微小RNA-142-3p靶向Rictor诱导动脉粥样硬化相关的内皮细胞凋亡*
2020-12-03肖丽刘萍秦冰
肖丽, 刘萍, 秦冰
微小RNA-142-3p靶向Rictor诱导动脉粥样硬化相关的内皮细胞凋亡*
肖丽, 刘萍, 秦冰△
(中山大学附属第三医院神经内科,广东 广州 510630)
探讨微小RNA-142-3p (miR-142-3p)对动脉粥样硬化(atherosclerosis,AS)进程中人主动脉内皮细胞(human aortic endothelial cells,HAECs)凋亡的影响及作用机制。HAECs经氧化型低密度脂蛋白(oxidized low-density lipoprotein,ox-LDL)作用后,采用RT-qPCR检测miR-142-3p的表达水平。Annexin V-FITC/PI双染法流式细胞术(flow cytometry,FCM)和caspase-3活性检测试剂盒检测细胞凋亡。使用TargetScan等生物信息学软件预测miR-142-3p的潜在靶基因,双萤光素酶报告基因实验验证miR-142-3p与Rictor mRNA 3′-UTR直接靶向结合。在ox-LDL诱导HAECs凋亡过程中miR-142-3p表达显著上调(<0.05,<0.01)。过表达miR-142-3p促进HAECs凋亡,相反,抑制miR-142-3p的表达水平可以部分程度缓解ox-LDL介导的内皮细胞(endothelial cells,ECs)凋亡。进一步研究发现,为miR-142-3p的下游靶基因,沉默基因抑制了miR-142-3p抑制物(miR-142-3p inhibitor)的抗凋亡作用。Akt/eNOS信号通路参与了miR-142-3p对ECs凋亡的调控。抑制miR-142-3p表达可促进靶基因表达并激活Akt/eNOS信号通路从而发挥抗凋亡的内皮保护作用。
微小RNA-142-3p;人主动脉内皮细胞;细胞凋亡;Rictor;动脉粥样硬化
动脉粥样硬化(atherosclerosis,AS)是一种炎症性疾病,其启动因素为血管内皮细胞(endothelial cells,ECs)损伤[1]。氧化型低密度脂蛋白(oxidized low-density lipoprotein,ox-LDL)作为AS的重要危险因素之一,可以诱导ECs发生凋亡,继而导致血管内膜增生、炎症细胞浸润、脂质沉积和斑块破裂[2]。因此,抑制ox-LDL诱导的ECs凋亡对AS的预防和治疗有重要意义。微小RNA(microRNA, miRNA, miR)是真核生物进化中,一种高度保守的、新颖的、内源性的非编码小RNA,其通过降解或转录抑制靶RNA,负性调控超过30%的基因表达[3]。近年来有研究报道miR-142-3p在心肌细胞凋亡、纤维化和内皮屏障破坏等多种心血管疾病中发挥重要调控作用[4]。本研究通过制备ox-LDL诱导的人主动脉内皮细胞(human aortic endothelial cells, HAECs)凋亡模型,探讨miR-142-3p对ox-LDL诱导的HAECs凋亡的作用及机制,为AS的防治提供一定的实验依据。
材料和方法
1 材料
HAECs、内皮细胞培养基和内皮细胞生长因子购自ScienCell;胎牛血清(fetal bovine serum, FBS)、总RNA提取试剂Trizol、Opti-MEM培养基和Lipofectamine2000购自Invitrogen; ox-LDL购自北京协生生物有限公司; miRNA阴性对照模拟物(negative control mimic, NC mimic)、miR-142-3p模拟物(miR-142-3p mimic)、miRNA阴性对照抑制物(NC inhibitor)、miR-142-3p抑制物(miR-142-3p inhibitor)、siRNA和阴性对照siRNA (NC siRNA)购自广州锐博生物科技有限公司; LY294002、L-NAME、caspase-3活性检测试剂盒、CCK-8检测试剂盒和Annexin V-FITC/PI凋亡检测试剂盒购自江苏碧云天生物科技有限公司; MTT购自AMRESCO; TaqMan MicroRNA Assays购自Applied Biosystems; mRNA实时荧光定量PCR试剂盒(SYBR®Premix Ex TaqTMII Kit)购自TaKaRa;引物由上海生工生物工程有限公司合成;Western blot实验中所用的Ⅰ抗[Rictor (sc-81538)、p-Akt (Ser473)(sc-514032)、Akt (sc-81434)、p-eNOS (Ser1177 )(sc-81510)、eNOS (sc-376751)、GAPDH (sc-32233)和β-actin (sc-130065)]购自Santa Cruz;辣根过氧化物酶标记羊抗兔IgG购自KPL;pMIR-REPORT萤光素酶报告载体购自Ambion;抗CD31抗体(ab28364)购自Abcam; Alexa Fluor 488标记的荧光Ⅱ抗购自EarthOx。
