Bioactivity Determination and Control Effect Evaluation of Three Plant Secondary Metabolites against Semiaphis heraclei
2021-02-26PanpanSunLuyaoHuangMinLiLongtaiJuYumengWuJiaLi
Panpan Sun,Luyao Huang,Min Li,Longtai Ju,Yumeng Wu,Jia Li
College of Pharmaceutical Science,Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Jinan 250355,China
Abstract[Objective]The paper was to clarify the bioactivity of trans-2-hexenal,oregano oil and thyme oil against Semiaphis heraclei and the synergistic effect of orange peel essential oil and organosilicon on the aphidicidal activity of the three agents.[Method]With S.heraclei,the dominant species of aphids in Lonicera japonica thunb.,as the test insect,the bioactivity and control effect were evaluated by the method of leaf dipping and foliar spraying.[Result]The indoor toxicity of thyme oil was the highest,with the LC50of 1.793 mg/L.Adding additives significantly increased the toxicity of the agents to S.heraclei.Among them,trans-2-hexenal+OSi,oregano oil+OSi and thyme oil+OSi had obvious synergistic effects,with the toxicity coefficients of 1.80,1.48 and 1.45,respectively.Field test showed that the corrected control effect of thyme oil was the highest after conventional spraying,and the toxicities of the three agents were higher than that of the control group at 7 d post spraying.Under the condition of 20% reduction of three agents and adding organosilicon,the control effect was increased by about 10% at 1 d post spraying,which was higher than that of the control group at 4 d post spraying,and reached over 98% at 14 d post spraying.[Conclusion]Thyme oil has the highest toxicity and control effect on S.heraclei.Three agents combined with organosilicon have the obvious effect of reducing the quantity and increasing the efficiency,which has the potential for further development.
Keywords Lonicera japonica;Semiaphis heraclei;Plant secondary metabolites;Additive
Lonicera japonica thunb.is one of the commonly used bulk medicinal materials[1],and its high quality and efficient cultivation is particularly important for the development of the traditional Chinese medicine industry.Aphid is an important pest that affects the yield and quality of L.japonica.Studies have found that Semiaphis heraclei is the main insect pest harming L.japonica in Shandong Province[2].Unreasonable use of chemical pesticides by farmers in pest control,such as exceeding the prescribed dose,high utilization frequency and single pesticide,leads to the increase of pesticide residues,resulting in soil and water pollution.How to develop green and efficient targeted pesticides has become a hotspot of current research[3].Plant secondary substances have a wide range of sources,diverse modes of action and low toxicity to non-target organisms,and their insecticidal active ingredients can be used as raw materials for the development of new pesticides[4].
Secondary substances in plants can poison or inhibit the growth,development and reproduction of phytophagous insects[5],while volatile substances produced by insect-infested plants also have certain effects on insects[6].In recent years,plant secondary substances have been extensively studied in the field of pest control.Hori[7]measured the toxicity of 10 plant essential oils against peach aphid,and thyme oil had the highest toxicity.Benellia et al.[8]found that oregano oil had insecticidal activity against peach aphid,with the LC50of 2.1 mL/L.Cheng et al.[9]reported that trans-2-hexenal has significant insecticidal activity against pinewood nematode,and significantly inhibited its oviposition,growth,development and reproduction.At present,no relevant studies on the control of these three plant secondary substances against S.heraclei have been found.Orange peel essential oil and organosilicon are often used as pesticide additives.Whether they have synergistic effect on the aphidicidal activity of three plant secondary substances has not been reported.
Therefore,the biological activities of trans-2-hexenal,oregano oil and thyme oil against S.heraclei were determined,and orange peel essential oil and organosilicon were selected to carry out synergistic test and evaluation of field control effect.The control effects of three plant secondary substances were compared with 1.3% matrine AS and 20% imidacloprid EC,to provide a basis for the development of novel botanical aphidicides.
