A meta-analysis of the safety of clopidogrel and tegrarol in patients with non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome after PCI in China
2020-09-18XiaoMinGaoBinHuDuXiaLiuYaXuQinZhao
Xiao-Min Gao, Bin Hu, Du-Xia Liu, Ya Xu, Qin Zhao✉
1. Tibetan medicine screening laboratory, xizang university for nationalities, xianyang,shaanxi 712082, China; Basic research laboratory of life sciences, medical science department, Tibet minzu university 2. Nanchang University 330027
Keywords:Acute coronary syndrome NSTE-ACS Ticagrelor Clopidogrel Meta analysis
ABSTRACT Objective: Meta-analysis was performed to evaluate the safety of clopidogrel and tigrel in the treatment of non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome after intervention. Methods: by searching the databases of cnki, wanfang database, weipu network, bailian and so on, relevant literatures on oral clopidogrel sulfate and tigrel after interventional treatment of non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome were collected. Search the required literature according to the inclusion criteria and exclusion criteria. Risk assessment of the included literature was performed on the basis of Cochrane reviews or the Newcastle scale (NOS). Fixed two researchers randomly and the control group, experimental group into literature alone assessed, Use software Review Manager 5.3 analyze aspirin and clopidogrel, aspirin and ticagrelor drug for the safety of the drug after therapy intervention Meta analysis, merge effect value odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval, inspection heterogeneity and publication bias. Results: a total of 16 articles met the criteria, and 3007 patients were included in the meta-analysis. Compared with the clopidogrel sulfate group, the tigrilol group significantly reduced the incidence of major cardiovascular adverse events after interventional therapy for non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome(MACE) OR=0.37,95%Cl=(0.28 0.49)(P<0.00001)、Angina symptoms OR=0.46, 95%Cl= (0.26 0.81) (P=0.008)、Non-fatal heart infarction OR=0.38, 95%cl = (0.26 0.81) (P=0.001)、heart failure OR=0.41, 95%cl = (0.18 0.96) (P=0.04)、cardiac death OR=0.31, 95%cl = (0.15 0.64) (P=0.002)、target vessel revascularization OR=0.46, 95%cl = (0.21 0.99) (P=0.05),However, increased respiratory distress OR=4.44, 95%cl = (2.08 9.45) (P<0.0001)、bleeding events OR=2.06, 95%cl = (1.30 3.27) (P=0.002)、arrhythmia OR=1.14, 95%cl = (0.85 1.54) (P=0.39). Conclusion: In the treatment of non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome after interventional surgery, compared with clopidogrel, Tigliero can reduce the incidence of major cardiovascular adverse events, angina symptoms, non-fatal cardiac infarction, heart failure, cardiogenic death, and target vessel revascularization, However, the incidence of dyspnea, bleeding events and arrhythmias increased.
1. Introduction
Non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome (nste-acs) is an acute and severe coronary artery disease, which is mainly caused by acute myocardial ischemia. Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is an important treatment that can relieve the clinical symptoms and improve the prognosis of most patients [1]. But after the patient underwent the interventional surgery, There is still the possibility of recurrent myocardial infarction, sudden cardiac death, bleeding or thrombosis.Antiplatelet aggregation drugs are first-line drugs for the treatment of coronary heart disease, and the postoperative drug safety of combining clopidogrel or ticagrelor on the basis of aspirin is particularly important.ticagrelor ACTS on P2Y12 ADP receptor, inhibits adenosine diphosphate (ADP) mediated platelet activation and aggregation, and plays an antiplatelet effect [2].Clopidogrel can selectively inhibit the combination of ADP and platelet receptor, inhibiting activation of ADP and glycoprotein GP Ⅱ b/Ⅲ a complex, thus inhibiting platelet aggregation. In this paper, meta analysis was performed to evaluate the safety of clopidogrel sulfate and ticagrelor was used after interventional surgery for non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome, so as to provide more evidence for clinicians to use drugs after interventional therapy for non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome.
