Identification and Detection of Dyeing Components in Counterfeit Cinnabar (Elutriation)
2020-11-30HailinRAN
Hailin RAN
Chongqing Institute for Food and Drug Control, Chongqing 401121, China
Abstract [Objectives] This study aimed to analyze the dyeing status and dyeing components of counterfeit cinnabar (elutriation), in order to provide technical basis for cinnabar (elutriation) supervision. [Methods] The scarlet 808 in cinnabar (elutriation) was identified qualitatively using thin-layer chromatography (TLC) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and the positive samples were confirmed by high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS). The conditions were as follows: column, Agilent Eclipse Plus C18; mobile phase, acetonitrile-0.1% formic acid (85∶15); detection wavelength, 520 nm; ion source, electrospray ion source; scanning mode, positive ion scanning; scanning range, 100-700 m/z; cone voltage, 3.5 kv; drying gas temperature, 350 ℃; drying gas flow rate,12 L/min. [Results] The thin-layer chromatography spots were clear and separated well. Among the 13 batches of samples, 12 batches were positive for scarlet 808. [Conclusions] The counterfeit cinnabar (elutriation) currently circulating in the market has dyeing problem, with scarlet 808 as the dye. The TLC, HPLC and HPLC-MS methods established in this article can quickly screen and confirm the scarlet 808 in cinnabar (elutriation).
Key words Cinnabar (elutriation), Dyeing, High performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry
1 Introduction
TheChinesePharmacopoeiastipulates that cinnabar is a sulfide mineral, and its mercury sulfide (HgS) content shall not be less than 96.0%[1]. Cinnabar is also called Dansha. The main components are HgS, MgS, Bi, Fe, Ba, Mn, Sb, As, Hg2+, HgCl2,etc[2]. Scarlet 808 is an azo synthetic pigment[3-4]. According to related report[5], such synthetic pigments have carcinogenic effect. The situation of adding this type of dye in cinnabar (elutriation) or impersonating cinnabar by adding this type of dye in carbonates is currently various serious on the market. It is necessary to establish fast and effective testing methods in order to carry out targeted supervision of the market. In this study, using scarlet 808 as a control, TLC and HPLC inspection methods for scarlet 808 in elutriating cinnabar were established, and the component was verified by HPLC-MS.
2 Materials
2.1 Instruments and equipmentThe instruments and equipment used mainly included high-performance liquid chromatograph (2010A, Shimadzu, Japan) equipped with diode array detector (SPD-M10A, Shimadzu, Japan) and LC/MS system (1200-6320 Ion Trap, Agilent, USA).
2.2 Reagents and drugsAcetonitrile was chromatographically pure (Fisher Chemical); cyclohexane, ethyl acetate,etc. were analytically pure (Beijing Chemical Plant); the purified water was prepared with RO-ZY-30 water purifier and Millipore Q pure water system. The thin-layer chromatography silica gel G plate was produced by Qingdao Ocean Chemical Plant. Scarlet 808 standard (batch No.111940-201603) was purchased from National Institutes for Food and Drug Control. Cinnabar (elutriation) samples were purchased from various medicinal wholesale markets across China. They were identified as counterfeiters by Chinese pharmacist Jiang Wanlang, deputy director of Chongqing Institute for Food and Drug Control, numbered as Z1 to Z13. The negative sample was genuine cinnabar specimen provided by the Chinese Medicine Herbarium of National Institutes for Food and Drug Control.
3 Methods and results
3.1 Thin-layer chromatographyA certain amount (0.2 g) of the powder of each sample was added with 10 mL of acetonitrile, sonicated for 10 min and filtered, and the filtrate obtained was used as the test solution. A certain amount (0.2 g) of the negative sample was prepared into negative control solution by the method described above. An appropriate amount of scarlet 808 standard was dissolved in acetonitrile to prepare into a solution of 0.1 mg/mL, which was used as the reference solution. A certain volume of the test solution, negative control solution and reference solution (10 μL for each) was loaded on the same silica gel G thin-layer plate, developed using cyclohexane-ethyl acetate (9∶1), taken out, air-dried, and inspected in daylight. The results show that among the 13 batches of samples, 12 batches showed the same red spots as the scarlet 808 standard, and the negative control had no interference (Fig.1).
3.2 High-performance liquid chromatography
3.2.1Chromatographic conditions. Column: Agilent Eclipse Plus C18(250 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 μm); mobile phase: acetonitrile-0.1% formic acid solution (85∶15); detection wavelength: 520 nm; column temperature: 30 ℃. Under these conditions, the scarlet 808 peak had better resolution and better peak shape. The positive sample showed the chromatographic peak with the same retention time as the scarlet 808 standard, while the negative control had no corresponding chromatographic peak (Fig.2).