1 Materials and Methods
1.1 Agents Trans-2-hexenal(purity≥98%),Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Technology Co.,Ltd.;oregano oil(88.3% carvacrol,2.5% thymol),thyme oil(phenol content ≥40%),Ji’an Guoguang Perfumery Plant;1.3% matrine AS,Shanxi Dewei Bencao Biotechnology Co.,Ltd.;20% imidacloprid EC,Hebei Yetian Agrochemical Co.,Ltd.;orange peel essential oil(OPEO),Anqiu Jinyinuo Biotechnology Co.,Ltd.;organic silicon(OSi),Hebei Shijiazhuang Zheng’an Agro-Science Co.,Ltd.;acetone,Tianjin Fuyu Fine Chemical Co.,Ltd.;Twin-80,Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co.,Ltd.
1.2 Materials The 3-year-old‘Damaohua’in Pingyi honeysuckle base in Shandong Province was selected,which had not been treated with pesticides before the test.S.heraclei was collected from‘Damaohua’without pesticide treatment in Pingyi base.
1.3 Indoor bioactivity assay The method of insect and leaf dipping was adopted[10]and slightly modified.The mother liquor of trans-2-hexenal,oregano oil and thyme oil was prepared with 2% acetone and 0.1%Twin-80.According to the activity range determined by the preliminary test,the mother liquor was diluted with sterile water into five different concentrations(Table 1).The wingless adult aphids with the same individual size were selected with a brush to the shoots of fresh,insect-free and harmless ‘Damaohua’,and the incision of ‘Damaohua’ shoot was wrapped with absorbent cotton soaked with sterile water and plastic wrap.After being dipped in the liquid for 5 s,the shoots with aphids were taken out immediately,and the excess liquid was blotted up with filter paper.Afterwards,the shoots were transferred to a petri dish(d=9 cm)which was then sealed with sealing film,and holes were punctured with insect needles to ensure air permeability.The aphids were arranged at the density of(40±5)individual/dish.2%Acetone was set as blank control,while 1.3% matrine AS and 20% imidacloprid EC were set as drug control.If the mortality rate in the 2% acetone control was greater than 20%,the trial should be repeated.All treatments were placed in the environment of temperature(25±1)℃ and relative humidity(60±5)%,and each treatment was repeated three times.After 24 h,the abdomen of insects was touched with a brush,and the insect was considered dead if there was no response.The number of dead and alive insects was recorded,and LC50of each agent was calculated.The agent with the smallest toxicity was taken as the standard agent to calculate the toxicity ratio.The toxicity ratio of an agent was the ratio of the LC50of the standard agent to the LC50of the agent.
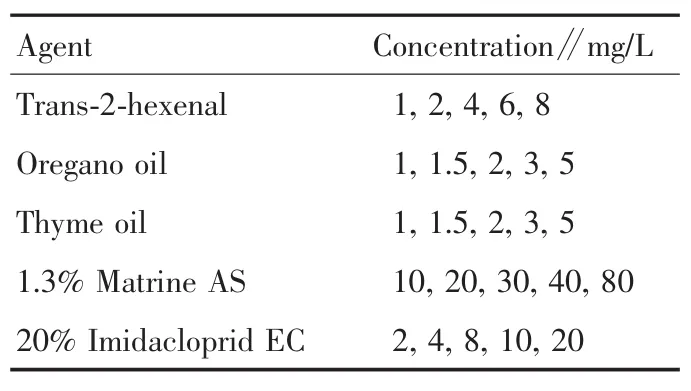
Table 1 Concentration of five agents
1.4 Synergistic effects of two additives and five agents on S.heraclei The OPEO and OSi(mass fraction)were added at the dose of 0.3% drug liquid,and OPEO and OSi control were designed.The determination method was the same as described in 1.3.If the mortality rate of OPEO and OSi was higher than 10%,the experiment should be repeated.The results were recorded,and the toxicity coefficient was calculated.Toxicity coefficient=LC50(single agent)/LC50(single agent+additive),and the synergistic effect of two additives on five agents were determined by the overlap of toxicity coefficient and 95% confidence interval[11].
