CO2 and photo-controlled reversible conversion of supramolecular assemblies based on water soluble pillar[5]arene and coumarin-containing guest
2021-04-02YufengCaoYanmeiChenZhechengZhangJinWangXiaoleiYuanQinZhaoYueDingYongYao
Yufeng Cao,Yanmei Chen,Zhecheng Zhang,Jin Wang,Xiaolei Yuan,Qin Zhao*,Yue Ding,Yong Yao*
School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nantong University, Nantong 226019, China
ABSTRACT In this communication,a new supramolecualr amphiphile was successfully constructed based on water soluble pillar[5]arene and a unique guest which contain a CO2 responsive tertiary amine unit and a UV responsive coumarin group.When guest molecule 1 dispersed in water,it self-assembled into sheet-like structures.Upon bubbling CO2,1 transformed into 1H due to the tertiary amine unit was protonated,accompany the nano-sheets transformed into vesicles.Further irradiation of 1H with 365 nm light for 3 h,the coumarin group reacted with each other to form bola-type amphiphie 2H.In this case, vesicles collapsed and re-assembled into nano-tubes.However,when addition of WP5 into the solution of 1H,the vesicles transformed into micelles,this is due to the formation of supramolecular amphiphile WP5&1H.Upon irradiation of WP5&1H with 365 nm light for 3 h,nano-ribbons observed instead of micelles in the solution.Notably,nanotubes from 2H could also transform into nano-ribbons after adding WP5.The selfassembly process and the resultant assemblies were characterized by TEM, SEM, DLS, SAXS and NMR technologies.Due to both CO2 and light are “green”for living organisms,we anticipated our system can offer the possibilities in “on demand” drug absorption and release.
Keywords:Pillar[5]arene Supramolecular assemblies Amphiphiles Reversible conversion Coumarin
Hiphiles are a useful type of compounds which contain both hydrophilic and hydrophobic units 1].When amphiphiles are dispersed in aqueous solution,they can self-assemble into various nanostructures,suchasvesicles[1 c,d],fibers[1e,f],ribbons[1g]etc.,through hydrophilic-hydrophobic interactions.On the other hand,amphiphiles also play an important role in living system,as we all know that cell membrane was self-assembled from amphiphilic phospholipids[1h].Different likeconventional amphiphiles,supraamphiphiles are fabricated from non-covalent interactions or dynamic covalent interactions 2].This dynamic property not only greatly speed the construction of supra-amphiphiles but also endows themwith interesting stimuli-responsiveness[2 a-d].Until now, various stimuli, such as light, pH, CO2, redox etc., have been employed to control the self-assembly behavior of supra-amphiphiles [3].Among all these stimuli, photo and CO2stimuli are of greatinterest duetotheir unique advantages.CO2as one of the most important metabolic substance of bodies,is a nontoxic,inexpensive and environmental friendly gas, while light has many advantages including easy availability, few by-products, high sensitively and excellent controllability[3 a-c].
Pillar[n]arenes [4], mainly including pillar[5]arene and pillar[6]arene, are a new type of classical macrocyclic hosts after crown ethers [5], cyclodextrins [6], calixarenes [7] and cucurbiturils [8].The repeating parts of pillar[n]arenes are linked by--CH2--at their 2,5-positions, forming a hydrophobic pillarlike cavity.Compared with crown ethers and calixarenes, pillar[n]arenes process a more rigid cavity, while compared with cyclodextrins,and cucurbiturils,they can be functionalized easier.Until now, the preparation, modification, host-guest interactions, and potential applications of pillar[n]arene have been widely investigated [9].
Although supra-amphiphile based on pillar[n]arenes hostguest chemistry have also been constructed, pillar[n]arene-based supra-amphiphiles with nontoxic,inexpensive and environmental friendly responsiveness have been reported rarely, especially one system can constructed various structures [10 ].
Herein,we designed and constructed a novel supraamphiphile based on water-soluble pillar[5]arene (WP5) and a coumarincontaining guest (1), which can generate various well-defined nano-structures under control (Scheme 1).It should pointed that 1 was responsive to both UV irradiation and CO2because it contain a photodimerization coumarin unit and a tertiary amine group.It was found that 1 could dissolve in DMF very well without forming assemblies (Fig. S9 in Supporting information).However, when 10.0 μL(10-3mol/L)DMF's solution of 1 was injected into 100 mL water under vigorous stirring,it can form homogeneous solution.What is more, Tyndall effect was observed clearly in this homogeneous solution (Fig.1b, inset), indicating the formation of nano-aggregates.Then the self-assembly behavior of 1 was investigated by using dynamic light scattering (DLS) and transmission electron microscopy(TEM)technologies.The DLS studies showed that the aggregates of 1 have an average diameter of 620 nm and a broad size distribution (Fig.1d).TEM experiments assisted in the visualization of the nano-assemblies from 1 in water.As shown in Fig.1a, numerous sheet-like nano-structures were clearly observed.An enlarged TEM image showed that the assemblies were with 1 μm in length and 200 nm in width(Fig.1b).Furthermore, small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS)measurements were performed for the determination of the thickness of the sheet-like assemblies.The profile showed a strong scattering at 1.61°(Fig.S10 in Supporting information), so the thickness of the structures was calculated to be 5.64 nm.Due to estimated length of 1 was about 3.12 nm(Fig.1e),so the thickness of the sheet-like nanostructures was close to the estimated length of 2 times of molecule 1,which indicating that the nano-sheets are formed by two molecule 1 stacking together through π-π interactions (Fig.1e).
