中国果园植保机械化技术与装备研究进展
2020-12-25郑永军陈炳太吕昊暾江世界
郑永军,陈炳太,吕昊暾,康 峰,江世界
·农业航空工程·
中国果园植保机械化技术与装备研究进展
郑永军1,陈炳太1,吕昊暾1,康 峰2,江世界1
(1. 中国农业大学工学院,北京 100083;2. 北京林业大学工学院,北京 100083)
果园植保是果园管理关键环节,其机械化发展水平直接影响水果种植的经济效益。为明确中国果园植保机械化技术与装备未来发展方向,该研究首先介绍了中国果园的主要种植方式、植保机械化发展水平及发展制约的因素,然后重点阐述了管道喷雾、风力辅助喷雾、静电喷雾、循环喷雾、变量喷雾和航空施药等植保机械化关键技术与装备的研究进展,概括分析了上述植保装备的农药利用率情况,最后结合中国果园种植特点提出了推广标准化果园种植方式、发展立体植保施药技术、推广专业化机械植保服务模式和研发智能植保机器人4个方面的建议,以期为中国果园植保机械化发展提供参考。
喷雾;机械化;农药;果园;植保机械;农药利用率;研究进展
0 引 言
水果已成为继粮食和蔬菜后的中国第三大种植业,据农业部规划,到2020年中国果园面积将稳定在1.33×107hm2[1]。在果园管理中,果园植保是保障水果稳产、增产的关键环节,其工作量约占果园管理总工作量的25%[2-3]。当前果园植保主要依赖喷施化学农药进行病虫害防治,先进的施药技术与植保机械是提升农药利用率、提高作业效率、增强防治效果的重要手段。
目前,中国果园施药仍以手动喷雾器大容量淋雨式喷雾法为主,用水量达600~1 200 L/hm2,农药利用率尚不足30%,造成大量药液浪费、环境污染及果品农药残留超标,严重时甚至导致作业人员中毒;而发达国家大量应用低容量、超低容量、循环喷雾等新技术,用水量低至200 L/hm2左右,施药量大大降低,农药利用率大幅提高[4]。关于植保机械,中国各类背负式手动(电动、机动)喷雾器社会保有量达1亿台以上,一台设备打遍百药防治各种病虫害是普遍情形[5];而发达国家已普遍采用机械施药,实现专业化植保。从成本上看,随着中国城市化进程加快,农村劳动力转移,人工施药成本增加且作业效率低,导致水果种植效益不断降低,水果产业发展缓慢。果园机械施药不仅用药少、农药利用率高,在降低劳动强度、提升作业效率、节约生产成本等方面也具有突出优势,是未来中国果园植保发展的必然趋势。
本文首先介绍中国果园的主要种植方式及其植保机械化发展水平,然后阐述当前植保机械化关键技术与装备研究进展,最后结合果园种植方式与植保机械研究现状,提出果园植保机械化发展建议。
1 果园种植方式与植保机械化发展水平
1.1 果园种植方式
中国果园品种繁多、地域分布广泛、种植历史悠久。
按照地形划分,主要分为丘陵山区果园和平原果园,但以丘陵山区果园为主,约占果园总面积的65%[6]。丘陵山区果园大多为陡丘陵和缓丘陵种植,仅有少许平地种植。特别是陡丘陵地区,坡度较大、崎岖不平,主要采用梯面种植方式,其垂直方向呈阶梯式,水平方向依山走势,由于山坡多为凸起状态,同一梯面种植果树并不在同一直线上,且不同阶梯弯曲度也不相同;缓丘陵地带存在沟沟坎坎且田块分散,阶梯种植或顺坡种植方式居多;坡度更小,地势更加平坦的平地果园则接近平原果园种植方式。
按照年代划分,主要分为传统果园和现代标准化果园,但以传统果园为主,约占果园总面积的75%[7]。传统果园有乔化稀植型和低矮密植型,目前以低矮密植型居多。以苹果为例,传统果园行距一般为4.0~5.0 m,株距3.0~4.0 m,树冠多为开心形,冠层高大、枝干粗壮,因建园时未考虑机械化作业需求及管理粗放等,易形成行间郁闭;现代标准化果园行距一般为3.0~4.0 m,株距1.0~1.5 m,树型有纺锤形、直干形、Y形等,冠幅小而细高,管理规范,易于机械化作业[8-12]。此外,果树设施栽培作为露地自然栽培的特殊形式,具有调控果实成熟期、延长果品供应期、扩大种植范围和控制病虫害传播等优点,在中国得到快速发展,其主要种植方式有日光温室、塑料大棚和避雨栽培等,目前在葡萄、草莓、樱桃、桃等果品种植中,应用较为成熟[13]。
1.2 果园植保机械化发展水平
受果园立地条件及种植方式等因素影响,中国果园植保机械化发展水平仍然偏低,资料显示丘陵山区果园仅为7.5%,平原果园为15%[3]。分析原因主要有:丘陵山区果园种植面积比例大,但其地形地势复杂,严重阻碍机械化施药;如陡丘陵果园地面植保机械根本无法进园,导致几乎无机可用;缓丘陵果园同样地势凹凸起伏,加之分散种植、分户管理,缺乏机械行走、转场农机道,导致机械化施药程度低。平原果园立体条件虽好,但由于以家庭种植方式为主,单户种植规模小,购买设备成本高、获益慢,影响了植保机械化发展;传统果园种植方式农艺管理较为粗放,行株距不规范、大树冠、平拉枝、行间郁闭,影响植保机械通过性。此外,植保服务体系不健全,技术推广培训不到位以及果农对机械施药认识不足等,均是限制植保机械化发展的重要原因。
2 果园施药技术发展
实现果园植保机械化,离不开先进的施药技术与植保机械。其中施药技术是果园喷雾作业的关键环节,目前国内果园施药技术主要包括管道喷雾、风力辅助喷雾、静电喷雾、循环喷雾、变量喷雾和航空施药等。如今施药技术与植保机械正逐渐向着智能、精准、高工效、低喷量的方向发展。
2.1 管道喷雾技术
管道喷雾技术指采用地下埋设管道,经立管联结地面高压软管和喷枪,通过药泵对药液加压送入管道后带动多个喷枪同时作业[14-15]。该技术多适用于中国丘陵山区果园,自20世纪80年代中期引入中国后得到不断推广[6],表1为果园管道喷雾技术在中国部分地区的应用发展。
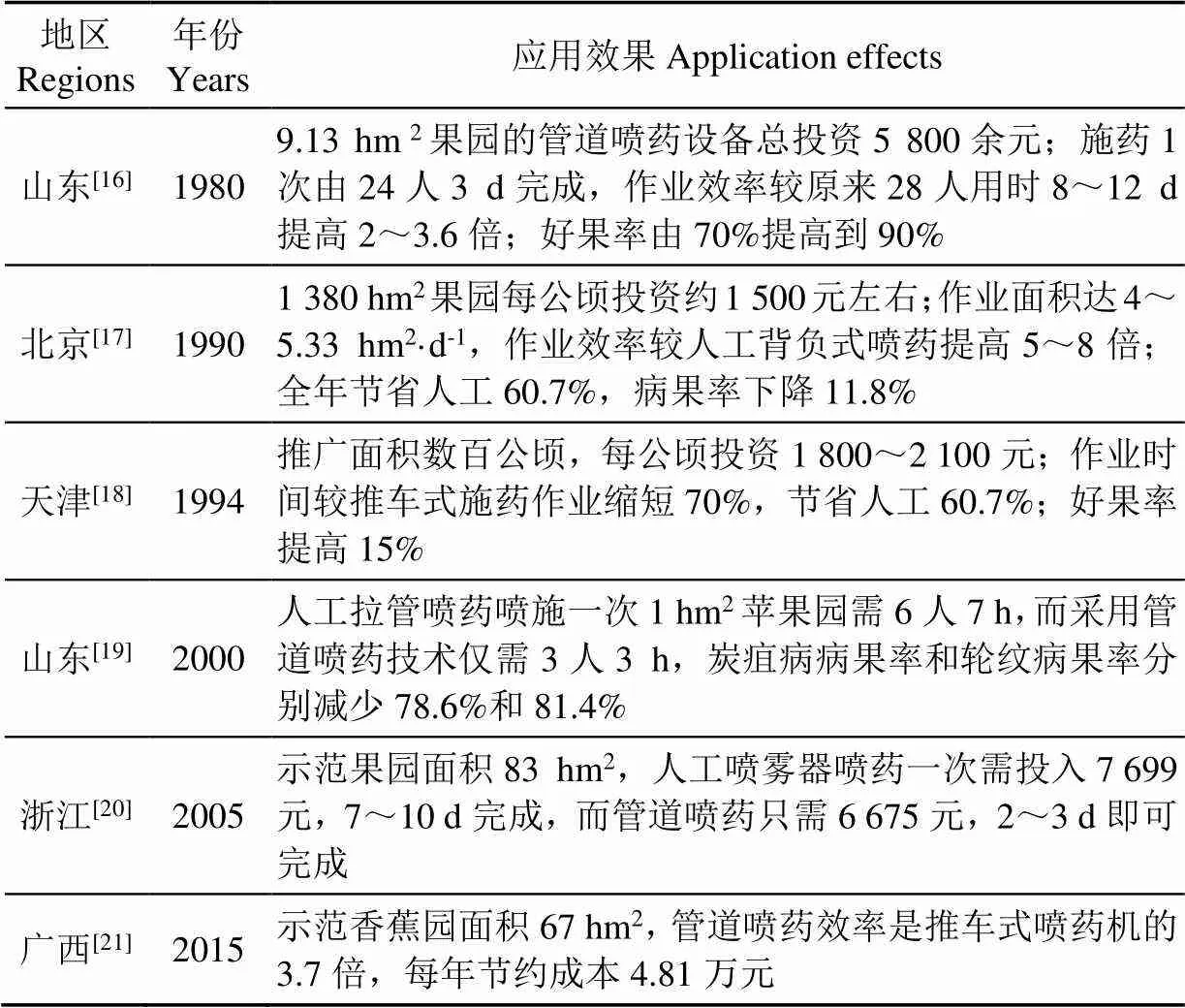
表1 管道喷雾技术应用效果
