Empirical Study on Impact of China’s Economic Growth on Agricultural Trade
2020-11-30DandanLIANG
Dandan LIANG
Pingdingshan University, Pingdingshan 467000, China
Abstract The proposal of "Belt and Road Initiative" has brought greater opportunities for the development of China’s agricultural trade, but in recent years, China’s agricultural trade deficit has shown a trend of gradually expanding. Based on the data of seven years from 2012 to 2018, this paper empirically analyzes the agricultural trade effect of China’s economic growth. It is concluded that the consumption effect of agricultural trade in China’s economic growth is anti-trade biased, the production effect and comprehensive effect of agricultural trade are pro-trade biased, and China’s terms of trade of agricultural products tend to improve. This paper puts forward some relevant suggestions from the aspects of export structure, production mode, agricultural product processing, logistics mode, e-commerce system, inspection and quarantine and so on.
Key words Economic growth, Agricultural trade, Terms of trade
1 Introduction
Against the backdrop of "the Belt and Road Initiative", the scale of China’s agricultural trade is constantly expanding. In 2018, China’s total trade in agricultural products was 203.908 billion USD, of which the total export of agricultural products was 77.559 billion USD, the total import of agricultural products was 126.349 billion USD, and the trade deficit in agricultural products reached 48.79 billion USD. It can not be ignored that with the continuous growth of economy, China’s trade deficit in agricultural products is gradually expanding. Based on this, using relevant models for reference, this paper is committed to objective and reasonable analysis and evaluation of the impact of China’s economic growth on agricultural trade, and puts forward corresponding measures and suggestions in accordance with the empirical results.
2 Establishment of the model
Drawing on the relevant model mentioned by Gong Guan (2001), this paper divides the impact of economic growth on agricultural trade into the following four effects[1-3].
2.1 Consumption effectThe consumption effect of economic growth of agricultural products is the relationship between the change of import demand of agricultural products and the change of national income caused by economic growth without changing the relative price of agricultural products, that is, whether the economic growth makes the country more dependent on domestic production of agricultural products or on trade imports.
(1)
whereADis the import demand of agricultural products,Yis the national income of the country,βdYandαdYare the marginal consumption and average consumption of agricultural products, respectively, andEdYis the income elasticity of the import demand of agricultural products.
IfEC>0, the consumption effect is pro-trade biased, that is, the share of import demand for agricultural products in total output increases with the increase of national income; ifEC<0, the consumption effect is anti-trade biased, that is, the share of import demand for agricultural products in national income decreases with the increase of total output.
2.2 Production effectThe production effect of the economic growth of agricultural products reflects the relationship between the growth of domestic production of agricultural products and the growth of national income.
(2)
whereASis the domestic output of agricultural products,βsYandαsYare the marginal supply and average supply of agricultural products, respectively, andEsYis the income elasticity of domestic supply of agricultural products.
IfEP<0, the production effect is pro-trade biased, that is, the share of domestic output of agricultural products in national income decreases with the increase of national income; ifEP>0, the production effect is anti-trade biased, that is, the share of domestic output of agricultural products in national income increases with the increase of total output.
2.3 Comprehensive effectThe comprehensive trade effect or net trade effect of the economic growth of agricultural products is the combined result of the consumption effect and production effect of the economic growth of agricultural products.
(3)
IfES>0, the comprehensive trade effect of agricultural economic growth is pro-trade biased; ifES<0, the comprehensive trade effect of agricultural economic growth is anti-trade biased.
2.4 Terms of trade effectFor the economies of big countries, the changes in the trade volume of agricultural products will have an impact on their own terms of trade.
(4)
(5)
whereQ1AandQ2Brepresent the excessive demand for agricultural products in country 1 and the excessive demand for agricultural products in country 2, respectively.
WhenβdY<βsY,dp/dλ>0, the terms of trade of agricultural products are improved; whenβdY>βsY,dp/dλ<0, the terms of trade of agricultural products are deteriorated.