2. Materials and methods
2.1 Literature inclusion criteria
Patients with non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome treated by interventional therapy independent of age, gender and operation time were the study subjects. and the diagnostic criteria for coronary heart disease, acute coronary syndrome and non-STsegment elevation were referred.
patients on the basis of oral aspirin, the experimental group combined with oral tigravil and the control group combined with oral clopidogrel, the dose is not limited
Case control principle should be complied with;4.safety indicators: (1)major adverse cardiac events MACE;(2) symptoms of angina;(3) non-fatal myocardial infarction;(4) bleeding events;(5) heart failure;(6)Cardiac death;(7) target vessel for blood revascularization;(8)Difficulty breathing today;(9) arrhythmia.
Exclusion criteria :(1) overview, conference documents, expert comments, lectures, case reports, etc.(2) there is no relevant literature in the control group or the control group does not meet the requirements;(3) literature with incomplete or unavailable experimental data;(4) repetitive literature.
2.2 Literature retrieval strategy
Computer retrieval of China national knowledge network, wanfang database, weipu network, hundred chain and other databases.The Chinese search terms were "ticagrelor", "clopidogrel", "non-ST segment", "acute coronary syndrome", "intervention or PCI".
2.3 Literature selection and data extraction
The two evaluators will select the literature according to the inclusion criteria and the exclusion criteria respectively, and check each other. If there is any objection, the literature will be discussed or decided by a third party.Literature was extracted including the first author, year of publication, number of cases in the experimental group and control group, gender, age, intervention measures, outcome indicators, and follow-up time.
2.4 Quality evaluation of included literature
Cochrane was used to evaluate the included RCT literature.1. Sequence generation: using random number table, computer random, envelope, lottery, etc.2. Distribution hiding: centralized distribution, drug containers with the same appearance, serial Numbers, opaque envelopes, etc.3. Blind method: blind method is adopted;4. Incomplete outcome data: no outcome data was lost, and intentional analysis was adopted;5. Alternative outcome report: no alternative outcome report;6. No other source of bias. The retrospective literature used the Newcastle scale (NOS) to assess the risk of bias, including selection, comparability and outcome. The stars of NOS ranged from 0 to 9 stars and 5 stars of > could be included in the meta-analysis, among which Ye M, Zhang yunmei and zhang guixia were rated as 7, 6 and 6 stars.The quality of the included RCT literature was evaluated according to the above criteria: those meeting all the above criteria were "grade A", those meeting some of the above criteria were "grade B", and those meeting almost all of the above criteria were "grade C".
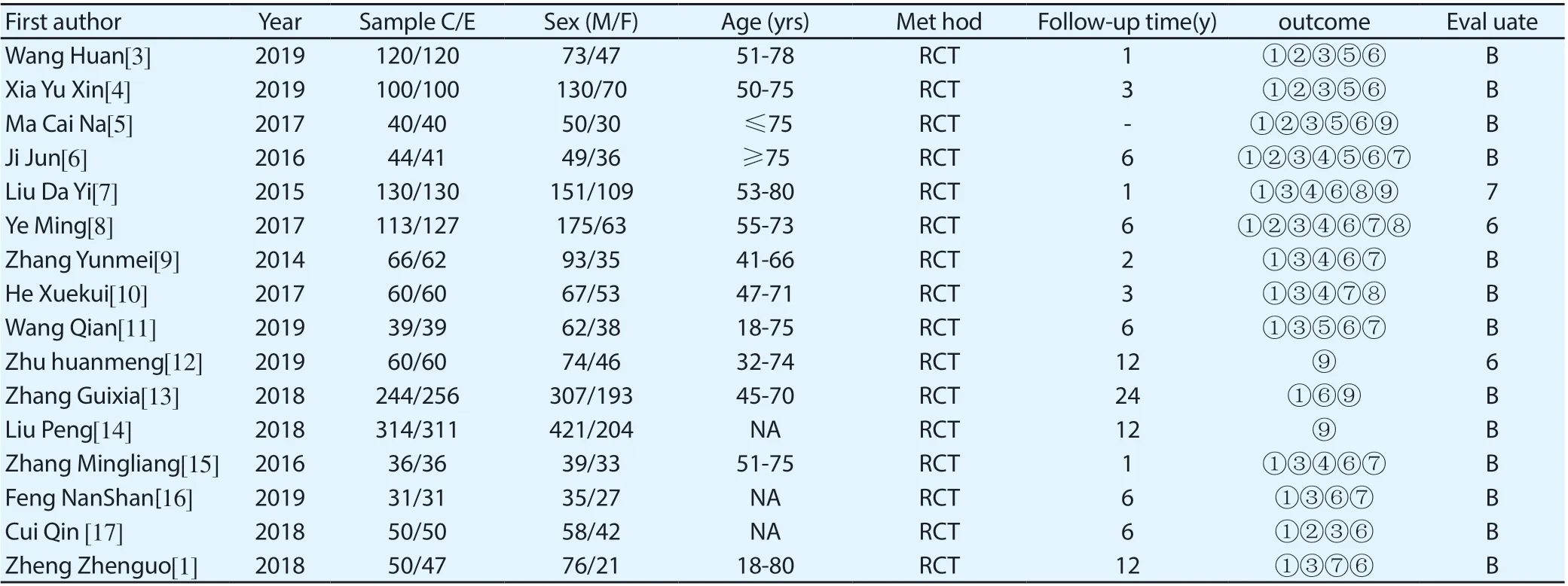
Table 2. Included literature and quality
2.5 Statistical methods and result analysis
