the novel crystal of enantiomer of(R,R,R)-BN -COTh has been explored.The enantiomer molecules packing along b-axis to form a larger and extended assembly packing due to intermolecular interactions between the enantiomer molecules and chloroform molecules in crystal.
Keywords:Binaphthylcyclooctaterthiophene Dinaphthylcyclooctaterthiophene Double helix Crystal structure Chirality
Being composed of four thiophene rings fused to cyclooctatetraene(COT),COTh possesses special saddle-shaped molecular structure,which is usually employed as an important building block in organic functional materials.As early as in 1974 [1], the first isomer of COTh was reported by Kauffmann.Over the past four decades,many work about the derivatives based on COTh units in both organic synthesis and applications have been carried out[2].Among them,all thiophene-based double helix has a novel helical structure, in which two single helices are intertwined with each other via the C -C single bonds [3-6].Such DNA-like double helical motifs connected by covalent bonds show extraordinary aesthetically pleasing structures, which are very rare to be presented in the literature.In our previous work,we have focused on synthesis and property research of COThs and their derivatives,including double helicenes [4-7].Our recent double helices constructed with COTh units[8](Fig.1)show the same molecular frameworks of double helices constructed by cyclooctatetraphene(COPh) units, reported by Rajca [9] (Fig.1) and Wong [10].These derivatives have not only novel helical structures but also potential applications in supramolecular polymer[11,12],molecular muscle[13,14] and self-assembly [15], and therefore have attracted continuous attention.
In these pioneering work, the structures of double helices are constructed of COTh [3,8,16] and COPh [9,10] composed of thiophene and benzene ring,respectively.In this work,both COTh(marked by a pink circle, Fig.1) and cycloocta-dinaphthyldithiophene (CONT, marked by a green circle, Fig.1) are employed as building blocks for construction of a new double helix, binaphthylcyclooctaterthiophene (BN -COTh).As model compound,dinaphthylcyclooctaterthiophene(DN-COTh)has been investigated together with BN-COTh to enrich the study of such novel double helix.The introduction of an aromatic photoluminescence (PL)group,naphthylene to the molecular framework is to functionalize molecule in material science, such as photoluminescence and circularly polarized luminescence(CPL),etc.Besides the synthetic work, herein, we have obtained their racemic crystal structures,done their chiral resolutions,studied on their chiral properties.In addition, the novel crystal of enantiomer of (R,R,R)-BN-COTh has been explored.
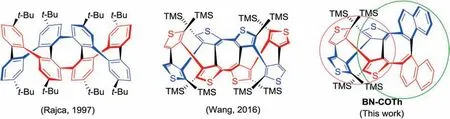
Fig.1.The molecular structures of covalent bonds linked double helices based on phenyl and thienylunits.
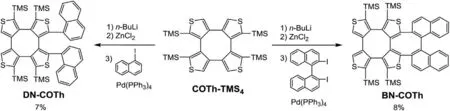
Scheme 1.The synthetic route to DN-COTh and BN-COTh.
The synthetic route to BN-COTh and DN-COTh constructed with CONT and COTh is shown in Scheme 1.As revealed in our previous work, the deprotonation of COTh-TMS4in the presence of n-Buli exhibited high ipsilateral selectivity [8].On the basis of this deprotonation selectivity,COTh-TMS4is treated with 2.0 equiv.of n-BuLi, the formed bicarbonate anions are transferred to Negishi regents by quenching with 2.2 equiv.of ZnCl2, and subsequent Negishi couplings with 1-iodonaphthalene and 2,2'-diiodo-1,1'-binaphthalene are occurred to obtained racemic DN-COTh and BNCOTh in 7%and 8%yields,respectively.The characterization data of chemical structures for DN-COTh and BN-COTh are shown in Figs.S1-S8 (Supporting information).The low synthetic yields mainly depend on two factors.One is the rigid molecular structure of COTh-TMS4formed by the repulsion of steric hindrance between its TMS groups.Molecular rigidity makes Ar-I molecule hard to fit the fixed spatial orientation of Negishi reagent from COTh-TMS4for the coupling procedure.Another one is the intramolecular tension of DN-COTh and BN-COTh,which is higher than that of COTh-TMS4.Normally, it is hard to make target molecule with high intramolecular tension from its precursor bearing low intramolecular tension.
