应用于矿井巷道的无线传感网络路由协议
2020-10-13郑欢欢白鱼秀张雅琼
郑欢欢 白鱼秀 张雅琼

摘 要: 构建基于无线传感器网络的煤矿智能监控系统能有效推进煤矿的智慧化建设,而矿井巷道无线传感器网络拓扑呈长距离带状,容易造成能耗不均、形成热区的问题。提出改进LEACH协议形成适用于矿井巷道环境下的网络路由协议:通过优化簇头阈值选取和非均匀竞争半径的簇头筛选机制控制簇头数目和位置,优化簇的划分;在簇头与sink节点进行路由选择时,将剩余能量作为节点间权值计算的重要参数,从而减少能量较小节点转发过路数据的概率,更好的均衡网络节能能耗。实验仿真结果表明,改进协议在存活节点个数和消耗总能量方面的性能优于LEACH和LEACH-C协议,有效均衡了网络能量消耗,延长了网络生命周期。
关键词: 无线传感器网络; 非均匀分簇; 多跳路由
中图分类号: TP393 文献标志码: A
Abstract: The intelligent monitoring system of coal mine based on wireless sensor network can effectively promote the intelligent construction of coal mine. The wireless sensor network topology of mine roadway is long-distance belt, it is easy to cause the problem of uneven energy consumption and hot area. In this paper, an improved LEACH protocol is proposed to form a network routing protocol to be suitable for mine tunnel environment. The number and location of cluster heads are controlled by optimizing the threshold selection of cluster heads and the screening mechanism of non-uniform competition radius, and the division of clusters is optimized. When routing between cluster heads and sink nodes is selected, the remaining energy is taken as an important parameter for the calculation of weights between nodes, so as to reduce the small amount of energy. The probability of transmitting the passing data by point can better balance the energy consumption of the network. The simulation results show that the performance of the improved protocol is better than that of LEACH and LEACH-C in terms of the number of surviving nodes and the total energy consumption.
Key words: wireless sensor network; uneven cluster; multi-hop routing
0 引言
無线传感器网络是由大量传感器节点组成的具有有限信息感知、信息处理和信息传递的自组织网络。由于传感器节点体积小、成本低、计算能力强等优点,无线传感器网络广泛应用于环境监视,医疗监测,军事侦察、智慧矿山等领域。但是其传感器节点依靠不能补充的电池作为能量来源,能耗的不均衡就会导致节点能量过快耗尽,影响网络有效生存时间和网络整体性能。为了解决能量均衡消耗问题,通过自适应分簇的LEACH协议[1]应运而生。此后,很多学者在此基础上进行了更多的改进和优化。这些算法的基本思想主要是三大类:一类是通过加入不同的控制因子来改进簇头的阈值计算[2-3],综合多方面的因素完成簇头的选择;第二类是改变数据传输的通信路径[4],第三类是通过不同的分簇方式达到均衡能耗的目的[5-6]。但是上述路由算法多适用于大面积监测区域,不适合应用于矿井的长距离带状区域[7]。为了解决这一特殊环境中容易造成的“热区”问题以及汇聚节点的特殊位置,本文在LEACH协议簇头的阈值选择中综合考虑节点剩余能量、到汇聚节点的距离和节点周围的其他节点数目因素,采用非均匀分簇和簇间的多跳转发策略,较好的均衡了无线传感器网络节点的能量,延长了网络的生存周期。
1 LEACH协议概述
1.1 LEACH协议简介
LEACH协议是一种经典的自适应分簇路由协议,可以在网络中动态地根据阈值规则选择簇头节点,使每个节点具有一样的被选概率,尽可能的平均能量消耗,延长网络生存时间。
3 实验仿真及分析
3.1 实验环境
实验使用Matlab对本文改进的协议进行仿真,并和LEACH,LEACH-C协议进行对比。实验参数设置如表1所示。
3.2 实验结果分析
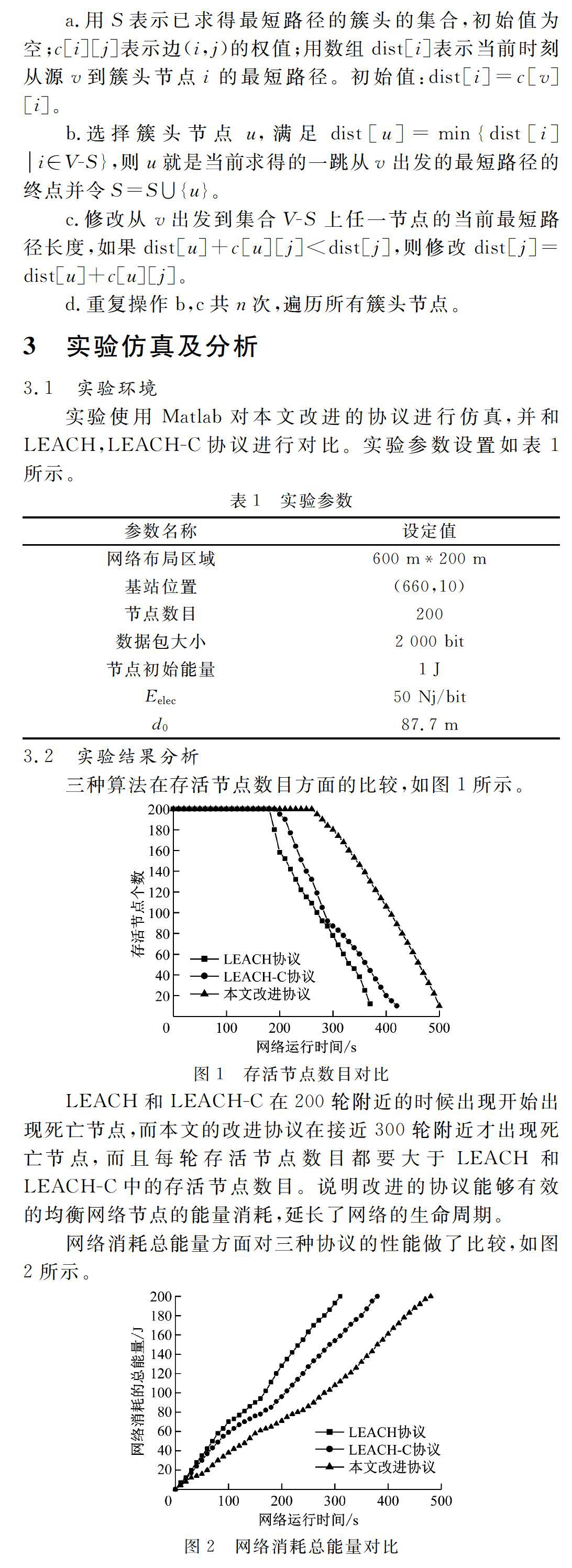
三种算法在存活节点数目方面的比较,如图1所示。
LEACH和LEACH-C在200轮附近的时候出现开始出现死亡节点,而本文的改进协议在接近300轮附近才出现死亡节点,而且每轮存活节点数目都要大于LEACH和LEACH-C中的存活节点数目。说明改进的协议能够有效的均衡网络节点的能量消耗,延长了网络的生命周期。