从表1可以看出,管道喷雾技术在中国应用分布广泛,且较人工背负式、推车式及车载式喷药省工省时、效率高、投资少、效益好,能够有效控制病虫害发生和蔓延。但由于该技术仍然存在管道压力分布不均时常爆管、管道药液残留腐蚀、郁闭果园施药人员易中毒等问题,后续仍需进行针对性研究。
2.2 风力辅助喷雾技术
风力辅助喷雾技术是利用高速风机产生的强气流,将经过药泵和喷头雾化形成的细小雾滴吹送到果树冠层,进而达到果树防虫治病的效果[22]。该技术既能保证喷雾距离,又能增强雾滴穿透性和沉积均匀性,同时气流扰动叶片翻转提高了叶片背面药液附着率,自20世纪80年代引进中国,经过多年研究改进,已取得长足发展。
国内学者王荣等[23]通过改进风机蜗壳结构使出口风速提高61.5%;刘青等[24]通过在风筒中加装导流器使喷洒幅宽提高22%~46%;祁力钧等[25]通过CFD仿真与试验发现距风机中心2.4 m处雾滴沉积量分布平均相对误差最低为33%;张晓辛等[26]通过优化导流片与喷头喷射角度,使风速和喷雾量分布曲线与树冠轮廓高度吻合。风力辅助喷雾技术的不断进步,为风送喷雾机在中国的应用发展提供了良好的技术基础。
2.3 静电喷雾技术
静电喷雾技术源于20世纪40年代的法国,指通过高压静电发生装置让静电喷头与靶标之间形成电场,使带电雾滴与冠层形成“静电环绕”效应并在静电力、气流曳力和重力作用下快速沉积到靶标,从而增加雾滴在作物表面的附着能力[27-28]。该技术能够显著提高雾滴沉积量,特别是作物背面雾滴沉积率,一度成为国内学者研究的热点。
针对静电喷雾技术在果园的应用,舒朝然等[29]采用数理方法建立了树冠静电喷雾过程的电子-机械模型,精确表达了树冠静电喷雾过程中荷电雾滴的沉积机制,验证了果园静电喷雾的可行性,且其研究表明:雾滴粒径在30~80m时,雾滴荷电性能最好,考虑自然蒸发和风的影响,建议作业雾滴粒径谱宽范围以50~100m为宜;周良富等[30]提出风送喷雾与静电喷雾相结合,并通过响应面模型分析法研究了感应电压、风机频率、喷雾距离和喷雾压力等工作参数对叶背面雾滴覆盖率的影响,结果表明该模型决定系数为93.68%,相对误差小于10%,工作参数对响应面模型有显著性影响;除此,周良富等[31]还设计了双气流道辅助静电喷头,通过试验表明该喷头在喷雾压力0.4 MPa、感应电压6 kV、采集距离1.0 m以内条件下,静电喷雾叶背面雾滴覆盖密度较非静电喷雾提高15%以上。上述研究均为果园静电喷雾机的研制及部件选择、作业参数匹配等提供了良好的理论依据。
2.4 循环喷雾技术
循环喷雾技术最早出现在20世纪70年代[32-33],那时国外果园趋于矮化种植,原来高达近4.0 m的果树冠层降到2.5 m以下,使其能够被横跨覆盖喷雾,并且采用药液回收装置拦截并收集未沉积的药液回收再利用成为可能,由此循环喷雾应运而生[4]。循环喷雾种类繁多,主要可概括为“П”型罩盖型、收集器型、反射型和气流循环型4 种类型。随着技术发展,多技术融合,各类型之间区别已不再明显,如“П”型罩盖型与气流循环型相结合。Ade等[34]通过葡萄喷雾试验发现,循环喷雾较普通风送喷雾地面流失量减少5%,雾滴沉积率提升至87%;Peterson等[35]通过改进循环喷雾风机配置方案,进一步提高了循环喷雾的工作性能。
2.5 变量喷雾技术
果园变量喷雾技术最早开始于20世纪70年代,是将对靶喷雾与变量控制相结合,通过非接触式靶标探测技术获得树冠特征信息,在大量试验基础上建立与树冠特征信息适应的喷雾决策模型,依据模型反馈的喷雾参数进行动态调节,最终实现变量喷雾[36]。该技术核心是靶标探测技术,重点是变量控制系统,表2为目前最具代表性的靶标探测技术原理及优缺点,表3为变量控制系统及其效果。
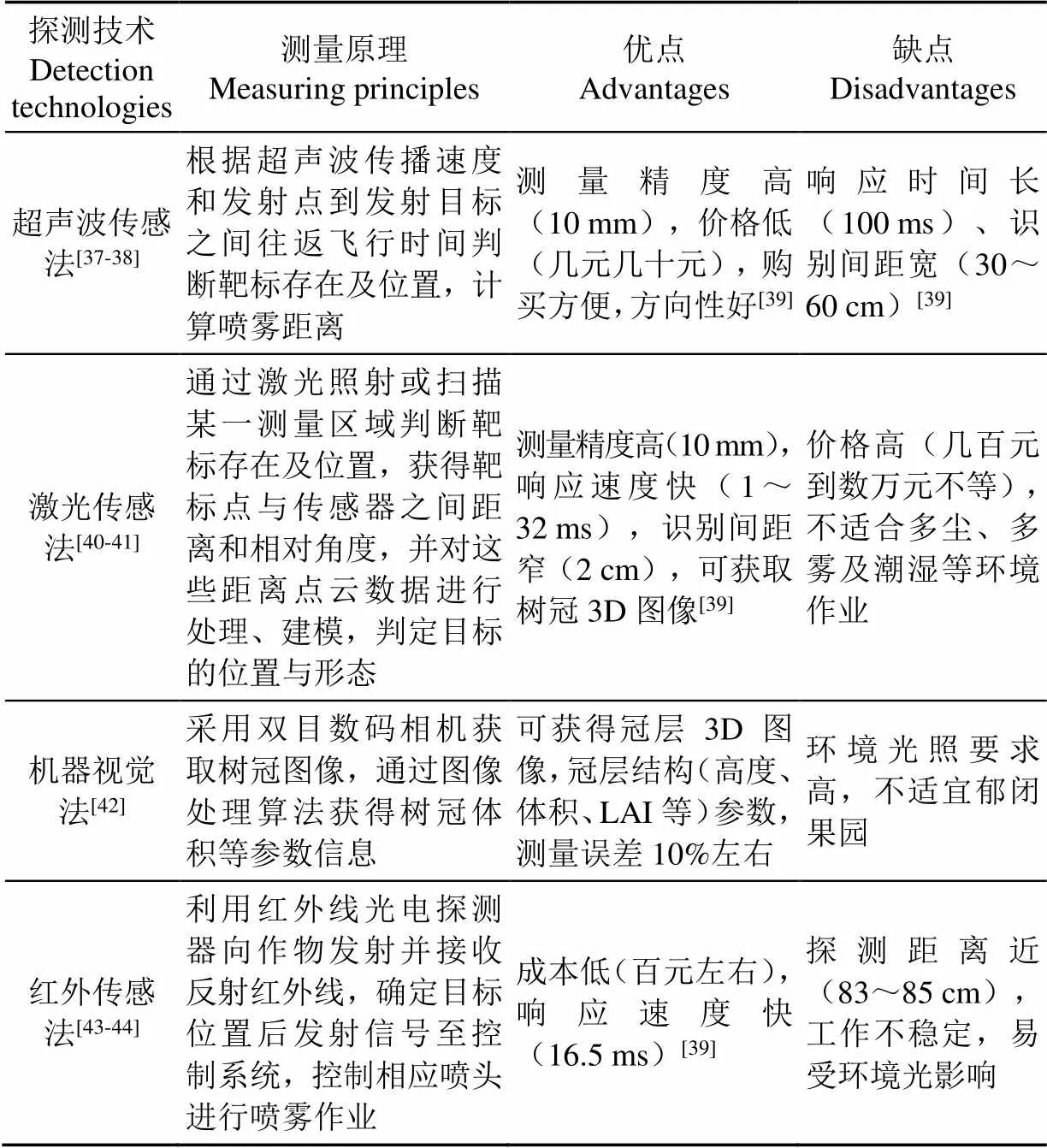
表2 靶标探测技术原理及其优缺点

表3 变量控制系统及其作业效果
2.6 航空施药技术
航空施药技术指利用飞机或其他飞行器将农药从空中均匀喷施在目标区域的施药方法[51-52]。2010年以来,随着植保无人机在中国的迅速发展,以植保无人机为应用载体的低空低量航空施药技术已逐步成为研究热点[53-58]。植保无人机施药药箱容量一般在5~20 L(最近两年相继出现过药箱容量大于30 L的植保无人机,但是应用相对较少),喷洒幅宽在5~20 m,果园植保时飞行高度一般设置距离冠层顶端1.5~2.0 m,距地面高度至少为3.5~4.0 m[59]。该技术具有作业效率高、作业效果好、应急能力强等优点,应用前景广阔。
3 果园植保机械研究进展
植保机械是果园植保的关键装备,依托施药技术发展,植保机械也获得了快速发展,经过了从手动到机动、从粗放到精细、从地面到航空的发展历程[60]。目前,果园植保机械主要分为地面植保机械和航空植保机械,地面植保机械除半机械化植保机具外,主要包括管道喷雾设施、风送喷雾机、静电喷雾机、循环喷雾机和变量喷雾机等;航空植保机械则主要为植保无人机,包括单旋翼无人直升机和多旋翼植保无人机等。
3.1 半机械化植保机具
半机械化植保机具主要指各类型背负式喷雾器/机、背负式热力烟雾机、担架式(框架式、车载式)及推车式(手推式)机动喷雾机等,发达国家已多采用标准化果园种植方式,农机农艺融合程度深,机械化植保专业程度强,该类机具主要在其设施果园中仍有使用。中国大部分果园农艺特点机械化作业适应性差,仍以半机械化植保机具为主。其中背负式手动喷雾器体力耗费大,背负式机动喷雾机质量重,施药人员易劳累,随着技术推广成熟,两类机型正逐渐被背负式电动喷雾器取代。目前典型半机械化植保机具相关技术参数,如表4所示。
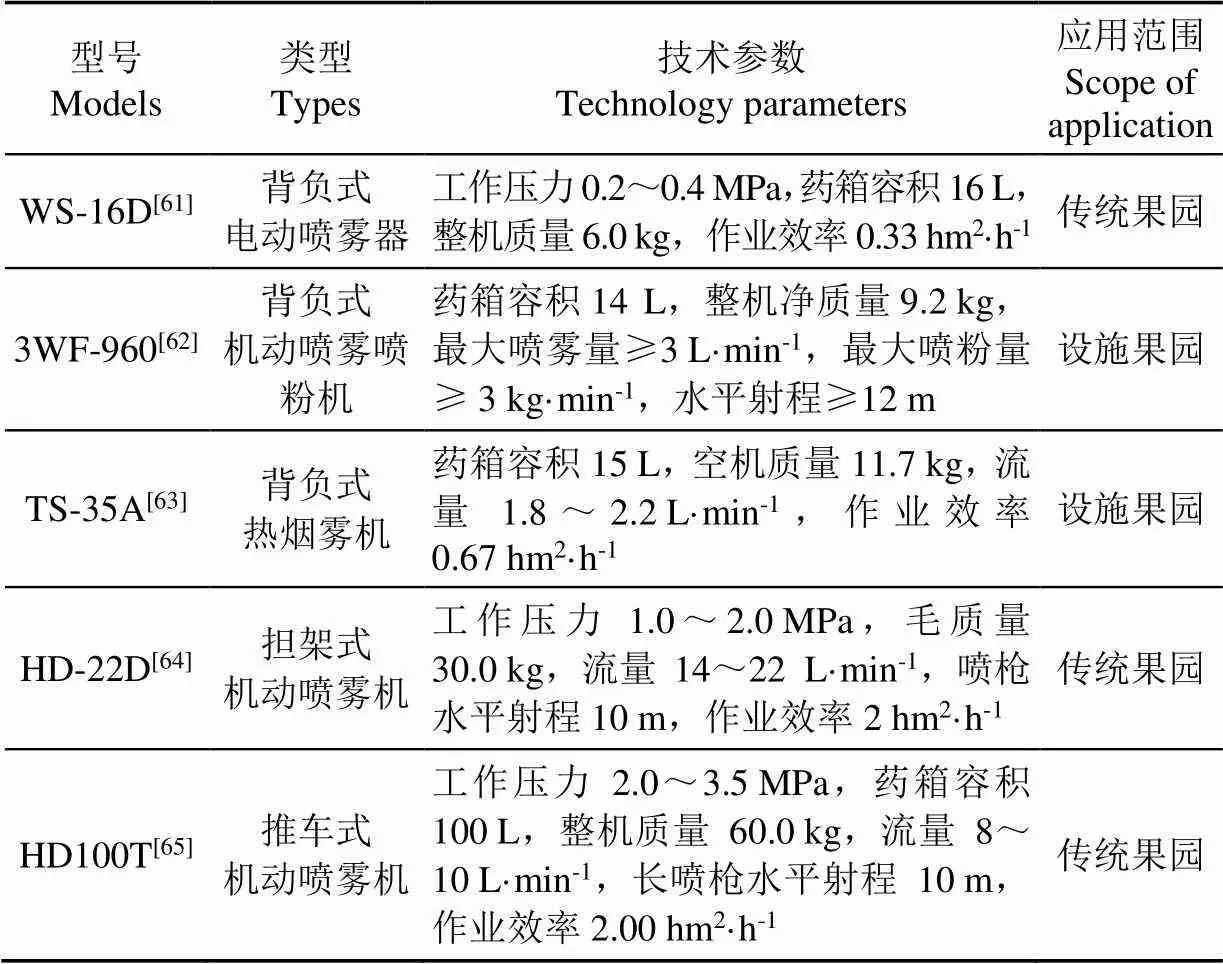