2 方法
2.1细胞培养原代HAECs接种在含FBS(50 mg/L)、青/链霉素和生长因子的内皮细胞专用培养基中,培养条件为37℃、5% CO2培养箱内培养,待细胞长至80%融合度进行传代,稳定培养至第3~6代的细胞用于后续实验。
2.2细胞表型鉴定将细胞接种到12孔板,待细胞贴壁后培养细胞至融合度达30%~50%。采用75%乙醇在室温条件下固定细胞15 min, PBS洗涤3次后, 1% Triton-100室温下破膜10 min,5% BSA室温条件下封闭30 min。加入1∶100稀释的抗CD31抗体4℃孵育过夜,PBS洗涤3遍,再加入1∶400稀释的Alexa Fluor 488标记的羊抗兔IgG, 37℃避光孵育30 min,DAPI染核,荧光显微镜下观察并拍照。
取80%~90%融合的细胞,胰酶消化后,离心去上清,1% Triton X-100室温破膜10 min, 5% BSA封闭30 min。加入1∶100稀释的抗CD31抗体4℃孵育过夜, PBS清洗后再经Alexa Fluor 488标记的羊抗兔IgG, 37℃避光孵育30 min,流式细胞术检测。
2.3细胞转染和细胞处理按照说明书分别将50 nmol/L的miR-142-3p mimic和miR-142-3p inhibitor转染至HAECs,阴性对照组分别转染NC mimic和NC inhibitor,之后再经ox-LDL(100 mg/L)作用24 h。为检测Akt/eNOS信号通路的作用,HAECs首先经过生理盐水、LY294002(20 μmol/L)或L-NAME(100 μmol/L)处理2 h,之后转染miR-142-3p inhibitor或NC inhibitor,再经ox-LDL(100 mg/L)作用24 h。救援实验:HAECs中分别共转染miR-142-3p inhibitor和50 μmol/L Rictor siRNA或NC siRNA,之后再经ox-LDL(100 mg/L)作用24 h。
2.4caspase-3活性检测和流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡首先将待检测的各组细胞密度调整为5×106/L,离心弃掉上清液,使用PBS洗涤2次,加入100 μL裂解缓冲液,冰上放置15 min,涡旋振荡15 s,离心5 min。取10 μL蛋白上清液,加入90 μL caspase-3活性检测液,再加入10 μL Ac-LEHD-pNA,避光反应1~2 h后检测结果。
将HAECs悬液以1×109/L的浓度接种至6孔板,收集经不同处理后的细胞并用Annexin V-FITC/PI凋亡检测试剂盒染色,流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡率。Annexin V-FITC+PI-细胞为早期凋亡细胞,凋亡率(%)=早期凋亡细胞数/所检测细胞总数×100%。
2.5CCK-8实验测定细胞活力HAECs接种于96孔板,每孔100 μL,将培养板置于37℃、5% CO2的培养箱中培养1 d后,在不同处理组的每孔加入10 μL CCK-8溶液,孵育2 h后在450 nm波长下于酶标仪测量吸光度()值。每个样品重复5次。
2.6RT-qPCR检测miRNA的水平Trizol提取总RNA,采用TaqMan MicroRNA Assay Kits在7900HT实时荧光定量PCR仪上检测各组样本中miR-142-3p的表达,以U6作为内参照,相对表达量按照2-ΔΔCt法计算。miR-142-3p的正向引物序列为5'-GGGTGTAGTGTTTCCTACTT-3',反向引物序列为5'-TTTGGCACTAGCACATT-3'; U6的正向引物序列为5'-CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA-3',反向引物序列为5'-AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT-3'。