3 Selection of data
The original data involved in the samples selected in this paper include some indexes mainly measured by GDP, such as economic growthY, agricultural product importAD, and domestic agricultural product outputAS, as shown in Table 1.

Table 1 China’s economic growth, agricultural imports and domestic agricultural output (100 million USD)
4 Process of empirical analysis
According to formula (1), (2), (3), (4), (5) in the second part, combined with the selected original data, the corresponding effects of China’s economic growth of agricultural trade are as follows.
4.1 Consumption effectAs can be seen from Table 2, during the seven years from 2012 to 2018, the consumption effect of China’s economic growth on agricultural trade was pro-trade biased in 2012 and 2017, respectively; in the period from 2013 to 2016 and 2018, the consumption effect of China’s economic growth on agricultural trade was anti-trade biased. This shows that during the sample period examined, although the agricultural trade effect of China’s economic growth reflected by consumption effect was not very stable, it tended to be anti-trade biased on the whole, that is, the share of China’s import demand for agricultural products in national income decreased with the increase of national income.
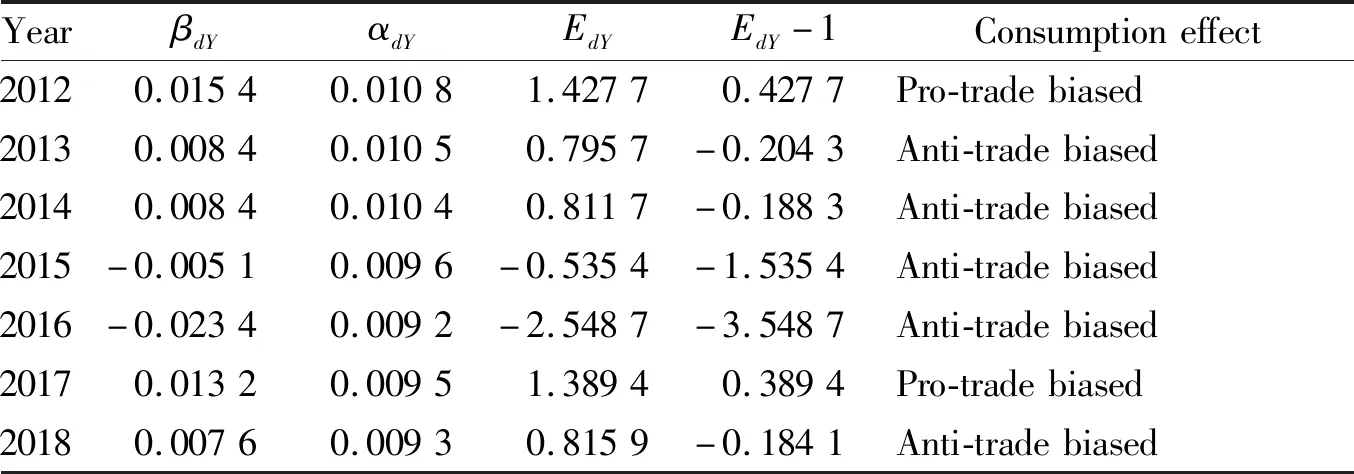
Table 2 Consumption effect of agricultural trade of China’s economic growth
4.2 Production effectAccording to the results of Table 3, during the seven years from 2012 to 2018, the production effects of China’s economic growth on agricultural trade were all pro-trade biased. This shows that during the sample period examined, the agricultural trade effect of China’s economic growth reflected by the production effect was stable, that is, the share of domestic agricultural output competing with the import of agricultural products in national income decreased with the increase of national income.
