The incidence and prediction of tuberculosis in China
2020-11-04RunHuaLiJingHuangShunYingLuoMeiYingZhang
Run-Hua Li ,Jing Huang* ,Shun-Ying Luo ,Mei-Ying Zhang
1The Cancer Hospital of the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Zhejiang Cancer Hospital),Institute of Basic Medicine and Cancer (IBMC),Chinese Academy of Sciences,Hangzhou,Zhejiang 310022,China.
Abstract Objective:To explore the incidence trend of tuberculosis in China from 2009 to 2018,and make a short-term prediction,so as to provide reference for scientific formulation of prevention and control measures for tuberculosis and rational allocation of control and prevention resources.Methods:The grey model GM (1,1) model was used to build and predict the incidence of tuberculosis in China by extracting the data from 2009 to 2018 from the Statistical Yearbook of China.Results:The GM (1,1) prediction model was established to predict the incidence of tuberculosis.The GM (1,1)prediction model for tuberculosis incidence was (1) (k+1)=-2572.122087 e (-0.029096k)+2653.212087.The grey GM (1,1) prediction model for pulmonary tuberculosis case number was (1) (k+1)=-4092.009372 e (-0.024334k) +4199.703172.The above two models with high fitting accuracy were used to predict that the incidence of tuberculosis in 2019-2021 would be 56.77/100,000,55.14/100,000 and 53.56/100,000,respectively.The model predicted that the number of incident tuberculosis cases may be 790,242,771,245 and 752,704 from 2019 to 2021 in China,respectively.Conclusion:The projection shows that the incidence of tuberculosis may decrease,but the annual incident number of tuberculosis is still very high.We should continue to strengthen the prevention and standardized treatment of tuberculosis,and improve the early detection and treatment rates.
Keywords:Tuberculosis,Prediction,Incidence
Background
Tuberculosis is the chronic infectious disease caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis with pulmonary tuberculosis infection the most common,which can spread through the respiratory tract.No timely treatment will cause damage to the respiratory system,and this endanger life in severe cases.Tuberculosis the second most common infectious disease in China,which causes a great social and economic burden to the population [1].Therefore,it is of great significance to study the morbidity and prevalence trends of these diseases.China is one of the 22 countries with a high tuberculosis burden,accounting for 10 percent of global tuberculosis cases in 2015 [2].
Timely understanding and mastering the epidemic and development of tuberculosis is conducive to the timely formulation of guidelines and policies,better control and prevention of the infectious disease for the"early detection,early isolation,early treatment"strategy.In this paper,by using the statistical data of 2009-2018 China national statistical bureau for tuberculosis infection situation,we used the grey model grey model GM (1,1) for fitting and accuracy test to extrapolate and predict for the next three years 2019-2021 incidence of tuberculosis to provide scientific basis for formulating targeted health policy for the government management department,so as to effectively curb the tuberculosis epidemic situation.
Materials and methods
Data Sources
The incidence and number of tuberculosis in China from 2009 to 2018 were obtained by extracting the data from the Statistical Yearbook of China from 2010 to 2019 from national statistical bureau.
GM (1,1) modeling steps [3]
Once accumulation
The original data column was χ(0)=(χ(0)(1),χ(0)(2),…,χ(0)(n)),and we do once accumulation for it to weaken the randomness and strengthen its regularity,and then get a new sequence : χ(1)=(χ(1)(1),χ(1)(2),…,χ(1)(n)),where, χ(1)
Generate the mean
Z(1)was generated by the adjacent mean of χ(1),where,k=2,3,…,n.
Establishment of model

Model Test Residual sequence of relative error test
Absolute error ε(n)=(ε(1),ε(2),…ε(n))=(χ(0)(1)–(0)(1),χ(0)(2) -(0)(2),…,χ(0)(n)-(0)(n)),where x is the actual value andis the predicted value.The relative error sequence ∅=,Mean relative errorthe smaller the relative error and average relative error are required to be,the better.It is generally believed that it is satisfactory within 5%,and it can be used according to the actual situation within 20%.