2.7Western blot检测蛋白水平提取各细胞样本总蛋白,定量,与上样缓冲液按比例混匀,100℃水浴加热5 min,经8% SDS-PAGE后电转移至PVDF膜上, 5%脱脂牛奶室温封闭1 h,加入Ⅰ抗, 4℃孵育过夜, TBST洗涤3次,每10 min换液1次;加入Ⅱ抗, 37℃孵育45 min, TBST洗涤3次,每15 min换液1次,在暗室中压片,然后显影、定影。
2.8RT-qPCR检测mRNA的表达Trizol提取各组细胞样本的总RNA,以β-actin为内参照,检测各样本Rictor的mRNA表达水平。两步法PCR扩增标准程序为: 95℃预变性30 s; 95℃ 5 s, 60℃ 30 s, 40个循环。采用2-ΔΔCt法计算各样本相对表达量。Rictor的正向引物为5'-GGAAGCCTGTTGATGGTGAT-3',反向引物序列为5'-GGCAGCCTGTTTATGGTGT-3';GAPDH的正向引物序列为5'-AAGGTGAAGGTCGGAGTCAAC-3',反向引物序列为5'-GGGGTCATTGATGGCAACAATA-3'。
2.9双萤光素酶报告基因实验生物信息学预测显示miR-142-3p与Rictor的3'-UTR存在结合位点,将含有结合位点与突变位点的Rictor 3'-UTR片段分别插入萤光素酶报告基因载体构建野生型载体pMIR-Rictor-3'-UTR与突变型载体pMIR-Rictor-3'-UTR Mutant,取生长状态良好的HAECs,分别将pMIR-Rictor-3'-UTR、pMIR-Rictor-3'-UTR Mutant与NC mimic、miR-142-3p mimic共转染并置于37℃、5% CO2的培养箱内继续培养48 h,检测各组细胞的萤光素酶活性。
3 统计学处理
采用SPSS 23.0软件进行统计学分析。计量资料用均数±标准差(mean±SD)表示,组间比较采用方差分析,以<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
结果
1 血管内皮细胞鉴定
原代HAECs接种在含FBS、青/链霉素和生长因子的内皮细胞专用培养基中,培养条件为37℃、5% CO2培养箱内培养,待细胞长至80%融合度时进行传代,稳定培养至第3~6代的细胞于倒置荧光显微镜下观察示,所培养细胞CD31表达阳性,见图1A。流式细胞术结果显示,培养细胞CD31阳性表达率为(98.4±0.9)%,见图1B。这说明本实验所用细胞为血管内皮细胞。
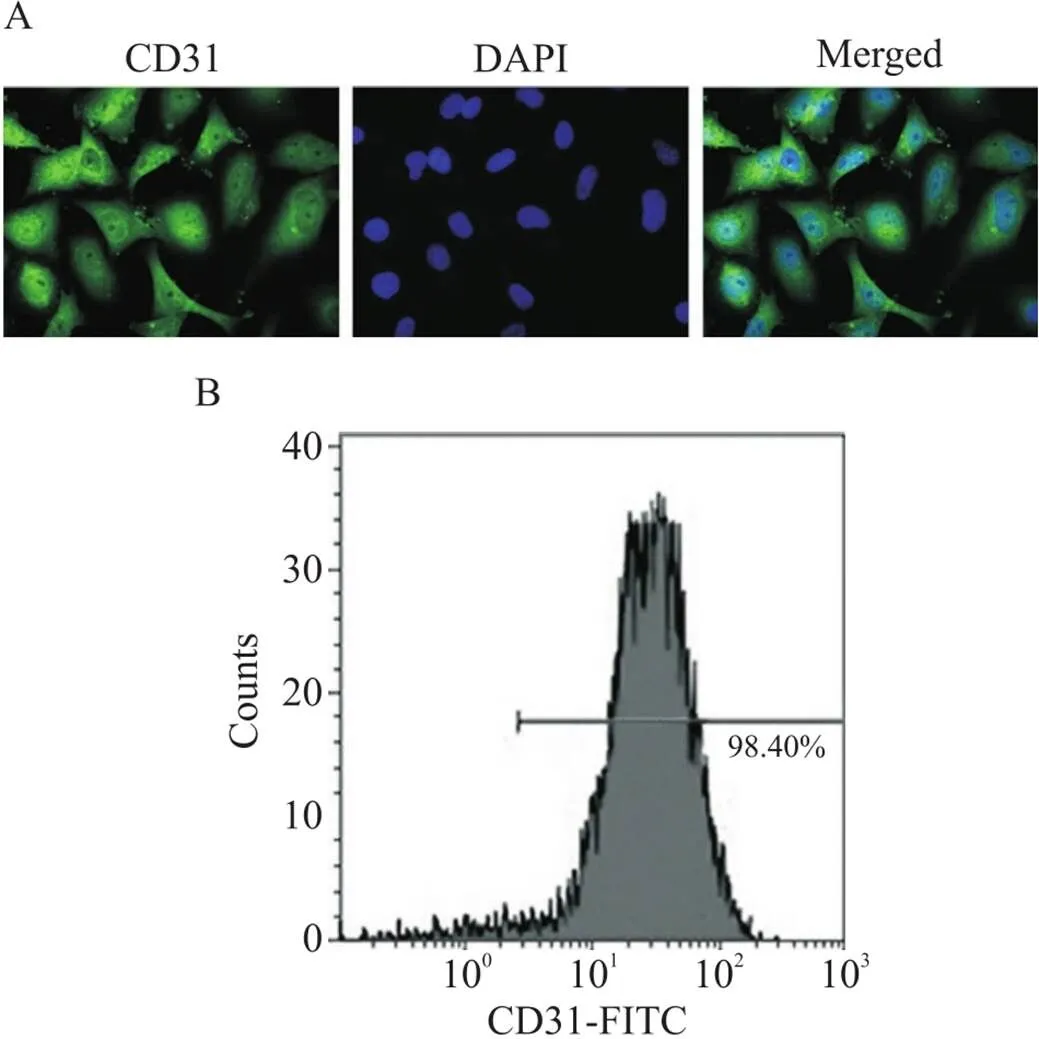
Figure 1. Identification of vascular endothelial cells. A: immunofluorescence staining of CD31 in the vascular endothelial cells (×400); B: the expression of CD31 in the vascular endothelial cells was measured by flow cytometry.
2 miR-142-3p在HAECs凋亡过程中表达上调
HAECs中加入ox-LDL (100 mg/L)分别培养不同时间(0~24 h),caspase-3活性测定和流式细胞术检测显示ox-LDL呈时间依赖性地诱导HAECs发生凋亡(<0.05或<0.01),见图2A、B,且细胞活力显著下降(<0.05或<0.01),见图2C。RT-qPCR检测HAECs凋亡过程中miR-142-3p表达的变化,结果显示随着HAECs凋亡率的升高, miR-142-3p的表达逐渐上调(<0.05或<0.01),见图2D。
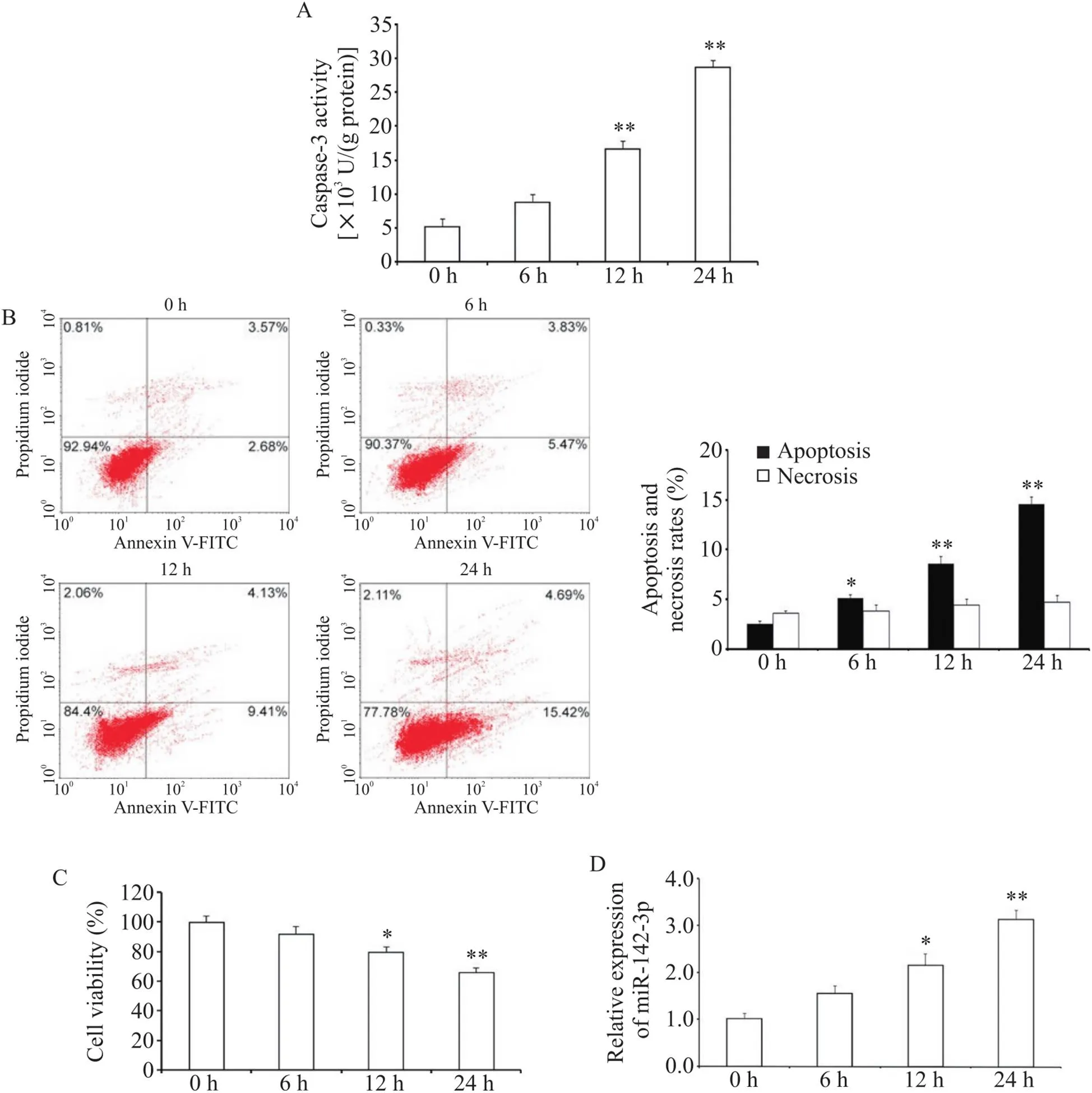
Figure 2. Effects of ox-LDL on the apoptotic and the expression of miR-142-3p in HAECs. A: caspase-3 activity of HAECs was detected; B: flow cytometric analysis of apoptosis and necrosis; C: the viability of HAECs was measured by CCK8 assay; D: relative expression level of miR-142-3p in HAECs was analyzed by RT-qPCR. Mean±SD. n=3. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs 0 h group.
