Clinical observation of acupuncture plus Frenkel exercises for ataxia after cerebral stroke
2020-10-23LuHai鲁海ZhangChunhong张春红BaiWeijing白玮婧RenXuesong任雪松ZhangBo张博ZhangZhilong张智龙MengFanzheng孟凡征WangLi王丽WangZhenzhen王珍珍WuLianzhong武连仲
Lu Hai (鲁海),Zhang Chun-hong (张春红),BaiWei-jing (白玮婧),Ren Xue-song (任雪松),Zhang Bo(张博),Zhang Zhi-long (张智龙),Meng Fan-zheng (孟凡征), Wang Li (王丽), Wang Zhen-zhen (王珍珍),Wu Lian-zhong(武连仲)
1 First Teaching Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional ChineseMedicine,Tianjin 300193,China
2 Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Tianjin 301617,China
3 Academic Experience Inheritance Studio of National FamousChinese Medicine Practitioners Wu Lian-zhong,Tianjin 300381,China
4 Academic Experience Inheritance Studio of Master of Traditional ChineseMedicine ShiXue-m in,Tianjin 300381,China
5National Clinical Research Center for ChineseMedicine Acupuncture and Moxibustion,Tianjin 300381,China
6 Tianjin Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine Affiliated Hospital,Tianjin 300120,China
7 Tianjin Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, NankaiHospital,Tianjin 300100,China
Abstract
Keywords:Acupuncture Therapy; Rehabilitation; Ataxia;Poststroke Syndrome;Cerebral Infarction
Post-stroke ataxia (PSA) refers to a group of clinical symptoms commonly seen in patients with posterior circulation infarction[1].Imaging study usually reveals infarction in the cerebellum,brainstem and basal ganglia,which is generally caused by vertebrobasilar ischem ia. Cerebellar ataxia resulting from damages to cerebellum or brainstem usually manifests as loss of balance,poor coordination in movements,and involuntary motions with irregular strength,range,speed and rhythm[2].Cerebral ataxia caused by infarction in the basal ganglia usually presents as m ilder symptoms compared with cerebellar ataxia and the activities of daily living (ADL) are basically possible. Loss of normal motor patterns,especially balance dysfunction, w ill hinder the self-care abilities in daily life and increase the risk of tumble in PSA patients (the rate of tumble in 3 months after stroke is 27%), not only severely affecting the recovery and ADL,but also increasing the risk of a second stroke[3].Currently,acupuncture and rehabilitation training can produce satisfactory efficacy in treating PSA.Among all the acupuncture methods in treating PSA,scalp acupuncture is the predom inant one[4-6],while rehabilitation therapy most often uses functional electrical stimulation[7-10]and functional exercises[11-12].There were few studies exploring the synergistic effect of combining body acupuncture and functional exercises, and the studies usually targeted at cerebellar ataxia.This trial combined the m ind-refreshing and balance-restoring acupuncture method and Frenkel exercises to treat lower-limb dysfunction in PSA, aim ing to provide reference for clinical treatment of lower-limb ataxia after posterior circulation stroke.
1 Clinical Materials
1.1 Diagnostic criteria
1.1.1Diagnostic criteria in Westernmedicine
TheChinese Guidelines on Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Ischem ic Stroke2014[13]issued by the Chinese Society of Neurology of Chinese Medical Association was referred in this trial.Acute onset:topical neurological deficit, overall neurological deficit was rare;symptoms and body signs lasted for more than a couple of hours (thrombolysis could be considered based on the indications); head CT or MRI exam ination excluded cerebral hemorrhage and other diseases;head CT or MRI examination confirmed the infarction.
1.1.2 Diagnostic criteria in traditional Chinese medicine(TCM)
TheGuidelines on Diagnosis and Treatment of Common Diseases in Internal Medicine of Traditional Chinese Medicine[14]issued by the China Association of Chinese Medicine was referred.Primary symptoms:hem iplegia, unconsciousness, slurred speech or aphasia,hem iparesthesia, one side of the mouth drooped and deviated tongue;secondary symptoms:headache,dizziness, changes in pupil, choke when drinking water,unable to blink one eye,loss of coordination;acute onset,mostly with a clear cause and precursory symptoms; people over 40 years old were more likely to be affected. The diagnosis was confirmed when two or more primary symptoms, or one primary symptom and two secondary symptoms were met,w ith comprehensive consideration of the onset,causing factors, precursory symptoms and age; when the above conditions were m issed,the diagnosis can still be confirmed by imaging test.
