Analysis of 54 cases of COVID-19
2021-01-12WeiYiYangZhenLeiRanRanWangLiQinYingBi
Wei-Yi Yang,Zhen Lei*,Ran-Ran Wang,Li Qin,Ying Bi
1Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong 637000, China.2Wuhan Red Cross Hospital, Wuhan 430021,China.
Abstract Objective: The clinical features and test results of 2019-nCoV pneumonia (COVID-19) were analyzed retrospectively in order to understand the diagnostic significance of clinical test index, and to summarize the experience of clinical treatment.Methods:From February 10thto February 28th,2020,54 patients with COVID-19 from Wuhan Red Cross hospital were included, whose clinical data were analyzed and integrated.The clinical manifestation and laboratory examination were analyzed by descriptive statistical analysis. Results: The average age of the patients was 63.9 years (40-84 years).The median time from onset to diagnosis was 6.5 days (2-20 days),and the median time from onset to first hospitalization was 8 days(3-20 days).The main manifestations were that the percentage of neutrophil increased and the number of lymphocyte decreased in most cases.Most of them were combined with liver damage and myocardial cell damage, and chest CT showed lesion of bilateral lung.Conclusion: In addition to the nucleic acid test of 2019-nCoV, some laboratory tests may indicate COVID-19 in the early stages.The clinician may conduct repeated follow-up examinations to assess the progress and outcome of the disease.
Keywords:COVID-19,Clinical manifestation,Laboratory examination,Diagnostic significance,Follow-up
Background
Novel coronavirus pneumonia (NCP) refers to pneumonia caused by the infection of the new type of coronavirus(2019-nCoV).The outbreak of 2019-nCoV pneumonia (COVID-19) in Wuhan in January 2020 spread rapidly all over the country within a short period of time, and the global spread trend appeared,which not only endangered people’s health, but also had a huge impact on the social economy [1].The cumulative number of people infected with the COVID-19 in the world has exceeded 23 million, and the death toll has exceeded 800,000.Though the epidemic situation in some countries has been, the vaccine is successfully developed, any country is at risk of rebound.Of 24:00 on August 27, 2020, a total of 85,013 cases with COVID-19 have been reported in China, of which 68,139 cases in Hubei Province.Among them, 63,627 cases were cured and discharged,and 4,512 cases died [2].As one of the designated hospitals in Wuhan, Wuhan Red Cross Hospital is responsible for the diagnosis and treatment of a large number of patients with COVID-19.This study collected the clinical data of 54 patients, and their clinical manifestations and laboratory examination characteristics to provide guidance for the evaluation of NCP.According to the research of Lan L et al,as the number of confirmed cases continues to rise, the number of patients in the recovery phase is increasing.There have been occasional cases of discharged patients,whose retesting of nucleic acid of 2019-nCoV turning positive and lesions of lungs are progressing again [3].At present, most of the 54 patients have recovered well, and none of them have been converted to positive of the retesting of nucleic acid of 2019-nCoV.However, according to the research on pulmonary function rehabilitation of these patients, we found that irreversible pulmonary fibrosis and consolidation remained, especially the elderly and patients with multiple diseases.In the future, it may be necessary to evaluate the imaging manifestations of chronic patients to assess whether there are recurrences and long-term complications in this study.
Methods
General information
Information of 54 patients with NCP who were isolated and treated were collected from February 10 to February 28, 2020 from fever ward of Wuhan Red Cross Hospital.All the above patients had been collected samples of nasopharyngeal swabs, sputum,lower respiratory tract secretions,stool and urine in our hospital.According to the relevant national biosafety regulations, the samples were sent for real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR, which showed that the nucleic acid of SARS-CoV-2 virus was positive.
Epidemiological investigation
An epidemiological survey was conducted in accordance with Diagnosis and Treatment of Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia (trial version sixth) issued by the office of the National Health Council [4].This includes whether there was exposure to infector with NCP (nucleic acid test was positive) within 14 days prior to onset of the disease, to patients with fever or respiratory symptoms from the community where the case was reported,and agglomerative disease.
