糖尿病合并恶性肿瘤患者行护理风险管理的价值研究
2020-11-23陈春玲叶玉环
陈春玲 叶玉环
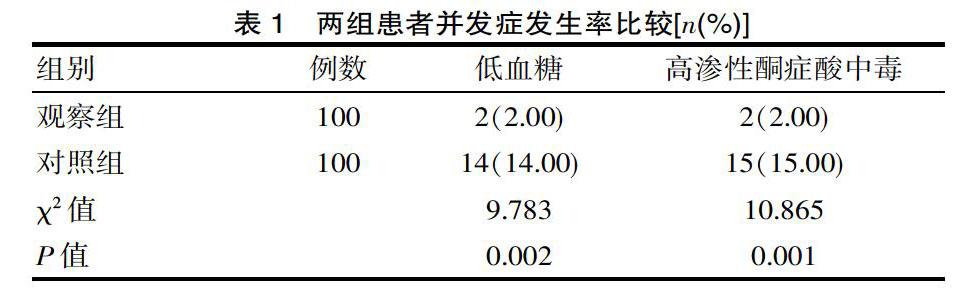
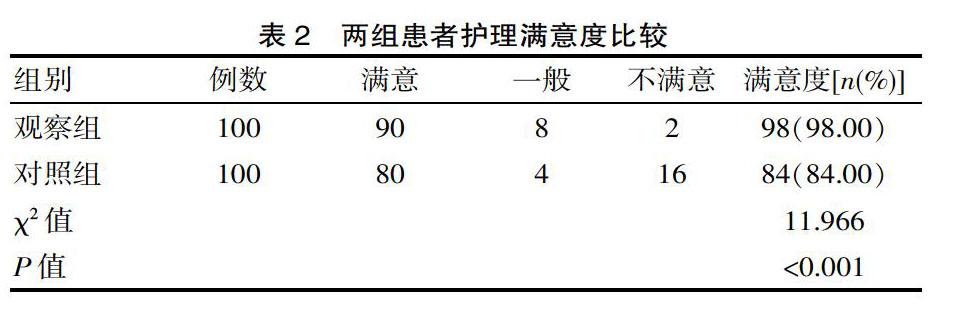
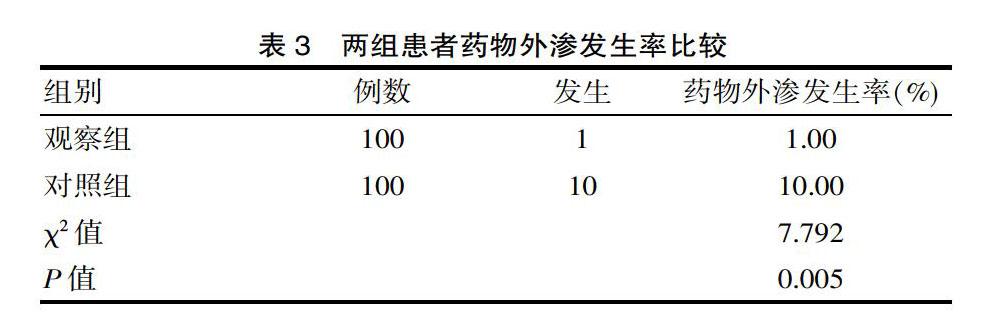
[摘要] 目的 分析糖尿病合并恶性肿瘤患者行护理风险管理的价值。方法 糖尿病合并恶性肿瘤患者作为该次研究的主要对象,总例数200例,患者收取时间在2018—2019年度,研究对象200例使用电脑随机分配方式分为两组,其中100例作为观察组(实施护理风险管理)、100例作为对照组(实施常规护理),将两组各项指标进行对比。结果 观察组低血糖发生率2.00%、高渗性酮症酸中毒发生率2.00%低于对照组患者,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。观察组护理满意度98.00%显著高于对照组护理满意度84.00%,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。观察组药物外渗发生率1.00%低于对照组患者,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论 通过对糖尿病合并恶性肿瘤患者行护理风险管理,取得显著的管理效果,值得在临床中推广及运用。
[关键词] 糖尿病;恶性肿瘤;护理风险管理
[中图分类号] R47 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1672-4062(2020)09(b)-0089-03
Study on the Value of Nursing Risk Management for Patients with Diabetes Malignant Tumors
CHEN Chun-ling, YE Yu-huan
Department of Oncology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xiamen University, Xiamen, Fujian Province, 361000 China
[Abstract] Objective To analyze the value of nursing risk management for patients with diabetes malignant tumors. Methods Diabetes patients with malignant tumors were the main subjects of this study. The total number of cases (selected number) was 200. The patients were collected from 2018 to 2019. The 200 subjects were divided into two groups using a computer random allocation method. 100 cases were taken as the observation group (implementing nursing risk management), and 100 cases were taken as the control group (implementing routine nursing). The indicators of the two groups were compared. Results The incidence of hypoglycemia in the observation group was 2.00% and the incidence of hypertonic ketoacidosis was 2.00% lower than those in the control group,the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). The 98.00% nursing satisfaction of the observation group was significantly higher than the 84.00% nursing satisfaction of the control group,the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). The incidence of drug extravasation in the observation group was 1.00% lower than that in the control group,the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). Conclusion Through the nursing risk management of patients with diabetes and malignant tumors, significant management effects have been achieved, which is worthy of promotion and application in clinical practice.
[Key words] Diabetes; Malignant tumor; Nursing risk management
近年來,由于生态环境和人们生活习惯不断变化,导致恶性肿瘤、糖尿病发病率也不断增加,上述两种疾病易对患者健康造成影响,对患者机体造成损害,从而降低患者生活质量。目前临床对于恶性肿瘤主要以化疗手段为主,但化疗药物易损伤人体胰腺,进而导致胰岛素分泌减少,引发糖代谢紊乱情况加重,增加各类并发症风险,比如酮症酸中毒、低血糖等,同时增加患者死亡风险[1]。研究显示[2],在化疗期间,合并糖尿病酮症酸中毒的病死率达到5%。而常规护理在该疾病的护理中缺乏针对性、主动性和全面性,进而导致护理效果不佳,无法提升护理质量以及改善患者预后。而在护理过程中实施一项有效的管理措施,能显著提高管理效果,利于管理工作顺利进行。目前护理风险管理在临床广泛应用,其与常规管理相比,具有多种优势,能显著提高患者的护理效果,降低化疗过程中的不良反应,保障每例患者的健康安全,促进患者早期康复。风险管理主要是指对潜在和现有的风险识别、评价以及处理,以此达到降低风险事件发生的目的,从而使风险事件对医院以及患者安全的危害降至最低。而如何对糖尿病合并恶性肿瘤患者的护理风险进行识别和处理为临床护理难点[3]。因此,该次研究选择2018—2019年度200例糖尿病合并恶性肿瘤患者作为研究对象,并探讨其行护理风险管理的效果,现报道如下。
