Effects of progressive muscle relaxation therapy on Maintenance hemodialysis patients:a systematic review and meta-analysis
2021-02-23XiaoXiaoYangLuYaoHuoYuanYuanChenFanJieMeng
Xiao-Xiao Yang,Lu-Yao Huo,Yuan-Yuan Chen,Fan-Jie Meng
1Graduate college, Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 301600, China.2First Teaching Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine.3National Clinical Research Center for Chinese Medicine Acupuncture and Moxibustion.4College of Health Engineering,Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Tianjin 301600,China.
Abstract Objective:This study aimed to evaluate the effects of progressive relaxation therapy on patients with maintenance hemodialysis. Methods: A literature search was performed using PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, and Wanfang Data from inception to July 2020.Randomized controlled trials on the use of progressive muscle relaxation therapy in maintenance hemodialysis patients were selected.The primary outcomes were the depression and anxiety.Secondary outcomes included fatigue and sleep.Two reviewers proceeded study selection and quality assessment of included trials and performed heterogeneity of included studies before meta-analysis.Results:A total of 8 studies,which comprised a total of 668 participants were included in the final meta-analysis.The results showed that progressive muscle relaxation therapy could reduce the depression of patients(MD=-5.11,95%CI:-6.74 to-3.48,P<0.001),reduce the anxiety(SMD=-1.27,95%CI:-1.73 to-0.82,P < 0.001), relieve fatigue symptoms (MD = -0.87, 95% CI: -1.20 to -0.53, P < 0.001 ), improve the sleep quality(MD =-1.69, 95% CI:-1.95 to -1.42,P< 0.001).Conclusion:Progressive muscle relaxation therapy has positive effects on depression, anxiety, fatigue and sleep quality in patients with maintenance hemodialysis.While concurrent evidence is insufficient,and further studies of high quality are needed to strengthen the conclusion.
Keywords: Progressive Muscle Relaxation therapy, Maintenance hemodialysis, Depression, Anxiety, Fatigue,Meta-analysis
Background
End-stage renal disease (ESRD) is the terminal stage of various chronic renal diseases, which are the irreversible damage of renal function.In recent years,the incidence of ESRD in the world has gradually increased, which has become a public health problem that seriously endangers human health and increases the economic burden [1, 2].Global Burden of Disease study finds that between 100 and 2,500 people per million people worldwide have ESRD [3].At present,only renal replacement therapy (RRT) can relieve and treat ESRD clinically, RRT includes kidney transplant and dialysis treatment.Due to the lack of kidney source, the high cost and complications after kidney transplantation, hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis have become one of the main methods of replacement treatment for patients with end-stage renal disease [4].Patients with maintenance hemodialysis (MHD) are prone to a variety of psychological disorders due to various conditions such as disease status and economy[5].Anxiety and depression are the most common and important mental disorders among hemodialysis patients, with adverse effects on the course of disease[6].It is estimated that the incidence of depression in maintenance hemodialysis patients is 30%–70%, and the incidence of anxiety is 25%–70%, its incidence is much higher than that of the general population [7, 8].However, depression easily leads to sleeping disorder in patients.According to the survey, the incidence of sleep disorder was 40% to 85%, insomnia can lead to circadian disorders, high blood pressure, high blood sugar and decreased body immunity [9].It seriously affects the health and easily leads to fatigue of dialysis patients.The prevalence of reported fatigue among the patients undergoing chronic hemodialysis is 60%–97%[10].Depression and anxiety can damage the physical and mental health of ESRD patients,reduce the quality of life, affect the outcome of the disease, and increase the hospitalization rate and mortality.With the progress of dialysis technology, the survival time of MHD patients is continuously prolonged and their quality of life becomes increasingly important [11].However, there is no effective solution to the adverse emotions and fatigue of maintenance hemodialysis patients currently.If long-term application of drug treatment, patients will not only become dependent on drugs and have other adverse reactions, but may further increase the renal burden.Therefore, it is very important to take effective non-drug interventions to reduce the negative emotions of hemodialysis patients and relieve their fatigue symptoms.
In recent years, progressive muscle relaxation therapy has been applied in the clinical treatment of a variety of psychosomatic diseases, which have been proved to be effective in improving physiological functions and reduce negative emotions [12, 13].Moreover, the UK’s National Institute of Health and Care Optimization treatment guidelines recommend psychological intervention as first-line treatment before medication.In psychological intervention,progressive muscle relaxation therapy is widely studied and considered to be an effective option for treating adverse emotions [14].Progressive muscle relaxation therapy as a method of stress management,it is through repeated retraction and relaxation of the muscles to reduce the skeletal muscle tension and sympathetic nerve excitability,to combat the emotional disorder caused by psychological stress,and to achieve the purpose of mental relaxation[15,16].
