A systematic review on the neuropharmacological activities of Oligosaccharide ester in Polygalae Radix
2021-02-04JieZhangChuanxinLiuYuluLiangYihongLiChenningZhangJianmeiHuang
Jie Zhang,Chuanxin Liu,Yulu Liang,Yihong Li,Chenning Zhang,Jianmei Huang*
1 Beijing University of Chinese Medicine,School of Chinese Materia Medica,Beijing,China.
Abstract Polygalae Radix,which has a long history of medical use in traditional Chinese medicine,is multifunctional such as tranquilize mind,relieve swelling and remove phlegm.It has been demonstrated that Polygalae Radix oligosaccharide ester is the main active component which excutes the neuropharmacological activities like antidepression,anti-dementia and neuroprotection.In this review,the chemical structure,pharmacology,pharmacokinetics and processing mechanism of Polygalae Radix oligosaccharide ester are summarized so as to provide reference for its further development and utilization.
Keywords: Polygala Radix,Oligosaccharide ester,Chemical structure,Pharmacology,Pharmacokinetics,Processing
Background
Polygalae Radix(PR) is the dry root ofPolygala tenuifoliaWilld.andPolygala sibiricaL..PR has the functions of tranquilizing the mind,benefiting wisdom,reducing swelling and removing phlegm,commonly used to treat insomnia,dreamlessness,forgetfulness,palpitations,trances,phlegm cough,carbuncle and swelling toxin,sore breasts and so on.In recent years,scholars have conducted a lot of studies on PR,showing that the main components of PR include saponins,oligosaccharide esters (OEs),xanthones,alkaloids,organic acids,polysaccharides and flavonoids,etc [1].Saponins have a variety of activities such as sedation [2],hypnosis [3],anti-dementia [4],anti-depression [5],anti-oxidation [6],analgesic,expectorant [7],antibacterial and anti-inflammatory [8].OE has been reported to have antidepressant [9],antidementia [10] and neuroprotective [11] effects.Xanthones have antitumor [12] and antimutagenic [13]activities.
In recent years,the neuropharmacological activity of OE has received increasing attention.Pharmacological studies have shown that OE isolated from PR has antidepressant,antidementia and neuroprotective effects [14].This paper reviews the current status of research on the chemical structure,pharmacological activity,pharmacokinetics and processing transformation of OE.It also provides a reference for the further development and application of OE.
Chemical structure
OE is highly abundant in PR and is related to the neuroprotective effect of PR.The structure of OE is an ester formed by combining sucrose or oligosaccharides(sucrose linked to glucose or rhamnose,forming oligosaccharide through glycosidic bonds) with organic acids (including acetic acid,cinnamic acid,benzoic acid and their derivatives),while the molecule contains no more than five monosaccharides.Up to now,more than 100 kinds of OE have been isolated and identified from family Polygalaceae.PR mainly contains more than 40 kinds of OE,including Tenuifoliose A~Q,Tenuifoliside A~E,Sibiricose A1~A7,3,6’-disinapoylsucrose (DISS),etc.The parent nucleus and substituents of OE in PR are shown in Figure 1 and the structures are shown in Table 1.
Pharmacology
Previous studies on OE isolated from PR revealed its effects on the nervous system,including antidepressant,antidementia,neuroprotective effects.The main neuropharmacological effects of OE are listed in Table 2.Among them,DISS,Sibiricose A5 and Sibiricose A6 have good antidepressant effects,especially DISS.Tenuifoliside B is the main active ingredient in enhancing cognitive function.Tenuifoliside C and Tenuifoliside A have neuroprotective effects.
Antidepressant effect
Depression is a mental disorder characterized by marked and persistent depression.There are currently more than 300 million people worldwide who suffer from depression.Depression has became the psychiatric disorder with the highest rate of disability and mortality [23].In modern pharmacology,OE isolated from PR has good antidepressant effects by mechanisms involving 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)and (-)-noradrenaline (NE) nerve function,hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis (HPA) function,and oxidative stress.