1.2 Inclusion criteria
Conformed to the diagnostic criteria in both TCM and Western medicine; it was the first time ever presenting as lower-limb ataxia, lasting for 15-180 d; age ranged 40-70 years old; w ith clear consciousness and stable vital signs,who were able to cooperate during treatment and exam inations; informed consent.
1.3 Exclusion criteria
With disorder of consciousness and an unstable condition;hereditary ataxia;abnormal intracranial vascular network, or coupled with brain tumor, brain trauma, or parasitic encephalopathy; accompanied by severe disorders involving liver, kidney, hematopoietic system or metabolic system,mental disorders or dementia; a suspected or confirmed history of alcohol or drug abuse, or other conditions believed to lower the possibility of recruitment or make the recruitment more complicated,such as frequent change in work environment or an unstable living environment that may cause loss to follow up; women in pregnancy or lactation period.
1.4 Elim ination and dropout criteria
Those with incomplete data were elim inated; those who showed poor compliance and quitted before the end of the trial; those who failed to stick w ith the treatments adopted in the trial but adopted or changed to other treatments.
1.5 Statistical methods
All data were processed using SPSS version 19.0. The repeatedly measured measurement data that conformed to or substantially conformed to normal distribution were expressed as mean±standard deviation (±s) and analyzed using univariate analysis of variance for repeated measures;the ranked data were exam ined by Wilcoxon rank-sum test;the enumeration data were processed using Chi-square test.P≤0.05 was taken to indicate statistical significance.
1.6 Quality control
To ensure the quality of the trial, the research staff all received relevant trainings for well mastering the diagnosis and treatment of PSA, acupuncture operation,rehabilitation exercises,and observation and exam ination of the involved indexes. We were required to rigorously fill in the case report form(CRF)and record the detailed information of each case.The supervisor inspected the study regularly and selected samples random ly to check the consistency between the firsthand data and the recorded data.The statistician began to intervene in the early stage and supervised the whole process of the trial. The data managing center was in charge of timely collection and filing of the firsthand data. The firsthand data had to be real and complete, w ith the corresponding exam ination reports attached in the end. There needed to be notes clearly explaining the reason and time when any change was made, together w ith the signature of the one who recorded the change.
1.7 General data
A total of 120 PSA patients were recruited in this trial,all from the First Teaching Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Tianjin Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine Affiliated Hospital and Tianjin Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine,Nankai Hospital,between December 2013 and December 2017.This is a multi-centered random ized controlled trial, which used computer to random ize the subjects into an observation group and a control group at 1:1 w ith concealed allocation method(the random numbers were sealed in opaque envelopes,one in each,indicating the corresponding grouping information),w ith 60 cases in each group. There were 3 dropout cases in the observation group and 2 dropout cases in the control group, who quitted halfway since they failed to complete the required treatment.
The valid cases were taken into statistical analysis,including 57 cases in the observation group and 58 cases in the control group. There were no significant differences in the data of gender, average age and mean disease duration between the two groups (allP>0.05),(Table 1).
2 Treatment Methods
Each recruited patient was given individualized basic treatment according to theGuidelines on Diagnosis and Treatment of Common Diseases in Internal Medicine of Traditional Chinese Medicine, including blood pressure,glucose and lipid control, antiplatelet aggregatiion and brain nerve nutrition supplement, etc.