The molecular structures of BN-COTh and DN-COTh are confirmed by X-ray single crystal analyses.Their specific single crystal data are listed in Tables S1 and S2(Supporting information).The single crystal structure of BN-COTh is shown in Fig.2A,which belongs to monoclinic system, space group P121/n1.BN-COTh possesses double helical molecular structure, in which there are two eight-membered rings composed with COTh and COPhTh units fused together in the molecular center to form the new double helix, different from the reported cases contained COTh[3,8,16] or COPh [9,10] only.In the crystal of BN-COTh, the two naphthyl groups in the molecule are approximately vertical with dihedral angle of 81.6°(Fig.2A), the average dihedral angle between naphthyl moiety and the linked thiophene ring is 51.5°.Fig.2B shows the packing of BN-COTh, in which two pairs of enantiomers are stacked in a unit cell.The two enantiomers, (S,S,S)-BN-COTh (red) and (R,R,R)-BN-COTh (blue) are stacked closely via two intermolecular interactions of C 33···H32 (2.824 Å), and each enantiomer is stacked via an intermolecular interaction of H42A ···H44B (2.343 Å) along a-axis.
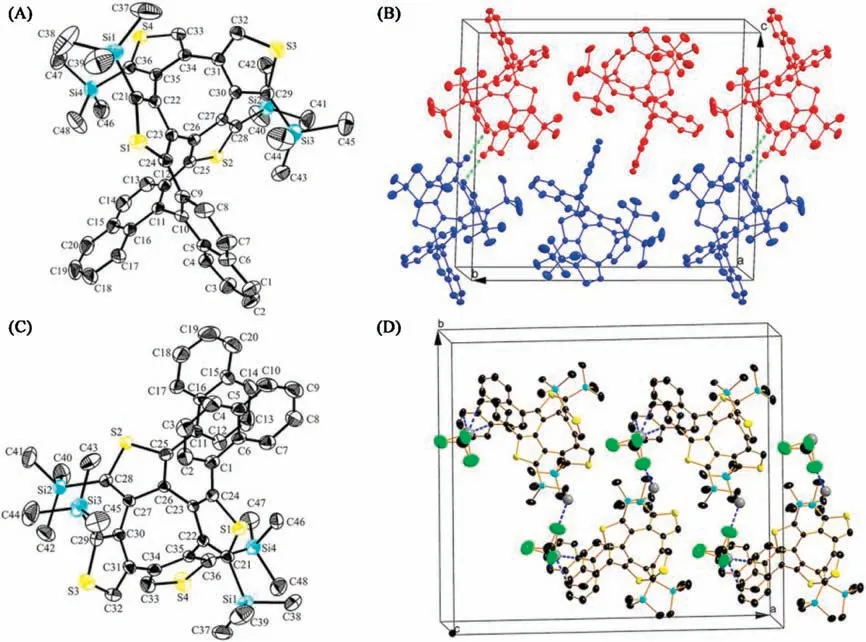
Fig.2.The crystal structures and packings of BN-COTh(A,B)and DN-COTh(C,D).Carbon,silicon,sulfur and chlorine atoms are depicted with thermal ellipsoids set at 30%probability level.Hydrogen atoms are omitted for clarity.
DN-COTh belongs to the orthorhombic system, space group Fdd2.The two naphthyl groups are parallel and ipsilateral with a small dihedral angle of 7.5°in DN-COTh (Fig.2C).However, the average dihedral angle between naphthyl moiety and the linked thiophene ring is 74.6°,which is bigger than the dihedral angle of 51.5°in BN-COTh.Such dihedral angle difference is the key role to explain the distinction between their spectroscopic behaviors.In packing of DN-COTh,the molecule of chloroform is observed with 1:1 ratio to molecule DN-COTh.The multiple intermolecular interactions exist between DN-COTh and chloroform,such as Cl ···H(Cl2···H42B: 2.947 Å) and H···C (H49···C14: 2.812 Å, H49···C16:2.812 Å, H49···C20: 2.895 Å).The three H···C interactions are observed between chloroform and one enantiomer(such as(R,R)-DN-COTh), while the Cl ···H interaction is found between chloroform and another enantiomer(such as(S,S)-DN-COTh)to form the zigzag packing in the crystal (Fig.2D).