表4 典型半机械化植保机具及其技术参数
由于中国果园仍以家庭小规模种植为主,半机械化植保机具以其价格低、操作简单、无使用条件限制,一定程度上能够满足植保作业要求,至今仍是广大果农的首选,在中国各地区、各种植园中广泛应用。但与发达国家相比,这类机具80%左右仍处于发到国家20世纪五六十年代的水平[5],作业效率低、药液浪费大,农药利用率低,尤其对树冠高大、枝叶茂密的果园,雾滴很难穿透果树冠层,使其受药均匀。此外,还存在施药人员中毒概率高、雾滴飘失严重等问题,因此提升中国果园植保机械化水平任重道远,意义重大。
3.2 管道喷雾设施
管道喷雾设施相比半机械化植保机具,在集中连片管理、大中型机械进园难的丘陵山区果园具有突出优势,已获得相当地区农户的认可。管道喷雾设施主要包括管道喷雾首部、地下管道系统和地面喷雾系统3部分,其中管道喷雾首部包括水源、药池、电源、电动机和药泵等,电动机功率一般选择3~4 kW;地下管道系统主要由主管、支管和立管构成,主管多采用直径20 mm的PVC管,支管上一般每隔50 m安装一根立管,立管长20~30 cm,露出地面约10~15 cm作为出药口,每个出药口控制喷药面积0.20~0.33 hm2;地面喷雾系统由耐压胶管和喷枪构成,胶管和立管连接,喷枪数量根据实际情况配置[66]。
管道喷雾设施在应用中由于作业人数不同,管道压力分布不均,时常会发生爆管问题;作业后管道中存在药液残留,残留液用清水冲洗既造成农药浪费,又污染环境;此外在行间郁闭、枝繁叶密的复杂成龄果园环境中,不仅施药困难,而且容易造成施药人员中毒。为此,国内学者进行了多项研究和改进工作,研发了多项管道喷雾设施新成果(表5),有效促进了上述问题的解决。

表5 管道喷雾设施研究成果
因中国丘陵山地果园种植面积比例过大,宜机化改造尚需时日,因此管道喷雾设施在不短的时期内仍然具有广阔的发展前景。
3.3 风送喷雾机
风送喷雾机是目前果园植保中应用最多的机具,其核心部件是风机和导流装置。风机分为轴流风机和离心风机;导流装置分为导流板和导流管,导流管有多导管式结构和加农炮式结构,这些设计较好的满足了果园多品种、多种植方式的植保需求[72]。
3.3.1 国外风送喷雾机发展现状
目前,欧美、日、韩等国生产的果园风送喷雾机技术先进、产品成熟。著名生产企业有意大利CAFFINI公司、荷兰MUNCKHOF公司、丹麦HARDI公司、日本丸山制作所及韩国ASIA TECH公司等。部分典型产品相关技术参数如表6所示。
总体来看,欧美果园多以牵引式和悬挂式大中型风送喷雾机为主,功率大、射程远、药箱容积大、风机风量高,适合宽行窄株、树冠高大的标准化果园;日韩果园种植方式与中国相似,多以自走式中小型风送喷雾机为主,其功率较欧美低,具有结构紧凑、通过性好、药箱容积小等特点,适合果树行株距基本一致,密集程度低的果园。
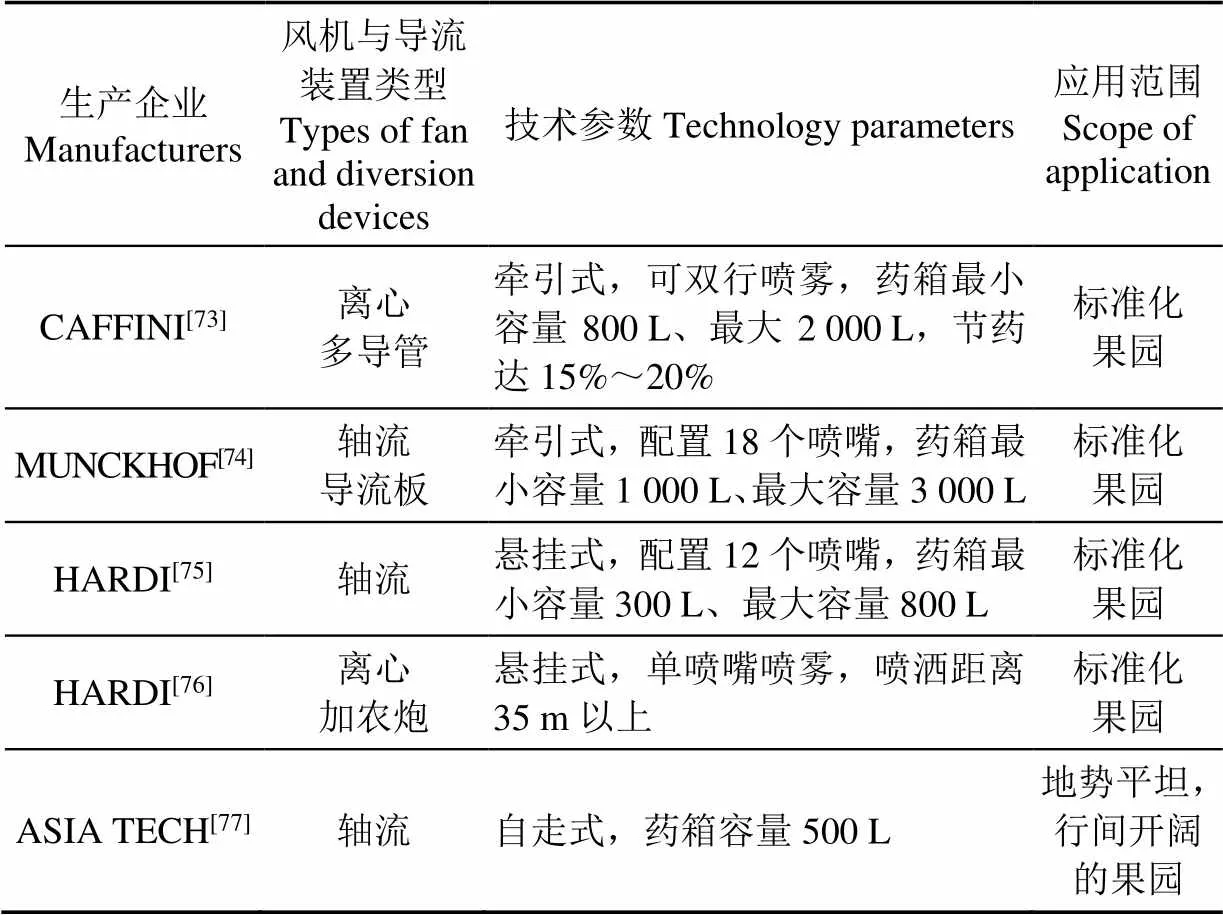
表6 国外典型风送喷雾机技术参数
3.3.2 国内风送喷雾机研究进展
直接引进国外大中型风送喷雾机,其在中国果园适用性较差,因此国内研发团队纷纷展开攻关,针对中国果园种植方式特点研发了多种风送喷雾机,典型成果如表7所示。
从表7可以看出,针对中国果园低矮密植种植方式特点,自走式(轮式驱动、履带底盘)风送喷雾机因其结构紧凑、通过性强,受到国内广大学者青睐,研发人员较多。在导流装置设计方面,除常规圆环形喷头布置形式,亦有学者改进为垂直喷杆式、多柔性导管式、立管式和蝶形风箱等,适应了中国果园类型多样的植保需求。目前国内代表性生产企业有中农丰茂、永佳动力、中农博远等,典型成熟的风送喷雾装备相关技术参数如表8所示。
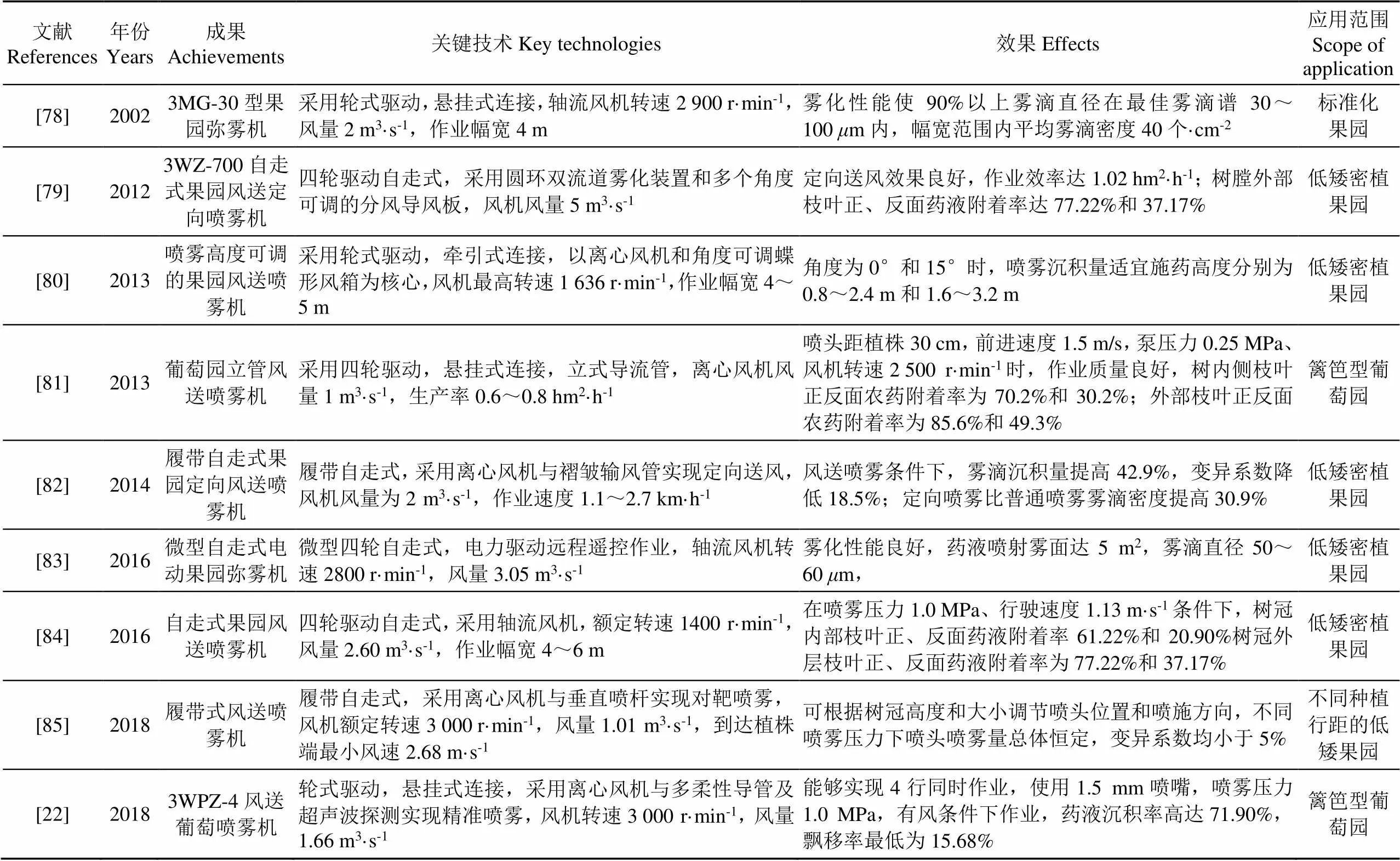
表7 风送喷雾机典型研究成果
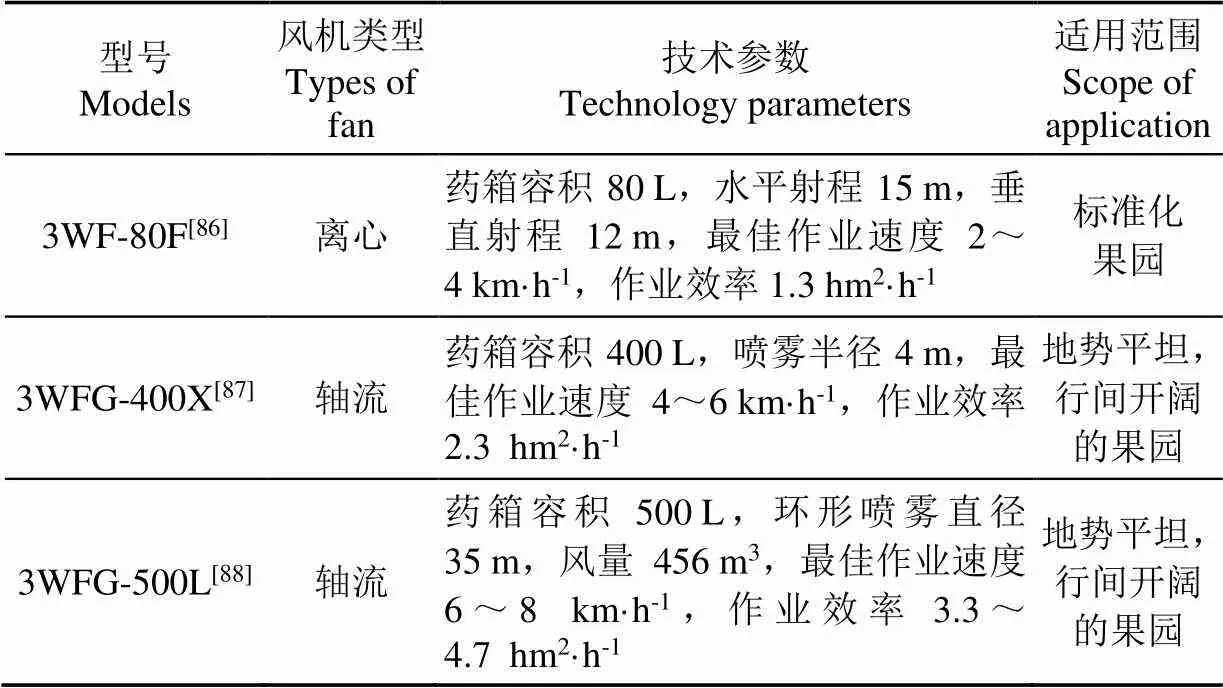
表8 国内典型风送喷雾机技术参数
果园风送喷雾机相比半机械化植保机具优势众多,然而由于风送喷雾机多为连续型喷雾方式,加之其强气流作用,作业过程中仍有大量雾滴脱离靶标和飘移损失,造成农药浪费和环境污染,因此仍需进一步加强研究。
3.4 静电喷雾机
进入21世纪,随着静电喷雾技术的快速发展,果园静电喷雾机因其具有雾滴飘移少、环境污染小、水药用量低及农药利用率高等优点得到推广应用。
3.4.1 国外静电喷雾机发展现状
国外果园静电喷雾机著名生产企业有美国ESS公司、BRUSHHOUND公司及意大利MARTIGNANI公司等。图1a为MARTIGNANI公司生产的典型静电喷雾机,该喷雾机采用牵引方式连接于拖拉机后方,通过离心风机将荷电雾滴输送到果树冠层,药箱容积1 000 L,作业幅宽4.6~5.8 m,可节约用水达90%,主要适用于篱笆型标准化果园,而对其静电喷雾系统的介绍及使用效果尚无文献研究[89]。ESS公司静电喷雾机是在MaxCharge™静电喷头基础上根据果园实际应用条件研制的,适用于行距宽、冠层高、树冠厚的果树,图1b为该公司典型产品,采用3点悬挂方式连接于拖拉机后方,最小药箱容积212 L,最大流量5.03 L/min,雾滴粒径为40m[90]。

图1 果园静电喷雾机
3.4.2 国内静电喷雾机研究进展
国内学者对果园静电喷雾机的研究,主要集中在多技术集成的样机研制方面,表9为国内研发团队成功研制的静电喷雾样机及其测试效果。