1.5 Pot spraying test The field application concentration of agents was determined by pot spraying test,and the specific steps were as follows.When the potted ‘Damaohua’ in greenhouse grew to 6-10 leaves,each plant was inoculated with(20±5)individuals of S.heraclei,and covered with insect proof net.The number of insects was investigated after 24 h,and the aphids were supplemented if the number was not enough.When the number of insects was stabilized, agents were sprayed with a small hand-held sprayer.According to the results of pre-test and indoor bioactivity assay,the treatments were designed as follows:trans-2-hexenal 500 times and 650 times dilution(1.7,1.3 g/L),oregano oil 650 times and 850 times dilution(1.4,1.1 g/L),thyme oil 850 times and 1 000 times dilution (1.1,0.9 g/L);the concentrations of 1.3% matrine AS and 20% imidacloprid EC were determined according to the field recommended dose,which was 2.5 and 2 g/L,respectively.A pot of L.japonica was regarded as a treatment,and each treatment was repeated three times.And those sprayed with water were set as control.The number of survival aphids was recorded at 3,7 and 10 d post spraying,and the corrected control effect was calculated through the reduction rate of insects.

1.6 Evaluation of field control effect In the initial incidence period of aphids,agents were sprayed on April 23,a sunny day,in Pingyi honeysuckle base in Shandong Province.With water as the blank control,a total of 12 treatments were designed in the test,and each treatment was repeated three times.Each plot covered an area of 16 m2,with a total of 36 plots.1.3%Matrine AS and 20% imidacloprid EC were sprayed according to field recommended dose of the products,and the concentration of the rest was determined as follows according to the results of pot spraying test.
Conventional group:trans-2-hexenal 1.7 g/L,oregano oil 1.4 g/L,thyme oil 1.1 g/L,water consumption 20 L/667m2;1.3% matrine AS 2.5 g/L,20% imidacloprid EC 2 g/L,water consumption 30 L/667m2;water treatment was set as blank control.
0.3 % OSi treatment group:trans-2-hexenal 1.3 g/L,oregano oil 1.1 g/L,thyme oil 0.9 g/L,water consumption 20 L/667m2;1.3% matrine AS 2 g/L,20% imidacloprid EC 1.6 g/L,water consumption 30 L/667m2;water treatment was set as blank control.Ten plants of L.japonica were selected in each plot,and five-point sampling method was adopted to randomly select branches with a length of 15 cm and consistent growth from the five directions of east,south,west,north and middle of each plant and tagged.A 1 m protection line was set around the test area and between the plots respectively to prevent interference.The nozzle of manual sprayer was partial to the lower side of the plant,so that the positive and negative sides of the leaves were evenly wetted without liquid drops.The number of survival aphids was recorded at 0,1,4,7,10 and 14 d post spraying,and the corrected control effect was calculated.
1.7 Data processing The LC50and 95% confidence interval of agents were calculated by SPSS 21.0 software.The corrected control effect was converted to percentage,and the difference of field control effect was analyzed by Duncan’s new multiple range method.
2 Results and Analysis
2.1 Indoor bioactivity assay The results showed that thyme oil had the highest toxicity against S.heraclei with the LC50of 1.793 mg/L,12.88 times of that of 1.3% matrine AS and 2.44 times of that of 20% imidacloprid EC.The toxicity of trans-2-hexenal and oregano oil was 6.98 times and 11.99 times of that of 1.3% matrine AS,1.32 times and 2.27 times of that of 20% imidacloprid EC,respectively.The toxicities of the five agents against S.heraclei successively were thyme oil>oregano oil>trans-2-hexenal>20% imidacloprid EC>1.3% matine AS(Table 2).