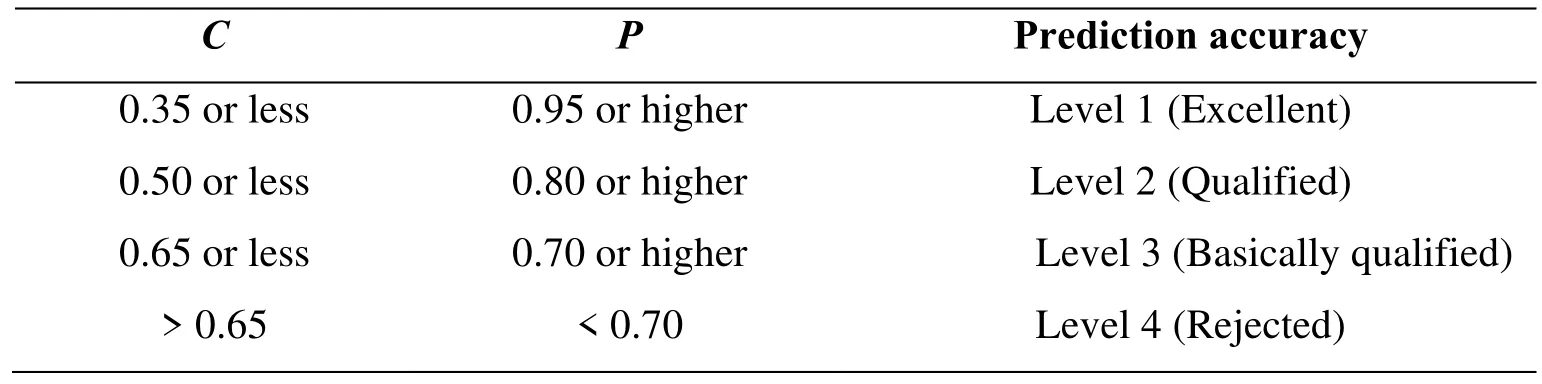
Table 1 The accuracy rating of GM (1,1) grey model prediction
Test of fitting Effect
The test of grey model fitting effect usually adopts the posterior difference method.The model can be used for extrapolation prediction only after the accuracy of the test of fitting effect is qualified.Calculate standard deviation S1and S2of the original sequence X(0)and the residual sequenceε(0),then the posterior difference ratio C and small error probabilityPare calculated:where,C=S2/S1,P=0.6745S1which consists from the number of basic events/n.According to the posterior difference ratio C and small error probability P,the accuracy of the model can be generally divided into four grades,as shown in table 3.The smaller C is,the better.The smaller C value is,the more concentrated the difference between the calculated value and the actual value is. The larger thePvalue is,the better; the larger thePvalue is,the smaller the difference between the residual and the mean residual value is than the point of 0.6475S1given value,so the higher the fitting accuracy of the model is.
If the model fitting accuracy is level 1 or level 2,the fitting effect is better,and the extrapolation prediction can be carried out according to the following formula.
All operations were deduced by SAS 9.4 statistical software [4].
Results
Incidence of tuberculosis in China from 2009 to 2018
The data showed that the incidence rate and case number of tuberculosis showed a decreasing trend,as shown in Figure 1.The incident rate consistently decreased by 26.9% to 59.27 per 100,000 in 2018 from 81.09 per 100,000 in 2009.And the incident case number of tuberculosis consistently decreased to about 0.82 million in 2018 from more than one million in 2009.