从表9可以看出,静电喷雾机中感应式充电是使用最普遍的方式,且静电喷雾一般与风送喷雾相结合,克服了自身的局限性,在此基础上融合气力辅助喷雾、对靶喷雾等技术,更加提高了靶标雾滴密度、药液覆盖率以及农药利用率。目前,国内市场商业化产品有博远3WFQD-1600风送静电喷雾机,该机采用牵引式连接于拖拉机后方,工作压力0.5~2.5 MPa,喷洒幅宽8~12 m,可减少30%~60%农药使用量。然而,因环境参数(温湿度、悬浮颗粒物、污染气体、气流速度等)、作业参数(充电方式、充电电压、作业速度、喷雾方向、喷雾距离、喷雾量等)及靶标参数(材质、叶面积指数、叶片倾角等)等对雾滴沉积的影响机理尚未清楚,果园静电喷雾装备成熟商业化产品仍然较少,而且距离广泛推广应用还有较大差距。
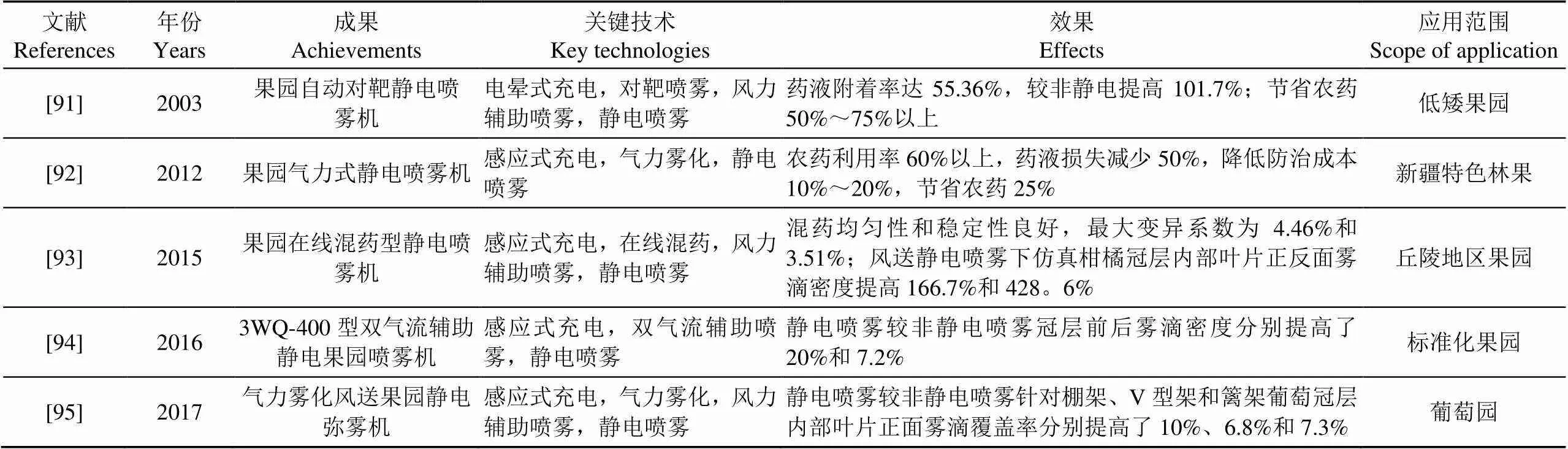
表9 静电喷雾机典型成果
3.5 循环喷雾机
3.5.1 国外循环喷雾机发展现状
欧美矮化果园种植方式发展后,风送喷雾机单侧喷雾大量雾滴脱离靶标、无法回收利用问题变得凸显,循环喷雾机能够有效解决这一问题,受到人们广泛重视。
图2所示Nestor循环喷雾机为国外典型循环喷雾机型之一,该机采用牵引方式连接于拖拉机后方,药箱容量2 000 L,作业幅宽0.94~2.70 m,适宜树冠高度2.10~2.35 m[96]。此外,据LIPCO公司资料显示其生产的循环喷雾机在果树枝叶稀疏时药液回收率达70%,枝叶茂盛时药液回收率亦有20%;MUNKHOF公司制造的循环喷雾机根据枝叶茂密程度,药液回收率在30%~60%[32]。可见循环喷雾在增强雾滴沉积、减少雾滴飘失、提升药液回收利用方面具有重大优势。

图2 Nestor循环喷雾机
3.5.2 国内循环喷雾机研究进展
国内果园种植方式与欧美果园区别明显,循环喷雾机在中国适用程度低,因此目前中国学者对循环喷雾机的研究较少。中国农业大学宋坚利等[97-98]曾于2012年针对葡萄园研发了“Π”型循环喷雾机并开展了防飘失性能试验,结果表明该机比普通风送喷雾机雾滴飘失减少97.9%,地面流失量减少99.3%,极大的减少了农药浪费;山东农业机械科学研究院牛萌萌等[99]同样针对葡萄设计了高地隙隧道式循环喷雾机(图3),该机采用乘坐式设计,结构紧凑、通过性强,“Π”型立杆长1.30 m,间距1.20 m,最大通过高度1.90 m,最大喷幅达8.10 m,经试验其药液回收率达7.33%。

图3 高地隙隧道式循环喷雾机
综上可知,循环喷雾机能够显著降低雾滴飘移量和地面流失量,有效回收药液进而提高农药利用率;但因其主要适用于特定矮化种植园,现阶段中国该类果园种植方式尚未普及,农艺条件发展不足,导致循环喷雾机仍未在中国获得广泛关注。
3.6 变量喷雾机
3.6.1 国外变量喷雾机发展现状
风送喷雾机连续喷雾方式存在严重地农药过量喷洒和树隙无效喷雾问题,果园变量喷雾机是解决该问题的有效手段[100-102],成为广大学者研究的热点。图4为国外典型果园变量喷雾机机型,该机通过在HARDI公司生产的LE-600喷雾机上模块化植入变量喷雾系统形成,采用悬挂方式连接于拖拉机后方,药箱容量600 L[103]。总体来说,国外对果园变量喷雾机的研究领先中国,一般是通过在已有喷雾机上模块化加装变量喷雾系统融合而成。目前,果园变量喷雾机在欧美一些国家和地区已实现产业化发展和小规模应用。

图4 果园变量喷雾机
3.6.2 国内变量喷雾机研究进展
国内对变量喷雾机的研究起步晚、发展快。针对果园变量喷雾机,研究人员开展了一系列探索并研发了成套样机,如葛玉峰等[104]利用CCD摄像法实时采集树木图像,依据图像处理结果进行施药决策,建立了室内农药自动精确喷雾系统,表10为国内研发团队研制的部分典型果园变量喷雾机样机及其测试效果。
从目前国内技术研发结果看,超声波传感法和激光传感法应用前景较好,其次是红外探测法,机器视觉法目前研究更多集中于作物种类、部位及形态结构识别上,能为精确控制和精准定位提供信息,但在图像处理速度、田间作业环境实时检测等方面还存在诸多不足;此外在冠层参差不齐、枝叶时疏时密等复杂条件下,目标检测可靠性、稳定性、喷雾实时精准调节等方面还有所欠缺,总体上仍处于样机试验阶段,尚未形成产业化成果。

表10 果园变量喷雾机典型成果
3.7 植保无人机
相比地面植保机械,植保无人机地形适应能力强,不受作物长势限制,成本低、安全性好,已成为重要的植保机具。据相关部门统计,截至2018年底,中国已有300多家植保无人机生产企业,开发近250多种机型,全年销售量达1万多台,全国作业面积达1.78×107hm2,实现了“人机分离、人药分离”,安全高效作业[110]。目前,国内部分植保无人机典型机具相关技术参数如表11所示。
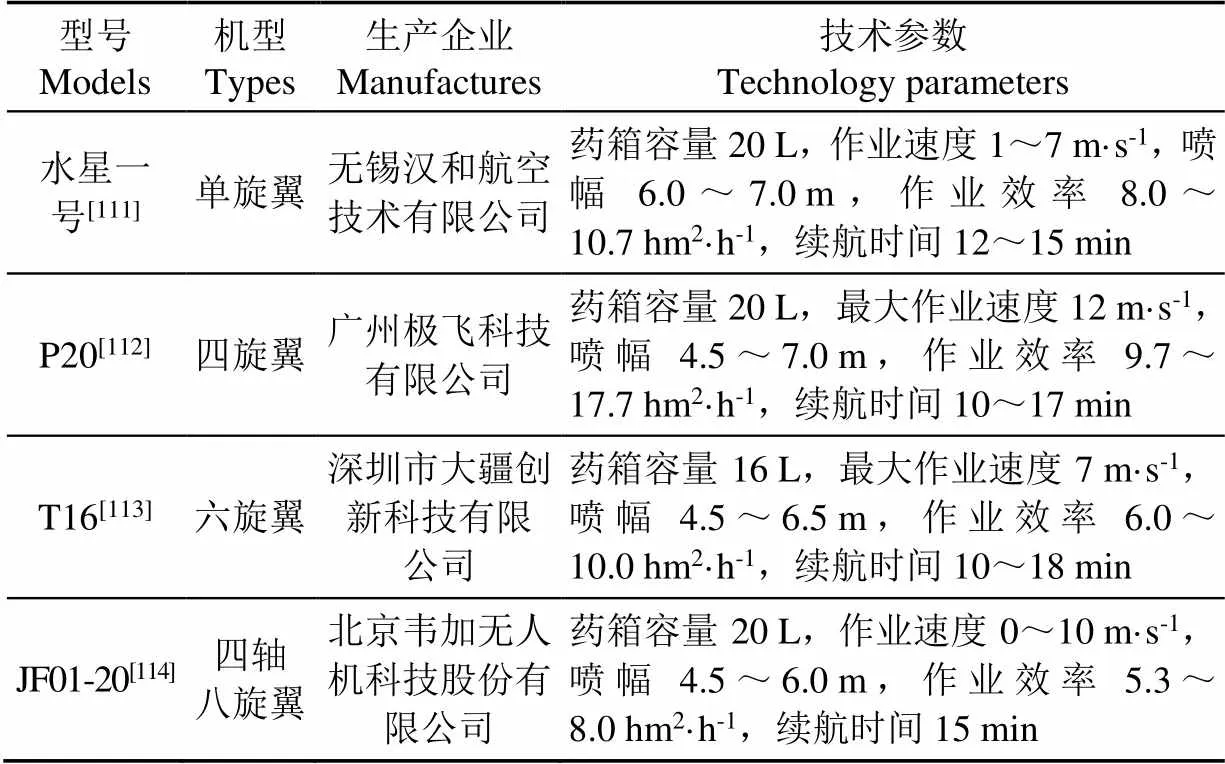
表11 植保无人机技术参数
为满足植保无人机果园精准喷洒作业要求,提升果园喷雾效果,国内研究人员分别从作业模式、旋翼风场及作业参数等方面开展了一系列研究[115-117]。
在作业模式方面,根据果树分布及生长状况,果树作业模式可以分为手动喷洒、连续喷洒和定点喷洒,为使冠层与无人机保持恒定高度,部分机型已实现仿地形飞行功能,提升了施药精准性和作业安全性。表12为果园主要施药作业模式及其特点。
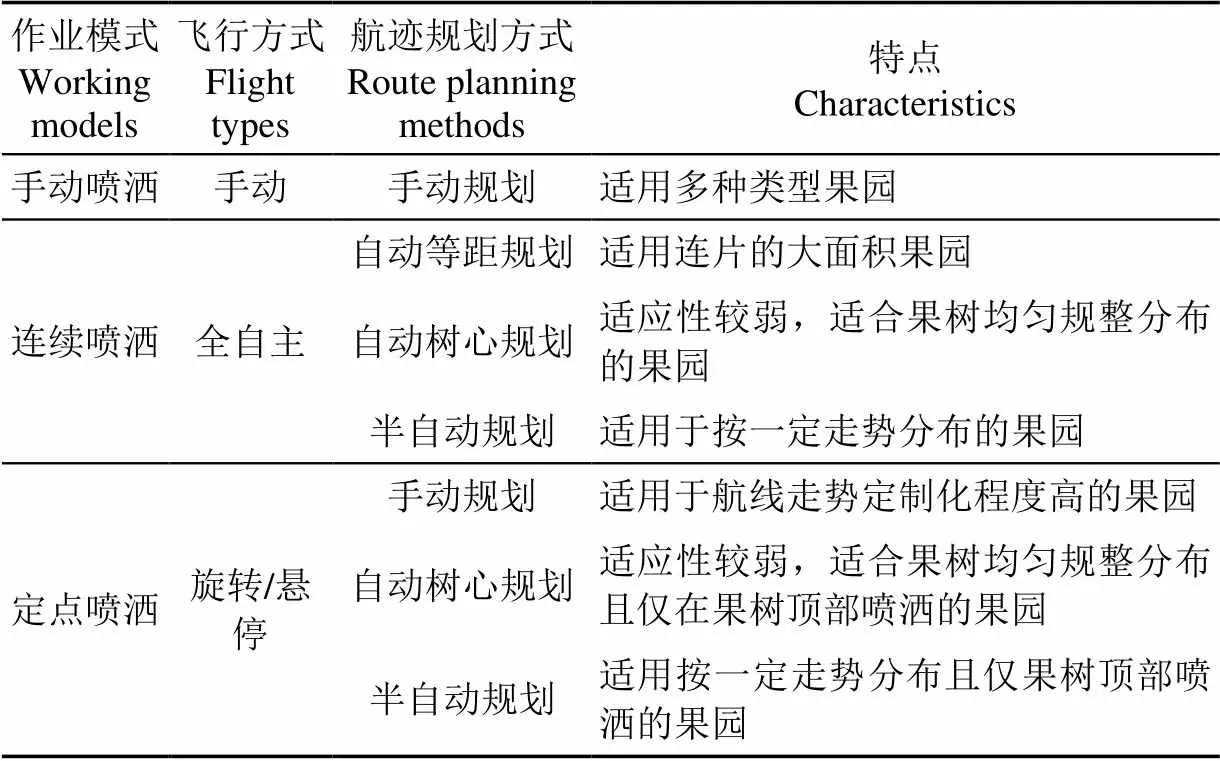
表12 果园主要施药作业模式及其特点
在旋翼风场方面,植保无人机下方有无树冠对风场影响重大。杨风波等[118]、Zheng等[119]利用CFD仿真分别对单旋翼和多旋翼无人机无树冠条件下的风场分布规律进行了模拟分析,得到悬停高度2、3和5 m时对应的最小风速分别为1.33×10-4、2.02×10-4和1.87×10-4m/s,可见随悬停高度增加,风场最小风速先增大后减小,悬停高度3 m时适宜田间喷洒作业。张豪等[120]等利用CFD仿真建立了六旋翼无人机无树冠和有树冠条件下的气流分布三维模型,对比结果表明:无树冠时,旋翼下方0.2 m处气流速度最大,接近8.0 m/s,由于空气阻力作用,0.2~0.6 m区域,气流速度迅速由8.0 m/s衰减至4.0 m/s,并在0.6~1.7 m区域内形成速度稳定区,约3.0~4.0 m/s;当存在树冠时,0~0.6 m区域内由于气流未受冠层影响,速度变化规律与无树冠时基本一致,但在0.6~1.7 m区域内,随冠层压力损失系数增加,气流速度衰减加快,冠层压力损失系数为6~10时,气流速度均接近0;由此可见果树冠层对旋翼下洗气流有明显阻挡作用,且树冠越密气流穿透性越小。实际果树喷雾时,不同生长期,冠层疏密不同,因此为取得最佳喷雾效果,针对不同冠层密度的果树选择怎样的机型仍然有待深入研究。