Studies have shown that progressive muscle relaxation therapy can improve depression and anxiety in patients with maintenance hemodialysis, and improve fatigue and sleep quality.However, it has not been confirmed by systematic reviews.Therefore, the purpose of this study was to conduct a systematic literature search and critically analyze the available evidence to evaluate the effect of progressive muscle relaxation therapy on alleviating negative mood,fatigue and sleep quality in patients with maintenance hemodialysis.
Methods
Inclusion criteria
Types of study.Randomized controlled trials (RCTs)and pilot studies that applied a randomized controlled design.Non-Chinese and non-English language studies were not included.
Types of participants.Hemodialysis patients aged ≥18 years with dialysis duration ≥3 months, no limit in the primary disease.Patients with other mental illnesses and those taking other anti-depression and anxiety drugs were excluded.
Types of interventions.The intervention group was treated with progressive muscle relaxation therapy combined with conventional therapy, while the control group was treated with conventional therapy, such as routine clinical monitoring or psychological nursing,etc.Progressive muscle relaxation therapy: the patient recumbent with feet wider than shoulder-width apart,put arms on both sides of the body, palms up, the instructor instructs the patient to take a deep breath in a gentle, slow, quiet tone, and tighten the muscle group 10 s–15 s,relax the muscle group 15 s–20 s,the whole group of 16 muscle group, that is, from bipedal, on to the legs, thighs, hips, waist, abdomen, chest, neck,shoulders, arms, hands, face one by one, complete,focus on each group of muscle contraction and relaxation feeling.Outcome assessment must include one or more of depression, anxiety, fatigue, and sleep quality scores.
Types of outcome measures.Main outcomes:Self-rating Depression Scale(SDS)were used to assess the level of depression; Self-rating Anxiety Scale(SAS), Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HARS) were used to assess the level of anxiety.Secondary outcomes: Revised Piper Fatigue Scale (RPFS) were used to assess the level of fatigue; Pittsburgh sleep quality index(PSQI) were used to assess the quality of sleep.
Search methods
We searched the following electronic databases from inception to July, 2020: PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library,China National Knowledge Infrastructure, and Wanfang Data.The following search terms were employed: “progress* muscle relax*”, “progress*relax*”, “progress* relax* train*”, “progress* muscle relax*”, “renal dialys” “hemodialys*”, “extracorporeal dialys*”, “haemodialys*”, “maintained hemodialys*”,“hemotodialys*”, “blood dialys*”, “HD”, “MHD”.Take PubMed as an example, the specific retrieval strategy is shown in Table 1.
Data extraction
Two researchers independently extracted data from the included trials using standardized data extraction tables,including year, author, country, sample size, patient baseline characteristics, treatment duration,interventions and outcomes.Any differences were resolved through discussion.
Risk of bias assessment
The risk of bias in the included studies was assessed by 2 researchers using the Cochrane Collaboration Risk of Bias Tool, for risk assessment of bias in RCTs.Seven items were included: generation of random order,concealment of random scheme allocation, blind method for research objects and intervention implementers, blind method for outcome evaluators,
integrity of outcome indicator data, possibility of selective reporting of research results, and other sources of bias.The evaluator should make a low bias risk, high bias risk and unclear judgment for each project.
Statistical analysis
RevMan 5.3 software was used for meta-analysis of the data.Firstly, the χ2test was used to test the heterogeneity between literature results.If the test results were P > 0.1 and I2< 50%, the fixed effect model was used for meta-analysis.If P<0.1,I2≥50%,and no clinical heterogeneity was determined, the random effect model was used for meta-analysis.If the source of heterogeneity could not be determined,descriptive studies were used.For continuous data, if the results obtained by the same measuring tool are adopted, the difference in mean is used as the effect analysis statistics.If different measurement tools are used for the same variable, standardized mean difference (SMD) is used as the effect analysis statistic.
Results
Study selection and inclusion process
Through database search, a total of 1,088 potentially relevant studies were identified.Of those, 186 articles were duplicated.Of the remaining 902 articles, 845 were excluded by reading the title and abstract filters.In the remaining 57 articles, through searching and reading the full text, excluding non-randomized controls and research data to obtain fruitless clinical trials, 8 articles were finally included.These 8 articles included a total of 668 patients.Details of the selection process were illustrated in Figure 1.