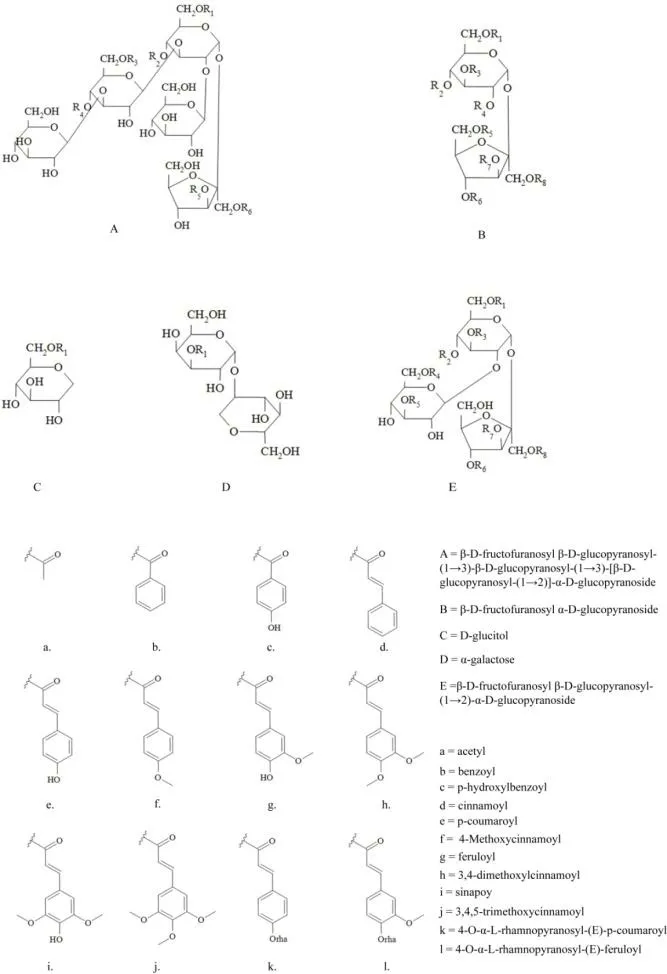
Figure 1.Parent nucleus and substituents of OE isolated from PR
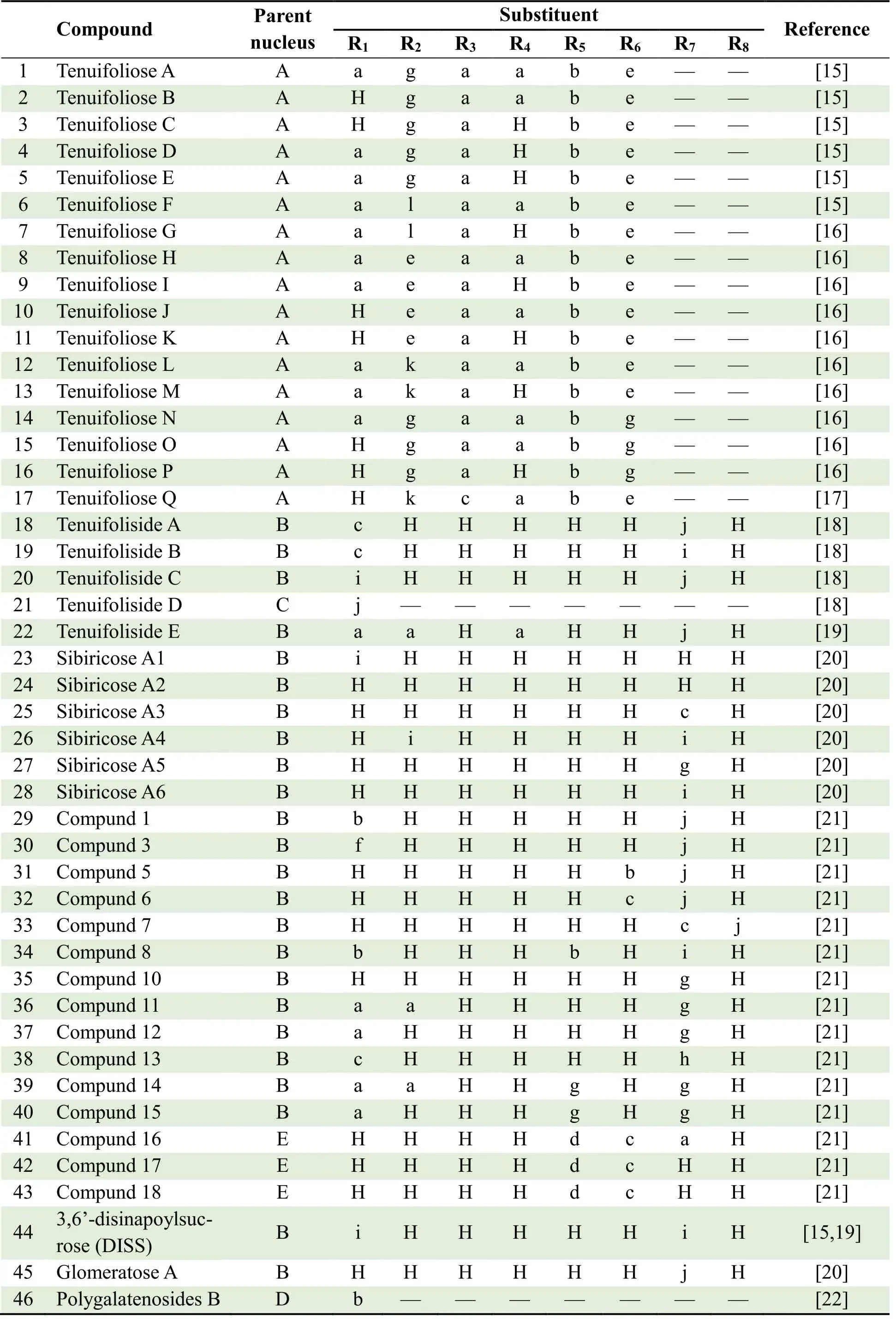
Table 1.OE isolated from PR
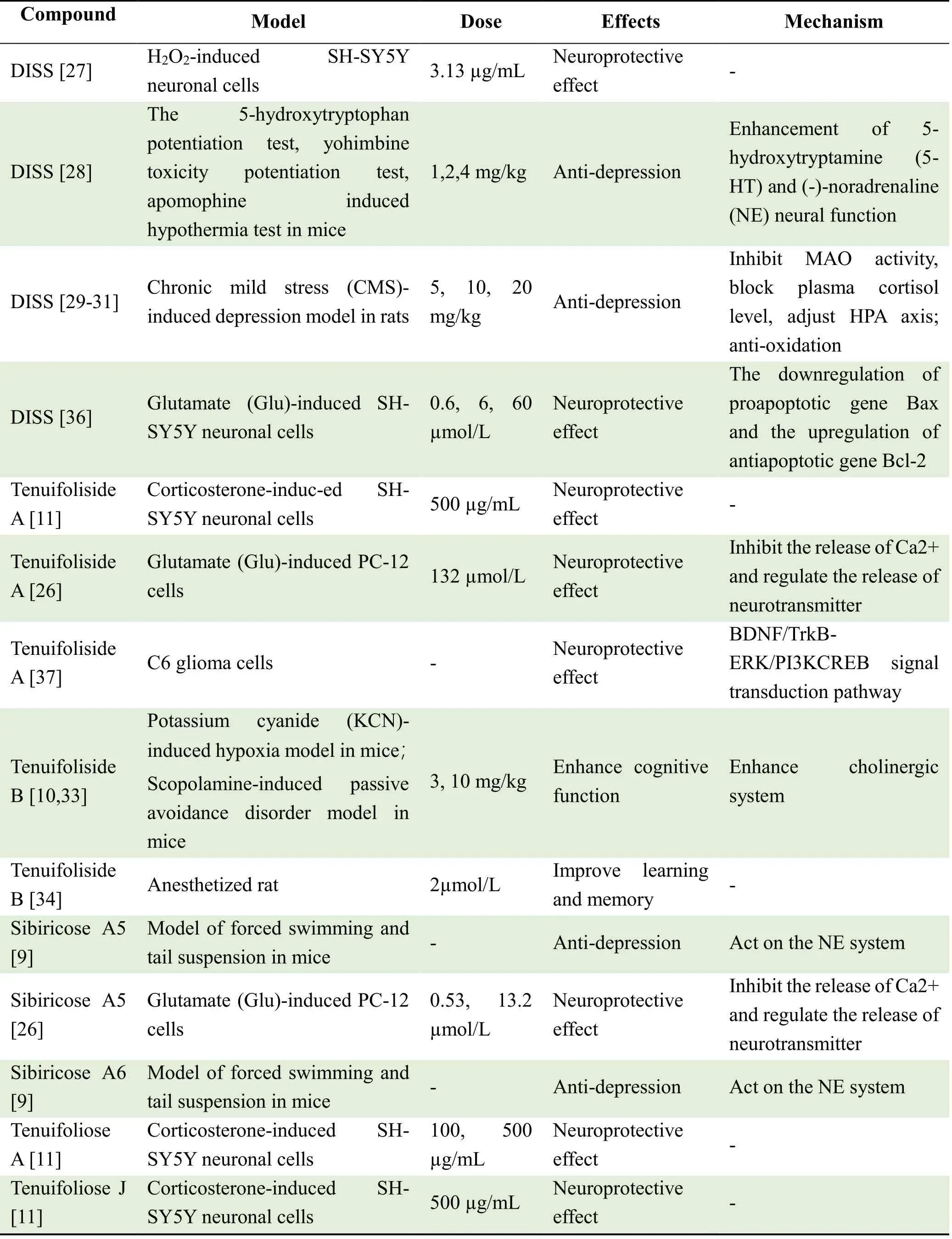
Table 2.Pharmacological effects of OE
Studies have shown that the extracts of YZ (Yuanzhi,or PR)-30% and YZ-50% ,which are rich in OE,can significantly improve the depressive state of mice and reduce their immobility time in tail suspension and forced swimming tests [9].Further study on YZ-50%showed that it antagonized the increase of CRH,ACTH and COR in the serum of Chronic Stress Depression Model Rats [24].In addition,YZ-50% can also promote the repair of damaged neurons by upregulating the expression of BDNF and TrkB mRNA,resulting in antidepressant effect [25].Sibricose A5 and Tenuifoliside A protect PC12 cells from glutamateinduced injury,and whether the mechanism is to regulate the release of neurotransmitters by inhibiting intracellular Ca2+release remains to be further explored[26].
DISS is the most abundant OE isolated from PR,with outstanding antidepressant activity [27-31].The antidepressant activity of DISS may be associated with enhanced 5-HT and NE neurological function,which enhances 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP)-induced headshaking behavior in mice,potentiates the toxicity of yohimbine (YOH),and antagonizes the hypothermia of mice induced by apomophine (APO) [28].It was shown that DISS significantly reduced the levels of CORT,CRH and ACTH in the serum of chronically stressed rats and also increased the mRNA expression levels of