3 Rictor是miR-142-3p在HAECs中的靶基因之一
利用生物信息学软件(TargetScan、miRanda和miRDB)预测miR-142-3p可能的靶基因,挑选出作为下一步的研究对象。如图3C所示,Rictor的3'-UTR含有miR-142-3p的结合位点,有可能是miR-142-3p的直接靶基因。为研究miR-142-3p对Rictor蛋白和mRNA表达的影响,将miR-142-3p mimic和miR-142-3p inhibitor转染入HAECs。ox-LDL处理抑制了Rictor蛋白的表达,与miR-142-3p的表达呈负相关; miR-142-3p mimic显著降低了Rictor蛋白的表达,而miR-142-3p inhibitor上调了Rictor蛋白的表达水平(<0.05),见图3A。此外,miR-142-3p mimic和miR-142-3p inhibitor的转染对Rictor mRNA的表达无明显影响(图3B),提示miR-142-3p有可能在转录后水平调控基因的表达。
为进一步验证miR-142-3p是否与Rictor mRNA的3’-UTR直接结合,我们采用双萤光素酶报告基因实验进行鉴定。结果显示,与NC mimic组相比, miR-142-3p mimic与pMIR-Rictor-3'-UTR共同转染后萤光素酶活性显著降低(<0.01),而miR-142-3p mimic和pMIR-Rictor-3'-UTR Mutant共转染组的萤光素酶活性则无明显变化,见图3D。这说明miR-142-3p可以通过结合Rictor 3'-UTR上的预测靶位点直接抑制Rictor的表达,而将预测的靶位点突变后,miR-142-3p对Rictor的抑制作用基本消除。因此,在HAECs中是miR-142-3p的直接靶基因之一。

Figure 3. Experimental validation of Rictor as a target gene of miR-142-3p in HAECs. The HAECs were transfected with NC mimic, miR-142-3p mimic, NC inhibitor and miR-142-3p inhibitor, and further exposed to ox-LDL at 100 mg/L for 24 h. A: the protein expression of Rictor was measured by Western blot; B: the mRNA expression of Rictor was measured by RT-qPCR; C: the putative target site of Rictor mRNA 3'-UTR was determined by computational predictions; D: the HAECs were transfected with pMIR-Rictor-3'-UTR or pMIR-Rictor-3'-UTR Mutant and miR-142-3p mimic or NC mimic, and luciferase activity was measured. Mean±SD. n=3. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs NC mimic group; #P<0.05 vs NC mimic+ox-LDL group; △P<0.05 vs NC inhibitor group; ▲P<0.05 vs NC inhibitor+ox-LDL group.
4 下调miR-142-3p抑制HAECs的凋亡