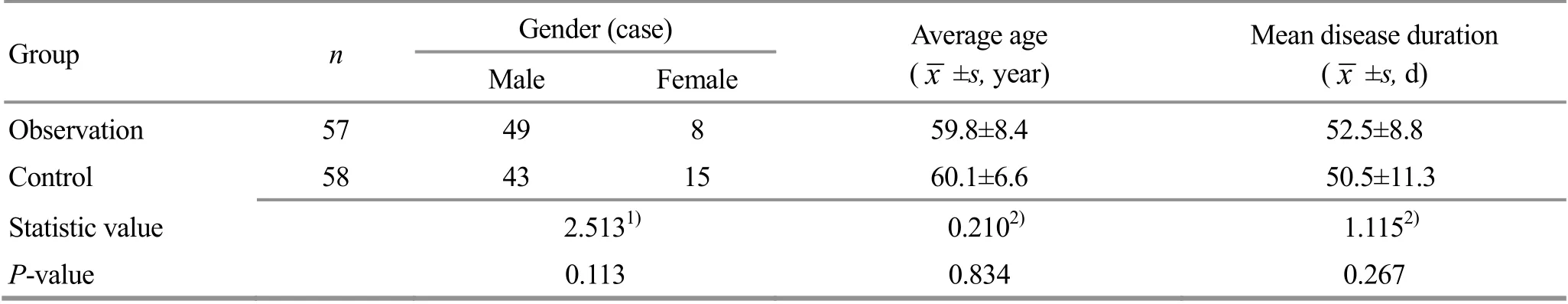
Table 1. Com parison of the general data between the two groups
2.1 Observation group
Patients in the observation group received m ind- refreshing and balance-restoring acupuncture combined w ith Frenkel exercises.
2.1.1 M ind-refreshing and balance-restoring needling method
Acupoints:Shuigou(GV 26),Yintang (GV 29),Shangxing(GV 23),Baihui(GV 20),Fengfu(GV 16),bilateral Neiguan(PC 6),Sanyinjiao(SP 6),Fengchi(GB 20), Wangu (GB 12), Tianzhu (BL 10) and cervical Jiaji (EX-B 2).
Operation:Hwato disposable acupuncture needles of 0.30 mm in diameter and 40-75 mm in length were chosen for treatment (Suzhou Medical Appliance Factory, China). After standard sterilization for topical skin, the acupoints were punctured in the follow ing sequence:bilateral Neiguan(PC 6),(perpendicularly punctured for 0.5-1.0 cun, w ith two hands performing tw irling and lifting-thrusting reducing manipulation simultaneously for 1 m in), Sanyinjiao (SP 6), (obliquely punctured by the medial edge of tibia at 45° for 1.0-1.5 cun,w ith lifting-thrusting reinforcing manipulation,making the affected limb tw ist for 3 times), Fengchi (GB 20), (obliquely punctured towards the inner canthus of the other side for 1.0-1.5 cun), cervical Jiaji (EX-B 2),(punctured obliquely towards the spine,w ith even reinforcing-reducing manipulation performed for 1 min),Wangu (GB 12) and Tianzhu (BL 10), (perpendicularly punctured for 1.0-1.5 cun, w ith small-amplitude highfrequency twirling reinforcing manipulation performed by two hands simultaneously for 1 m in).From treatment day 1 till day 3,Shuigou(GV 26)was punctured(obliquely towards the nasal septum for 0.5 cun, twirled for 360° in one same direction first,then w ith heavy bird-pecking reducing manipulation performed till tearing or moisturizing of the eyeball);from treatment day 4, Yintang (GV 29) was needled(obliquely downwards by 0.3-0.5 cun, w ith bird-pecking reducing manipulation),Shangxing (GV 23)was punctured with the needle tip towards Baihui (GV 20)(the needle was inserted for 2 cun,w ith tw irling reducing manipulation performed for 1 m in). Needles in the acupoints mentioned above were retained for 20-30 min except Shuigou (GV 26). Besides, w ith Hwato disposable acupuncture needle of 0.30 mm in diameter and 75 mm in length, Fengfu (GV 16) was punctured w ith the needle tip towards the laryngeal prom inence when the patient took a sitting position w ith lowered head.Vibrating manipulation was performed as the needle went deeper after it reached beneath the skin,and the needle was removed immediately once the patient's body shook. The treatment was conducted once a day, 5 times a week, for a total of 4 weeks.2.1.2 Rehabilitation training
The lower-limb Frenkel exercises[11]were adopted.
Four positions,i.e.supine,sitting,standing and walking, were employed. The key point was to teach the patients to focus attention and learn how to use the visual sense to replace the lost proprioception.
Supine position: Flexion and extension of one side lower limb (the patient was asked to bend the knee and move the heel on the treatment table till the leg extended); abduction and adduction of the hip joint (with the hip and knee joints extending, the patient glided the lower limbs on the table; w ith the knee bent and the heel staying still on the table);flexion and extension of the hip and knee joints(the heel was raised up from the table and put on the knee of the other side and then glided along the tibia towards the other foot); simultaneous flexion and extension of the lower limbs (the heels glided on the treatment table,making the lower limbs flex and extend concurrently);alternate flexion and extension of the lower limbs(while the heels were gliding on the table, one leg was doing flexion and extension and the other leg was doing abduction and adduction).