glucocorticoids and NR3C2 [29].On the other hand,DISS inhibited the activity of MAO-A and MAO-B,decreased Malondialdehyde (MDA) levels,and enhanced Superoxide dismutase activity in rats [30].These findings suggest that DISS may mediate antidepressant effects through the HPA axis,MAO,and oxidative system.In addition,DISS increased the mRNA and protein levels of cell adhesion molecule L1(CAM-L1),cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element binding protein (CREB) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the hippocampus of CMS rats.These NE-regulated plasticity genes and neurotrophic factors are involved in synaptic plasticity and neuronal growth,and their increased expression may be one of the molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying the antidepressant effects of DISS [31].
Anti-dementia effect
Dementia is a group of syndromes in which cognitive impairment is the main clinical manifestation.Most patients are accompanied by psychiatric-behavioral abnormalities.Cognitive Impairment and behavioral abnormalities eventually lead to occupational impairment and decreased social functioning of patients,as well as a huge economic burden on society[32].In recent years,OE isolated from PR has been reported to have anti-dementia effects,of which Tenuifoliside B is considered to be the main active ingredient in enhancing cognitive function.Ikeya [10]and Fumito [33] found that Tenuifoliside B had a protective effect against KCN-induced hypoxia in mice,and also improved scopolamine-induced passive avoidance behavior in rats,a process that may be accomplished by enhancing the cholinergic system.Li et al.