与对照组相比,miR-142-3p过表达可以促进ox-LDL诱导的HAECs凋亡,相反,转染miR-142-3p inhibitor可显著降低ox-LDL介导的HAECs凋亡(<0.05或<0.01),见图4A、B。此外,在本实验中ox-LDL作用后HAECs的活力下降,过表达miR-142-3p使HAECs的活力进一步下降,而下调miR-142-3p可以增强HAECs的活力(<0.05),见图4C。
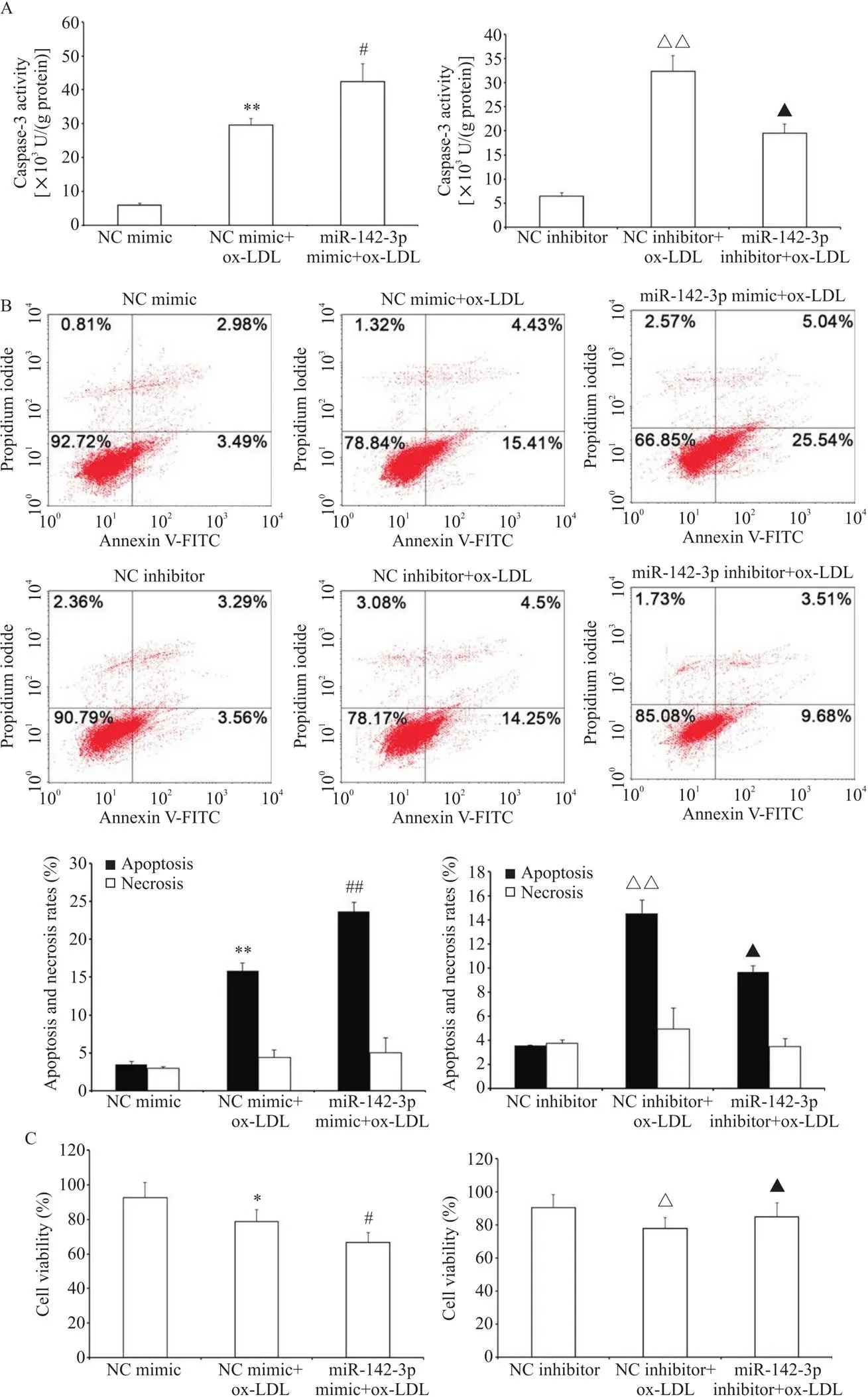
Figure 4. Influence of miR-142-3p on apoptosis of HAECs induced by ox-LDL. A: the activity of caspase-3 was determined by luminescent substrate assays; B: the apoptosis and necrosis of HAECs were detected by flow cytometry; C: comparison of the viability of HAECs. Mean±SD. n=3. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs NC mimic group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs NC mimic+ox-LDL group; △P<0.05, △△P<0.01 vs NC inhibitor group; ▲P<0.05 vs NC inhibitor+ox-LDL group.
5 miR-142-3p通过靶向Rictor调节HAECs凋亡
为进一步明确基因在miR-142-3p调控HAECs凋亡中发挥的作用,我们进行了救援实验。结果显示,转染miR-142-3p inhibitor上调了Rictor蛋白的表达(<0.05),而miR-142-3p inhibitor与si-Rictor共转染导致Rictor蛋白表达水平显著下降(<0.01),见图5A。caspase-3活性检测和流式细胞术凋亡检测结果显示, miR-142-3p inhibitor减轻了ox-LDL介导的HAECs凋亡(<0.05),而当转染si-Rictor抑制Rictor蛋白的表达后,miR-142-3p inhibitor的内皮保护作用也相应被消除(<0.05或<0.01),见图5B、C。
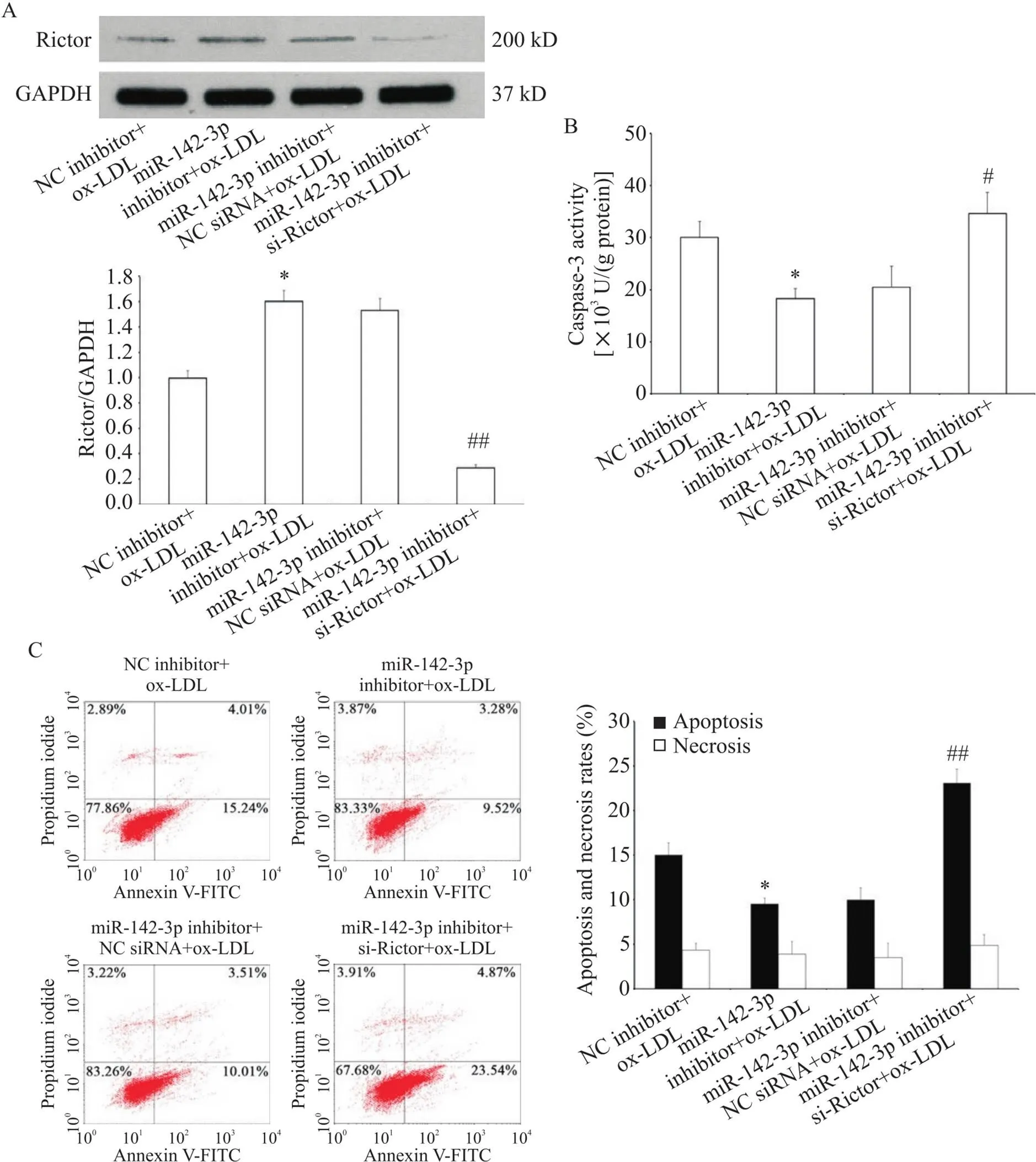
Figure 5. miR-142-3p modulated the apoptosis of HAECs by targeting Rictor. A: Rictor protein level in HAECs was decreased by transfection with si-Rictor (measured by Western blot); B: down-regulation of Rictor by si-Rictor blocked the suppressive effect of miR-142-3p inhibitor on caspase-3 activity in ox-LDL-treated HAECs; C: the apoptosis and necrosis of HAECs were detected by flow cytometry. Mean±SD. n=3. *P<0.05 vs NCinhibitor+ox-LDL group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs miR-142-3p inhibitor+NC siRNA+ox-LDL group.