Sitting position: Let the patient touch the hand of the physical therapist (PT) w ith his foot, and the PT changed the position of the hand each time; the patient was then asked to lift his lower limb and step on the footprint drawn in advance; then the patient sat still for a couple of m inutes;w ith the knees together,the patients stood up and sat down repeatedly.
Standing and walking positions: The patient moved his foot back and forth across a straight line; walked along a curve; walked between two parallel lines; tried to walk follow ing the footprints drawn in advance.
The patients practiced the rehabilitation exercises for 30 min right after the acupuncture session, once a day,5 sessions a week, for a total of 4 weeks.
2.2 Control group
The control group only received the same mind- refreshing balance-restoring acupuncture method as the observation group, w ith the same points, operation and treatment course.
3 Therapeutic Efficacy Observation
3.1 Items for observation
The international cooperative ataxia rating scale(ICARS)[11]and Berg balance scale (BBS) were used to score the lower-limb function before treatment, after treatment and at the 3-month follow-up; Barthel index (BI) was adopted to evaluate the ADL[15].
第三,在预算管理的责任层面。责任部门是预算的具体编制和实施部门,其有专门的预算员依照一定的标准负责相关的监督工作,以确保预算工作的合理开展。
3.1.1 ICARS score
The ICARS mainly consists of items of posture and gait dysfunction,dynam ic function,language dysfunction and eyeballmovement dysfunction.The score ranges from 0 to 100 points. A higher score means more severe ataxia.0-20 points:m ild ataxia;21-50 points:moderate ataxia;51-70 points:severe ataxia;≥71 points:complete loss of the ability for self-care in daily life.
3.1.2 BBS score
BBS mainly covers the items of change from sitting to standing,standing unsupported,sitting unsupported,change from standing to sitting, transfers, standing w ith eyes closed,standing w ith feet together,reaching forward while standing,retrieving objects from floor while standing, turning trunk w ith feet fixed, turning 360°, stool stepping and tandem standing and standing on one leg. The score ranges from 0 to 56 points. A lower score indicates worse balance dysfunction.0-20 points: wheelchair bound; 21-40 points: walking w ith assistance; 41-56 points: independent.
3.1.3 BI score
The items in BImainly include feeding,bathing,personal groom ing,dressing,bowel and bladder continence, getting on/off the toilet, transfers, walking and stair climbing. The maximum score is 100 points,and the lowest is 0 point. A higher score suggests better self-care ability.≤40 points:highly dependent;41-60 points:moderately dependent;61-99 points:m ildly dependent;100 points,substantially independent.
3.2 Criteria for efficacy evaluation
BBS score was taken to estimate the clinical efficacy[16].The score reduction rate was calculated based on Nimodipine method. Score reduction rate =(Pre-treatment score- Post-treatment score)÷ Pre-treatment score × 100%.
Recovered: The score reduction rate ≥85%.
Effective: The score reduction rate ≥20% but <50%.
Invalid: The score reduction rate <20%.
3.3 Safety evaluation
The physical markers (body temperature, respiration,heart rate and blood pressure) and biochem ical indexes (blood, urine and stool routines, and liver and kidney functions) were checked before and after treatment to ensure the safety and discover potential side effects.Any adverse reactions and events associated with acupuncture and rehabilitation exercises (fainting during acupuncture, needle stuck, needle bent, needle broken, bleeding, hematoma and intensive pain, etc.)were recorded in details and treated immediately.Severe cases should be followed up until the reactions were completely gone.
3.4 Treatment results
3.4.1 Comparison of the clinical efficacy
The markedly effective rate was 70.2% and the total effective rate was 96.5% in the observation group,versus 39.7% and 87.9% in the control group, and the between-group differences in the markedly effective rate and the total effective rate were statistically significant (P<0.01,P<0.05).Please see Table 2 for details.

Table 2. Com parison of the clinical efficacy between the two groups (case)
3.4.2 Comparison of the ICARS score
Therewasno significant difference in the ICARS score between the two groups before treatment (P>0.05);the between-group differences in the ICARS score were statistically significant after treatment and at the follow-up(P=0.05,P<0.05).The intra-group overall comparisons showed that the ICARS score varied significantly (P<0.01);the between-group overall comparisons showed that the differences in the ICARS scores were statistically insignificant (P>0.05).The interaction effect between time and group factors was statistically insignificant (P>0.05). Please see Table 3 for details.