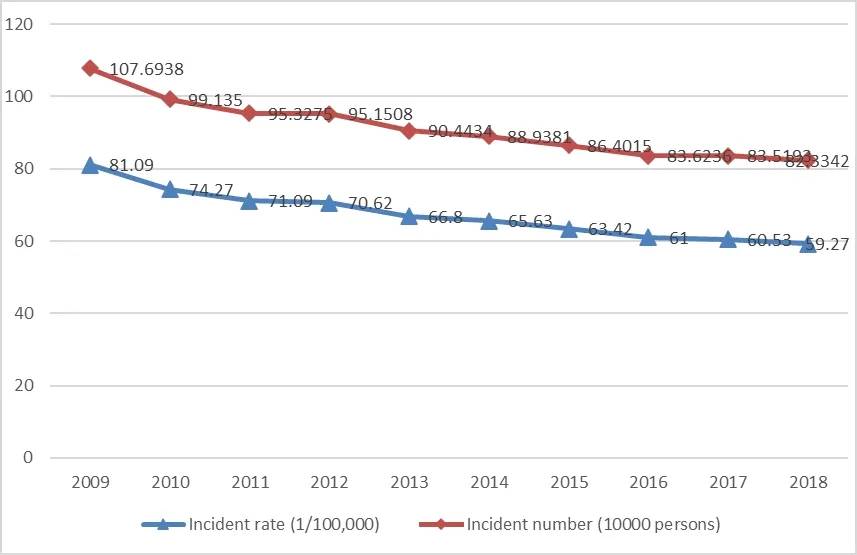
Figure 1 Incident rate and number of tuberculosis in China from 2009 to 2018 (1/100,000)
GM (1,1) model of the incidence of tuberculosis in China
According to the data in Table 1,SAS 9.4 software was used to calculate the incidence of tuberculosis in China from 2009 to 2018 according to the above steps,and a GM (1,1) model was established.The results are shown in Table 3.Among them,the undetermined coefficient α=0.029096,μ=77.198344,thus the GM(1,1) model of tuberculosis incidence prediction was:(1)(k+1)=-2572.122087e(-0.029096k)+2653.212087,in the relative error test,the average relative error △=0.80196%.
The undetermined coefficient α=0.024334,μ=102.194505,and the grey GM(1,1) prediction model was(1)(k+1)=-4092.009372 e(-0.024334k)+4199.703172.In the residual test,the average relative error was 0.89986% (see Table 3).
Test of fitting Effect
For the grey model of tuberculosis incidence,the posterior difference ratioC1=0.097310,the probability of small errorP1=1 were calculated,and the prediction accuracy was level 1.For the grey model of the number of pulmonary tuberculosis patients,the posterior difference ratioC2=0.12220 was calculated,the probability of small errorP2=1,and the prediction accuracy was level 1.Therefore,models of tuberculosis can be extrapolated for prediction.
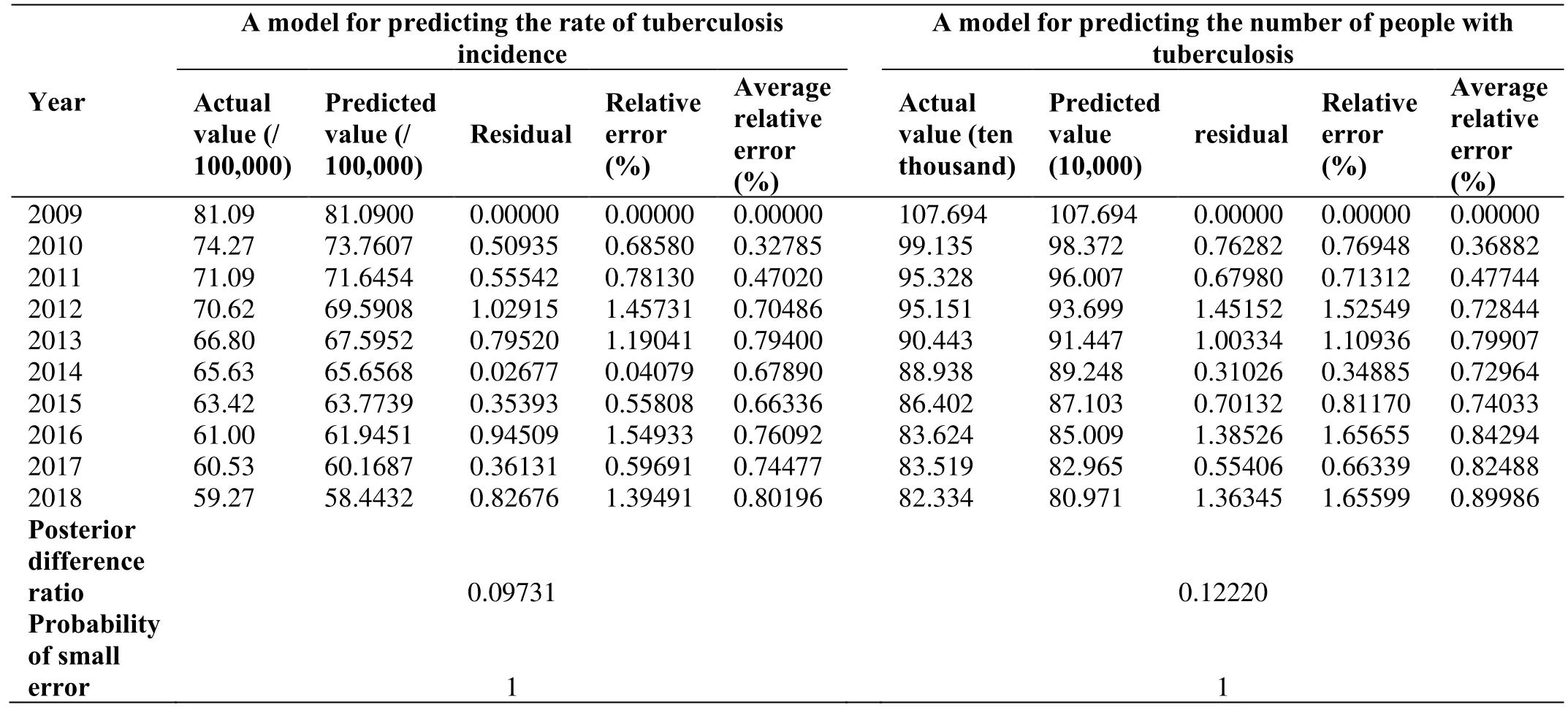
Table 2 GM (1,1) model test of tuberculosis incident rate and number in China from 2009 to 2018
Prediction for 2019-2021 of tuberculosis
