Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Linoleic Acid in Polygonati Rhizoma
2020-11-03ZHOUZhunYUANHnWenPENGCiYunJIANYuQingZHOUXuDongLIBinSHENGWenBingGONGLiMinHEShuJinWANGWeiLIUChngXio
ZHOU Zhun,YUAN Hn-Wen,PENG Ci-Yun,JIAN Yu-Qing,ZHOU Xu-Dong,LI Bin,SHENG Wen-Bing,GONG Li-Min,HE Shu-Jin,WANG Wei*,LIU Chng-Xio
a.Sino-Pakistan TCM and Ethnomedicine Research Center,Innovative Materia Medica Research Institute,School of Pharmacy,Hunan University of Chinese Medicine,Changsha,Hunan 410208,China
b.Hunan Xinhui Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd.,Changsha,Hunan 410000,China
c.Tianjin Institute of Pharmaceutical Research,Tianjin 300193,China
Keywords
Polygonati Rhizoma(Huang Jing,黄精)
Linoleic acid
Qualitative analysis
Quantitative analysis
Thin layer chromatography(TLC)
High performance liquid chromatography(HPLC)
†These authors contributed equally.
ABSTRACT
Objective To explore the major compound in Polygonati Rhizoma(Huang Jing,黄精)for quality control.
Methods The major compound was isolated and analyzed by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry(LC-MS),and subsequently further identified by nuclear magnetic resonance(NMR).Thin layer chromatography(TLC)was optimized based on the previous methods reported in the Chinese Pharmacopeia(2015 edition).
Results The major compound was isolated from the natural material and identified as linoleic acid.A high performance liquid chromatography(HPLC)method with robust linearity(R2=0.999 7),specificity,precision,stability,repeatability and recovery was developed for linoleic acid determination.TLC chromatogram was improved significantly after optimization for qualitative analysis.
Conclusions The optimized TLC method is practical and can be adopted for quality control of Polygonati Rhizoma(Huang Jing,黄精).The levels of linoleic acid vary between species of Polygonati Rhizoma(Huang Jing,黄精),with Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua(Jiang Xing Huang Jing,姜型黄精)showing the highest contents.This study provides valuable information for quality control of Polygonati Rhizoma(Huang Jing,黄精).
1 Introduction
Polygonati Rhizoma(Huang Jing,黄精),the rhizome of thePolygonatum kingianumColl.et Hemsl.(Da Huang Jing,大黄精),Polygonatum sibiricumRed.(Ji Tou Huang Jing,鸡头黄精)andPolygonatum cyrtonemaHua(Jiang Xing Huang Jing,姜型黄精)plants is widely used in traditional Chinese medicine(TCM)for diabetes,phthisis,hypertension,neurasthenia and tinea corporis treatments[1-4].This herbal medicine was first recorded inAppendant Records of Famous Physicians(Ming Yi Bie Lu,《名医别录》)[5].In addition,Polygonati Rhizoma(Huang Jing,黄精)is used as a functional food for its purported health effects[5].Its proposed pharmacological activities including anti-aging,hypoglycemic,hypolipidemic,antitumor,antibacterial and antiviral effects were investigated,and clinical application has been recently studied[6-9].
Although many compounds,including saponins,flavones,volatile oils,lignans,alkaloids,phytosterols and anthraquinones,are found in Polygonati Rhizoma(Huang Jing,黄精),no method of determination of the major compounds or Q-makers(chemical substances in TCM closely associated with the safety and effectiveness)have been developed for quality control[10-14].In theChinese Pharmacopoeia(2015 edition),total polysaccharides were selected as components for quality control of Polygonati Rhizoma(Huang Jing,黄精).It specified that the polysaccharide contents shall not be less than 7.0%,as determined using ultraviolet(UV)spectrophotometry[1].This method exhibits poor repeatability and stability for assessing the quality of Polygonati Rhizoma(Huang Jing,黄精)from different species,so there is in urgent need to develop a more sensitive and robust method for major compound determination.Herein,the common major compound in the three species of Polygonati Rhizoma(Huang Jing,黄精)was isolated and identified to be linoleic acid.Subsequently,a quantitative high performance liquid chrometofraphy(HPLC)method was established for determination of linoleic acid,and a thin layer chromatography(TLC)method for quality assessment of Polygonati Rhizoma(Huang Jing,黄精)was optimized and successfully applied for linoleic acid identification.