Diagnostic criteria, clinical classification and exclusion criteria
Referring to the Diagnosis and Treatment of Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia (version seventh), it is necessary to meet the diagnostic criteria for suspected cases and satisfy the criteria of etiological diagnostic at the same time: the nasopharyngeal swabs, respiratory tract, stool and urine must be ①positive for nucleic acid test of 2019-nCoV by real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR, ②that the result of the genetic sequencing of virus is highly homologous to 2019-nCoV known; serological testing must be ③positive for 2019-nCoV specific IgM and IgG antibodies, ④ 2019-nCoV specific IgG antibodies change from negative to positive or the recovery period is 4 times or more higher than the acute period.once satisfy one of the criteria, it can confirm the diagnosis.
Referring to the Diagnosis and Treatment of Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia (version seventh), the common type has symptoms such as fever, cough and pant, and pneumonia in imaging performance.Severe cases(a diagnosis is made if one of following satisfied):①shortness of breath:respiratory rate ≥30 times/min;②oxygen saturation ≤93% in resting state, arterial partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2)/fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2) ≤300 mmHg ( 1 mmHg = 0.133 kPa).Critical cases (a diagnosis is made if one of below is correct): ① respiratory failure and mechanical ventilation is required; ②shock; ③combined with other organ failure,intensive care is required.
Referring to the Diagnosis and Treatment of Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia (version seventh), the exclusion criteria of suspected cases must meet:①two consecutive 2019-nCoV acid tests are negative(at least 24 hours apart); ②the 2019-nCoV specific IgM and IgG antibodies are still negative 7 days after the onset of the disease.
Data collection
The information collected included demographics data,epidemic exposure history, previous medical history,laboratory examination, and examination results of chest imaging.The laboratory examination included blood routine, C-reactive protein (CRP), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), glutamic oxaloacetylase(AST), total bilirubin (TB), creatine kinase (CK),creatine kinase isoenzyme (CK-MB), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), creatinine (Cr), D-dimer,prothrombin time (PT), international normalized ratio(INR), etc.All data of patients were collected within 48 hours after admission.
Statistical processing
The clinical manifestation and laboratory examination were analyzed by descriptive statistical analysis.
Results
Epidemiological investigation
All the 54 patients lived in Wuhan for a long time, of which 39 patients were from the community where the cases were reported,17 patients indicated that they had exposed to patients with NCP (nucleic acid test was positive) before outset, and 20 patients were exposed to the cases with respiratory symptoms from the community where the cases were reported before outset.There males and 25 females, and the ratio of male to female was 1.16.The average age of the patients was 63.9 years (40-84 years).The median time from onset to diagnosis was 6.5 days(2-20 days),and the median time from onset to first hospitalization was 8 days(3-20 days).
Clinical manifestations
Symptoms:only 15 of 54 patients(27.8%)showed low fever or no fever (body temperature ≤38.0℃), but accompanied with cough and fatigue symptoms.39 patients (72.2%) had body temperature over 38℃, the highest was 39.8℃, and the average duration of fever was 10.6 days.Among 54 cases, 12 cases (22.2%) had chills;42(77.8%) cases had cough, of which 6 cases had slight cough, 36 cases had obvious dry cough; 24 cases(44.4%) had obvious weakness;9 cases(16.7%)had pant and dyspnea.Previous basic diseases: 15 cases were combined with hypertension, 8 cases(14.8%) with coronary heart disease and arrhythmia,and 5 case (9.3%) with diabetes.The rest of the patients had no basic diseases.
Laboratory examination
In 54 patients,the white blood cell count increased in 3 case (2 cases (66.7%) were diagnosed with bacterial pneumonia, 1 case (33.3%) was diagnosed with acute intestinal infection), and the rest were normal or decreased; the percentage of neutrophils (GRA)increased in a few patients (Figure 1); the number of lymphocyte(LYM)was generally decreased(Figure 2);the CRP was increased in most patients;aminotransferase level of most patients was slightly increased, several of which was more than 3 times; Cr increased slightly in a few patients; LDH increased slightly to moderately in most patients; the plasma D-dimer increased in most patients.
Imaging performance
Among 54 cases, hilum lesions accounted for 7.41%,peripheral lesions accounted for 37.0%, subpleural lesions accounted for 31.5%, and multiple lesions accounted for 24.1%.The characteristics of lesions:pure ground glass shadow accounted for 27.7%,shadow combined focal consolidation accounted for 27.7%, consolidation density accounted for 16.6%,focal consolidation accounted for 16.6%(Figure 3).