The results showed that acupuncture combined w ith rehabilitation exercisesand sole use of acupuncture can markedly improve the lower-limb posture and gait dysfunction in PSA patients in general;after treatment and at the follow-up,acupuncture plus rehabilitation exerciseswas superior to acupuncture alone comparing the improvement of lower-limb posture and gait dysfunction,but,generally speaking,there was no significant difference in the efficacy between the two methods;the time factor and treatment method factor did not produce significant interaction effect.
Table 3.Comparison of the ICARS score between the twogroups (±s, point)
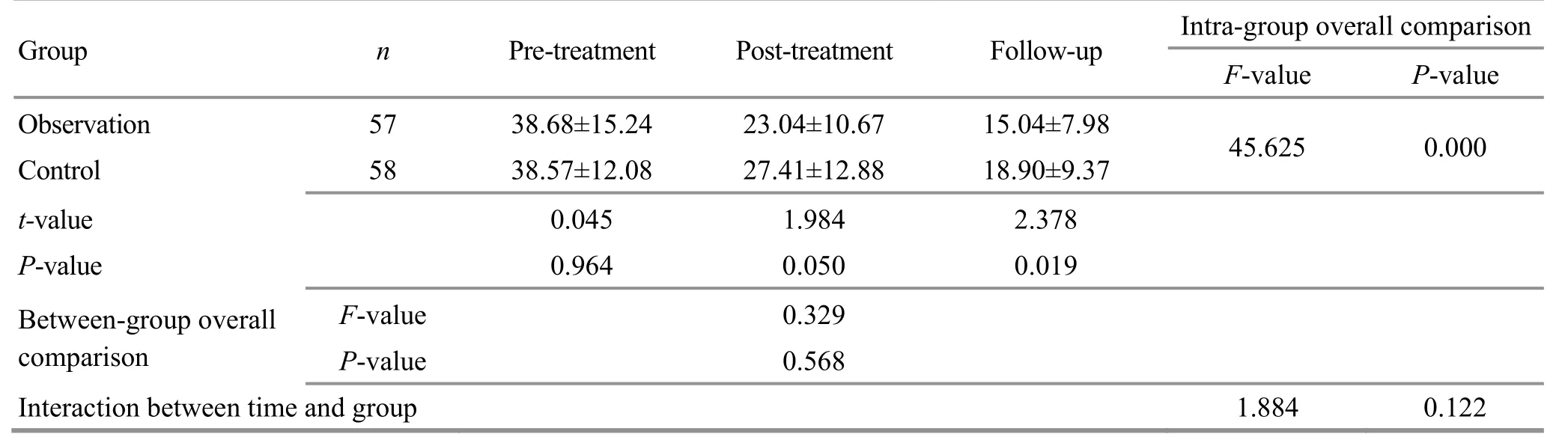
Table 3.Comparison of the ICARS score between the twogroups (±s, point)
Group n Pre-treatment Post-treatment Follow-up Intra-group overall comparison F-value P-value Observation 57 38.68±15.24 23.04±10.67 15.04±7.98 45.625 0.000 Control 58 38.57±12.08 27.41±12.88 18.90±9.37 t-value 0.045 1.984 2.378 P-value 0.964 0.050 0.019 Between-group overall comparison F-value 0.329 P-value 0.568 Interaction between time and group 1.884 0.122
3.4.3 Comparison of the BBS score
Before treatment,therewasno significant difference in the BBS score between the two groups (P>0.05); after treatment and at the follow-up,the between-group differences in the BBS scorewere statistically significant (bothP<0.01).The intra-group overall comparisons showed that the BBS score varied significantly (P<0.01);the between-group overall comparisons also demonstrated significant differences in the BBS score(P<0.05).The interaction effect between time and group factors was statistically significant (P<0.01).Please see Table 4 for details.
The results suggested that acupuncture plus rehabilitation exercises and sole use of acupuncture treatment both can markedly improve the lower-limb balance dysfunction in PSA patients;after treatment and at the follow-up,acupuncture plus rehabilitation exercises presented more significant advantage in improving the lower-limb balance dysfunction in PSA patients compared w ith acupuncture alone,and the between-group overall comparisons also revealed statistical significance; the time factor and treatment method factor produced significant interaction effect.