2 Experimental Metho d
2.1 Material and reagent
Linoleic acid was purchased from Baoji Herbest Bio-Tech Co.,Ltd.(Baoji,China).TLC plates(HSGF 254)were obtained from Yantai Jiangyou Silica Gel Development Co.,Ltd.(Yantai,China).HPLC grade methanol was used herein(Merck,Darmstadt,Germany)and all analytical grade solvent,including petroleum ether(PE),ethyl acetate(EtOAc),n-hexane,acetic acid,ethanol(EtOH)and methanol(MeOH),were obtained from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co.,Ltd.The TLC spots were viewed after spraying with 0.5% vanillin-H2SO4(prepared in the lab)and heating.All aqueous solutions were prepared with purified water from Cestbon Group(Shanghai,China).A total of 23 batches of Polygonati Rhizoma(Huang Jing,黄精)samples were collected from all over China(Table 1).

Table 1 Detailed information of Polygonati Rhizoma(Huang Jing,黄精)samples
2.2 Isolation and identification of major compounds of Polygonati Rhizoma(Huang Jing,黄精)
Several batches of sample powder(1 g)were extracted using methanol(10 mL)under ultrasonication for 30 min.The supernatant was centrifuged,filtered and then analyzed by liquid chromatograpgy-mass spestrometry(LC-MS).The major compound common to all species of Polygonati Rhizoma(Huang Jing,黄精)was determined.According to a previously reported isolation procedure[6],the major compound was traced in different fractions by LC-MS(Agilent 6 460 LC-QQQ-MS,Agilent Technologies,USA)and TLC,and then isolated by column chromatography.Its structure was elucidated by nuclear magnetic resonance(NMR),LC-MS and comparison with a certified standard.
2.3 Quantitative analysis of the major compound
2.3.1 Preparation of sample and standard solutionAccurately weighed linoleic acid(31.8 mg)was dissolved in a volumetric flask(25 mL)with methanol to prepare a stock solution.The stock solution was diluted to yield standard solutions with different concentrations and transferred to HPLC vials for analysis.All samples were dried to constant weight at 60 °C and powdered.The fine powder(1 g)was accurately weighed and extracted in a 50 mL conical flask with methanol(10 mL)under ultrasonic for 30 min.Methanol was used to compensate for any mass loss.The supernatant was concentrated at 12 000 rpm for 5 min,filtered through a 0.22 mm membrane filter,and transferred to a HPLC vial for further analysis.
2.3.2 Quantification by HPLCHPLC analysis was performed using Agilent 1 260 Infinity system(Agilent Technologies,USA).Agilent Eclipse XDB-C18 column(5 μm,4.6×250 mm)was used for quantitative analysis and 0.05% phosphoric acid and acetonitrile(10 :90,v/v)were used as part of the mobile phase at flow rate of 1 mL/min.The column temperature,injection volume and detection wavelength were optimally set to 30 °C,10 μL and 203 nm,respectively.The HPLC chromatographic profile of linoleic acid of Polygonati Rhizoma(Huang Jing,黄精)is shown in Figure 1.
2.3.3 Method developmentA total of six standard solutions at different concentrations were injected into the HPLC system for analyses under the optimized conditions.Specificity determination was achieved by comparative analysis of a blank solvent and sample solution.The calibration curve was established by plotting the peak areas(y)as a function of concentrations(x,μg/mL).Precision was evaluated by analyzing six replicates of sample A1,and six independent sample solutions of A1 in parallel were analyzed for repeatability.Stability tests were performed by analyzing sample A1 solution after 0,2,4,8,12 and 24 h.Almost equal amounts of linoleic acid were spiked into the sample,and six parallel analyses were performed after the sample solutions were prepared according to the aforementioned methods to evaluate recovery.
2.4 Qualitive analysis of the major compound of Polygonati Rhizoma(Huang Jing,黄精)
2.4.1 Preparation of sample and standard solutionsFine sample powder(2 g)was extracted with 20 mL methanol under ultrasonication for 30 min.The supernatant(15 mL)was added to silica gel(0.6 g),loaded in the silica gel column for chromatographic separation(200 - 300 mesh,1×12 cm),and subsequently diluted with PE/EtOAc(1 :1,v/v).The eluate(70 mL)was collected,evaporated,and the sample solution was obtained after dissolution of the residue in 0.4 mL chloroform.A standard solution of linoleic acid(1 mg/mL)was obtained by dilution of the stock solution.