Review Manager 5.3 software was used to describe the results, and the final results were combined odds ratio (OR) and 95%confidence interval (95%confidence interval, 95%CI).Heterogeneity was observed by 2 test: if P>0.10,I2<50%, indicating no statistical heterogeneity, the fixed effect model should be adopted, otherwise, the random effect model should be applied.The funnel plot was used to observe whether there was publication bias. When the corresponding points of each study were symmetrical in the midline, it was considered that there was no publication bias.
3. Results
3.1 Literature retrieval results and literature quality assessment
A total of 183 relevant literatures were retrieved. After excluding non-conforming literatures according to the literature inclusion criteria, 16 literatures were finally included for Meta analysis, including 3007 subjects.The literature selection process is shown in figure 1.The included literature and literature quality evaluation are shown in table 2.

Figure 1. Literature selection process
MACE heterogeneity analysis was conducted on 14 included articles [3-11, 13, 15-18],X2=3.97, the degrees of freedom are 13, P=0.99>0.1, I =0%, and fixed effect model analysis was used.Meta-analysis results showed that OR=0.37,95%Cl= (0.28 0.49) (P<0.00001), and ticagrelor group significantly reduced the occurrence of major cardiovascular adverse events compared with the clopidogrel group, showing a statistical difference.See figure 2 for details.
Heterogeneity analysis of 7 included articles [3-6, 8, 17] for symptoms of angina pectoris,X 2=0.93, the degrees of freedom are 6,P=0.99>0.05, I =0%, using fixed effect model analysis.Meta-analysis results showed that OR=0.46, 95%Cl= (0.26 0.81) (P=0.008), and ticagrelor group significantly reduced the incidence of angina symptoms compared with the clopidogrel group, showing a statistical difference.See figure 3 for details.
Heterogeneity analysis of 13 included articles [3-11, 15-18] was conducted for non-fatal myocardial infarction events, X2=2.01, the degrees of freedom are 13, P=1>0.05, I =0%, and fixed effect model was used for analysis.Meta-analysis results showed that OR=0.38, 95%Cl= (0.26 0.81) (P=0.001), and ticagrelor group significantly reduced the occurrence of non-fatal mi compared with clopidogrel group, showing a statistical difference.See figure 4 for details.
Heterogeneity analysis was carried out for 5 included articles of heart failure [3-6, 11], X2=0.15, the degrees of freedom are 4,P=1>0.05, I =0%, and fixed effect model analysis was used.Metaanalysis results showed that OR=0.41, 95%Cl= (0.18 0.96) (P=0.04), and ticagrelor group significantly reduced the occurrence of nonfatal mi compared with clopidogrel group, showing a statistical difference.See figure 5 for details.
Heterogeneity analysis of 13 included articles [3-9, 11, 15-18] was conducted for cardiogenic death, X2=2.15, the degrees of freedom are 12, P=1>0.05, I=0%, and fixed effect model was used for analysis. The results of meta-analysis showed that OR=0.31, 95%Cl= (0.15 0.64) (P=0.002), and ticagrelor group significantly reduced the incidence of cardiogenic death compared with clopidogrel group, showing a statistical difference. See figure 6 for details.