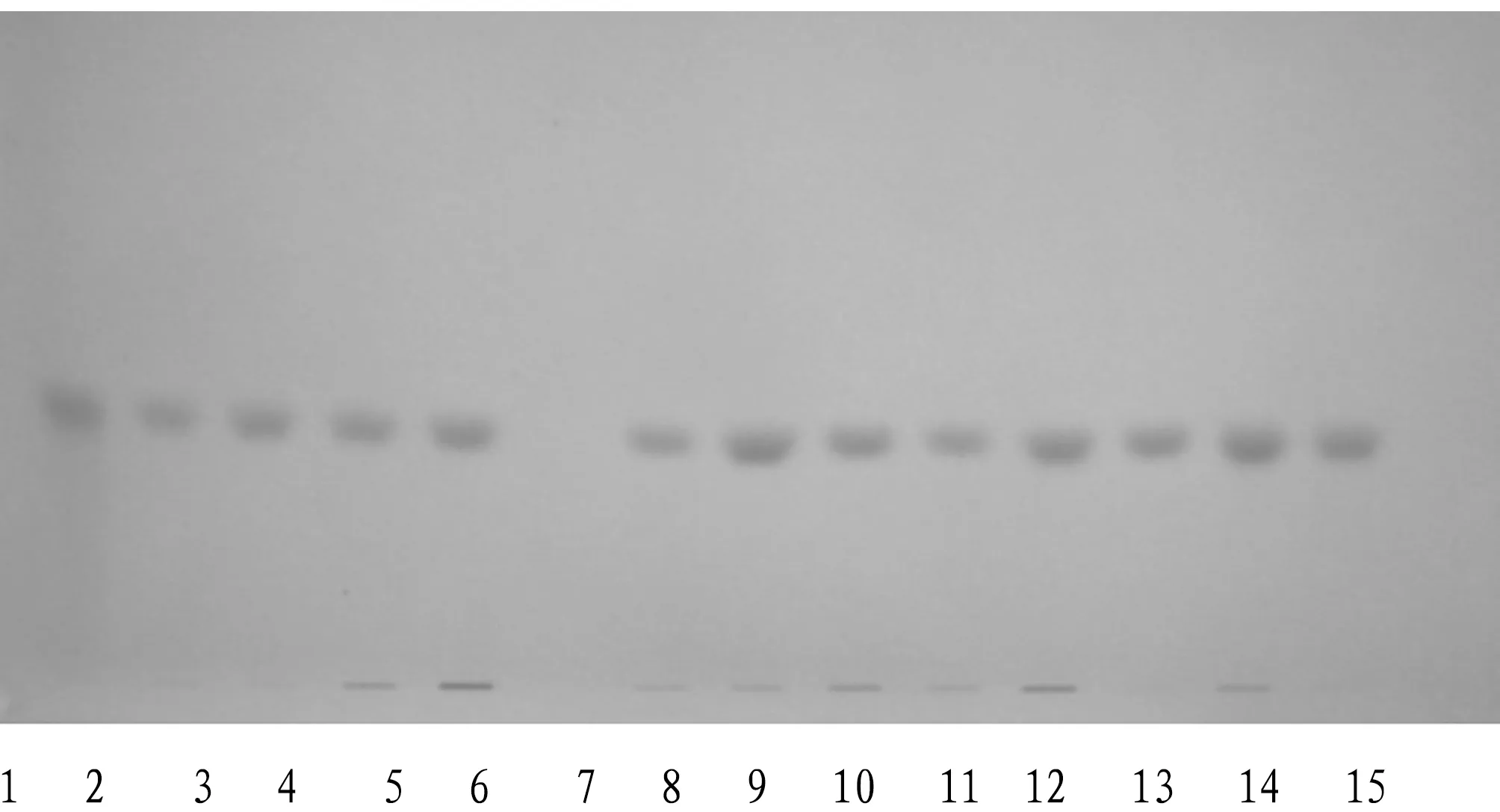
Note: 1. Scarlet 808 standard; 2. Z1; 3. Z2; 4. Z3; 5. Z4; 6. Z5; 7. Z6; 8. Z7; 9. Z8; 10. Z9; 11. Z10; 12. Z11; 13. Z12; 14. Z13; 15. Negative control.Fig.1 TLC chromatograms of scarlet 808 in cinnabar counterfeiters (elutriation)
3.2.2Preparation of solutions. An appropriate amount of scarlet 808 standard was dissolved in acetonitrile to prepare into a solution of 0.1 mg/mL as the reference solution. The test solution prepared in Section3.1was used as the test solution, and the negative control solution prepared in Section3.1was used as the negative control solution.