在作业参数方面,王娟等[121]开展了单旋翼无人机飞行高度10.5 m、11.5 m和12.0 m下的槟榔喷雾试验,张盼等[122]进行了四旋翼无人机作业高度0.5 m、1.0 m和1.5 m下的柑橘喷雾试验,结果均表明植保无人机果树施药具有最佳作业高度范围,超出或低于最佳范围,冠层雾滴沉积密度或沉积量减少。Lü等[123]在室内进行了四旋翼无人机0.3~1.0 m/s作业速度下的仿真茶树喷雾试验,陈盛德等[124]开展了六旋翼无人机不同速度下的柑橘田间试验,结果同样表明植保无人机施药具有最佳作业速度范围,超出或低于最佳范围,冠层雾滴沉积密度同样减小。可见,植保无人机作业参数是影响雾滴沉积效果的重要指标,针对特定果树选择适宜机型及最佳作业参数对实现最佳喷雾效果具有重要意义。
此外,Zhang等[125]将静电喷雾技术与植保无人机结合形成航空静电喷雾系统,较非静电喷雾雾滴密度提高13.6%;Zhang等[126]、Tang等[127]还研究了四旋翼无人机施药条件下,柑橘冠层形状对雾滴沉积效果的影响,为果园农艺农机融合发展提供了技术参考。
通过对植保无人机施药作业模式、旋翼风场、作业参数及其他方面研究表明,植保无人机施药能够一定程度满足果园植保需求,但其冠层雾滴穿透性差、雾滴分布不均匀等问题需要进一步解决。
4 结论与展望
进入新世纪以来,随着人们环保意识增强和对农药污染问题的重视,针对果园施药,越来越多的学者投入到降低农药使用量,提高植保机械化水平的研究中。从上述文献分析可以看出,现阶段中国果园植保半机械化植保机具应用最广泛,用药量最大、浪费最严重、农药利用率最低;其他地面植保机具中,风送喷雾机应用较普遍,对提高农药利用率,减少药液损失有很大帮助;静电喷雾机、循环喷雾机和变量喷雾机多处在样机试验阶段,未形成产业化发展;航空植保机具特别是植保无人机多方面优势明显,正处于蓬勃发展阶段,但雾滴穿透能力弱,续航时间段尚是其发展制约因素。为进一步提升果园植保机械化水平,推进水果产业健康发展,可重点加强以下几个方面研究工作:
1)推广标准化果园种植方式
随着土地流转政策支持与家庭农场建设实施,针对中国丘陵山区缓坡、平地地带田块分散种植的果园,通过土地承包,集中连片管理,大力推进园区阶梯改坡、陡坡改缓坡、缓坡改平地等宜机化改造,推广标准化果园种植方式,对于提高果园植保机械化水平意义重大。
2)发展立体植保施药技术
随着航空施药技术不断发展,果树连续、定点喷洒作业模式应用成熟,针对槟榔、香蕉等树冠高大、叶面宽厚、行间郁闭的果园,发展地空协同立体植保施药技术,通过研发小微型地面植保机具与植保无人机结合,有望解决该类果园施药难、受药不均、机械化作业水平低的问题,将是未来重点研究方向。
3)大力推广专业化机械植保服务模式
随着中国城市化进程加快,农村劳动力紧缺,果园人工采用半机械化植保机具施药效率低、成本高,针对此类问题,大力推广专业化机械植保服务模式,让专业的人做专业的事,让少数的人干更多的活,让施药成本更低,让果农收益更高,专业化机械植保前景广阔。
4)研发智能植保机器人
针对中国广泛种植的低矮密植果园,加强小微型智能植保机器人研发,使其能够精量对靶喷雾,实现送风量、药流量智能精准调节,如发展植保无人机随速变量、仿冠层飞行施药技术等,以期达到单位面积果园定量化、精量化、均匀性施药要求。
[1] 2020年果园面积要稳定在2亿亩. [2020-10-17] https://news. cnhnb.com/rdzx/detail/384719/
[2] 常有宏,吕晓兰,蔺经,等. 我国果园机械化现状与发展思路[J]. 中国农机化学报,2013,34(6):21-26. Chang Youhong, Lü Xiaolan, Lin Jing, et al. Present state and thinking about development of orchard mechanization in China[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2013, 34(6): 21-26. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 赵映,肖宏儒,梅松,等. 我国果园机械化生产现状与发展策略[J]. 中国农业大学学报,2017,22(6):116-127. Zhao Ying, Xiao Hongru, Mei Song, et al. Current status and development strategies of orchard mechanization production in China[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2017, 22(6): 116-127. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 何雄奎. 高效施药技术与机具[M]. 北京:中国农业大学出版社,2012.