6 Akt/eNOS信号通路参与了miR-142-3p对HAECs凋亡的调控
如图6A、B所示, ox-LDL作用24 h可降低HAECs中磷酸化Akt (Ser473)和eNOS (Ser1177)水平,而抑制miR-142-3p的表达部分逆转了这种趋势;相反的,转染miR-142-3p mimic可减弱Akt和eNOS的磷酸化(<0.05)。采用CCK-8法评估实验浓度的选择性Akt阻断剂LY294002和eNOS抑制剂L-NAME对HAECs的细胞毒性,结果显示,与对照组相比, 20 μmol/L LY294002和100 μmol/L L-NAME作用2 h对HAECs的活力无显著影响,见图6C。选择性Akt阻断剂LY294002显著抑制了miR-142-3p inhibitor介导的Akt和eNOS磷酸化; eNOS抑制物L-NAME仅减少eNOS的磷酸化而对Akt磷酸化无明显影响,见图6D。当Akt/eNOS信号通路被LY294002或L-NAME阻断后,miR-142-3p inhibitor保护HAECs免受ox-LDL诱导凋亡的作用也被相应消除(<0.01),见图6E、F。以上研究表明, miR-142-3p inhibitor对HAECs的保护作用是通过激活Akt/eNOS信号通路实现的。
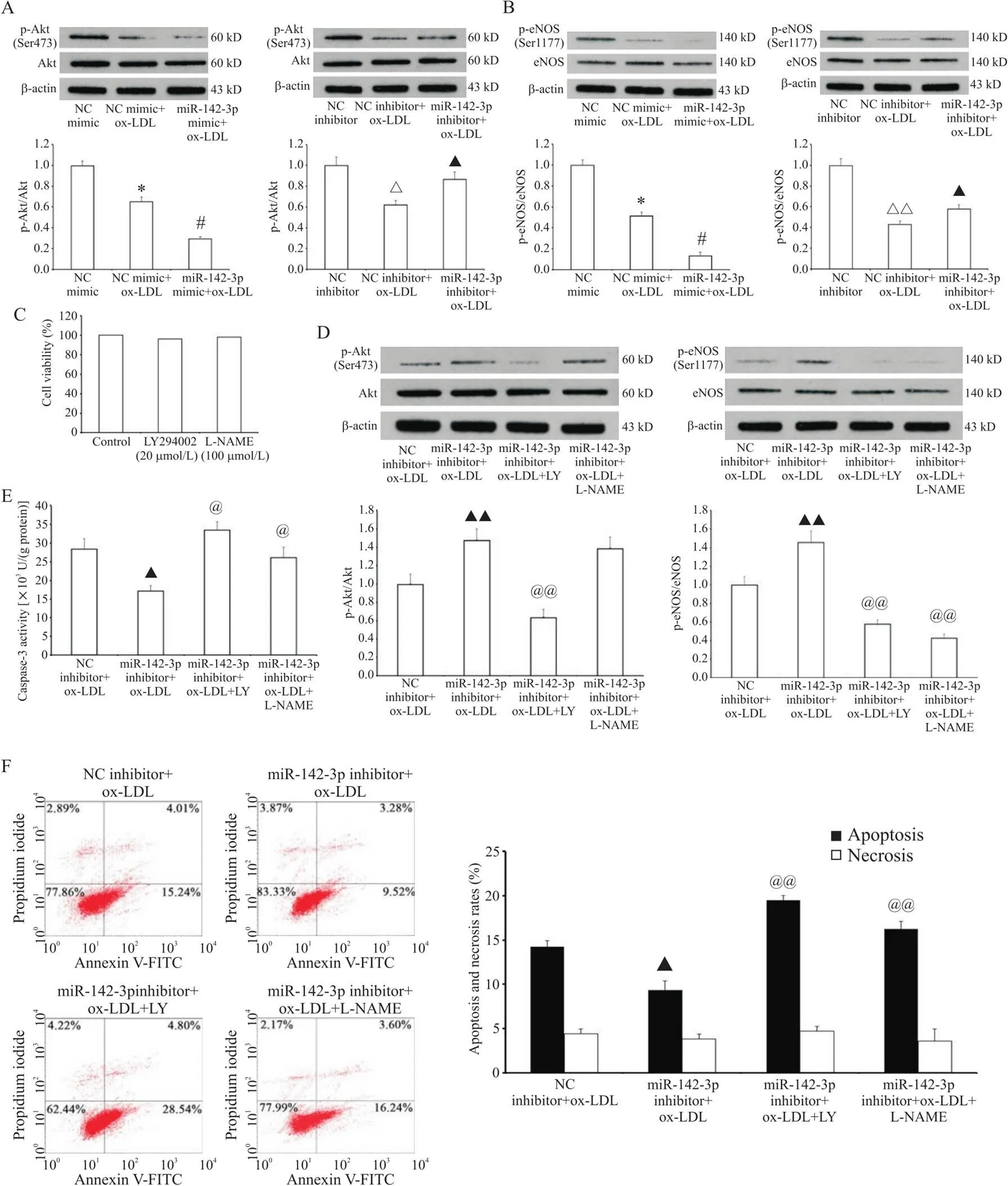
Figure 6. Down-regulation of miR-142-3p reduced the apoptosis of HAECs via Akt/eNOS signaling pathway activation. A and B: HAECs were exposed to ox-LDL (100 mg/L, 24 h) after miR-142-3p mimic or inhibitor transfection, and the phosphorylation of Akt and eNOS was detected by Western blot; C: HAECs were treated with LY294002 (LY, 20 μmol/L) or L-NAME (100 μmol/L) for 2 h, and the viability was measured by CCK-8 assay; D: the protein levels of Akt, p-Akt, eNOS and p-eNOS were measured by Western blot; E: the caspase-3 activity was detected by enzyme assay; F: the apoptosis and necrosis were detected by flow cytometry. Mean±SD. n=3. *P<0.05 vs NC mimic group; #P<0.05 vs NC mimic+ox-LDL group; △P<0.05, △△P<0.05 vs NC inhibitor group; ▲P<0.05,▲▲P<0.01 vs NC inhibitor+ox-LDL group; @P<0.05, @@P<0.01 vs miR-142-3p inhibitor+ox-LDL group.