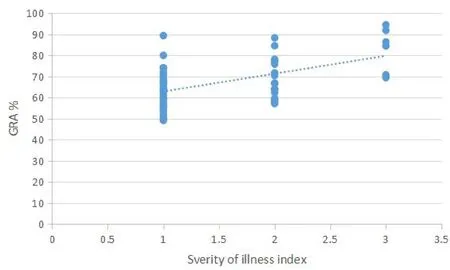
Figure 1 Relationship between the neutrophils (GRA) and the severity of illness.
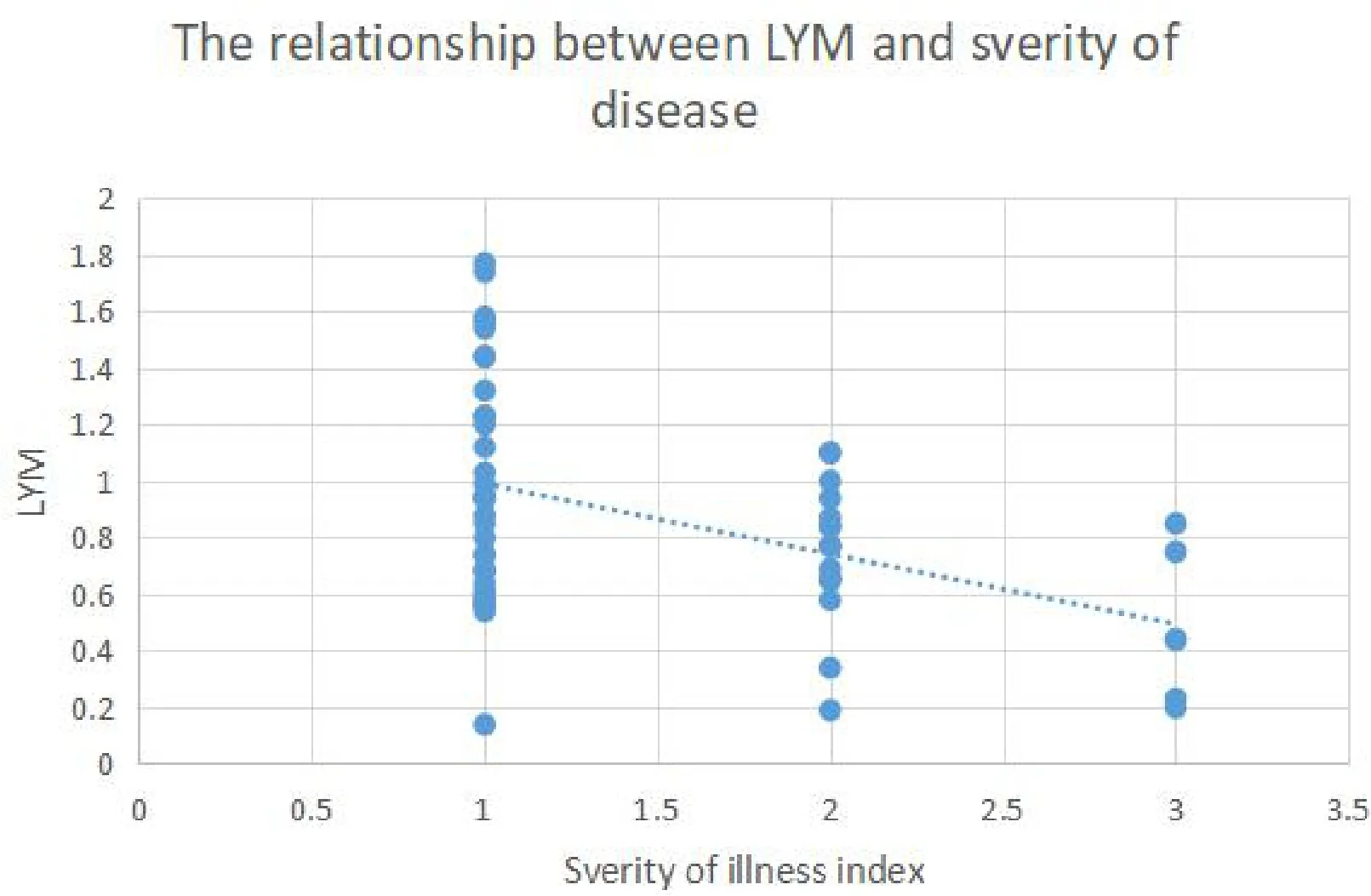