[5] 齐鹏. 常用植保机械简介[J]. 科学种养,2017,12(8):61-62. Qi Peng. Introduction to common plant protection machinery[J]. Scientific planting and nursing, 2017, 12(8): 61-62. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 宋淑然,李琨,孙道宗,等. 山地果园植保技术与装备研究进展[J]. 现代农业装备,2019,40(5):2-9. Song Shuran, Li Kun, Sun Daozong, et al. Research progress on plant protection technology and equipment in mountainous orchard[J]. Modern Agricultural Equipment, 2019, 40(5): 2-9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 杨鹏. 郁闭型果园遥控弥雾机的研制与试验[D]. 杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2016. Yang Peng. Development and Experimental Research of Canopy Type Remote Orchard Mist Sprayer[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 卢营蓬,易文裕,庹洪章,等. 果园喷雾机械现状及发展趋势[J]. 中国农机化学报,2018,39(1):36-41. Lu Yingpeng, Yi Wenyu, Tuo Hongzhang, et al. Present state and trends of orchard sprayer[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2018, 39(1): 36-41. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] Wertheim S J. Intensive apple orchards with slender spindles[J]. Acta Horticulturae, 1978(65): 209-216.
[10] Weber M S, Fokkema N J, Beek M A, et al. The super spindle system[C]. XXV International Horticultural Congress, 2000.
[11] 张林森,马锋旺,李丙智,等. 国外苹果高纺锤形整形技术与应用[J]. 中国果树,2007,31(6):69-70. Zhang Linsen, Ma Fengwang, Li Bingzhi, et al. Technology and application of apple high spindle shaping in foreign countries[J]. China Fruits, 2007, 31(6): 69-70. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 赵芳. 日本的果园管理[J]. 西北园艺,2003,16(4):54-55. Zhao Fang. Orchard management in Japan[J]. Northwest Horticulture, 2003, 16(4): 54-55. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 高东升. 中国设施果树栽培的现状与发展趋势[J]. 落叶果树,2016,48(1):1-4. Gao Dongsheng. Current situation and development trend of fruit tree protected cultivation in China[J]. Deciduous Fruits, 2016, 48(1): 1-4. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 李民宇. 果园管道自动顺序喷雾的喷雾装置设计及试验[D]. 广州:华南农业大学,2019. Li Minyu. Design and Experiment of Automatic Sequence Spray Device for Orchard Pipeline Spray[D]. Guangzhou: South China Agricultural University. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 王辉,石昌飞,宋淑然,等. 果园管道自动顺序喷雾控制系统设计[J]. 广东农业科学,2015,42(11):148-153. Wang Hui, Shi Changfei, Song Shuran, et al. Design of automatic sequence control system for orchard pipeline spray[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 42(11): 148-153. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 于绍夫,贾伯卿. 苹果园管道输液喷药新设施[J]. 中国果树,1980,3(12):36-38. Yu Shaofu, Jia Boqing. New facilities for pipeline spraying in apple orchard[J]. China Fruit, 1980, 3(12): 36-38. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 刘学文. 果园管道喷药技术的应用[C]. 北京昆虫学会成立四十周年学术讨论会,北京,1990:148-149.
[18] 万欣. 果园管道喷药技术[J]. 北京农业,1994,1(5):27. Wan Xin. Technology for orchard pipeline spray[J]. Beijing Agriculture, 1994, 1(5): 27. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 田文龙,钱玉军,胡文利,等. 密植果园微喷灌与管道喷药试验[J]. 山西果树,2000,21(2):23-24. Tian Wenlong, Qian Yujun, Hu Wenli, et al. Experiment on micro irrigation and pipeline spray in dense orchard[J]. Shanxi Fruits, 2000, 21(2): 23-24. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 王飞高,张大伟,林昌礼,等. 山地果园机械管道施药设施建设及其效益分析[J]. 中国南方果树,2005,34(5):73-74. Wang Feigao, Zhang Dawei, Lin Changli, et al. Facilities construction and benefit analysis for mountainous orchard pipeline spray[J]. South China Fruits, 2005, 34(5): 73-74. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 迟志广,方昭,林涛,等. 广西规模化蕉园机械化现状分析[J]. 热带农业科学,2015,35(8):37-41. Chi Zhiguang, Fang Zhao, Lin Tao, et al. Analysis on mechanization of large-scale banana plantation in Guangxi[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Agriculture, 2015, 35(8): 37-41. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 董祥,张铁,燕明德,等. 3WPZ-4型风送式葡萄喷雾机设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2018,49(S):205-213. Dong Xiang, Zhang Tie, Yan Mingde, et al. Design and experiment of 3WPZ-4 type air-assisted grape sprayer[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2018, 49(S): 205-213. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 王荣,党革荣,祁正梅,等. 葡萄园喷雾机风机蜗壳结构改进与性能试验[J]. 农机化研究,2015,37(8):170-173. Wang Rong, Dang Gerong, Qi Zhengmei, et al. Structure improving and performance experimenting of sprayer fan for vineyard orchard[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2015, 37(8): 170-173. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 刘青,傅泽田,祁力钧,等. 9WZCD-25型风送式超低量喷雾机性能优化试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2005,36(9):44-47. Liu Qing, Fu Zetian, Qi Lijun, et al. Characteristics optimization experiments of 9WZCD-25 air-blast and ultralow volume sprayer[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Machinery, 2005, 36(9): 44-47. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 祁力钧,赵亚青,王俊,等. 基于CFD的果园风送式喷雾机雾滴分布特性分析[J]. 农业机械学报,2010,41(2):62-67. Qi Lijun, Zhao Yaqing, Wang Jun, et al. CFD simulation and experimental verification of droplet dispersion of air-assisted orchard sprayer[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Machinery, 2010, 41(2): 62-67. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 张晓辛,吕晓兰,丁素明,等. 果园风送式喷雾机仿形喷雾试验研究[J]. 中国农机化,2011,32(3):68-72. Zhang Xiaoxin, Lü Xiaolan, Ding Suming, et al. Experimental research on profiling spray of air-assisted orchard sprayer[J]. Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2011, 32(3): 68-72. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] Zhang Wei, Hou Yongrui, Liu Xin, et al. Wind tunnel experimental study on droplet drift reduction by a conical electrostatic nozzle for pesticide spraying[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2017, 10(3):87-94.
[28] 周良富,张玲,薛新宇,等. 农药静电喷雾技术研究进展及应用现状分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(18):1-11. Zhou Liangfu, Zhang Ling, Xue Xinyu, et al. Research progress and application status of electrostatic pesticide spray technology[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(18): 1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 舒朝然,詹敏,盛茂领,等. 果树树冠静电喷雾的空间电荷效应分析[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报,2007,38(1):59-64. Shu Chaoran, Zhan Min, Sheng Maoling, et al. Analysis on the space charge effects in tree canopy electrostatic spraying[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2007, 38(1): 59-64. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 周良富,张玲,丁为民,等. 风送静电喷雾覆盖率响应面模型与影响因素分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(S2):52-59. Zhou Liangfu, Zhang Ling, Ding Weimin, et al. Droplet coverage response surface models and influencing factors of air-assisted electrostatic spray[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(S2): 52-59. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 周良富,张玲,薛新宇,等. 双气流道辅助静电喷头设计与试验[J]. 江苏农业科学,2017,45(24):192-196. Zhou Liangfu, Zhang Ling, Xue Xinyu, et al. Design and experiment of double air-assisted electrostatic nozzle[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences 2017, 45(24): 192-196. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 宫少俊,宋坚利. 隧道式循环喷雾机发展研究[J]. 北京农业,2007,14(9):55-58. Gong Shaojun, Song Jianli. Research on the development of tunnel circulating sprayer[J]. Beijing Agriculture, 2007, 14(9): 55-58. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] Beasley E, Rohrbach R, Mainland C, et al. Saturation spraying of blueberries with partial spray recovery[J]. Transactions of the ASAE, 1983, 26(3): 732-736.
[34] Ade G, Molari G, Rondelli V. Vineyard evaluation of a recycling tunnel sprayer[J]. Transactions of the ASAE, 2005, 48(6): 2105-2112.
[35] Peterson D L, Hogmire H W. Tunnel sprayer for dwarf fruit-trees[J]. Transactions of the ASAE, 1994, 37(3): 709-715.
[36] 周良富,薛新宇,周立新,等. 果园变量喷雾技术研究现状与前景分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(23):80-92. Zhou Liangfu, Xue Xinyu, Zhou Lixin, et al. Research situation and progress analysis on orchard variable rate spraying technology[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(23): 80-92. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[37] Hong Y, Zhu H P, Richard D, et al. Evaluation of ultrasonic sensor for variable-rate spray applications[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2011, 75(5): 36, 173-191.
[38] Rosell J, Sanz R. A review of methods and applications of the geometric characterization of tree crops in agricultural activities[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2012, 81(9): 124-141.
[39] 许林云,张昊天,张海峰,等. 果园喷雾机自动对靶喷雾控制系统研制与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(22):1-9. Xu Linyun, Zhang Haotian, Zhang Haifeng, et al. Development and experiment of automatic target spray control system used in orchard sprayer[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(22): 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[40] Francisco J, Jaime S, Pablo A, et al. LiDAR and thermal images fusion for ground-based 3D characterisation of fruit trees[J]. Biosysterm Engineering, 2016, 151(11): 479-494.
[41] Cai Jichen, Wang Xiu, Song Jian, et al. Development of real-time laser-scanning system to detect tree canopy characteristics for variable-rate pesticide application[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2017, 10(6):155-163.
[42] Francisco R, Zhang Q, John F, et al. Stereo vision three dimensional terrain maps for precision agriculture[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2008, 60(5):133-143.
[43] Qiu Wei, Zhao Sanqin, Ding Weimin, et al. Effects of fan speed on spray deposition and drift for targeting air-assisted sprayer in pear orchard[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2016, 9(4):53-62.
[44] 李丽,李恒,何雄奎,等. 红外靶标自动探测器的研制及试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(12):159-163. Li Li, Li Heng, He Xiongkui, et al. Development and experiment of automatic detection device for infrared target[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(12): 159-163. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[45] Gonzalez R, Pawlowski A, Rodriguez C, et al. Design and implementation of an automatic pressure-control system for a mobile sprayer for greenhouse applications[J]. Spanish Journal of Agricultural research, 2012, 10(4): 939-949.