2.4.2 Qualitative analysis by TLCThe sample and standard solutions(10 μL)were spotted in the form of 8 mm wide bands that were 10 mm from the bottom edge using a SP-20E sample applicator(Shanghai Kezhe Biochemical Technology Co.,Ltd.,China)on a silica gel plate.The samples were separated three times in a twin trough glass chamber(20×10 cm)using n-hexane/EtOAc/AcOH solvents at ratios of 8 :1 :0.2,2 :1 :0.1,and 5 :1 :0.1,respectively.The lengths of the three chromatogram runs were 8,2 and 6.5 cm,respectively.Visualization was performed using a GoodLook-1000 imaging system(Shanghai Kezhe Biochemical Technology Co.,Ltd.,China)after spraying with 1% H2SO4-vanillin and heating at 105 °C.
3 Results
3.1 Identification of the major compound of Polygonati Rhizoma(Huang Jing,黄精)
The major compound was isolated using the LC-MS and TLC procedures described above.The1H NMR spectrum showed signals corresponding to a fatty acid(Figure 2),but the structure could not be elucidated based solely on1H NMR or13C and 2D NMR spectra due to overlapping signals.However,it was suspected this compound was linoleic acid according to the nature of NMR spectrum and[M-H]-ion peak atm/z290 in the MS spectrum.This suspicion was confirmed by LC-MS analysis using a comparison with the known standard(Figure 3).
3.2 Quantification of linoleic acid by HPLC
3.2.1 Optimization of extraction conditions and method developmentMethanol,EtOH,EtOAc and PE were used for sample extraction,and MeOH resulted in the maximum yield of linoleic acid.In addition,methanol gave the better results when compared with 40%,60% and 80% methanol-water mixtures.The results showed no variations when extracted under ultrasonication or reflux.The ultrasonic method was selected and the extraction time was optimized at 30 min.
3.2.2 Method validation and sample analysesAs shown in Figure 4,the linearity of the linoleic acid calibration curve was acceptable(R2=0.999 7).No peak in the blank solvent was observed where linoleic acid was expected(Figure 1),indicating satisfactory specificity in compliance with the pharmacopeia requirements of determination.Relative standard deviations(RSDs)of the precision,repeatability and stability of the retention times were 0.08%,0.10% and 0.21%,respectively,while those of peak area were 0.10%,2.11% and 1.04%,respectively(Table 2).The recoveries of linoleic acid using the newly developed method was 101.7%,98.7%,98.9%,98.7%,99.0% and 101.9%,with an RSD of 1.5%.This indicated that the newly developed method was robust and credible for linoleic acid determination in Phlygonati Rhizoma(Huang Jing,黄精).All samples were prepared and injected into HPLC system using the method described above.The linoleic acid content of Phlygonati Rhizoma(Huang Jing,黄精)samples varied from 0.004 6% to 0.183 9%(Table 3),with the highest contents inPolygonatum cyrtonemaHua(Jiang Xing Huang Jing,姜型黄精).Although linoleic acid was the most abundant constituent in three species of Polygonati Rhizoma(Huang Jing,黄精),the levels in most species<0.1%.