Target vessel revascularization heterogeneity analysis was conducted for 8 included articles [6, 8-11, 11, 15-18], X2=1.40 the degrees of freedom are 7, P=0.99>0.05, I=0%, and fixed effect model analysis was used. The results of meta-analysis showed that OR=0.46, 95%Cl= (0.21 0.99) (P=0.05), and ticagrelor group could reduce the incidence of revascularization in target vessels compared with clopidogrel group, with no statistical difference. See figure 7 for details.
Three articles [7, 8, 10] were included for heterogeneity analysis, X2=4.26, the degrees of freedom are 2, P=0.12>0.05, I =53%, and fixed effect model was used for analysis. The results of metaanalysis showed that OR=4.44, 95% Cl= (2.08 9.45) (P<0.0001). Compared with the clopidogrel group, the increase trend of dyspnea in the ticagrelor group was statistically significant. See figure 8 for details.
Six articles [6-10, 15] were included for heterogeneity analysis, X2=0.53, the degrees of freedom are 5, P=0.99>0.05, I =0%, and fixed effect model was used for analysis. The results of meta-analysis showed that OR=2.06, 95% Cl= (1.30 3.27) (P<0.002). Compared with the clopidogrel group, the increase trend of dyspnoea in the ticagrelor group was statistically different. See figure 9 for details.
A total of 5 articles [5, 7, 12-14] were included for heterogeneity analysis, X2=5.97, the degrees of freedom are 4,P=0.20>0.05, I =33%, and fixed effect model was used for analysis. The results of meta-analysis showed that OR=1.14, 95% Cl= (0.85 1.54) (P=0.39), and there was no statistical difference in the increase trend of dyspnea in the ticagrelor group compared with the clopidogrel group. See figure 10 for details.
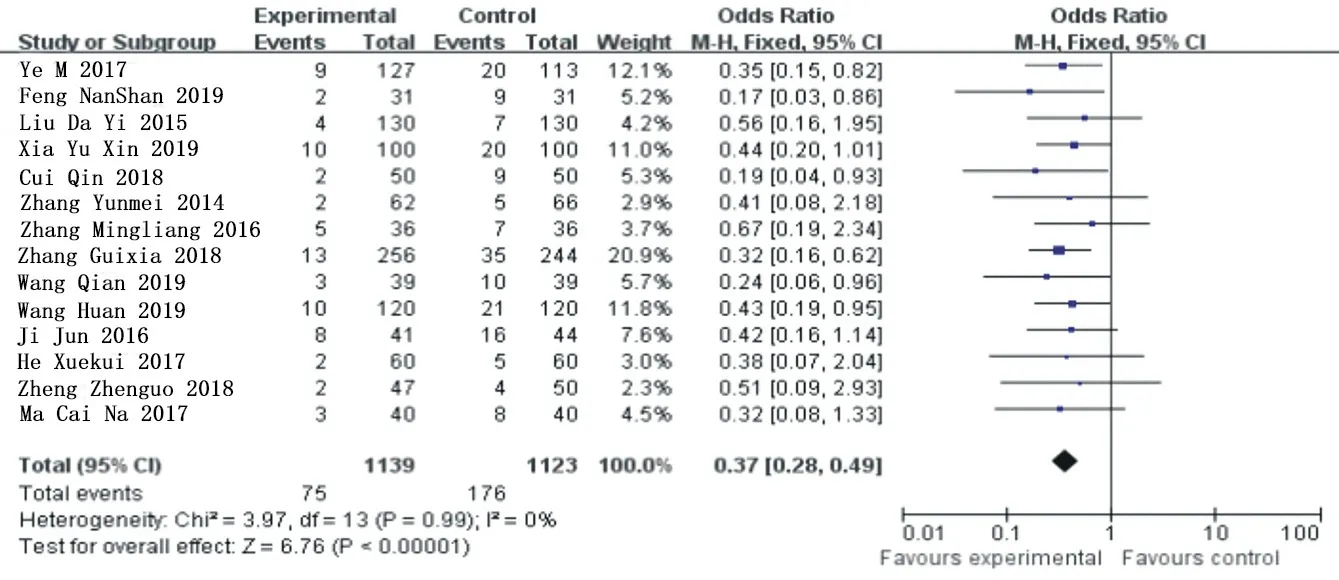
Figure 2.MACE subgroup analysis merges
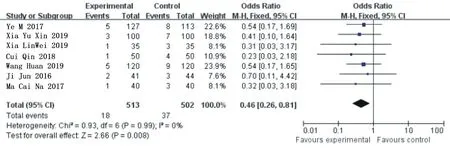
Figure 3.Combined subgroup analysis of angina symptoms
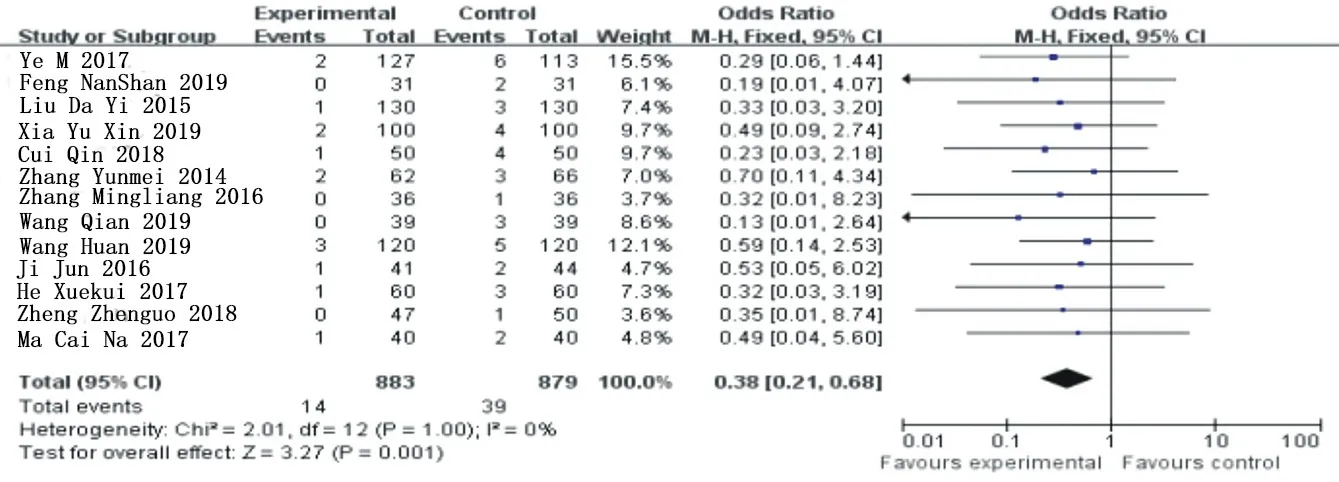