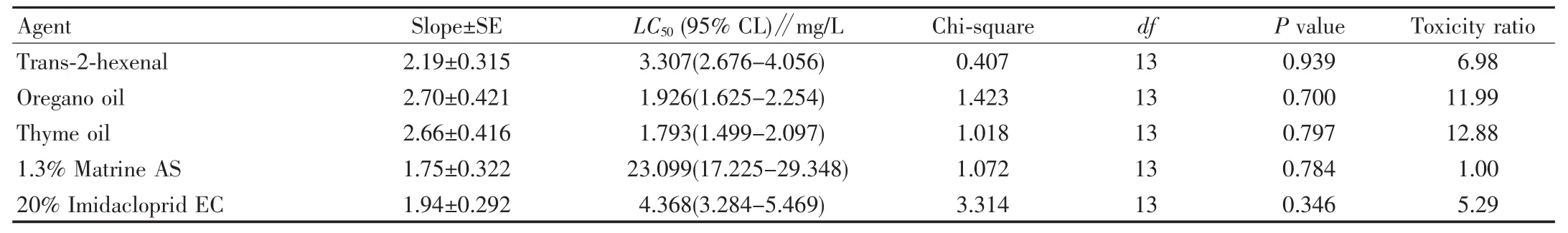
Table 2 Toxicity of five agents against Semiaphis heraclei
2.2 Synergistic effects of two additives and five agents on S.heraclei The toxicities of five agents against S.heraclei were enhanced by adding OPEO and OSi,and the LC50of trans-2-hexenal+OSi,oregano oil+OSi,thyme oil+OSi and 20% imidacloprid EC+OPEO were 1.835,1.300,1.240 and 2.021 mg/L,respectively.The 95% confidence interval did not overlap with the treatment without additives,indicating the synergistic effects were significant(Tables 2-3).The 95% confidence interval of 1.3% matrine AS with OPEO and OSi overlapped with that without additives,indicating that the two additives had no obvious synergistic effect on 1.3% matrine AS.

Table 3 Synergistic effects of two additives and five agents on Semiaphis heraclei
2.3 Pot spraying test Pot spraying test showed that when the concentrations of trans-2-hexenal,oregano oil and thyme oil were 1.7,1.4 and 1.1 g/L,the control effects on S.heraclei were still greater than 90% after 10 d.However,when the concentrations of trans-2-hexenal,oregano oil and thyme oil were 1.3,1.1 and 0.9 g/L,they had a good but slightly lower control effect on S.heraclei(Table 4).
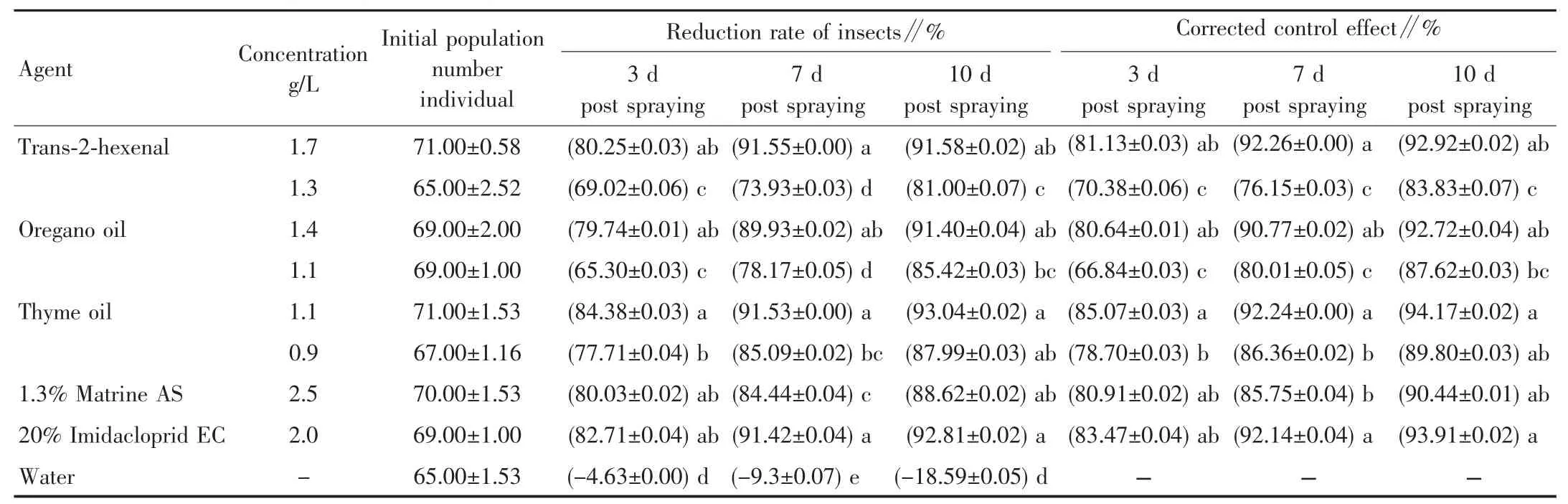
Table 4 Pot test of five agents against Semiaphis heraclei
2.4 Evaluation of field control effect The control effect of thymme oil was the highest at 1 d post spraying,and the corrected control effect was 70.67%,indicating good fast-acting property(Table 5).The control effects of thymme oil at 1 and 14 d post spraying were significantly higher than that of conventional treatment without additives(P<0.05).The trans-2-hexenal and oregano oil had poor fast-acting properties,and their effects on aphids were higher than that of conventional treatment without additives at 7 d post spraying,and decreased at 10-14 d post spraying.The control effects of the three treatments were increased by 10% at 1 d post spraying after OSi was added,which were gradually improved at 4-14 d post spraying and were slightly higher than those of other treatments(P<0.05).The control effect was still as high as 98% at 14 d post spraying,indicating that the addition of OSi improved the fast-acting property and persistence of plant secondary substances in the control of aphids.