3.3 Qualitative analysis of linoleic acid of Phlygonati Rhizoma(Huang Jing,黄精)by TLC
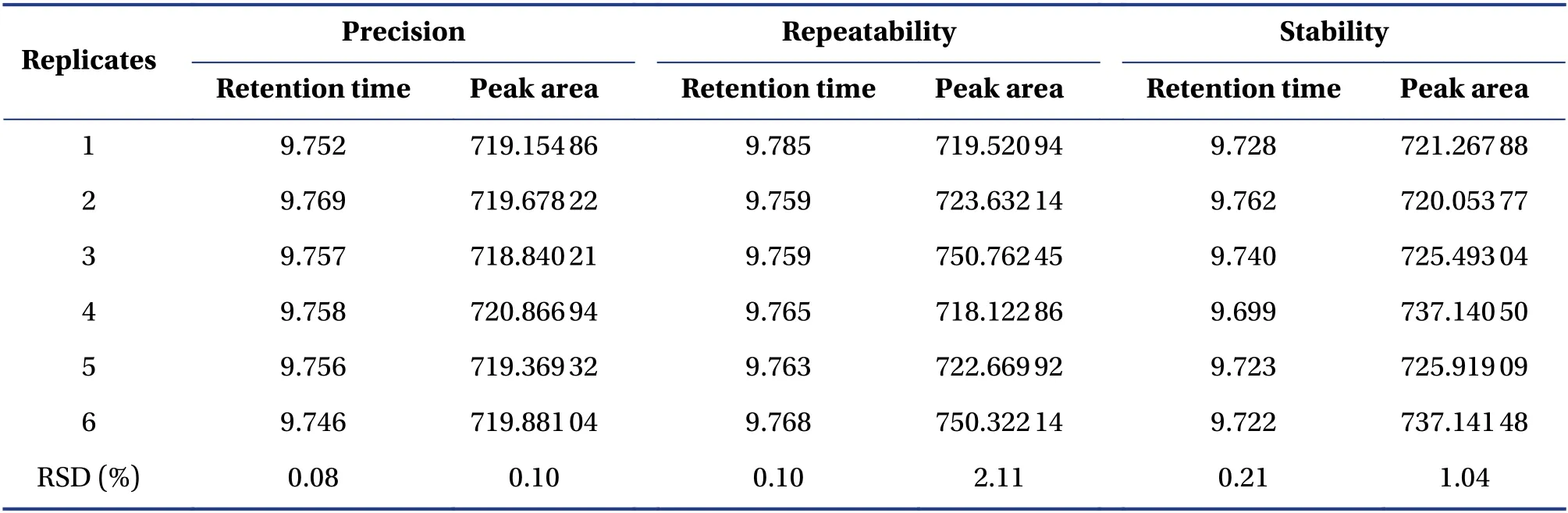
Table 2 Method validation of the quantitative analysis of linoleic acid
TLC analysis was first performed using the method described in theChinese Pharmacopeia,and a few unclear bands were observed on the plate(Figure 5).To optimize the chromatographic,silica gel column chromatography was applied to remove polar constituents,especially polysaccharides which were not the targets of the investigation but disturbed the TLC visualization.For separation of structurally similar compounds,the mobile phase was optimized as nhexane/EtOAc/AcOH.The optimal ratios of each solvent in mobile phase in terms of chromatogram running times and running length were also studied.More clear compound bands were observed in the optimal TLC(Figure 6),and more importantly the linoleic acid could be identified,indicating that this method is suitable for quality control of Polygonati Rhizoma(Huang Jing,黄精).
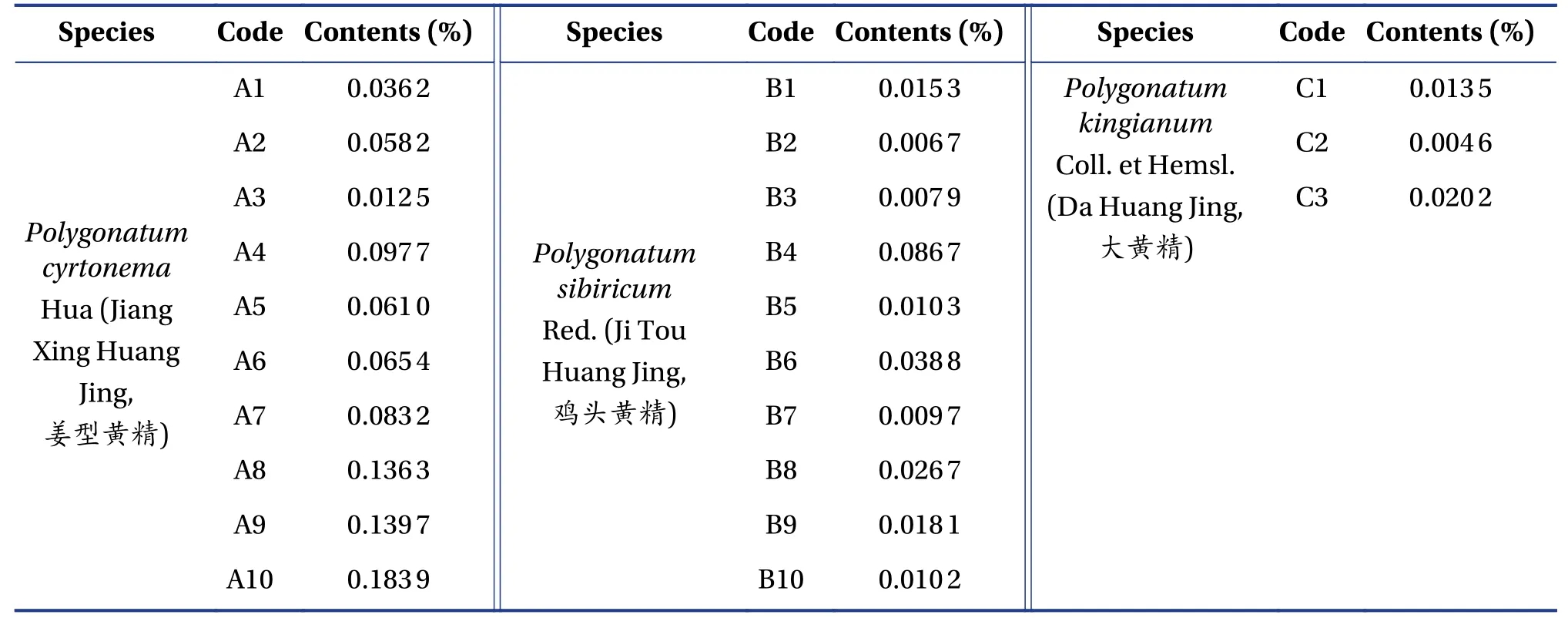
Table 3 Linoleic acid contents in Phlygonati Rhizoma(Huang Jing,黄精)
4 Conclusions
In the current study,diosgenin before or/and after hydrolysis of saponins was determined in Polygonati Rhizoma(Huang Jing,黄精)using HPLC.However,in our pre-experiment,no diosgenin either before or after hydrolysis was detected by the sensitive LC-MS methods.The common major compound in three species of Polygonati Rhizoma(Huang Jing,黄精)was determined and isolated using TLC and LC-MS.The structure of linoleic acid was determined based on NMR and MS data,as well as comparison with an authentic standard.HPLC method was subsequently developed for determination of linoleic acid,and the precision,repeatability,stability and recovery were acceptable.Moreover,qualitative analysis of linoleic acid by TLC was performed successfully.The linoleic acid contents inPolygonatum cyrtonemaHua(Jiang Xing Huang Jing,姜型黄精)were higher than those inPolygonatum sibiricumRed.