[34] found that Tenuifoliose B and Tenuifoliose C enhanced basal synaptic transmission in the dentate gyrus of anesthetized rats,thereby improving their learning and memory functions.In addition,OE isolated from PR attenuated oxidative damage and improved learning and memory in aging mice,which may be related to the regulation of AKT-CREB phosphorylation,thus increasing the expression of the downstream product BDNF [35].
Neuroprotective effect
In 2012,Huang et al.[11] found that Tenuifoliside A,Tenuifoliose A and Tenuifoliose J significantly protected corticosterone-induced SH-SY5Y neuronal cells and suggested that the protective effect of these compounds on neuronal cells may be related to the parent nucleus structure,type and location of subunits.Acetyl substitution may reduce the neuroprotective effect of OE,while ferulic acid substitution may enhance the neuroprotective effect.Yuan et al.[36]showed that DISS could attenuate glutamate-induced SH-SY5Y neuronal damage by inhibiting LDH release with a dose-dependent effect,and the possible mechanisms include up-regulation of the anti-apoptotic gene Bcl-2 and down-regulation of the pro-apoptotic gene Bax.Zhao et al.[37] found that Tenuifoliside A may exert neuroprotective effect in C6 glioma cells through the BDNF/TrkB-ERK/PI3KCREB signal transduction pathway.OE isolated from PR significantly attenuated Aβ25-35-induced damage in SH-SY5Y cells,which may be related to the reduction of oxidative stress,the regulation of AKT-CREBBDNF signaling pathway and inhibition of apoptosis[34].