Figure 2 Relationship between the number of lymphocyte (LYM) and the severity of illness.(
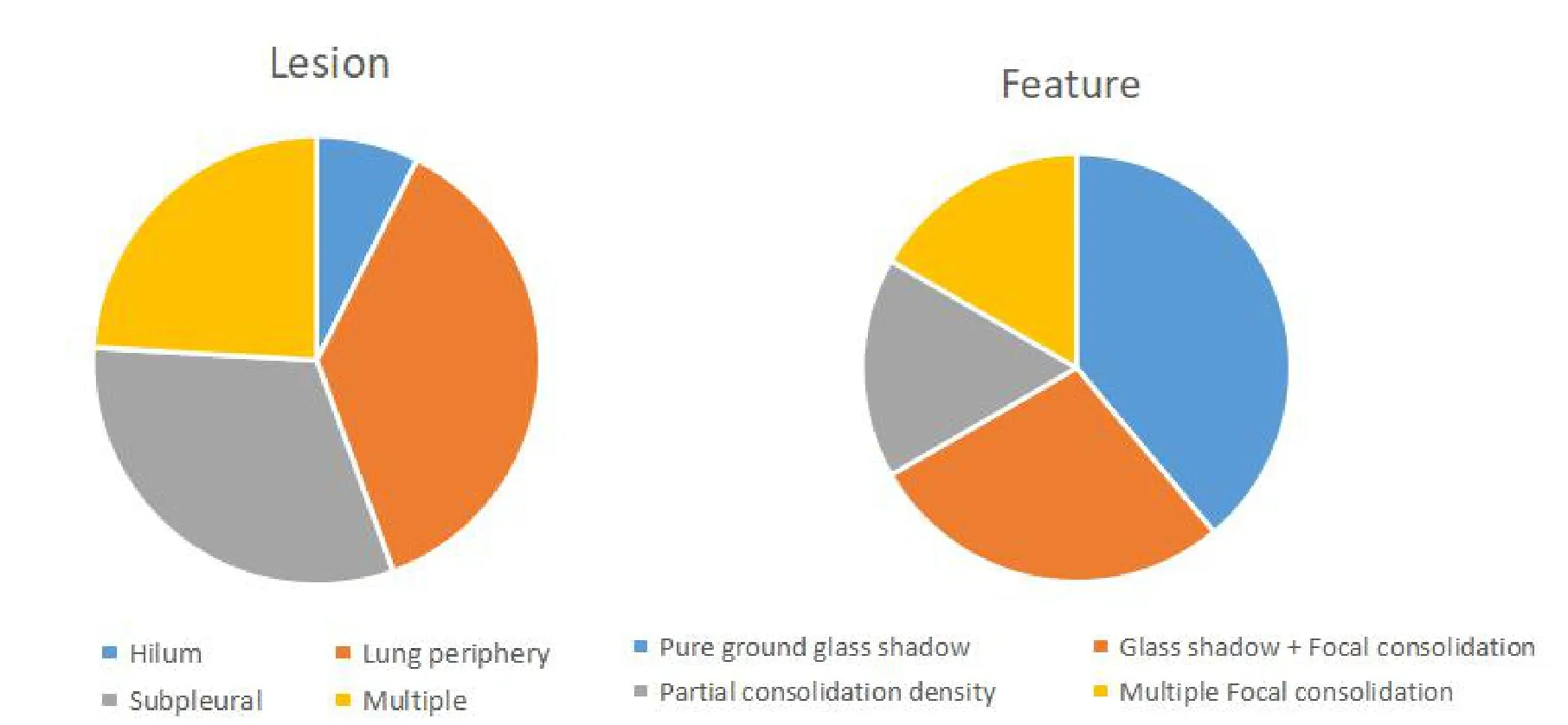
Figure 3 The distribution and manifestation of inflammation in the lung field.
