Diffusion of Innovative Behavior of the Public Toward Preparing FEMKs:From Innovative Characteristics to Personal Risk Perception and Behavioral Intention
2021-03-29ShuXianXuTingYuDuanShuTingWeiXiZheHeRuYiHouYiBoWu
Shu-Xian Xu,Ting-Yu Duan,Shu-Ting Wei,Xi-Zhe He,Ru-Yi Hou,Yi-Bo Wu
1#School of pharmacy,Shenyang pharmaceutical university,Benxi 117004,China;2#Department of humanities,arts and media,Changzhi Medical College,Changzhi 046000,China;3Department of clinical medicine,School of Basic Medicine,Shandong University,Jinan 250100,China;4School of pharmacy,Jiangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Nanchang 330004,China;5Department of humanities,arts and media,Changzhi Medical College,Changzhi 046000,China;6Key Research Base of Philosophy and Social Sciences in Shaanxi Province,Health Culture Research Center of Shaanxi,Xi'an 712046,China;7Peking University Health Science Center,Beijing 100191,China.
Abstract
Keywords:COVID-19,Emergency medicine kit,Diffusion of innovations,Structural equation model,Psychosomatic medicine,Affecting factors
Background
Coronavirus disease(COVID-19)exerts a serious impact on the psychological state and protective behavior of the public.After the occurrence of public health emergencies,scholars consider changes in the risk perception and choice of protective measures of the public as mechanisms of self-protection in the face of uncertain situations [1,2].Conversely,risk perception influences protective behavior[3,4].On another note,family emergency medicine kits(FEMKs)refer to drugs stored and used by residents at home[5].Especially during the COVID-19 pandemic,preparing these kits as an innovative product reduces the risk incurred when going out to buy medicine for family members with slight discomfort or emergency accidental injury[6].Despite the increasing concerns on the consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic on mental health,large-scale population-based studies that examine the associations of risk perception of COVID-19 to mental health and subsequent health measures remain lacking[7].Innovation diffusion theory is widely used in information technology innovation research.Five core dimensions,including relative advantages,compatibility,complexity,testability and observability,are introduced to explore how to promote the promotion of innovative products.To bridge the research gap,the current study explores the impact of innovation characteristics on personal risk perception and behavioral intention on the basis of this theory with a focus on the innovation characteristics of FEMKs to provide reference for related research.
Methods
Respondents
The participants were screened according to the following inclusion criteria:residents(1)living in Shanxi for at least three months(2)with basic reading ability and(3)participating on a voluntary basis and with informed consent.The exclusion criteria were(1)patients with mental illnesses or difficulty in understanding and(2)those participating in other similar studies during the research period.
Research methods
Questionnaire design.The questionnaire was composed of four parts.The first pertains to demographic sociological characteristics,such as gender,age group,location,level of education,marital status,monthly income per capita,occupation,and diagnosis of COVID-19-related pneumonia of relatives and friends.The second part uses the transtheoretical model to investigate the stages of action of residents,namely,pre-contemplation,contemplation,preparation,action,and termination stages,which are assigned to 1,2,3,4,1.
The third part was composed of two items regarding personal risk perception,namely,less frequent use of FEMKs will lead to (1)wastage and(2)drug expiration.The items were rated using a five-point Likert-type scale(1=strongly disagree,2=disagree,3=uncertain,4=agree,and 5=strongly agree).
The last part was based on diffusion of innovation theory.The questions aimed to examine the factors that influence the behavior of residents toward the preparation of FEMKs,such as relative advantages,compatibility,convenience of use,and observability.This part comprised a total of 19 items,which were rated using a five-point Likert-type scale(1=strongly disagree,2=disagree,3=uncertain,4=agree,and 5=strongly agree).
Sampling method.The study employed stratified sampling in 11 cities in Shanxi Province,selected 1-2 communities in each city for cluster random sampling,and recruited an investigator with relevant experience in the selected communities to disseminate the questionnaires.The Ethics Committee of Changzhi Medical College reviewed and approved the project.All participants expressed understanding of the content of the project and voluntarily participated in the survey.
Investigation methods.The investigators conducted the study in the form of one-on-one inquiry by individually adding the respondents to a WeChat group.Face-to-face inquiry was considered risky due to the particularity of the environment during the pandemic.The participants were provided with a QR code of or a link to the questionnaire.To ensure the authenticity and effectiveness of the outcome,the questionnaire was forwarded only once per respondent.The investigators answered the clarifications raised by the respondents but did not interfere with their choices.