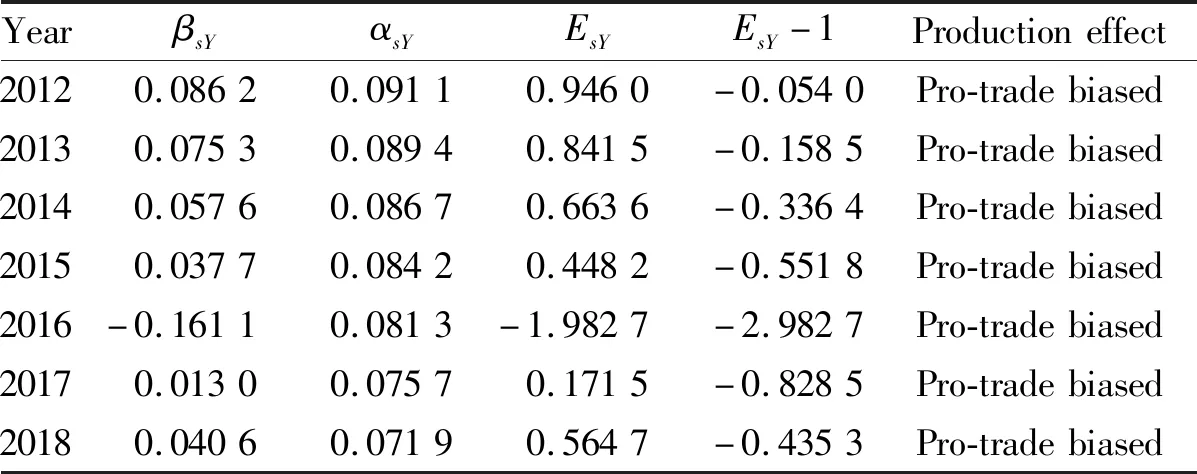
Table 3 Production effect of agricultural trade of China’s economic growth
4.3 Comprehensive effectFrom the empirical results of Table 4, we can see that the comprehensive effects of agricultural trade in the seven years from 2012 to 2018 were pro-trade biased.

Table 4 Comprehensive effects and terms of trade effects of agricultural trade of China’s economic growth
4.4 Terms of trade effectTable 4 shows that in five years (2012-2015, and 2018) in the whole sample period from 2009 to 2018, the value ofβdY-βsYwas negative, that is,dp/dλ>0, which indicated that the terms of trade of China’s agricultural products improved; the value ofβdY-βsYin 2016 and 2017 was positive, that is,dp/dλ<0, indicating that China’s terms of trade of agricultural products were deteriorating, but on the whole, with the continuous growth of economy, China’s terms of trade of agricultural products tended to improve.
5 Measures and suggestions
Based on the results of empirical analysis, the following measures and suggestions are put forward: (i) it is necessary to optimize the export structure of agricultural products, strengthen the brand construction of agricultural products, and expand the diversified international market; (ii) optimize agricultural production mode and vigorously promote large-scale operation in order to reduce the production cost of agricultural products[4]; (iii) make great efforts to develop the processing industry of agricultural products and improve the export added value of agricultural products; (iv) improve the logistics mode of agricultural products and enhance the logistics efficiency of agricultural products; (v) improve the e-commerce system of agricultural products, optimize the export process of agricultural products, and expand the trade of agricultural products; (vi) establish and improve the inspection and quarantine system of agricultural products, improve the quality of agricultural products, and actively deal with the international trade barriers of agricultural products[5].
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Application of Robust Strategies in Location Selection of Logistics Distribution Center for Fresh Agricultural Products
- Efficiency Assessment of Land Use Types in Tan Binh Commune, Dak Doa District, Gia Lai Province, Vietnam
- Some Thoughts on China’s Territorial Spatial Planning in the New Period
- Functional Positioning of Pastoral Complex in the Context of Rural Revitalization Strategy: A Case Study of Pavlo Eco Valley in Gaoan City of Jiangxi Province
- cDNA-SCoT Analysis of Differential Expressed Genes in Allium tuberosum Induced by Botrytis cinerea
- Identification and Detection of Dyeing Components in Counterfeit Cinnabar (Elutriation)