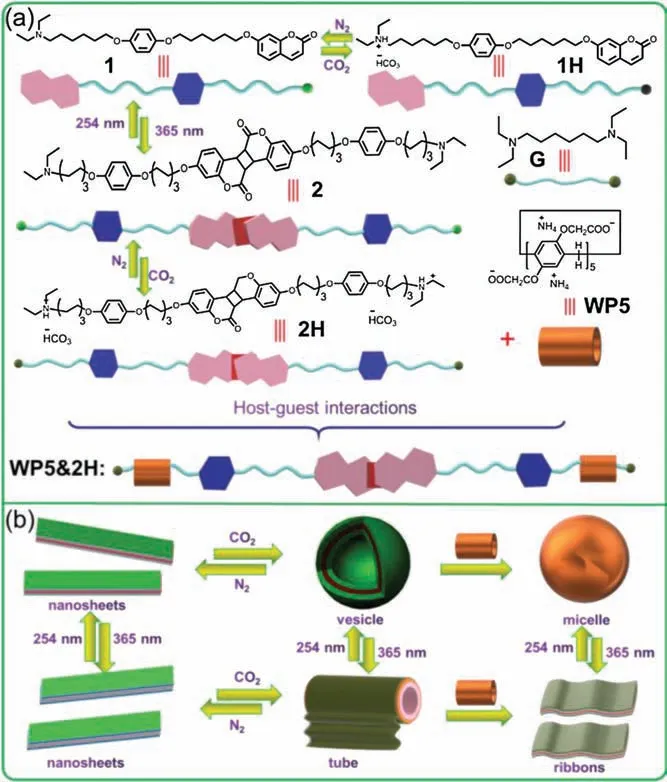
Scheme 1.(a)Chemical structures and cartoon representations of molecules 1,1H,2, 2H, G and WP5.(b) Cartoon representation of the gas and photo triggered transformation of the amphiphile in water.
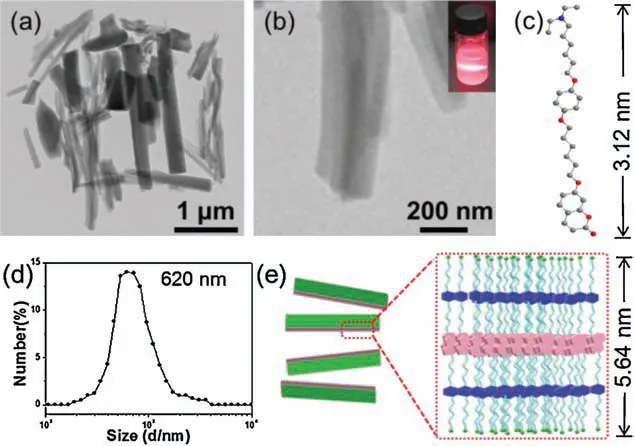
Fig.1.(a)TEM image of 1 self-assembly in water.(b)Enlarged TEM image of(a).(c)Calculated minimize energy model of molecule 1.(d) DLS study of 1 in water.(e)Cartoon representation of 1 self-assembly into bilayer nano-sheets.
As we all known that tertiary amine unit can react with CO2in water to form charged ammonium bicarbonate, which can be recovered upon bubbling with N2[11].As shown in Fig.2a, when CO2(1 MPa,10 min) was bubbled into aqueous solution of 1, the turbid dispersion became a transparent solution.On the other hand, Tyndall effect was observed clearly in this transparent solution (Fig.2b, inset), indicating that nanoassemblies were formed by 1H.DLS investigation showed that the average diameter of the assemblies from 1H was about 33 nm with narrow distribution (Fig.S11 in Supporting information).Furthermore,hollow vesicles with diameter about 30 nm were visually observed by TEM image,which consistent with the DLS result.The thickness of the vesicles was calculated to be 5.5 nm(Fig.2b,inset),which is also 2 times extended length of 1H,suggesting the vesicles have a bilayer wall (Fig.1d).
Due to the poor solubility of 1 in water,we choose G with two tertiary amine units as a model compound.From1H NMR, we found that G can bonding with WP5 after bumbling CO2(Fig.S8 in Supporting information) [3a].So in our system, a supramolecular amphiphile was easily constructed by mixing WP5 and 1H.Although Tyndall effect could also be observed in the solution WP5&1H (Fig.2c), the DLS study showed great difference compared with 1H itself.From DLS investigations we found that the diameter of the assemblies changed from 33 nm to 300 nm(Fig. S12 in Supporting information), indicating different nano-structures formed in solution.TEM image showed that the vesicles were transformed into solid particles with diameter about 300 nm upon addition of WP5(Fig.2c,inset),consisted with the DLS studies.The self-assembly process might be that WP5&1H self-assembled into small micelles in water first,then small micelles further aggregate together to form large multi-molecular micelles (Fig.2d).