Statistical methods.SPSS16.0 software was used to establish a database for statistical description;the Chi square test was used to analyze the influence of demographic characteristics on behavioral intention;Amos 21.0 was used to fit the sample data to structural equation modeling (SEM);and the maximum likelihood robust method was used to estimate the parameters.The commonly used evaluation standards of SEM are CMIN/DF,goodness-of-fit index(GFI),adjusted goodness-of-fit index(AGFI),comparative fit index(CFI),root mean square error of approximation(RMSEA),normal fit index(NFI),and Tucker-Lewis index(TLI).Significance was set to P<0.05.
Quality control of questionnaire survey.Before distributing the questionnaires,the members of the research team trained the investigators on how to brief the participants regarding the research objective and how to explain the questions and responses without influencing the judgment of the participants.During data sorting,screening of IP address,submitting the questionnaire once,eliminating questionnaires with response times less than 1 min,and logically verifying and repeatedly proofreading the data were conducted to ensure completeness,integrity,and accuracy.
Reliability and validity of the questionnaire
The study collected a total of 1,606 valid questionnaires for a response rate of 100% and effectivity rate of 97.33%.The questionnaire aimed to collect information of the influencing factors of the diffusion of innovation.The Cronbach coefficient of each factor reached more than 0.7 for an overall Cronbach’s coefficient of 0.884.Exploratory factor analysis revealed a total of four factors including relative advantage,compatibility,convenience of use and observability,and the division of the obtained factors was consistent with the theoretical framework.The cumulative contribution rate was 61.03%,and the scales for factors influencing the diffusion of innovation were within acceptable levels of reliability and validity.
Results
Basic information
Out of the 1,606 residents,52.7% were female.The number of people under 18,18~25,26~30,31~40,41~50,51~60 and over 60 was the same.Urban residents composed the majority of the participants(54.23%).Undergraduate students and married residents accounted for the largest proportions(25.16% and 59.46%,respectively)of the sample.Residents who never smoked or drank alcohol accounted for the vast majority.Moreover,the proportion of respondents with less reported infections of COVID-19 among family members and friends reached 2.30%.However,COVID-19 covers a wide area.In the study area,several widespread cases (69.30%) were noted.Additionally,the number of respondents identified in the pre-contemplation,contemplation,preparation,action,and termination stages were 73(4.55%),410(25.53%),402(25.03%),621(38.67%),and 100(6.23%),respectively.Single factors indicated that age,education,marital status,drinking,and infection among relatives and friends displayed significant differences in the behavior of preparing FEMKs(P<0.01),whereas smoking exhibited significant differences in the behavior of preparing FEMKs(P<0.05).Table 1 provides the details of the result.