[46] Womac A, Bui Q D. Design and tests of a variable-flow fan nozzle[J]. Transactions of the ASAE, 2002, 45(2): 287-295.
[47] 魏新华,蒋杉,孙宏伟,等. PWM间歇喷雾式变量喷施控制器设计与测试[J]. 农业机械学报,2012,43(12):87-93,129. Wei Xinhua, Jiang Shan, Sun Hongwei, et al. Design and test of variable rate application controller of intermittent spray based on PWM[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2012, 43(12): 87-93, 129. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[48] 邱威,丁为民,傅锡敏,等. 果园喷雾机圆环双流道风机的设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(12):13-17. Qiu Wei, Ding Weimin, Fu Ximin, et al. Design and experiment of ring double-channel fan for spraying machine in orchard[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(12): 13-17. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[49] 丁天航,曹曙明,薛新宇,等. 果园喷雾机单双风机风道气流场仿真与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(14):62-68. Ding Tianhang, Cao Shuming, Xue Xinyu, et al. Simulation and experiment on single-channel and double-channel airflow field of orchard sprayer[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(14): 62-68. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[50] Aljaz O, Tone G, Marko H, et al. Real-time positioning algorithm for variable-geometry air-assisted orchard sprayer[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2013, 98(8):175-182.
[51] He Xiongkui, Bonds Jane, Herbst Andreas, et al. Recent development of unmanned aerial vehicle for plant protection in East Asia[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2017, 10(3):18.
[52] Wang Shilin, Song Jianli, He Xiongkui, et al. Performances evaluation of four typical unmanned aerial vehicles used for pesticide application in China[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2017, 10(4):22-31.
[53] Wang Linhui, Lan Yubin, Yue Xuejun, et al. Vision-based adaptive variable rate spraying approach for unmanned aerial vehicles[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2019, 12(3):18-26.
[54] Qin Weicai, Xue Xinyu, Zhang Shaoming, et al. Droplet deposition and efficiency of fungicides sprayed with small UAV against wheat powdery mildew[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2018, 11(2):27-32.
[55] Meng Yanhua, Lan Yubin, Mei Guiying, et al. Effect of aerial spray adjuvant applying on the efficiency of small unmanned aerial vehicle for wheat aphids control[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2018, 11(5):46-53.
[56] Zheng Yongjun, Yang Shenghui, Zhao Chunjiang, et al. Modelling operation parameters of UAV on spray effects at different growth stages of corns[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2017, 10(3):57.
[57] 秦维彩,薛新宇,周立新,等. 无人直升机喷雾参数对玉米冠层雾滴沉积分布的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(5):50-56. Qin Weicai, Xue Xinyu, Zhou Lixin, et al. Effects of spraying parameters of unmanned aerial vehicle on droplets deposition distribution of maize canopies[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(5): 50-56. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[58] Liao Juan, Zang Ying, Luo Xiwen, et al. Optimization of variables for maximizing efficacy and efficiency in aerial spray application to cotton using unmanned aerial systems[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2019, 12(2):10-17.
[59] 何雄奎. 中国精准施药技术和装备研究现状及发展建议[J].智慧农业,2020,2(1):133-146. He Xiongkui. Research progress and developmental recommendations on precision spraying technology and equipment in China[J]. Smart Agriculture, 2020, 2(1): 133-146. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[60] 傅锡敏,吕晓兰,丁为民,等. 我国果园植保机械现状与技术需求[J]. 中国农机化,2009,16(6):10-13. Fu Ximin, Lü Xiaolan, Ding Weimin, et al. Present state and technical requirement about orchard plant protection machinery in China[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2009, 16(6): 10-13. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[61] WS-16D背负式电动喷雾器[EB/OL]. [2020-10-02] https://www. nongjitong. com/product/1522_ws-16d_ spray_machine. html.
[62] 3WF-960背负式机动喷雾喷粉机[EB/OL]. [2020-10-02] https://item. jd. com/25147383035. html.
[63] TS-35A背负式热力烟雾机[EB/OL]. [2020-10-02] https://item. jd. com/68984797912. html.
[64] HD-22D担架式机动喷雾机[EB/OL]. [2020-10-02] https://item. jd. com/1713681083. html.
[65] HD100T推车式机动喷雾机[EB/OL]. [2020-10-02] https://item. jd. com/26021986433. html.
[66] 马锞,李建国,赖旭辉,等. 果园管道喷药系统建设及效益分析[J]. 中国南方果树,2018,47(2):165-166. Ma Ke, Li Jianguo, Lai Xuhui, et al. System construction and benefit analysis for orchard pipeline spray[J]. South China Fruits, 2018, 47(2): 165-166. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[67] 宋淑然,洪添胜,孙道宗,等. 基于微机的管道恒压喷雾控制装置:CN101690923A[P]. 2010-04-07.
[68] 宋淑然,阮耀灿,洪添胜,等. 果园管道喷雾系统药液压力的自整定模糊PID控制[J]. 农业工程学报,2011,27(6):157-161. Song Shuran, Ruan Yaocan, Hong Tiansheng, et al. Self-adjustable fuzzy PID control for pressure of pipeline spray system in orchard[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2011, 27(6): 157-161. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[69] 吴伟锋,洪添胜,代秋芳,等. 基于Zigbee的多节点管道喷雾压力控制系统研究[J]. 农机化研究, 2019,41(10):52-57. Wu Weifeng, Hong Tiansheng, Dai Qiufang, et al. Research of multi-node pressure control system for pipeline spray based on ZigBee[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2019, 41(10): 52-57. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[70] 李致. 基于管道喷雾的在线混药技术及装置[D]. 广州:华南农业大学,2018. Li Zhi. On-line Mixing Pesticide Technology and Device Based on Pipeline Spraying[D]. Guangzhou: South China Agricultural University, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[71] 李民宇,宋淑然,代秋芳,等. 管道自动顺序喷雾架设计及喷雾有效性试验[J]. 农机化研究,2020,42(1):153-160. Li Minyu, Song Shuran, Dai Qiufang, et al. Design and experiment of automatic sequential pipeline spray frame and spraying validity[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2020, 42(1): 153-160. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[72] 施鹏,薛新宇,王振龙,等. 果园动力底盘喷雾机的发展现状[J]. 中国农机化学报,2013,34(6):27-31. Shi Peng, Xue Xinyu, Wang Zhenlong, et al. Present situation of development on the dynamic chassis orchard sprayer[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2013, 34(6): 27-31. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[73] 王艳红. 2018意大利EIMA农机展上的植保机械[J]. 农业工程,2018,8(11):2-3. Wang Yanhong. Plant protection machinery showed in Italy agricultural machinery exhibition 2018[J]. Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 8(11):2-3. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[74] MUNCKHOF制造导流板式风送喷雾机[EB/OL]. [2020-10-02] https://www.agriexpo.cn/prod/munckhof/product-184798-82698.html.
[75] HARDI制造轴流风送喷雾机[EB/OL]. [2020-10-02] https://www.agriexpo.cn/prod/hardi/product-169215-13149.html.
[76] HARDI制造加农炮式风送喷雾机[EB/OL]. [2020-10-02] https://hardi-international.com/sprayers/mistblowers/zenit-orchard/cannon#nav.
[77] ASIA TECH公司制造自走式风送喷雾机[EB/OL]. [2020-10-02] https://www.agriexpo.cn/prod/asia-technology- co-ltd/product-180444-55544.html.
[78] 张晓辉,郭清南,李法德,等. 3MG30型果园弥雾机的研制与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2002,33(3):30-33. Zhang Xiaohui, Guo Qingnan, Li Fade, et al. Development of 3MG-30 orchard mist sprayer[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2002, 33(3): 30-33. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[79] 邱威,丁为民,汪小旵,等. 3WZ-700型自走式果园风送定向喷雾机[J]. 农业机械学报,2012,43(4):26-30. Qiu Wei, Ding Weimin, Wang Xiaochan, et al. 3WZ-700 self-propelled air-blowing orchard sprayer[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2012, 43(4): 26-30. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[80] 徐莎,翟长远,朱瑞祥,等. 喷雾高度可调的果园风送喷雾机的设计[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报:自然科学版,2013,41(11):229-234. Xu Sha, Zhai Changyuan, Zhu Ruixiang, et al. Design of an orchard air-assisted sprayer with adjustable spray height[J]. Journal of Northwest A&F university (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 41(11): 229-234. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[81] 李超,张晓辉,姜建辉,等. 葡萄园立管风送式喷雾机的研制与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(4):71-78. Li Chao, Zhang Xiaohui, Jiang Jianhui, et al. Development and experiment of riser air-blowing sprayer in vineyard[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(4): 71-78. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[82] 张晓辉,姜宗月,范国强,等. 履带自走式果园定向风送喷雾机[J]. 农业机械学报,2014,45(8):117-122. Zhang Xiaohui, Jiang Zongyue, Fan Guoqiang, et al. Self-propelled crawler directional air-blowing orchard sprayer[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2014, 45(8): 117-122. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[83] 荣喃喃,王冉冉,郭鹏军,等. 微型自走式电动果园弥雾机的研制与试验[J]. 农机化研究,2016,38(10):92-95. Rong Nannan, Wang Ranran, Guo Pengjun, et al. Design and experiment of the micro self-propelled electric sprayer in orchard[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2016, 38(10): 92-95. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[84] 丁素明,薛新宇,张玲,等. 自走式果园风送喷雾机的研制[J]. 中国农机化学报,2016,37(4):54-58. Ding Suming, Xue Xinyu, Zhang Ling, et al. Design on self-propelled air-blowing orchard sprayer[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2016, 37(4): 54-58. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[85] 樊桂菊,王永振,仉利,等. 履带风送式喷雾机的设计与试验[J]. 农机化研究,2018,40(5):117-120. Fan Guiju, Wang Yongzhen, Zhang Li, et al. Design and experiment of caterpillar air-assisted orchard sprayer[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2018, 40(5): 117-120. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[86] 3WF-80F风送喷雾机[EB/OL]. [2020-10-02] http://www. sprayerchina.com/product/26.html.
[87] 3WFG-400X风送喷雾机[EB/OL]. [2020-10-02] http://www. sprayerchina.com/product/28.html.
[88] 3WZ-500L自走式风送喷雾机[EB/OL]. [2020-10-02] https://www.nongjitong.com/product/604_3wz_500l_spray_machine.html.
[89] Duo wing jet静电喷雾机[EB/OL]. [2020-10-02] https://www.agriexpo.cn/prod/martignani-srl/product-179347-86640.html.
[90] 100SR静电喷雾机[EB/OL]. [2020-10-02] https://www.agriexpo.cn/prod/electrostatic-spraying-systems/product-173798-55984.html.
[91] 何雄奎,严苛荣,储金宇,等. 果园自动对靶静电喷雾机设计与试验研究[J]. 农业工程学报,2003,19(6):78-80. He Xiongkui, Yan Kerong, Chu Jinyu, et al. Design and testing of the automatic target detecting, electrostatic, air assisted, orchard sprayer[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2003, 19(6): 78-80. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[92] 周艳,祁力钧,贾首星,等. 果园气力式静电喷雾机的开发及应用前景[J]. 安徽农业科学,2012,40(7):4429-4430. Zhou Yan, Qi Lijun, Jia Shouxing, et al. The development of pneumatic electrostatic spraying in orchard and the application prospect[J]. Anhui Agricultural Science, 2012, 40(7): 4429-4430. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[93] 杨洲,牛萌萌,李君,等. 果园在线混药型静电喷雾机的设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(21):60-67. Yang Zhou, Niu Mengmeng, Li Jun, et al. Design and experiment of an electrostatic sprayer with on-line mixing system for orchard[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(21): 60-67. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[94] 周良富,张玲,薛新宇,等. 3WQ-400型双气流辅助静电果园喷雾机设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(16):45-53. Zhou Liangfu, Zhang Ling, Xue Xinyu, et al. Design and experiment of 3WQ-400 double air-assisted electrostatic orchard sprayer[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(16): 45-53. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[95] 王志强,郝志强,刘凤之,等. 气力雾化风送式果园静电弥雾机的研制与试验[J]. 果树学报,2017,34(9):1161-1169. Wang Zhiqiang, Hao Zhiqiang, Liu Fengzhi, et al. Design and experiment of an air-atomized, air-assisted and electrostatic orchard sprayer[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2017, 34(9): 1161-1169. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[96] Nestor循环喷雾机[EB/OL]. [2020-10-02] https://www. agriexpo. cn/prod/weremczuk-fmr-sp-z-o-o/product-170611- 17417. html.