3.4.4 Comparison of the BI score
Before and after treatment, there were no significant differences in the BI score between the two groups(bothP>0.05);at the follow-up,the between-group difference in the BI score was statistically significant (P<0.05). The intra-group overall comparisons showed that the BI score varied significantly between different time points (P<0.01);the between-group overall comparisons revealed insignificant difference in the BI score (P>0.05). The interaction effect between time and group was statistically significant (P<0.05). Please see Table 5 for details.
The results suggested that acupuncture combined w ith rehabilitation exercises and acupuncture alone both can notably improve the ADL in PSA patients; at the follow-up, acupuncture plus rehabilitation exercises showed more significant advantage in ameliorating the ADL in PSA patients compared w ith acupuncture alone,but the overall comparison did not reveal statistical significance;the time factor and treatment method factor did not produce significant interaction effect.
3.4.5 Adverse reactions
There did not occur any severe adverse reactions in the two groups during treatment.
Table 4.Com parison of the BBS score between the two groups (±s, point)
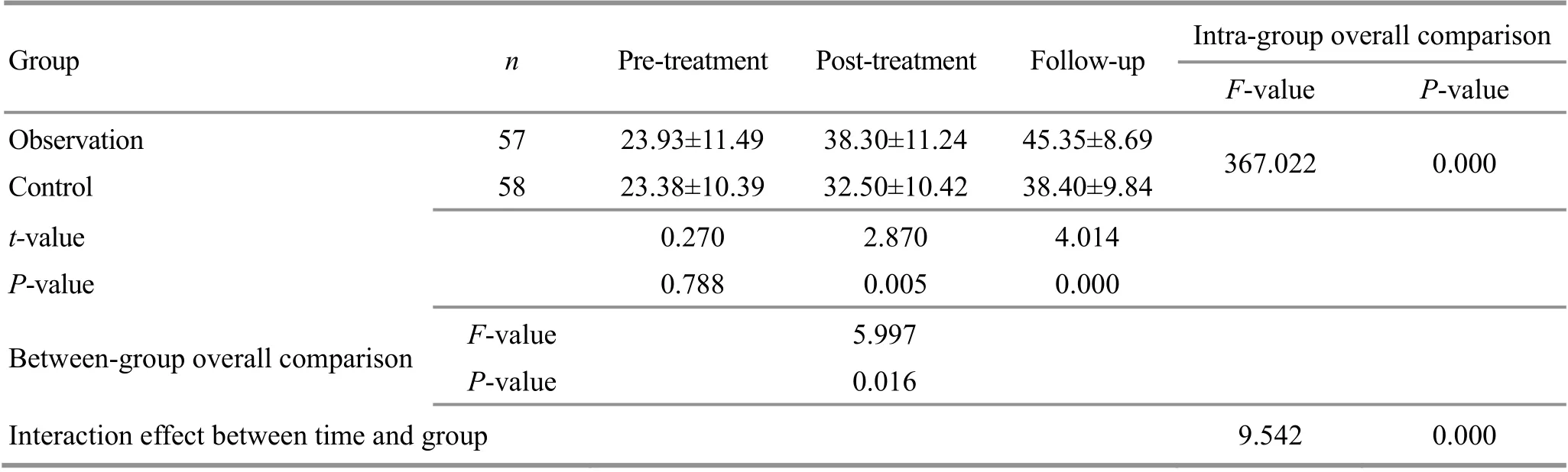
Table 4.Com parison of the BBS score between the two groups (±s, point)
Group n Pre-treatment Post-treatment Follow-up Intra-group overall comparison F-value P-value Observation 57 23.93±11.49 38.30±11.24 45.35±8.69 367.022 0.000 Control 58 23.38±10.39 32.50±10.42 38.40±9.84 t-value 0.270 2.870 4.014 P-value 0.788 0.005 0.000 Between-group overall comparison F-value 5.997 P-value 0.016 Interaction effect between time and group 9.542 0.000
Table 5. Comparison of the BI score between the two groups (±s, point)
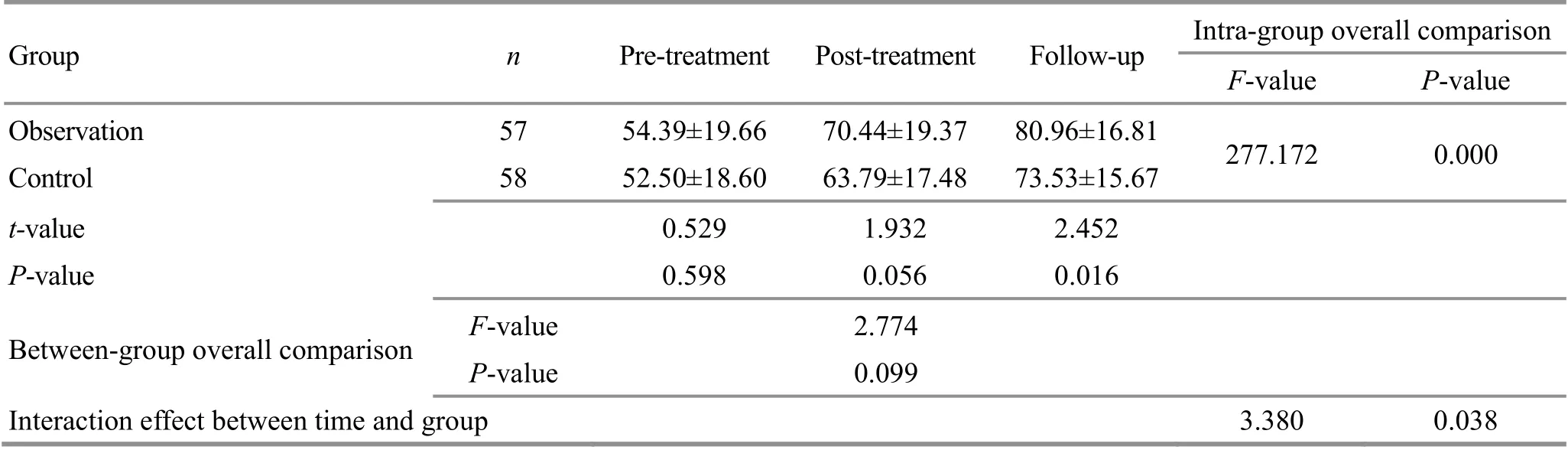