讨论
ECs凋亡在内皮功能障碍和AS发生过程中发挥重要作用。ox-LDL是AS启动和发展的重要危险因素,本研究以ox-LDL诱导的HAECs为模型探讨AS进程中与ECs凋亡相关的miRNAs。
近年来研究表明,miRNAs广泛参与了血管新生、损伤、炎症和衰老等众多病理生理过程[5]。此外,越来越多的研究证实在AS背景下,存在很多差异表达的miRNAs调控ECs的活力和死亡[6]。寻找凋亡相关的miRNAs及其下游靶基因为研究ECs功能障碍和AS治疗提供了新的策略。本研究发现抑制miR-142-3p的表达可以上调靶基因并激活Akt/eNOS信号通路从而发挥抗凋亡的内皮保护作用。
miR-142-3p定位于人染色体17q22,已被证实在多种肿瘤中表达下调。例如, miR-142-3p通过靶向调控HMGB1在非小细胞肺癌(non-small-cell lung carcinoma, NSCLC)中抑制肿瘤细胞增生并诱导凋亡[7]。此外,miR-142-3p与心血管系统疾病也密切相关,在缺氧复氧诱导心肌细胞凋亡和纤维化过程中miR-142-3p是重要的调节因子[8]。另一项新近研究表明,血小板来源的miR-142-3p通过血小板来源的微粒转移至ECs,作用于下游靶基因从而诱导ECs凋亡[9]。与此相一致,我们研究也发现,miR-142-3p在ox-LDL诱导HAECs凋亡过程中表达明显上调。过表达miR-142-3p促进了HAECs凋亡,而抑制miR-142-3p可以发挥抗凋亡的内皮保护作用。ox-LDL根据作用的浓度和时间不同,可以诱导ECs发生凋亡、坏死和增生[10]。ox-LDL浓度小于10 mg/L可以促进ECs增生;浓度大于50 mg/L促进ECs凋亡;浓度大于250 mg/L主要诱导ECs发生坏死[11]。在本研究的实验条件下,100 mg/L ox-LDL作用24 h显著抑制了HAECs的存活和生长,过表达miR-142-3p加重了这种抑制作用,而下调miR-142-3p削弱了这种抑制作用。100 mg/L ox-LDL处理(0~24) h对HAECs坏死率无显著影响,转染miR-142-3p inhibitor可以轻微降低细胞坏死率,但差异无统计学显著性。
mTOR是一种进化上高度保守的非典型的丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶,属于磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶相关激酶(phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinase,PIKK)蛋白家族。近年来大量的研究表明,mTOR信号通路异常与衰老、2型糖尿病、肿瘤和神经退行性疾病等多种重大疾病的发生和发展密切相关。mTOR在生物体内以mTOR-Raptor复合物(mTORC1)和mTOR-Rictor复合物(mTORC2)的形式存在。mTORC2是由mTOR、mLST8/GβL及Rictor(rapamycin-insensitive companion of mTOR)和mSin1(mammalian stress-activated protein kinase- interacting protein 1)组成的多蛋白激酶复合物,其中Rictor是mTORC2特异性的组成蛋白,并是其发挥生物学作用必不可少的组成部分。mTORC2的主要功能是作为蛋白激酶B(PKB/Akt)的激酶磷酸化其473位丝氨酸(Ser473),在PKB/Akt的激活中起重要作用[12]。Akt激活后可通过磷酸化下游靶蛋白eNOS、BAD caspase-9、Fox1、Fox3, YAP和MDM2发挥促进存活和抑制凋亡作用[13]。在这些靶蛋白中,eNOS活性障碍使NO生物活性降低,导致AS发生。研究表明,Rictor/Akt/eNOS途径在调控血管内皮细胞凋亡和功能障碍方面发挥重要作用。下调Rictor表达抑制Akt活化,减少了ECs增生、迁移和血管新生[14],促进了ECs凋亡[15]、炎症[16]和衰老[17]。相反的,成纤维细胞生长因子(fibroblast growth factor,FGF)、血管内皮生长因子(vascular endothelial growth factor,VEGF)[18]和14,15-环氧二十碳烯酸[17]可促进Rictor蛋白表达及Akt磷酸化,抑制血管内皮细胞凋亡和衰老。ox-LDL诱导的ECs衰老和氧化应激通过抑制Akt/eNOS通路实现[19]。在本研究中,我们发现过表达miR-142-3p降低了Rictor的表达并抑制Akt磷酸化活化,而miR-142-3p表达抑制可以促进Rictor蛋白的表达水平和Akt活化。进一步采用萤光素酶报告基因实验证实是miR-142-3p的直接靶基因之一。沉默之后miR-142-3p inhibitor的内皮保护作用也相应消除。ox-LDL抑制了Akt/eNOS活性,HAECs的凋亡率相应增加。尽管miR-142-3p inhibitor增强了Akt/eNOS活性,加入LY294002和L-NAME减少了Akt/eNOS磷酸化,同时也逆转了miR-142-3p inhibitor的抗凋亡作用。
综上所述,抑制miR-142-3p可以通过激活Rictor/Akt/eNOS信号通路而缓解HAECs的凋亡。本研究为防治内皮细胞功能障碍和AS提供新的治疗靶点和思路。
[1] Paone S, Baxter AA, Hulett MD, et al. Endothelial cell apoptosis and the role of endothelial cell-derived extracellular vesicles in the progression of atherosclerosis[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2019, 76(6):1093-1106.