Fig.2.(a)The optical photographs of aqueous solution:left,1(10-6 mol/L,10 mL);middle, after bubbling CO2 (10 min); right, further addition of WP5 (10-3 mol/L,0.01 mL).(b) TEM image of 1H in water. (c) TEM image of WP5&1H.(d) Cartoon representation of the self-assembly process of 1 after bubbling CO2 and further addition of WP5 in water.
On the other hand,irradiation of coumarin at λ >350 nm could yield quantitatively coumarin dimer (Fig.S13 in Supporting information).It is reasonable to speculate that we can utilize irradiation to control the self-assembly behavior in water.Just as expected,when the solution of 1H was irradiated with UV light for 3 h, nano-tubes with several pm in length and 500 nm in width were observed instead of vesicles(Fig.3a).From an enlarged TEM image of a nanotube we found that the nanotubes were actually constructed by nano-ribbons rolling together(Fig.3b).SEM image also confirmed the formation of nanotubes(Fig.3c).However,the vesicles reformed upon the solution of 2H irradiated with 254 nm light overnight(Fig.S14 in Supporting information).Different like the formation of nanotubes, large area of nano-ribbons were obtained when irradiation of WP5&1H with 365 nm UV light for 3 h(Fig.3d).The thickness of the ribbons was calculated to be 5 nm from an enlarged TEM image (Fig.3e) and SEM image (Fig.3f),which similar to the molecular length of WP5&2H.The nanoribbons from WP5&2H are very stable and could not further selfassembly into nano-tubes due to the large size of WP5 restrain them rolling together (Fig. S15 in Supporting information).Interestingly, the nanoribbons destroyed and re-assembly into micelles upon irradiation with 254 nm light overnight(Fig. S16 in Supporting information).However, the irradiation of the nanosheets from 1 with 365 nm UV light could not change its morphology, large area of sheet-like structures were observed in TEM image (Fig.S17 in Supporting information).So, from above investigation we can obtain nano-materials with different morphologies as we want by tuning the self-assembly conditions.It should be pointed that the nanosheets are very stable in solution,but the vesicles, micelles, tubes and ribbons can just stable in solution about 2 days.
In conclusion, a new supramolecular amphiphile was successfully constructed based on water soluble pillar[5]arene and a unique guest which contain a CO2responsive tertiary amine unit and a UV responsive coumarin group.When the guest molecule 1 dispersed in water, it self-assembled into sheet-like structures.Upon bubbling CO2, 1 transformed into 1H due to the tertiary amine unit was protonated, accompany the nano-sheets transformed into vesicles.Further irradiation of 1H with 365 nm light for 3 h,the coumarin group reacted with each other to form bolatype amphiphie 2H.In this case, vesicles collapsed and reassembled into nano-tubes.However,when addition of WP5 into the solution of 1H, the vesicles transformed into micelles, this is due to the formation of supramolecular amphiphile WP5&1H.Upon irradiation of WP5&1H with 365 nm light for 3 h, nanoribbons observed instead of micelles in the solution.Notably,nanotubes from 2H could also transform into nano-ribbons after adding WP5.The self-assembly process and the resultant assemblies were characterized by TEM, SEM, DLS, SAXS and NMR technologies.Due to both CO2and light are"green"for living organisms,we anticipated our system can offer the possibilities in “on demand” drug absorption and release.
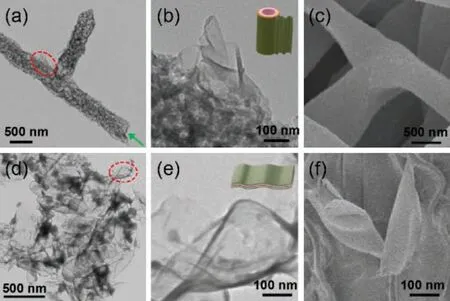
Fig.3.(a) TEM image of nanotubes from 2H.(b) An enlarged TEM image of nanotube. (c)SEM image of nanotubes from 2H.(d)TEM image of nanotubes from WP5&2H.(e)An enlarged TEM image of nanoribbon. (f)SEM image of nanoribbons from WP5&2H.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos.21801139, 21871227), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province(No.BK20180942) and the Natural Science Foundation of Nantong University for High-Level Talent(No.03083004).
Appendix A.Supplementary data
Supplementarymaterialrelatedtothisarticlecanbefound,inthe online version,at doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2020.03.058.
杂志排行
Chinese Chemical Letters的其它文章
- A biomass based photonic crystal made of “konjac tofu”
- Hydrothermal-assisted grinding route for WS2 quantum dots (QDs)from nanosheets with preferable tribological performance
- Superiority of poly(L-lactic acid) microspheres as dermal fillers
- Zwitterionic comb-like lipid polymers encapsulating linalool for increasing the fragrance retention time
- Construction of a nano-rectangular Zn-Nd complex with near-infrared luminescent response towards metal ions
- Synthesis and structure of Au19Ag4(S-Adm)15 nanocluster:Polymorphs and optical properties