Table 1 PubMed retrieval strategy

Figure 1 Flowchart of the study
Study characteristics
The included studies were published from 2017 through 2019.The major publishing countries are China (n = 6), Indonesia (n = 1), and Turkey (n = 1).The total duration of the intervention ranged from 4 to 8 weeks, with each intervention lasting from 15 minutes to 40 minutes and the number of interventions per week ranges from 2 to 14.Characteristics of included studies are summarized in Table 2.Most of the patients included in this study were male.The average age of the patients was about 50 years old and the dialysis time varied from 1 to 3 years.There was no incidence of mental illness and the patient's acceptance of dialysis treatment is more acceptable.
Risk of bias assessment
The bias risks of the included studies are shown in Figure 2.Each study reported that patients were randomly divided into experimental and control groups,but only two studies provided details of the randomization process [21, 22].None of the 8 studies reported allocation concealment.With regard to selective reporting bias, we judged that expected outcomes were stated in all trials.
Efficacy analysis
Depression.Four articles reported depression symptoms .Results of the heterogeneity test were (P=0.07,I2=58%).Meta-analysis using the random effect model showed that the progressive muscle relaxation therapy group improved patients’ depression mood better than the control group, with statistically significant differences (MD = -5.11, 95% CI (-6.74,-3.48),P<0.001)(Figure 3).
Anxiety.Six articles reported anxiety symptoms.SMD was used to standardize the study results.The heterogeneity test results were (P<0.001, I2=81%).Heterogeneity exists between studies, excluding clinical heterogeneity.Meta-analysis using a random effects model showed that the progressive musclerelaxation therapy group improved patients’ anxiety mood better than the control group, with a significant difference (SMD = -1.27, 95% CI (-1.73, -0.82), P <0.001)(Figure 4).Since this study used different scales for measurement, subgroup analysis was used for different scales.Five of the articles used SAS, random effect model results showed that the progressive muscle relaxation treatment group was better than the conventional treatment group in improving anxiety,the difference was statistically significant (SMD = -1.43,95% CI (-1.84, -1.02), P < 0.001); one article used HARS, random effect model results showed that the progressive muscle relaxation treatment had better effects in improving anxiety than the conventional treatment group, the difference was statistically significant(P=0.03).

Table 2 Characteristics of the included studies.
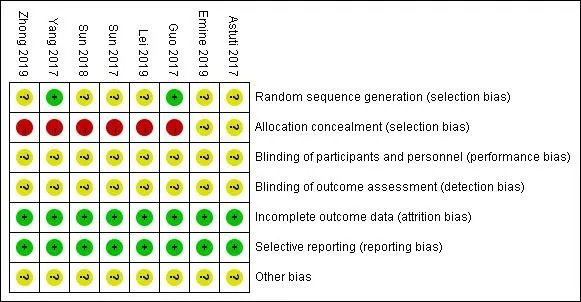
Figure 2 Risk of bias summary.