BN-COTh shows a short wavelength peak at 225 nm and shoulder peak at 285 nm,while DN-COTh has a peak at 231 nm and a shoulder peak at 306 nm(Fig.3).The shoulder peak intensity of BN-COTh is much higher than that in the case of DN-COTh.Compared to DN-COTh, BN-COTh has better intramolecular conjugation due to its smaller average dihedral angle between naphthyl moiety and the linked thiophene ring (Fig.2).Such conjugation difference is also presented in their emission behaviors.BN-COTh shows single emission peaked at 420 nm,while DN-COTh exhibits shorter emission peak at 406 nm(Fig.3).
The chiral resolutions of rac-DN-COTh and rac-BN-COTh were done by chiral HPLC with hexane as eluent for rac-DN-COTh and hexane/isopropanol (99.7:0.3, v/v) as eluent for rac-BN-COTh,respectively.The enantiomers of both DN-COTh and BN-COTh were obtained successfully with high ee value (≥97%)as shown in Fig.S11 (Supporting information).
All enantiomers of DN-COTh and BN-COTh possess moderate optical rotations as shown in Table 1.The CD spectra of the enantiomers were given in Fig.4.We can see that all enantiomers exhibit characteristic mirror positive and negative CD spectra images in dichloromethane with remarkable cotton effect.
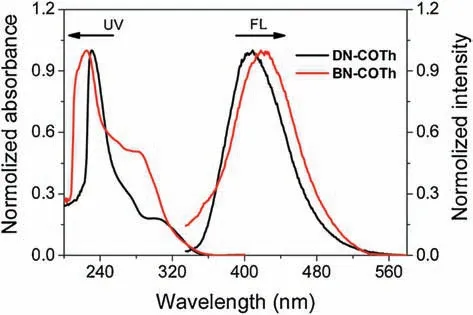
Fig.3.The normalized UV -vis and fluorescence spectra of DN-COTh and BN-COTh in THF ([C ]=1.0×10-5 mol/L,λex = 300 nm).
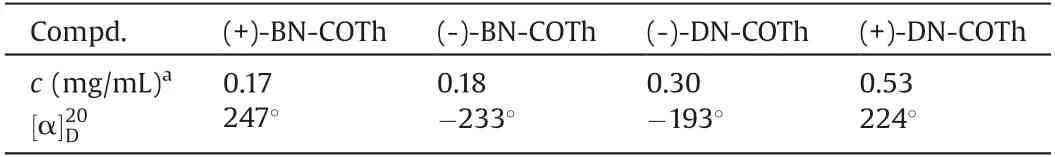
Table 1 The specific optical rotation data of enantiomers in CH2Cl2.
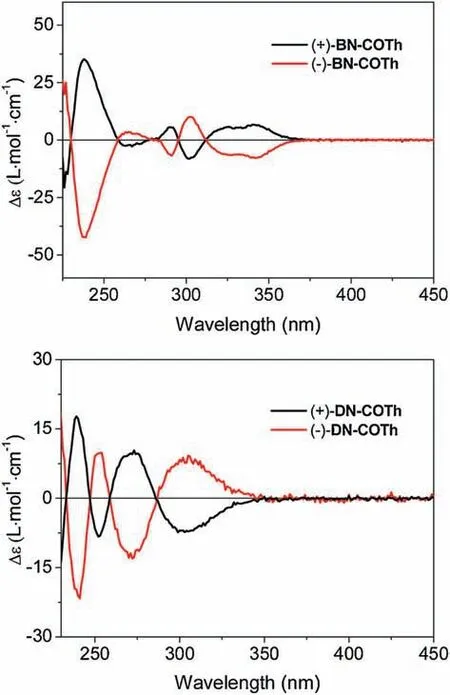
Fig.4.CD spectra of BN-COTh and DN-COTh in CH2Cl2 at 20°C.
Fortunately, the single crystal of enantiomer BN-COTh was obtained via solvent evaporation method and characterized as shown in Fig.5.The absolute configuration of (R,R,R)-BN-COTh is confirmed by an X-ray crystallographic analysis.(R,R,R)-BN-COTh belongs to monoclinic system, space group P1211 (the single crystal data is exhibited in Table S3 in Supporting information).The two naphthalene rings in molecule are almost vertical with dihedral angle of 74.1°,close to its recemate as shown as 81.6°.The average dihedral angle between naphthalene ring and thiophene ring is 52.5°,which is very close to its recemate as shown as 51.5°.The torsion angle of COT in COTh of molecule (R,R,R)-BN-COTh is about 58.5°(C6-C7-C10-C11), and another torsion angle of 62.3°(C1-C2-C15-C16) is observed from the COT in CONT of the molecule.Both two torsion angles are much smaller than that as shown as 77.8°[8] in COTh itself due to introduction of binaphthyl moiety with high intramolecular steric tension in(R,R,R)-BN-COTh.