3 Discussion
Water-soluble pesticides are difficult to be absorbed by leaves because of their waxy surface.There are cement layers and wax layers in the body wall of aphids,and it is difficult for the pesticide with weak permeability to enter the insect body through the epidermis of aphids,so the control effect is not ideal in practical application[12-13].The three plant secondary substances selected in this study are oily liquids with small molecules and strong permeability,which can easily penetrate through waxy leaves and destroy the body wall of aphids.Indoor toxicity assay showed that the toxicities of trans-2-hexenal,oregano oil and thyme oil against S.heraclei were significantly higher than that of 1.3% matrine AS,and was slightly higher than that of chemical pesticide 20% imidacloprid EC.However,the mechanism of action of these three plant secondary substances on S.heraclei should be further explored.
Pesticide additives have good wetting,extension and permeability properties[14],which improve the deposition amount of drug liquids on the target,make the drug liquids spread on the target and be easily absorbed,and directly destroy the wax layer of body wall of the target insects to improve the insecticidal activity of the agent,thereby achieving the effect of reducing the quantity and increasing the efficiency[15].It has been reported that d-limonene,the main ingredient in orange peel essential oil,has a significant synergistic effect on imidacloprid in the control of Aphis sp.[16].The addition of organosilicon significantly improves the control effect of chlorantraniliprole on Cnaphalocrocis medinalis[17].These two additives can increase the maximum retention and deposition of drug liquids on leaves by decreasing the surface tension of drug liquids,thereby playing a synergistic role.In this study,organosilicon had an obvious synergistic effect on three plant secondary substances.Whether the synergistic mechanism is consistent with previous reports needs further study.
The prices of trans-2-hexenal,oregano oil,thyme oil,1.3% matrine AS,20% imidacloprid EC and organosilicon were 2.0,0.6,0.4,0.12 and 0.05 yuan/mL,respectively.In the initial incidence stage of aphids,the mixture of three plant secondary substances and organosilicon could reduce the dosage of agents by 20%,and the control effect reached 98% at 14 d post spraying.Compared with 1.3% matrine AS and 20% imidacloprid EC,the water consumption was reduced by 33.33%,and the input cost was similar.In the later stage,the apidicidal active ingredients in oregano oil and thyme oil can be further mined,and mixed with botanical agents with high apidicidal activity.The preparation can be developed combined with the factors influencing control effect in the field,so as to realize more efficient,green and low-cost control against aphids.
杂志排行
植物病虫害研究(英文版)的其它文章
- Discussion on Fresh Agricultural Products Ordering and Preservation Strategy under New Normal Carbon Emission Constraint
- Green Prevention and Control Technology of Pests in Cotton Fields in Shandong Province
- Green Prevention and Control Technology against Main Diseases and Insect Pests of Facility Tomato
- Key Points of Prevention and Control Technology against Pear Powdery Mildew
- Mechanism and Application of Plant Rhizospheric Bacillus sp.for Growth Promotion and Disease Prevention
- Preliminary Investigation and Analysis of Alien Pests at Panjin Port