Chest CT showed that patients suffered from a lot of lesion in bilateral lung, which showed that there were patchy ground glass opacity scattered or diffused in the bilateral lung, especially in the outer part of the lungs,and consolidation in some areas; fine grid like shadow of interlobular lesion presenting “paving stone sign”may appear in the lung of some severe patients; the structure of bronchial vascular bundle was twisted,and the lung volume decreased obviously of some patients;pleural effusion and pleural lesions are rare.
Typical case
Mild infection.There was a total of 40 (74.1%) mild cases.They had mild clinical symptoms, such as fever,respiratory symptoms, and showed the imaging manifestations of pneumonia.Respiratory support(oxygen therapy)and circulatory support were used for treatment,combined antiviral and antibacterial therapy.They recovered quickly and it was not easy to leave lung lesions.
A typical case report:female,44 years old.Fever for 14 days, chest tightness and fatigue for 1 week.The patient began to have fever on January 20th, 2020,with a body temperature up to 38.5 ℃, with a mild cough occasionally, no dyspnea, no wheezing, no vomiting and diarrhea.On January 20th, she went to Wuhan Xiehe Hospital.Chest CT showed that there were scattered patches in her both lungs (Figure 4).She was admitted to the hospital with the nucleic acid test of 2019-nCoV was positive.Since onset, she had poor mental, sleep, and appetite.Physical examination showed clear breath sounds in her both lungs, no dry and wet rales and pleural friction sounds were heard.Her lymphocyte was decreased slightly; CRP was increased slightly.After the treatment (non-invasive ventilator assisted ventilation, circulatory support,renal replacement therapy, antiviral, antibacterial and glucocorticoid therapy), by given Abidol orally and treated with moxifloxacin, methylprednisolone, and peramivir intravenously.Her body temperature returned to normal and she stopped coughing.We had been followed the patient, she is in good health condition currently and has no respiratory symptoms.Severe infection.There were 14 (25.9%) severe cases in total.They were older, had multiple complications and more serious clinical symptoms, such as respiratory failure and cyanosis.Respiratory support(oxygen therapy, high-flow nasal cannula oxygen inhalation,non-invasive ventilator assisted ventilation),circulatory support, and renal replacement therapy were used for treatment, combined with antiviral,antibacterial and glucocorticoid therapy.Their recovery rate is slower and they were more likely to have pulmonary fibrosis.A typical case report: male,60 years old, with a history of hypertension for more than 10 years.Fever for one week, chest tightness and shortness of breath for 3 days.History of present illness: the patient started fever without obvious cause a week ago,the body temperature was as high as 38℃,he felt chest tightness then went to Wuhan Xiehe Hospital for diagnosis and treatment.Chest CT showed that there was infection in his both lungs(Figure 5).He was admitted to the hospital with his nucleic acid test of 2019-nCoV was positive.He has poor mental health,sleep, appetite, and no significant changes in physical strength and weight.Physical examination: unclear breath sounds in both lungs, some dry and wet rales and pleural friction sounds were heard.Laboratory examination: percentage of neutrophil, CRP,aminotransferase, creatin, plasma D-dimer were increased.After antiviral therapy (oxygen therapy,circulatory support,antiviral and antibacterial therapy),his body temperature returned to normal and felt breathing smoothly.Following the patient, he is in good health condition currently and has no respiratory symptoms.
Discussion
Coronaviruses are a large class of natural viruses that infect vertebrates,such as human,mouse,pig,cat,dog,wolf, chicken, cattle and poultry.2019-nCoV belongs to the novel coronavirus of beta family.It has a coating and its particles are round or oval in shape, often polymorphic, with a diameter of 50-200 nm.S Protein is one of the main proteins of virus, and its coding gene is used for virus typing.The N Protein encapsulates the viral genome and can be used as diagnostic antigen [5].Current research indicates that 2019-CoV-2 is the seventh coronavirus found among humans and its natural host may be the bats[6].Recent studies have shown that the main routes of transmission of NCP are respiratory droplets and close contact,and a few of them are spread through aerosols and digestive tract.The virus enters cells through the combination of spike protein and ACE2(angiotensin-converting enzyme 2), and then invades the respiratory system, liver, heart and other systems.Due to the high expression of 2019-nCoV receptor ACE2 in alveolar cells of Asian population,it is regard as susceptible population[7].