Pharmacokinetics
Kawashima et al.[38] found that Tenuifoliside A and Tenuifoliside C were absorbed into the blood after the production of 3,4,5-trimethoxycinnamic acid (TMCA)by the action of intestinal microorganisms,and that TMCA had a sedative effect in a stress-induced rat model.Another study also found that TMCA and TMCA-CH2were the metabolites of DISS,Tenuifoliside B,Sibiricose A1,Sibiricose A6,and arillanin A.TMCA was easily absorbed through rat gastrointestinal cell membranes and its bioavailability was high [39,40].
Metabolites in plasma and bile after intravenous injection (i.v.) of DISS in rats were analyzed by LCMS/MS.The metabolites of DISS in vivo were mainly its isomers,and phase I metabolites included demethylated DISS and sinapic acid,and phase II metabolites were mainly sulfated isomers and glucuronide isomers at low levels [41].Analysis of plasma and urine after intragastric administration (i.g.)to rats showed that the OE containing sinapic acid was the active component of PR.The results showed that the main metabolites of DISS in rat feces included dehydroxylated hydrogenation products,reduced hydrogenation products,hydroxylmethylation products and ester bond cleavage products,the metabolites of DISS in plasma included TMCA,and the metabolites of DISS in urine was 3-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxy)propionic acid [42].
A similar study showed that DISS was detected in plasma,bile,liver,kidney,heart,cerebrospinal fluid and brain tissue of SD rats after oral administration of methanolic extract of PR.TMCA was detected in rat liver,bile and fecal samples,suggesting that biotransformation of DISS occurred in the liver [43].Rats were intraperitoneally injected with DISS,Tenuifoliside A and Tenuifoliside B.Urine samples were collected and analyzed for metabolites.The results revealed that ester bond cleavage,glucuronidation and acyl migration were the main metabolic pathways of these three components.Sibiricose A6 is not only the main metabolite of DISS,but also one of the main OEs in PR [44].As an example,the putative metabolic pathways of DISS is shown in Figure 2.
At present,studies on OE isolated from PR are very limited,and experimental data on the pharmacokinetics of many monomers are still lacking,making it difficult to judge the developmental value of the monomer composition.Further studies on the absorption,distribution,metabolism and excretion of OE in vivo is of great significance for its rational development and utilization.
Processing transformation
The original plant of PR has the toxic effect of "halberd throat" and the main toxic components of PR are saponins.PR can be processed to reduce the toxicity and improve its therapeutic effect.Commonly used processing methods include core-removing,honey frying and licorice juice boiling.The PR processed with licorice juice enhances the effect of tonifying spleen,benefiting the Qi,tranquilizing mind and improving intelligence,while the honey-processed PR mainly strengthens the effect of moistening lung and resolving phlegm [45].It was found that the ester bond of OE was easily hydrolyzed and broken when heated with water,resulting in a decrease in OE content but an increase in Sinapic,Ferulic and p-coumaric acids [46-50].Whether the enhanced tranquilizing effect of PR is related to the hydrolysis of OE needs further study.
The content of OE showed different trends after processing with honey and boiling with licorice juice.The contents of Sibiricose A5,Sibiricose A6,DISS and Tenuifoliside B were significantly decreased,while the content of Glomeratose A was increased in PR prepared by licorice juice.Compared with the original plants,the contents of Sibiricose A6 and Glomeratose A in the honey-processed PR significantly increased,but the contents of the other three components decreased.The increase of Sibiricose A6 content may be related to the hydrolysis of Sibiricose A6-containing structures such as DISS [46].The transformation mechanism of OE in PR after processing with licorice juice was analyzed by simulated processing techniques.The results are shown in Table 3.