Through the model test fitting effect,the incidence of tuberculosis model was fitted for precision,and can be further to predict using GM (1,1) model.The model predicted that the national tuberculosis incidence from 2019 to 2021 would be 56.77/100,000,55.14/100,000 and 53.56/100,000,respectively.From 2019 to 2021,the number of incident tuberculosis cases in China may be 790,242,771,245 and 752,704,respectively(showed in Figure 2 and Figure 3).
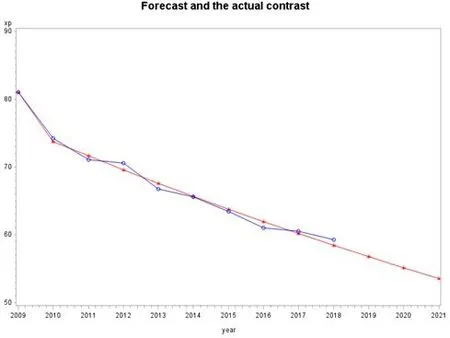
Figure 2 Forecast and the actual value contrast of the tuberculosis incident rate (1/100,000)

Figure 3 Forecast and the actual value contrast of the tuberculosis incident number (10,000)
Discussion
It is of great significance to study the morbidity and epidemic regularity of infectious diseases and predict the future development trend for the control and prevention of diseases.The theory of the Grey system is proposed by Professor Deng in 1982,and the prediction model by the grey system was called grey model,which referred to studying and finding some inherent law to predict development of some things by incomplete and a small amount of time series information [3].The most commonly used grey GM (1,1) model for the differential equation of first order,a variable model,on the less amount of data requirements,does not require the typical probability distribution,and allows to forecast less data.It is simpler,easier to promote than the traditional model,and thus has been widely used in many fields.In recent years,the model is applied to the prediction and forecast of infectious diseases for one of very important prediction methods,which is great significant for the prevention and treatment of infectious diseases [5,6].