Table 1 Comparison of the behavior of different individuals in preparing family emergency medicine kits
Diffusion of innovation theory of personal perceived risk and public behavior of preparing FEMKs
The average scores for relative advantages,compatibility,convenience of use,observability,and risk perception were 3.96,3.92,3.81,3.86,and 3.92,respectively.All influencing factors were significantly correlated at the 0.01 level of significance.The darker the color,the stronger the correlation(Table 2).
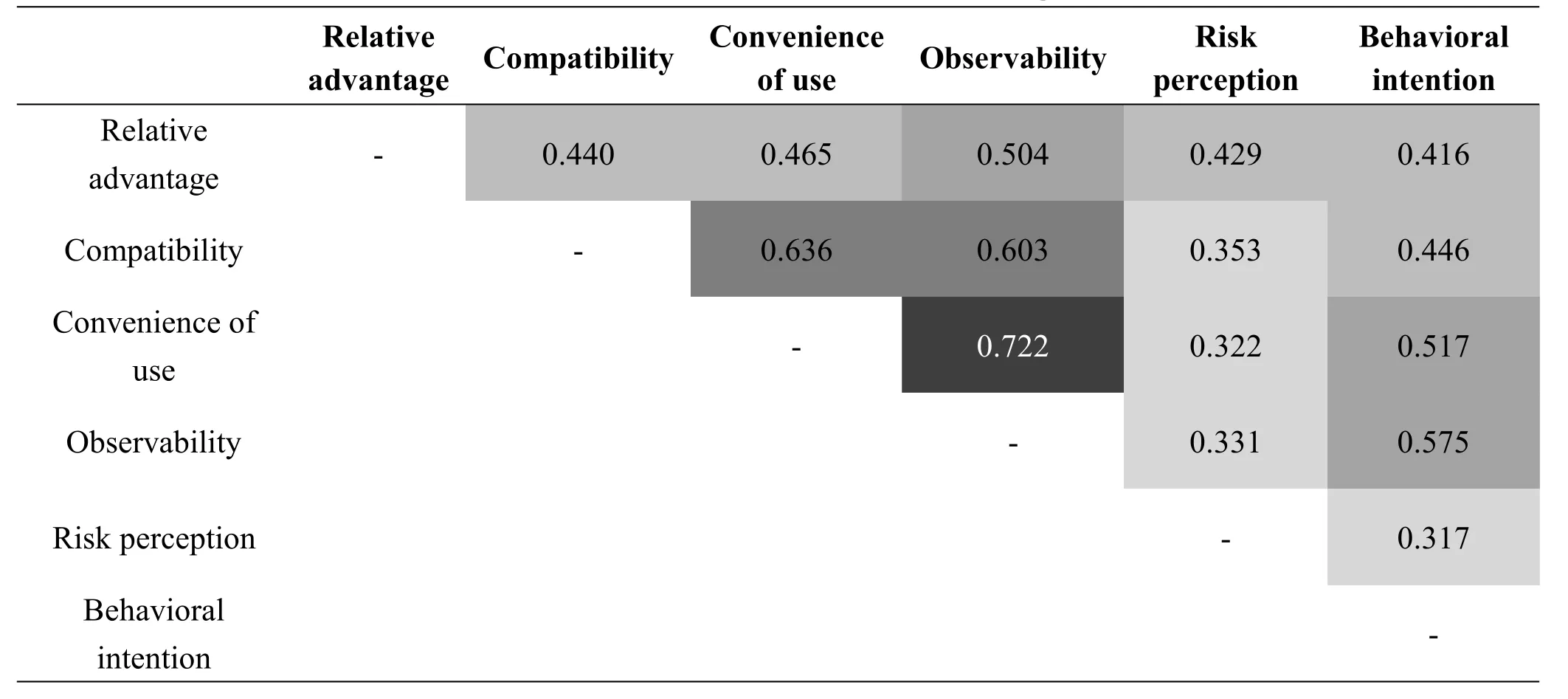
Table 2 The correlation between the affecting factors
Structural equation modeling
This model was repeatedly modified to fit the best behavior model for the public in preparing FEMKs(CMIN/DF=3.130<5,GFI=0.981>0.9,AGFI=0.971>0.9,CFI=0.984>0.9,RMSEA =0.036<0.08,NFI=0.976>0.9,TLI=0.978>0.9.All values are within acceptable ranges,which indicates that the model adapts to the survey data as a whole.Moreover,the model is scientific and effective.SEM indicated showed that only observability(0.968,P<0.001)exerted a significant direct impact on the public's behavior of preparing FEMKs,whereas personal risk perception(0.334,P<0.001)had a significant direct impact on behavioral intention.Relative advantage,compatibility,and convenience of use displayed significant impacts on behavioral intention by influencing individual perceived risk with mediating effects at 0.237,0.892,and 1.044,respectively(Figure 1).
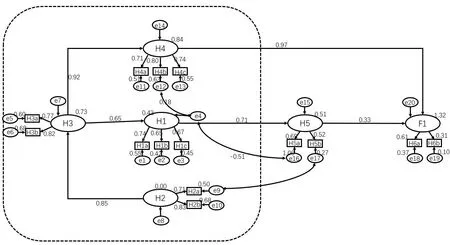
Figure 1 Structural equation modeling of the influencing factors of behavior of residents in preparing FEMKs
Discussion
Behavior of residents toward preparing FEMKs
Respondents that belong to the action stage comprise the largest proportion of the sample(38.67%)in terms of behavior,which indicates that such residents have prepared FEMKs.However,the mean score for behavioral intention was 2.92,which indicates that many residents remain in a period of transition from the contemplation to the preparation stage.In other words,the majority of residents realize the importance of preparing FEMKs and are ready to apply them to practice.The levels of safety and efficiency of seeking medical advice are relatively low due to the sudden outbreak;thus,the majority of residents recognized the importance of preparing FEMKs.As such,they are gradually undergoing a transition to the preparation stage during the COVID-19 transmission.Thus,the study applies the cross-theoretical model to the behavioral intention of residents to prepare FEMKs and takes effective measures for individuals across the abovementioned stages to enable the teaching of students according to their aptitudes[8,9].
Comparison of individual differences
According to demographics,people aged 26-40 are more active in preparing FEMKs,which may be related to the tendency of this age group to frequently suffer from various chronic diseases,to assume the role of maintaining the health status of family members,and to recognized the need of storing essential drugs at home.Additionally,the majority of this age group are working and are,thus,the backbone of social construction.Thus,they are more sensitive to the reception of external information,such as the spread of the pandemic.