[97] 宋坚利,何雄奎,张京,等. “Π”型循环喷雾机设计[J]. 农业机械学报,2012,43(4):31-36. Song jianli, He Xiongkui, Zhang Jing, et al. Design of Π-type recycling tunnel sprayer[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2012, 43(4): 31-36. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[98] 张京,宋坚利,何雄奎,等. “Π”型循环喷雾机防飘性能试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2012,43(4):37-39. Zhang Jing, Song Jianli, He Xiongkui, et al. Anti-drift performance experiment of Π-type recycling tunnel sprayer[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2012, 43(4): 37-39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[99] 牛萌萌,方会敏,乔璐,等. 高地隙隧道式循环喷雾机设计与试验[J]. 中国农机化学报,2019,40(11):41-48. Niu Mengmeng, Fang Huimin, Qiao Lu, et al. Design and experiment of high clearance type recycling tunnel sprayer[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2019, 40(11): 41-48. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[100] Sun Hong, Li Minzan, Zhang Qin. Detection system of smart sprayers: Status, challenges, and perspectives[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2012, 5(3):10-23.
[101] 邱白晶,闫润,马靖,等. 变量喷雾技术研究进展分析[J]. 农业机械学报,2015,46(3):59-72. Qiu Baijing, Yan Run, Ma Jing, et al. Research progress analysis of variable rate sprayer technology[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2015, 46(3): 59-72. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[102] Berk P, Belšak A, Stajnko D, et al. Intelligent automated system based on a fuzzy logic system for plant protection product control in orchards[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2019, 12(3):92-102
[103] Gil E, Llorens J, Llop J, et al. Variable rate sprayer Part 2-Vineyard prototype: Design, implementation, and validation[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2013, 95(3): 136-150.
[104] 葛玉峰,周宏平,郑加强,等. 基于机器视觉的室内农药自动精确喷雾系统[J]. 农业机械学报,2005,36(3):86-89. Ge Yufeng, Zhou Hongping, Zheng Jiaqiang, et al. Indoor pesticide smart spraying system based on machine vision[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2005, 36(3): 86-89. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[105] 宋淑然,陈建泽,洪添胜,等. 果园柔性对靶喷雾装置设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(10):57-63. Song Shuran, Chen Jianze, Hong Tiansheng, et al. Design and experiment of orchard flexible targeted spray device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(10): 57-63. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[106] 金鑫,董祥,杨学军,等. 3WGZ-500型喷雾机对靶喷雾系统设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2016,47(7):21-27. Jin Xin, Dong Xiang, Yang Xuejun, et al. Design and experiment of target spraying system of 3WGZ-500 sprayer[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(7): 21-27. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[107] 姜红花,白鹏,刘理民,等. 履带自走式果园自动对靶风送喷雾机研究[J]. 农业机械学报,2016,47(S1):189-195. Jiang Honghua, Bai Peng, Liu Limin, et al. Caterpillar self-propelled and air-assisted orchard sprayer with automatic target spray system[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(S1): 189-195. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[108] Qiu Wei, Zhao Sanqin, Ding Weimin, et al. Effects of fan speed on spray deposition and drift for targeting air-assisted sprayer in pear orchard[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2016, 9(4):53-62.
[109] 李龙龙,何雄奎,宋坚利,等. 基于变量喷雾的果园自动仿形喷雾机的设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(1):70-76. Li Longlong, He Xiongkui, Song Jianli, et al. Design and experiment of automatic profiling orchard sprayer based on variable air volume and flow rate[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(1): 70-76. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[110] 兰玉彬,陈盛德,邓继忠,等. 中国植保无人机发展形势及问题分析[J]. 华南农业大学学报,2019,40(5):217-225. Lan Yubin, Chen Shengde, Deng Jizhong, et al. Development situation and problem analysis of plant protection unmanned aerial vehicle in China[J]. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 2019, 40(5): 217-225. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[111] 水星一号单旋翼植保无人机[EB/OL]. [2020-10-02] http://www.hanhe-aviation.com/sxyh.html
[112] 极飞P20植保无人机[EB/OL]. [2020-10-02] https://www. xa.com/p20-2018.
[113] 大疆T16植保无人机[EB/OL]. [2020-10-02] https://www.dji.com/cn/t16?site=brandsite&from=nav.
[114] 韦加JF01-20植保无人机[EB/OL]. [2020-10-02] http://www.vigauav.com/index.php/product-product-dataId-20.html.
[115] Yang Fengbo, Xue Xinyu, Zhang Ling, et al. Numerical simulation and experimental verification on downwash air flow of six-rotor agricultural unmanned aerial vehicle in hover[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2017, 10(4):41-53.
[116] Hou Chaojun, Tang Yu, Luo Shaoming, et al. Optimization of control parameters of droplet density in citrus trees using UAVs and the Taguchi method[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2019, 12(4):1-9.
[117] Zhou Qingqing, Xue Xinyu, Qin Weicai, et al. Optimization and test for structural parameters of UAV spraying rotary cup atomizer[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2017, 10(3):78-86.
[118] 杨风波,薛新宇,蔡晨,等. 多旋翼植保无人机悬停下洗气流对雾滴运动规律的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(2):64-73. Yang Fengbo, Xue Xinyu, Cai Chen, et al. Effect of down wash airflow in hover on droplet motion law for multi-rotor unmanned plant protection machine[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(2): 64-73. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[119] Zheng Y, Yang S, Liu X, et al. The computational fluid dynamic modeling of downwash flow field for a six-rotor UAV[J]. Frontiers of Agricultural Science and Engineering, 2018.
[120] 张豪,祁力钧,吴亚垒,等. 基于Porous模型的多旋翼植保无人机下洗气流分布研究[J]. 农业机械学报,2019,50(2):112-122. Zhang Hao, Qi Lijun, Wu Yalei, et al. Spatio-temporal distribution of down wash airflow for multi-rotor plant protection UAV based on porous model[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2019, 50(2): 112-122. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[121] 王娟,兰玉彬,姚伟祥,等. 单旋翼无人机作业高度对槟榔雾滴沉积分布与飘移影响[J]. 农业机械学报,2019,50(7):1-14. Wang Juan, Lan Yubin, Yao Weixiang, et al. Effects of working height of single-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle on drift and droplets deposition distribution of areca canopies[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2019, 50(7): 1-14. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[122] 张盼,吕强,易时来,等. 小型无人机对柑橘园的喷雾效果研究[J]. 果树学报,2016,33(1):34-42. Zhang Pan, Lü Qiang, Yi Shilai, et al. Evaluation of spraying effect using small unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) in citrus orchard[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2016, 33(1): 34-42. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[123] Lü Meiqiao, Xiao Shupei, Tang Yu, et al. Influence of UAV flight speed on droplet deposition characteristics with the application of infrared thermal imaging[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2019, 12(3):10-17.
[124] 陈盛德,兰玉彬,周志艳,等. 小型植保无人机喷雾参数对橘树冠层雾滴沉积分布的影响[J]. 华南农业大学学报,2017,38(5):97-102. Chen Shengde, Lan Yubin, Zhou Zhiyan, et al. Effects of spraying parameters of small plant protection UAV on droplets deposition distribution in citrus canopy[J]. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 2017, 38(5): 97-102. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[125] Zhang Yanliang, Lian Qi, Zhang Wei. Design and test of a six-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) electrostatic spraying system for crop protection[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2017, 10(6):68-76.
[126] Zhang Pan, Deng Lie, Lü Qiang, et al. Effects of citrus tree shape and spraying height of small unmanned aerial vehicle on droplet distribution[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2016, 9(4): 45-52.
[127] Tang Y, Hou C J, Luo S M, et al. Effects of operation height and tree shape on droplet deposition in citrus trees using an unmanned aerial vehicle[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2018, 148: 1-7.
Research progress of orchard plant protection mechanization technology and equipment in China
Zheng Yongjun1, Chen Bingtai1, Lyu Haotun1, Kang Feng2, Jiang Shijie1
(1.,,100083,; 2.,,100083,)
Orchard spray is a key link to orchard production, due to it occupied nearly 25% of the total workload of orchard management. Moreover, the degree of plant protection mechanization directly affects the economic benefits of fruits. In this review, the orchard characteristic, the general situation of plant protection mechanization and the reasons restricting its development were introduced briefly, in order to clarify the future progress of mechanization technology and equipment for the orchard plant protection in China. The main reason impeding the development of plant protection mechanization can be a large proportion of hilly orchards, including gradient, slope and flat orchard, together with a very complex planting environment. Since the standardized modern orchards are being promoted, the scale is still small, due partly to the extensive management in traditional orchards the high price. Currently, the plant protection mechanization level of flat orchard was 15%, whereas, the hilly orchard was only 7.5%. Therefore, the progress of key plant protection mechanization technologies and equipment was presented in detail, further to improve the mechanization level of plant protection. For example, the pipeline spraying technology and equipment brought good benefits and spraying effects to the hilly orchard, while, the application of air-assisted spraying technology and equipment improved the mechanized operation level of the flat orchard. Electrostatic spraying technology and equipment were especially used to enhance the droplet coverage rate on the back of leaves. While the tunnel spraying technology and equipment increased the droplet density on the canopies, to recovery the droplet that left the target, indicating that it can effectively improve the pesticide utilization. Variable rate spraying technology and equipment were becoming a hot research topic, particularly on the precise control of spray on demand. The core technology of variable rate spraying was target detection, such as ultrasonic detection, laser detection, infrared detection, machine vision methods. The ultrasonic and laser detection methods have achieved the best application. Since 2010, the great development and application of aerial spraying technology and equipment have been widely recognized. Especially, the unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) of rotor plant protection has become one of the most popular machines with small size, fast flight speed and strong terrain adaptability among the agricultural aerial equipment. In this review, the research state of rotor plant protection UAV in orchard was introduced from three aspects: operation model, downwash flow field, and working parameters. Plant protection equipment can offer some suggestions for the development of plant protection mechanization from these aspects: promoting standardized models of orchard plant, developing stereo spraying technology, promoting specialized and mechanical service model of plant protection, thereby for the intelligent robots of plant protection.
spraying; mechanization; pesticides; orchards; plant protection machinery; pesticide utilization rate; research progress
郑永军,陈炳太,吕昊暾,等. 中国果园植保机械化技术与装备研究进展[J]. 农业工程学报,2020,36(20):110-124.doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.20.014 http://www.tcsae.org
Zheng Yongjun, Chen Bingtai, Lyu Haotun, et al. Research progress of orchard plant protection mechanization technology and equipment in China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2020, 36(20): 110-124. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.20.014 http://www.tcsae.org
2020-07-30
2020-10-03
国家重点研发计划项目(2018YFD0700603);山东烟台校地融合发展项目
郑永军,博士,教授,博士生导师,主要从事农业智能装备和无人机应用研究。Email:zyj@cau.edu.cn
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.20.014
S224
A
1002-6819(2020)-20-0110-15