(Ji Tou Huang Jing,鸡头黄精)andPolygonatum kingianumColl.et Hemsl.(Da Huang Jing,大黄精),and these chemical differences may manifest as variations of pharmacological effects.It is recommended that the linoleic acid content in Phlygonati Rhizoma(Huang Jing,黄精)should be ≥ 0.003%.However,to better clarify its medicinal properties and explore the Q-maker,further research on chemical constituents especially the common compounds between species,along with their pharmacological activities,should be performed.This study provides deep insight into the major compound or Q-marker of Polygonati Rhizoma(Huang Jing,黄精)and can serve as a reference for further TCM quality control research.
Acknowledgement s
We thank for the funding support from the National Standardization Construction in TCMs of China(No.ZYBZH-Y-HUN-23),National Key Research and Development Projects of China(No.2018YFC1707903)and Key Research and Development Projects of Hunan Province(No.2018SK2119).
Competing Interests
The authors declare no conflict of inter est.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Digital Chinese Medicine的其它文章
- Instructions for Authors
- A Preliminary Study on Legitimacy Identification Standards for Unconventional Treatment Technologies in Traditional Chinese Medicine
- A Metabolomics Study of the Volatile Oil from Prunella vulgaris L.on Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
- Fermentation Production of Ganoderma lucidum by Bacillus subtilis Ameliorated Ceftriaxone-induced Intestinal Dysbiosis and Improved Intestinal Mucosal Barrier Function in Mice
- Antioxidant,Antimicrobial and Wound Healing Potential of Helicteres isora Linn.Leaf Extracts
- A Network Pharmacology Study on the Effects of Ma Xing Shi Gan Decoction on Influenza