Educational background is closely related to the behavior of preparing FEMKs.People with higher educational achievements are more likely to exhibit high levels of health literacy,pay more attention to the health status of family members,and know how to improve effective protective measures.Moreover,educational background has a positive impact on the behavior of preparing FEMKs.This result is in line with those of Lin et al[10].The higher the level of education,the better the public protective behavior.Furthermore,marital status is closely related to the behavior of preparing FEMKs as married residents maintain strong family consciousness and common behaviors.The proportion of respondents with reported infection among relatives and friends is relatively small.However,the rate of infection covers a wide range of cities based on national statistics.As such,this aspect warrants further study.
In this regard,FEMKs more attention should be paid to children and the elderly,specifically left-behind children and elderly living alone,when promoting the preparation of FEMKs among the public.Considering the differences between residents' educational background is necessary to implement targeted intervention[11]and to formulate reasonable and feasible measures for promoting FEMKs.
Analysis of influencing factors based on structural equation modeling
The study observed that only observability exerts a significant direct impact on the public's behavior regarding the preparation of FEMKs with the largest and positive direct effects.Furthermore,innovative characteristics have an effective impact on the public's behavior of preparing emergency medicine kits.To effectively transmit its signaling value,a decisive factor for the test results pertains to whether the signal can be observed[12],that is,observability or the degree by which others perceive innovative achievements[13].The visibility of FEMKs among residents greatly promotes their behavior of preparing such kits.
Moreover,personal risk perception has a significant positive impact on the public’s intention to prepare FEMKs.Risk perception has been defined as the public's perception of uncertainty and the adverse consequences of participation in activities[14,15].Emergency medicine kits can be used to ensure the health of family members.However,the duration of drug storage may cause expiration or even waste.However,in the special period of COVID-19,residents' awareness of the risk of the epidemic has been extremely greater than the risk of drugs.Thus,psychological factors may exert a significant impact on behavioral intention.The stronger the public's perception of external risk,the more positive the behavior toward preparing FEMKs.In this regard,various departments in the government should coordinate to focus on publicizing the advantages and convenience of FEMKs and to guide residents in preparing emergency medicine kits through a risk analysis of epidemic conditions.
Relative advantage,compatibility,and convenience of use can influence individual risk perception[16].Moreover,relative advantage,compatibility,and convenience of use can directly or indirectly influence the public's risk perception of COVID-19 and of emergency medicine kits.In this manner,the public's psychological state is altered.Thus,medicine kits can be brought into full play during the epidemic due to their advantages.On the one hand,the emergence of family medicine kits can reduce exposure to infection caused by going out to buy drugs.On the other hand,the short-term role of FEMKs can reduce the long-term preservation risk caused by drug placement.Based on these results,the weight of the risk of FEMKs is sharply reduced.Thus,the public is more inclined toward the health threats brought by the pandemic,and the perception of innovation characteristics on individual risk becomes positive.
Future studies should focus on strengthening the behavioral intention toward the preparation of FEMKs in daily life.To achieve this goal,a combination of traditional and network media can be used to focus on public medical places,such as hospitals and pharmacies,to effectively increase the demand of residents.Additionally,emergency medicine kit products should be designed to be simple and easy to understand,and various types and quantities of drugs should be provided for residents of different ages and nature of work.
Conclusion
Residents are undergoing a period of change(i.e.,from the contemplation to the preparation stage).Thus,innovative characteristics can directly influence the behavior or behavioral intention of preparing FEMKs by influencing the public's risk perception.In the future,studies should focus on publicity and education of the behavior of preparing FEMKs to increase the awareness of residents and effectively improve the FEMKs level of importance given to this behavior.
Deficiency and future prospect
The study discussed the influence of various dimensions of diffusion of innovation theory on the behavior of preparing FEMKs.However,the study holds certain limitations.First,the data are self-reported.Therefore,eliminating recall bias is difficult.Second,the conclusion of the study pertains only to the relationship between the dimensional factors of diffusion of innovation theory and the current behavior of residents toward the preparation of FEMKs due to the use of cross-sectional data.The entire process of the investigation occurred during the COVID-19 outbreak with distinct pertinence and timeliness,such that the environmental changes may have influenced the residents' behavior toward preparing FEMKs.In the future,the long-term effects of various dimension factors of diffusion of innovation theory can be analyzed by data tracking.
杂志排行
Psychosomatic Medicine Resesrch的其它文章
- Applying Cognitive Behavior Therapy to Patients with Lung Cancer
- The Relationship Between Uncertainty in Illness,State Anxiety,and the Life Satisfaction of College Students During the COVID-19 Epidemic
- Contrast-induced Encephalopathy after Endovascular Embolization of an Anterior Communicating Artery Aneurysm:Case Report and Literature Review
- Awareness and Attitudes Toward In Vitro Fertilization in Patients with Infertility:A Cross-Sectional Study