Table 5. Comparison of the BI score between the two groups (±s, point)
Group n Pre-treatment Post-treatment Follow-up Intra-group overall comparison F-value P-value Observation 57 54.39±19.66 70.44±19.37 80.96±16.81 277.172 0.000 Control 58 52.50±18.60 63.79±17.48 73.53±15.67 t-value 0.529 1.932 2.452 P-value 0.598 0.056 0.016 Between-group overall comparison F-value 2.774 P-value 0.099 Interaction effect between timeand group 3.380 0.038
4 Discussion
PSA belongs to the scope of Gu Yao(shaking-bone)in traditional Chinese medicine(TCM).It is one of the common complications of stroke,usually manifested as tremor and weakness of limbs and difficulty walking[1].Gu Yao describes exactly the unstable state of the body.Speaking of the pathogenesis,it is generally caused by stagnation of qiand blood,blocked orifices and loss of the control of brain.It is located in the brain and involves the liver,spleen and kidney[17].Modern medicine holds that,damages to cerebellum,brainstem,cerebrum,vestibular system and spinalcord allcan lead to ataxic symptoms,presenting as decreased balance of the body,and decreased muscle tone of the distant muscles,etc.Cerebellum plays amore important role in the coordination of voluntary movements[15,18]. Injury to cerebellum after strokew illcause a series of lower-limb ataxic symptoms,including unsteady standing and gait,enlarged foot gap while standing or walking,upper limbs reaching forward as if going to fall, and difficulty standing on two legs or on one leg.The cerebrum,brainstem and cerebellum connect each other via numerous afferent and efferent nerve fibers;the cerebellum and brainstem share the same blood supply which belongs to the vertebrobasilar artery system[18].Therefore, a stroke affecting the cerebellum, brainstem and cerebrum often leads to ataxia.