Figure 3 Forest plot for relaxation therapy on depression

Figure 4 Forest plot for relaxation therapy on anxiety

Figure 5 Forest plot for relaxation therapy on fatigue

Figure 6 Forest plot for relaxation therapy on sleep
Fatigue.Five articles reported symptoms of fatigue in patients.The heterogeneity test results were(P=0.008,I2= 71%).Heterogeneity exists between studies,excluding clinical heterogeneity.Meta-analysis using a random effects model showed that the progressive muscle relaxation therapy group improved patients’fatigue state better than the control group, with a significant difference (SMD = -0.87, 95% CI (-1.20,-0.53),P<0.001)(Figure 5).
Sleep.Six articles used PSQI to evaluate sleep.The heterogeneity test results were (P = 0.31, I2= 17%).Meta-analysis using the fixed effect model showed that the progressive muscle relaxation therapy group improved patients' sleep better than the control group,with statistically significant differences (MD = -1.69,95%CI(-1.95,-1.42),P<0.00001)(Figure 6).
Discussion
Our review of the literature shows that progressive muscle relaxation therapy has been an important research topic in the field of mood, fatigue and sleep relief in maintenance hemodialysis patients.Progressive muscle relaxation technique makes the body consciously tense and relax muscles in accordance with a certain order, so that the individual enters a relaxed state.Thereby,the purpose of relieving psychological tension and reducing physical and mental fatigue is achieved[25,26].Progressive muscle relaxation training can reduce the muscle tension of the body skeletal muscle, make body and mind produce euphoric feeling,regulate the psychological function of the human body, and then reduce the anxiety level of patients,improve fatigue[27].The high treatment cost,long time, many complications and physiological discomfort brought to patients by long-term hemodialysis will have a negative impact on patients'mood, resulting in depression, anxiety and other adverse emotions [28].However, negative emotions can not only directly affect the patient's sleep, but also indirectly affect the patient's sleep by enhancing the inflammatory response and its secondary cardiopulmonary dysfunction, which further aggravates the patient's fatigue [29].Patients with maintenance hemodialysis master relaxation training under the guidance of professionals.Through repeated practice, they learn to consciously control their own psychological and physiological activities, so as to produce a relaxed state, so that the vagus nerve and sympathetic nerve activities are in a good balance state,which can improve the body's ability to resist stress,and adjusts the psychological and physiological dysfunction caused by stress, thereby improving the patient's bad mood, sleeping quality, and alleviating the patient's fatigue[30,31].
Upon the pooled analysis of all the studies, we found that patients utilizing progressive muscle relaxation techniques experienced a statistically significant as compared to individuals receiving usual nursing care.Studies have shown that depression and anxiety are closely related to the prognosis of maintenance hemodialysis patients.The more severe the degree of depression and anxiety, the worse the prognosis.Therefore, reducing the negative emotions of patients can significantly improve the fatigue and prognosis of patients.Progressive muscle relaxation training is applied more in clinic, itself belongs to a kind of body exercise, its theory thinks individual mood contains “body” and “mood” two parts, it not only can change the response of the body, but also can change the mood[32].Therefore, the patient consciously controls muscle activity, which can relax emotions indirectly, conducive to relieving negative emotions such as anxiety, fear, depression, and establishing a relaxed mood.Progressive muscle relaxation training improves the quality of life by improving the sleep quality of patients, alleviating negative emotions, regulating psychological functions,and alleviating fatigue symptoms.Progressive muscle relaxation techniques as a non-pharmacological intervention have been widely used in the clinical treatment of anxiety and pain relief.Progressive muscle relaxation technique as a non-pharmacological intervention has been widely used in clinical treatment of adverse mood and pain relief.Ju WX [33] found that progressive muscle relaxation therapy applied to abdominal surgery patients was effective for postoperative pain relief, Kim [34] et al.found that progressive muscle relaxation therapy applied to anxiety patients could significantly improve anxiety symptoms.
This review has several limitations.The strength of any meta-analysis to a certain extent depends on the homogeneity and quality of the studies included.A number of factors limit our reviews ability to draw strong conclusions for progressive muscle relaxation therapy.Firstly, in this study, only published Chinese and English literature were retrieved, which may lead to publication bias due to incomplete literature collection.Secondly, the content, frequency and duration of each intervention are not consistent, which may have a certain impact on the outcome of the merger and generate a certain risk of bias.Duration of intervention was short, ranging from 4 weeks to 8 weeks, making the long-term effect of MHD patients unknown.Thirdly,most of the included studies showed poor methodological quality based on the Cochrane Collaboration risk bias tool.To some extent, the credibility of the research results was affected;suggests future researchers should strictly ensure the quality of clinical trial methodology, pay attention to the implementation of the scheme of hidden especially blinded, avoid to produce selection and measurement bias.Fourth, due to the insufficient number of trials included in each result, publication bias was not assessed.
Conclusion
The purpose of this study was to determine the efficacy of progressive muscle relaxation therapy in patients on maintenance hemodialysis.The results of this meta-analysis provide evidence that progressive muscle relaxation therapy can reduce anxiety,depression, improve sleep quality and fatigue in maintenance hemodialysis patients.Progressive muscle relaxation training provides a low-cost, low-risk intervention for maintenance hemodialysis patients and is easily accepted by patients, which is worthy of promotion and application in clinical practice.At the same time, more centers, large samples and high-quality randomized controlled trials should be conducted in the future to provide further evidence-based evidence for clinical practice.