[2] Kattoor AJ, Pothineni NVK, Palagiri D, et al. Oxidative stress in atherosclerosis[J]. Curr Atheroscler Rep, 2017, 19(11):42.
[3] Khor ES, Wong PF. The roles of MTOR and miRNAs in endothelial cell senescence[J]. Biogerontology, 2020, 21(5):517-530.
[4] Zhao Z, Qu F, Liu R, et al. Differential expression of miR-142-3p protects cardiomyocytes from myocardial ischemia-reperfusion via TLR4/NFκB axis[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2020, 121(8/9):3679-3690.
[5]谭晓勇,方丹,吴剑波,等. miR-21对血管内皮功能及血管生成调节作用的研究进展[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2017, 33(12):2299-2304.
Tan XY, Fang D, Wu JB, et al. Advances on studies of miR-21 in vascular endothelial function and angiogenesis [J]. Chin J Pathophysiol, 2017, 33(12):2299-2304.
[6]王珏,赵海苹. MicroRNA调控缺血性及出血性脑血管病过程中免疫反应的研究进展[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2017, 33(2):369-374.
Wang J, Zhao HP.Progress in study of immune response regulated by microRNAs in process of ischemic and hemorrhagic cerebrovascular diseases[J]. Chin J Pathophysiol, 2017, 33(2):369-374.
[7] Xiao P, Liu WL. MiR-142-3p functions as a potential tumor suppressor directly targeting HMGB1 in non-small-cell lung carcinoma[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2015, 8(9):10800-10807.
[8] Wang Y, Ouyang M, Wang Q, et al. MicroRNA-142-3p inhibits hypoxia/reoxygenationinduced apoptosis and fibrosis of cardiomyocytes by targeting high mobility group box 1 [J]. Int J Mol Med, 2016, 38(5): 1377-1386.
[9] Bao H, Yao QP, Huang K, et al. Platelet-derived miR-142-3p induces apoptosis of endothelial cells in hypertension [J]. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand), 2017, 63(4): 3-9.
[10] Zhang Y, Xie Y, You S, et al. Autophagy and apoptosis in the response of human vascular endothelial cells to oxidized low-density lipoprotein [J]. Cardiology, 2015, 132(1): 27-33.
[11] Chen XP, Xun KL, Wu Q, et al. Oxidized low density lipoprotein receptor-1 mediates oxidized low density lipoprotein-induced apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells: role of reactive oxygen species[J]. Vascul Pharmacol, 2007, 47(1):1-9.
[12] Zou Z, Chen J, Yang J, et al. Targeted inhibition of Rictor/mTORC2 in cancer treatment: a new era after rapamycin[J]. Curr Cancer Drug Targets, 2016, 16(4): 288-304.
[13] Abeyrathna P, Su Y. The critical role of Akt in cardiovascular function[J]. Vascul Pharmacol, 2015, 74:38-48.
[14] Aimi F, Georgiopoulou S, Kalus I, et al. Endothelial Rictor is crucial for midgestational development and sustained and extensive FGF2-induced neovascularization in the adult[J]. Sci Rep, 2015, 5:17705.
[15] Jin YP, Valenzuela NM, Ziegler ME, et al. Everolimus inhibits anti-HLA I antibody-mediated endothelial cell signaling, migration and proliferation more potently than sirolimus[J]. Am J Transplant, 2014, 14(4):806-819.
[16] Barilli A, Visigalli R, Sala R, et al. In human endothelial cells rapamycin causes mTORC2 inhibition and impairs cell viability and function[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2008, 78(3):563-571.
[17] Yang C, Pan S, Yan S, et al. Inhibitory effect of 14,15-EET on endothelial senescence through activation of mTOR complex 2/Akt signaling pathways[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2014, 50(5):93-100.
[18] Dormond O, Madsen JC, Briscoe DM. The effects of mTOR-Akt interactions on anti-apoptotic signaling in vascular endothelial cells[J]. J Biol Chem, 2007, 282(32):23679-2386.
[19] Yao Y, Wang Y, Zhang Y, et al. Klotho ameliorates oxidized low density lipoprotein (ox-LDL)-induced oxidative stress via regulating LOX-1 and PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathways [J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2017, 16(1):77-86.
MicroRNA-142-3p modulates atherosclerosis-associated endothelial cell apoptosis via targeting Rictor
XIAO Li, LIU Ping, QIN Bing
(,,510630,)
To investigate the role of microRNA-142-3p (miR-142-3p) in endothelial cell apoptosis during atherosclerosis (AS) and the underlying mechanism.Human aortic endothelial cells (HAECs) were treated with oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL). The expression level of miR-142-3p was detected by RT-qPCR. Apoptosis was determined via flow cytometry (FCM) and caspase-3 activity assay. Prediction of the binding site between miR-142-3p and 3’-UTR of Rictor mRNA was performed by bioinformatics analysis and confirmed by dual-luciferase reporter assay.The expression of miR-142-3p was substantially up-regulated during the ox-LDL-elicited apoptosis in HAECs (<0.05,<0.01). Forced expression of miR-142-3p exacerbated apoptosis in HAECs whereas inhibition of miR-142-3p partly alleviated apoptotic cell death mediated by ox-LDL. Further analysis identifiedas a direct target gene of miR-142-3p, andknock-down abolished the anti-apoptotic effect of miR-142-3p inhibitor. Moreover, the Akt/endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) signaling pathway was found to mediate the beneficial effect of miR-142-3p inhibitor on endothelial cells apoptosis.Down-regulation of miR-142-3p inhibits endothelial cell apoptosis and atherosclerotic development by up-regulating the expression of Rictor and activating the Akt/eNOS signaling pathway.
MicroRNA-142-3p; Human aortic endothelial cells; Apoptosis; Rictor; Atherosclerosis
R543.5; R363.2
A
10.3969/j.issn.1000-4718.2020.11.002
1000-4718(2020)11-1928-10
2020-05-25
2020-10-06
国家自然科学基金资助项目(No. 81701167); 广东省自然科学基金资助项目(No. 2017A030310360)
Tel: 020-85252336; E-mail: qinbingsx@aliyun.com
(责任编辑:卢萍,宋延君)