This study adopted m ind-refreshing and balance- restoring acupuncture method plus Fenkel exercises to treat post-stroke ataxia.The m ind-refreshing and balance-restoring acupuncture method is modified based on the brain-refreshing and orifice-opening acupuncture method established by academ ician Shi Xue-m in. By selecting Shuigou (GV 26), Yintang (GV 29),Shangxing(GV 23),Baihui(GV 20),Fengfu(GV 16),bilateral Neiguan(PC 6),Sanyinjiao(SP 6),Fengchi(GB 20), Wangu (GB 12), Tianzhu (BL 10) and cervical Jiaji(EX-B 2),together with standard acupuncture manipulations,this study was to treat PSA through awakening the m ind and opening the orifices,unblocking the Governor Vessel and supplementing the essence.Neiguan(PC 6),Shuigou(GV 26),Yintang (GV 29),Shangxing (GV 23),Baihui(GV 20)and Sanyinjiao (SP 6) made a group of acupoints to benefit the brain and regulate the m ind, since awakening and regulating the m ind should be the essential prem ise in treating PSA. Fengfu (GV 16), Fengchi (GB 20), Wangu(GB 12) and Tianzhu (BL 10) are located in the occipital region. They can not only directly treat the root cause topically,but also unblock orifices and the Governor Vessel and supplement the essence via tracking along the meridians. Cervical Jiaji(EX-B 2)points are extra points, located in the nape on both sides of the cervical spine, parallel to the Governor Vessel and the Bladder Meridian of Foot Taiyang. Via unblocking and regulating qi and blood in the Governor Vessel and Bladder Meridian, cervical Jiaji (EX-B 2) can guide qi and blood to go up and nourish the brain and supplement the essence, treating both the root and superficial causes.The above acupoints can work together to improve the vertebrobasilar blood supply,so as to promote the recovery of the function of cerebellum and brainstem[19].
Frenkel exercises aim to train the central nervous system to relearn its functions.It makes use of and strengthens the compensatory feedback of the remaining disabled sensory systems such as vision,touch and hearing, to gradually build up a new motor pattern and restore the physical functions and daily living[20]. Frenkel exercises train people in supine, sitting and standing positions,aim ing to improve the coordination and balance of the limbs as well as the coordination between vision and body movements.Through repeated posture and movement trainings, it can strengthen the proprioception and ameliorate the balance function and state,to finally realize the synchronization of the eyes,upper and lower limbs.Besides,it helps patients to regain the central and vertical senses and maintain the range of motion of joints,and muscle force and endurance,in order to achieve higher accuracy, safety and efficiency in daily activities[11].
Modern rehabilitation theory holds that central nervous system still remains certain plasticity after a stroke,but exogenousmedications alone are far not enough.The combination of acupuncture and rehabilitation exercises offers both positive physical stimulation and balance function training,improving the centralm icroenvironment and feedback nervous system to let the advanced nervous system to relearn the motor control ability and regain the normal motor pattern. The results of the scales showed that the PSA patients in the two groups all showed significant improvements in walking posture and gait,balance state and ADL after treatment; the integrated method showed certain synergistic effect comparing the clinical efficacy and the improvement of balance function, as it acted faster in improving the lower-limb ataxic symptoms and tackling daily living difficulties,enhancing the coordination and recovering abilities of the limbs and torso, exerting satisfactory boosting and supportive effects. Therefore, this method is worthy of further application in treatment of post-stroke circulatory disturbance.

Conflict of Interest Theauthorsdeclare that there isno conflict of interest.Acknow ledgments Thiswork was supported by Special Research Project for National Clinical Research of Traditional Chinese Medicine,National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (国家中医药管理局国家中医临床研究基地业务建设科研专项, No.JDZX2012135).Statement of Informed Consent Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants.
Received:20 December 2019/Accepted:22 January 2020
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Clinical observation on electroacupuncture plus Yi Jin Jing (Sinew-transform ing Qigong Exercises) for knee osteoarthritis
- Clinical efficacy comparison of moxibustion w ith different doses for knee osteoarthritis
- Clinical observation of acupuncture and traction plus Ba Duan Jin (Eight-brocade Exercise) for improving discogenic low back pain
- Clinical observation on acupoint injection for back pain in patients w ith primary osteoporosis
- Clinical observation on Yi Jin Jing(Sinew-transform ing Qigong Exercises) plus tuina on the neck for stiff neck
- Efficacy evaluation of acupuncture plus rehabilitation training for post-stroke deglutition disorders of qi-deficiency blood stasis pattern