Current epidemiological surveys showed that COVID-19 was generally susceptible to all populations.In this study, the sex ratio was 1.16:1, and the average age was 63.9 years.Most of the cases were retired or unemployed, and combined with a variety of basic diseases.The results indicated that the middle-aged and old people with large range of activities and more leisure time were the high-risk group of infection.Most of the cases come from the community where there were cases reported, or had exposure to patient with COVID-19, which suggested that the disease was characterized by clustering.The current investigation indicated that the clinical manifestations of COVID-19 were mainly fever, dry cough and fatigue.A few cases had nasal congestion, runny nose, sore throat, myalgia and diarrhea symptoms.Of the 54 patients admitted to Wuhan Red Cross Hospital, 39 (72.2%) had fever, 36(66.6%) had dry cough, 24 (44.4%) had fatigue, and some patients had runny nose and sore throat, and no case presented with diarrhea and vomiting.Similar to a study conducted in 89 COVID-19 patients, fever(66.3%) , dry cough (57.3%) , and fatigue (33.7%)were the most common clinical symptoms[8].
Laboratory examination showed that in 54 cases,white blood cell count was normal or decreased in 51 cases (94.4%), neutrophil percentage was increased in 18 cases (33.3%), LYM was generally decreased, and CRP was increased in most patients to some extent.This suggests that cellular immunity was involved in the development of COVID, which was similar to the mechanisms of coronavirus pneumonia caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and middle east respiratory syndrome(MERS)in the past[9].
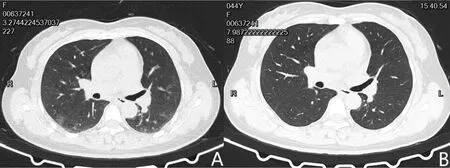
Figure 4 A (before treatment): small amount of ground glass was scattered in the upper and lower lobes of the right lung.B(after treatment):most lesions were absorbed and texture is clear.

Figure 5 A(before treatment):there were multiple ground glass opacity scattered or diffused in the bilateral lung,some lesions presenting “paving stone sign”.B (after treatment): most lesions were absorbed and dissipated,many fibrotic strips were left behind and the bronchial vascular fiber bundle were disorder in bilateral lung.
Some studies have shown that systemic viral infections cause a rise in serum enzymes [10].This study showed that most patients had slightly elevated levels of alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST), and glutamyltranspeptidase(GGT), a small percentage of patients had a mild increase in CK, and the majority had a mild to moderate increase in LDH.This suggests that the above elevated serum enzymes may be related to the 2019-CoV infection.2019-CoV infection also had a certain impact on blood coagulation function; a few patients had mild extension of PT, activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), and most patients had plasma D-dimer increased in varying degrees.This study suggests that only a small number of patients have a mild increase in Cr, suggesting that patients do not have severe renal damage.In a word, the 2019-CoV infection has caused different degrees of damage to many systemic functions, including liver,heart and blood coagulation.The specific damage mechanism needs further study.
Up to now, all the observation objects have recovered and discharged from hospital, and their condition and prognosis can be learned.Some patients were lost to follow,most patients are currently in good condition and have no respiratory symptoms.Older patients with multiple medical diseases may have a worse quality of patients have post-inflammatory pulmonary fibrosis at the time of discharge, some of which manifest as ordinary interstitial pneumonia or non-specific interstitial pneumonia; and have varying degrees difficulty breathing after the activity [11].Whether pulmonary fibrosis after inflammation can be completely absorbed and whether the impact on lung function will persist,only follow-up can answer.Based on the previous follow-up experience of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and middle east respiratory syndrome(MERS)and the current status of control of new coronary pneumonia, we need to strengthen the follow-up of discharged patients.To understand the outcome of pulmonary fibrosis after inflammation, carry out clinical observation of drugs when necessary.
Conclusion
This study was a single-center retrospective observational study with a small sample size.In a word,the middle-aged and old people with basic disease are the group of the disease.Once a fever, dry cough,fatigue and other symptoms showed, the patients should be timely treated, timely performed chest CT and nucleic acid test.Early detection and early treatment should be done.