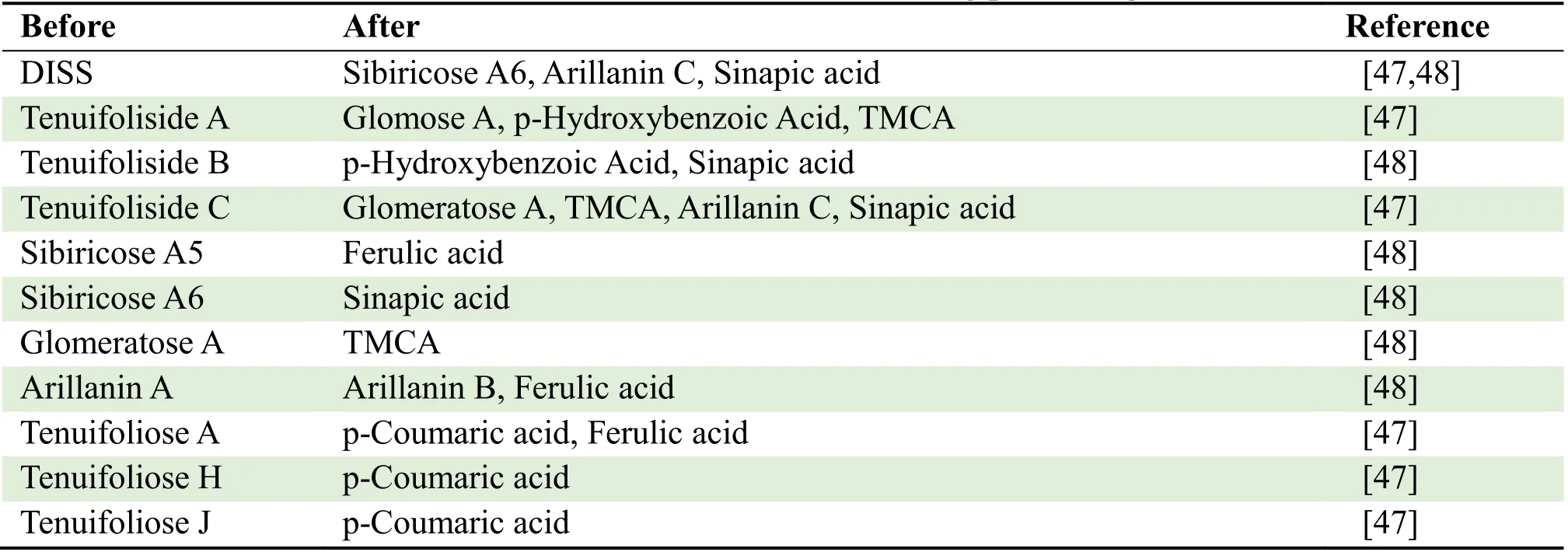
Table 3.Transformation of OE during processing
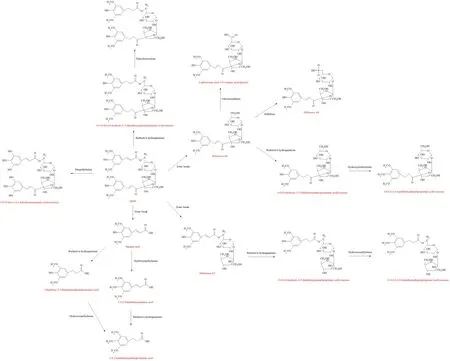
Figure 2.Putative metabolic pathways of DISS
Conclusion
PR,as a commonly used Traditional Chinese Medicine,has a long history of medicinal use and high medicinal value.Modern studies have shown that OE isolated from PR has neuropharmacological activities of antidepression,anti-dementia and neuroprotection,and has good prospects for development.Current studies have focused on the chemical structure and pharmacological activity of OE.There is still a lack of experimental data on the pharmacokinetics of many OE monomers,so it is difficult to judge the development value of the monomeric components.Further studies on the metabolic properties of OE isolated from PR and its metabolic processes in vivo using pharmacokinetics methods will be helpful for further evaluation and development of PR.
杂志排行
TMR Modern Herbal Medicine的其它文章
- The therapeutic efficiency of ursodeoxycholic acid on Gilbert syndrome complicated by aplastic anemia: a series of case reports
- Speech on the evidence-based traditional Chinese medicine research 20th anniversary conference
- The active ingredients of Huanglian Jiedu Decoction in treating COVlD-19 based on network pharmacology,molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation
- Study on the mechanism of Fructus Forsythiae and Folium Nelumbinis on acute pharyngitis based on network pharmacology
- Shiqi herbal tea reduces the susceptibility to H1N1 influenza virus in stressed mice.
- Uncovering the multi-target pharmacological mechanism of Xuebijing injection against sepsis by a systems pharmacology approach