The development coefficient α in the GM (1,1)model determines whether the model can be applied to the prediction of disease.When α ≤ 0.3,the GM (1,1)model can be used for medium and long term predictions.When 0.3 < α ≤ 0.5,the GM (1,1) model can be applied to short-term prediction [7].In this study,α1=0.029096 and α2=0.024334 met the above conditions for medium and long term predictions.Therefore,it is appropriate to use the grey GM (1,1)model to predict the incidence of tuberculosis.In this model test,the average relative error of the prediction model of tuberculosis was 0.80% and 0.90%,respectively.The two GM (1,1) models of the average relative error is within 5%,and the posterior differential ratio is less than 0.35,small error probability was 1,and the prediction accuracy level was the first optimal level,which shows that the GM(1,1) model can be better for tuberculosis incidence extrapolation prediction.
From the statistical data from 2009 to 2018,it can be seen that the incidence of tuberculosis and the number of cases declined.The predictive result of the GM (1,1) model showed that the number of incident cases of tuberculosis would be respectively 790,242,771,245 and 752,704 in the next three years in China.The model predicted that the number of cases of tuberculosis in China would show a downward trend from 2019-2021,but the number of incident cases is still at a high level.Tuberculosis as a common chronic infectious disease in China got preliminary control of the spread of tuberculosis by tuberculosis control and prevention efforts for 70 years,and especially since 1990,through nationwide implementation of the Directly Observed Treatment Short course (DOTS)strategy,morbidity and mortality rates are falling [7,8].But there also exists the enhancement of bacterium drug resistance and limited testing areas and treatment level at the primary health conditions,which may cause clinical misdiagnosis and missed diagnosis of tuberculosis cases,with the potential spreading risk.Additionally,coupled with the increase of the migrant population,and population aging degree,China with a large population is still one of 22 tuberculosis countries with high tuberculosis burden in the world[7,9].The disease prevention and control institutions at all levels should take comprehensive measures to strengthen operational training,focus on health education of tuberculosis prevention among high-risk groups,and raise the awareness rate of tuberculosis prevention knowledge among the public.Tuberculosis prevention and control institutions still should take measures to strengthen defense from spreading.More health education is needed to bring the public to better understand the policies and measures,and more effort should be put to make tuberculosis patients be detected and receive timely treatment and standardized management.The "early detection,early quarantine and early treatment" strategy is still very important for tuberculosis control and prevention.For patients diagnosed with tuberculosis,we first should effectively control the infection source,and according to actual patient condition,timely take effective treatment measures for tuberculosis patients with long-term follow-up to reduce the spreading efficiency of tuberculosis patients,and the survey of all tuberculosis patients contact helps to track tuberculosis cases in the population and contributes to improve the detection and cure rate of tuberculosis patients [10].
In addition,this study also has some limitations.Firstly,the data of this study were extracted from the Statistical Yearbook of China,among which the data of infectious diseases are mainly from the monitoring points of infectious diseases,while the quality of monitoring data of individual data may not be ideal.Secondly,the grey system prediction adopted the mathematical regularity of the original data,and cannot fully consider the impact of natural,social,environmental and other complex factors on the epidemic.Therefore,the possible impact of various complex factors on the epidemic should also be comprehensively considered when making health decisions based on the predicted results [11].
杂志排行
Food and Health的其它文章
- Experimental study on the improvement of insomnia model mice's symptoms by Sanwei Anmian Decoction and its disassembled prescription
- Prediction of syphilis incident rate and number in China based on the GM (1,1)grey model
- Visual analysis of the research hotspots of Neuman systems model in recent 20 years
- Application of self-directed teaching methods related to microlecture and flipped classroom in the teaching of obstetrics and gynecology in a non-directly affiliated hospital
- Discussion on the prevention and treatment of COVID-19 by Zhuang Medicine