3.2.3Comparison of the UV-Vis absorption spectra of the control reagent and the positive sample. The UV-Vis absorption spectrum (200-600 nm) of the detected component peak was extracted. The scarlet 808 standard and the positive sample had the maximum absorption at 255 and 519 nm, respectively (Fig.3).

Note: A. Scarlet 808 reference solution; B. Positive sample (Z1); C. Negative control.Fig. 2 HPLC chromatogram of scarlet 808 in counterfeit cinnabar (elutriation)
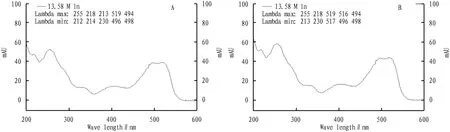
Note: A. Scarlet 808 standard; B. Positive sample.Fig. 3 UV-Vis absorption spectra of the corresponding chromatographic peaks of the standard and positive sample
3.2.4Results. The above HPLC method was used for detection. The results show that among the 13 batches of samples, 12 batches showed the same chromatographic peak as the scarlet 808 standard, consistent with the results of the TLC method. The negative control had no interference.
3.3 LC-MS
3.3.1Chromatographic conditions and mass spectrometry parameters. Column: Agilent Eclipse Plus C18(250 mm×4.6 mm, 5 μm); mobile phase: acetonitrile-0.1% formic acid solution (85∶15). For mass spectrometry, the conditions were as follows: ion source, electrospray ion source; scanning mode, positive ion scanning; cone voltage, 3.50 kv; drying gas temperature, 350 ℃; and drying gas flow rate, 12 L/min. Scanning mode: full scanning; scanning range: 100-700 m/z.
3.3.2Preparation of solutions. The reference solution prepared in Section2.2.2was used as the reference solution; the test solution prepared in Section2.1was used as the test solution; and the negative control solution prepared in Section2.1was used as the negative control solution.
3.3.3Comparison of mass spectrograms of the control reagent and the positive sample. The scarlet 808 standard was mainly m/z 368[M++H]+, consistent with the structure. The mass spectrum of chromatogram of positive sample had the same characteristics as the scarlet 808 standard (Fig.4).

Note: A. ESI+ mass spectrum of scarlet 808 standard; B. ESI+ mass spectrum of positive sample.Fig.4 LC/MS verification spectra
3.3.4Results. The samples positive for HPLC inspection were all subjected to LC-MS verification. The results show that the chromatographic peaks with the same retention time as the scarlet 808 standard in the samples had the same mass spectrum characteristics.
4 Discussion
After testing, it was found that 808 Scarlet is easily soluble in organic solvents such as ether, petroleum ether, n-hexane and acetonitrile. Considering the quickness and convenience in HPLC inspection, acetonitrile was used as the extraction solvent. TLC compared the two developing agents of n-hexane-diethyl ether (6∶1) and cyclohexane-ethyl acetate (9∶1), and the results show that cyclohexane-ethyl acetate was better.
It has been verified that the red dye in the cinnabar (elutriation) sample is consistent with the structure of the scarlet 808 dye reported in the literature. At present, the commercially available industrial dyes or coatings with scarlet 808 as the main component are represented by Dahongfen and Jinguanghong[2-3].
Among the 13 batches of samples tested, 12 batches were positive for scarlet 808, indicating that the current cinnabar counterfeiters (elutriation) mostly use scarlet 808 as the dyeing agent. It is hoped that the food and drug supervision department will take targeted measures to strengthen supervision.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Application of Robust Strategies in Location Selection of Logistics Distribution Center for Fresh Agricultural Products
- Empirical Study on Impact of China’s Economic Growth on Agricultural Trade
- Efficiency Assessment of Land Use Types in Tan Binh Commune, Dak Doa District, Gia Lai Province, Vietnam
- Some Thoughts on China’s Territorial Spatial Planning in the New Period
- Functional Positioning of Pastoral Complex in the Context of Rural Revitalization Strategy: A Case Study of Pavlo Eco Valley in Gaoan City of Jiangxi Province
- cDNA-SCoT Analysis of Differential Expressed Genes in Allium tuberosum Induced by Botrytis cinerea