In packing of(R,R,R)-BN-COTh,two(R,R,R)-BN-COTh molecules and two chloroformmolecules per unit cell are shown along b-axis(Fig.5B).The intermolecular interactions between (R,R,R)-BNCOTh and chloroformmolecule are observed with short distances of Cl 3···C44 (3.369 Å),Cl3···H44B(2.866 Å) and H49···S4(2.970 Å).Such intermolecular interactions make molecules packing along baxis to form a larger and extended assembly packing in crystal.
Up to now,only two types of chiral double helices constructed of COTh [8] and COPh [10], respectively.Each double helical scaffold has two single helices intertwined with each other via the C -C single bonds to form a special type of DNA-like molecular structure, which is important part in artificial simulation of DNA.Different from those pioneering work constructed with COTh or COPh only, (R,R,R)-BN-COTh is a novel one composed with two building blocks, COTh and CONT fused together in its molecular framework.The construction of BN-COTh provides a new route to design new double helices based on two or more building blocks,such as COTh and COPh.
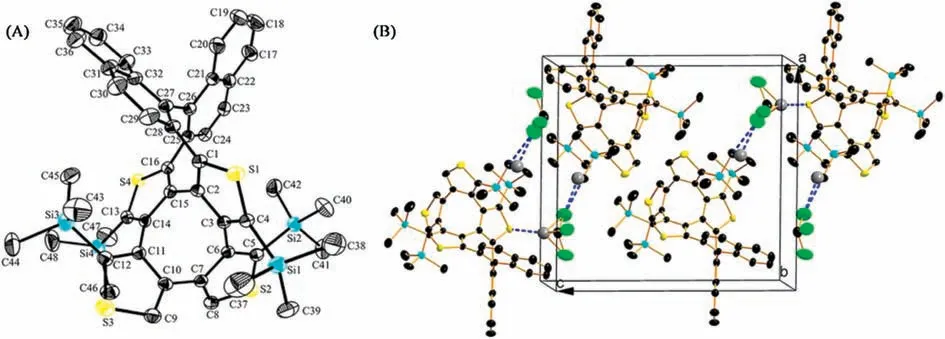
Fig.5.Single crystal (A) and crystal packing structure (B) of (R,R,R)-BN-COTh.Carbon, silicon, sulfur, and chlorine atoms are depicted with thermal ellipsoids set at 30%probability level.Part of hydrogen atoms are omitted for clarity.
In summary, two naphthyl-substituted COThs, BN-COTh and DN-COTh were synthesized and their crystal structures, photophysical behaviors and chiral properties were classically characterized.BN-COTh is a new double helical molecule constructed with two building blocks,COTh and CONT fused together to form its molecular framework.The molecular design strategy of BNCOTh provides a feasible route to functionalize the novel double helices in high level based on two or more building blocks,such as COTh, COPh and CONT. The studies on the longer chain double helices and their chirooptical properties, such as circularly polarized luminescence based on the aromatic photoluminescence groups such as naphthylene are in progress in our group.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that they have not any financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos.21672053 and 21672054), Innovation Scientists and Technicians Troop Construction Projects of Henan Province (C20150011).
Appendix A.Supplementary data
Supplementarymaterialrelatedtothisarticlecanbefound,inthe online version,at doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2020.05.040.
杂志排行
Chinese Chemical Letters的其它文章
- A biomass based photonic crystal made of “konjac tofu”
- Hydrothermal-assisted grinding route for WS2 quantum dots (QDs)from nanosheets with preferable tribological performance
- Superiority of poly(L-lactic acid) microspheres as dermal fillers
- Zwitterionic comb-like lipid polymers encapsulating linalool for increasing the fragrance retention time
- Construction of a nano-rectangular Zn-Nd complex with near-infrared luminescent response towards metal ions
- Synthesis and structure of Au19Ag4(S-Adm)15 nanocluster:Polymorphs and optical properties