Figure 4. Combined subgroup analysis of nonfatal myocardial infarction

Figure 5. Combined subgroup analysis of heart failure
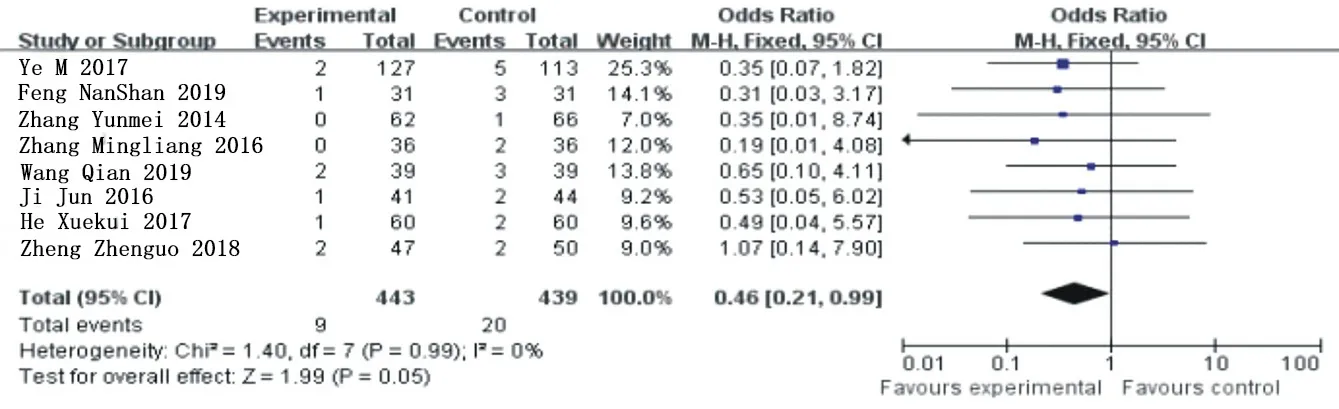
Figure 6. Subgroup analysis and combination of cardiogenic death
Figure 7. Combined subgroup analysis of target vessel revascularization

Figure 8. Combined subgroup analysis of dyspnea
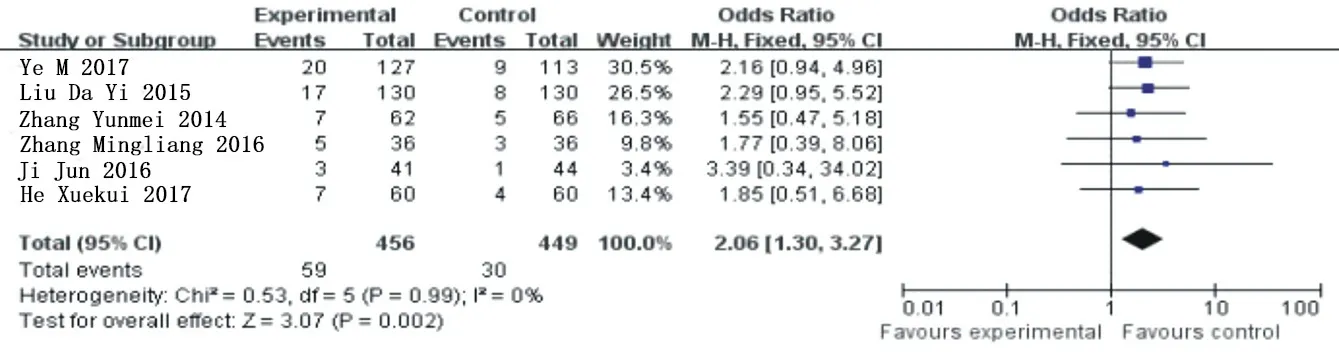
Figure 9.Combined subgroup analysis of bleeding events
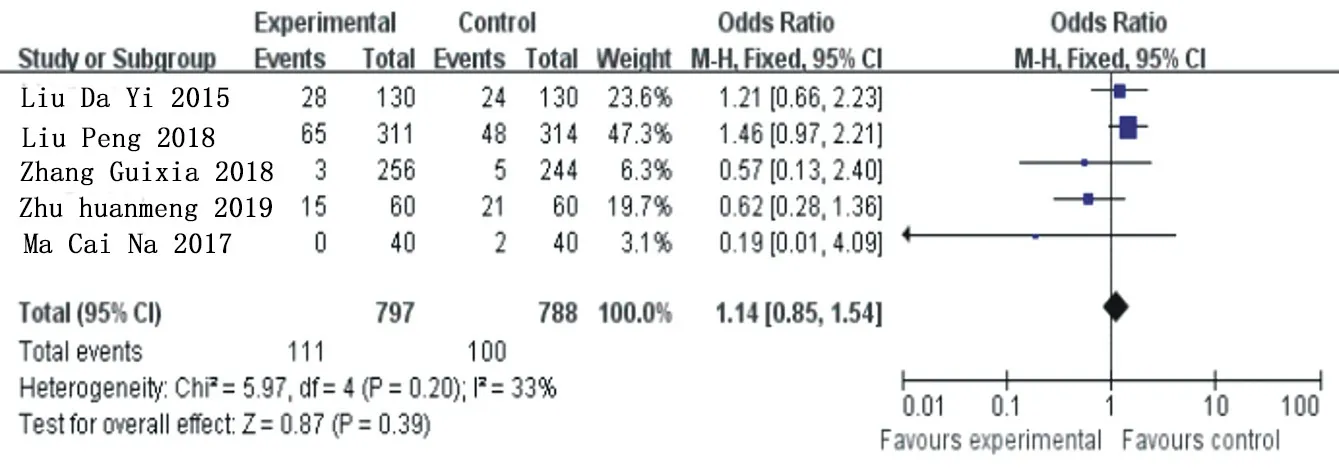
Figure 10. Subcombination and analysis of arrhythmia
3.3 Publication bias analysis
The funnel plot was drawn on the representatives of MACE and target blood vessel reconstruction, and the results showed that the study scatter points were basically located in the scope of the funnel plot, and the scatter points in the two graphs were basically symmetrical, suggesting that the publication bias of this metaanalysis was less likely. As shown in figure 11,12.
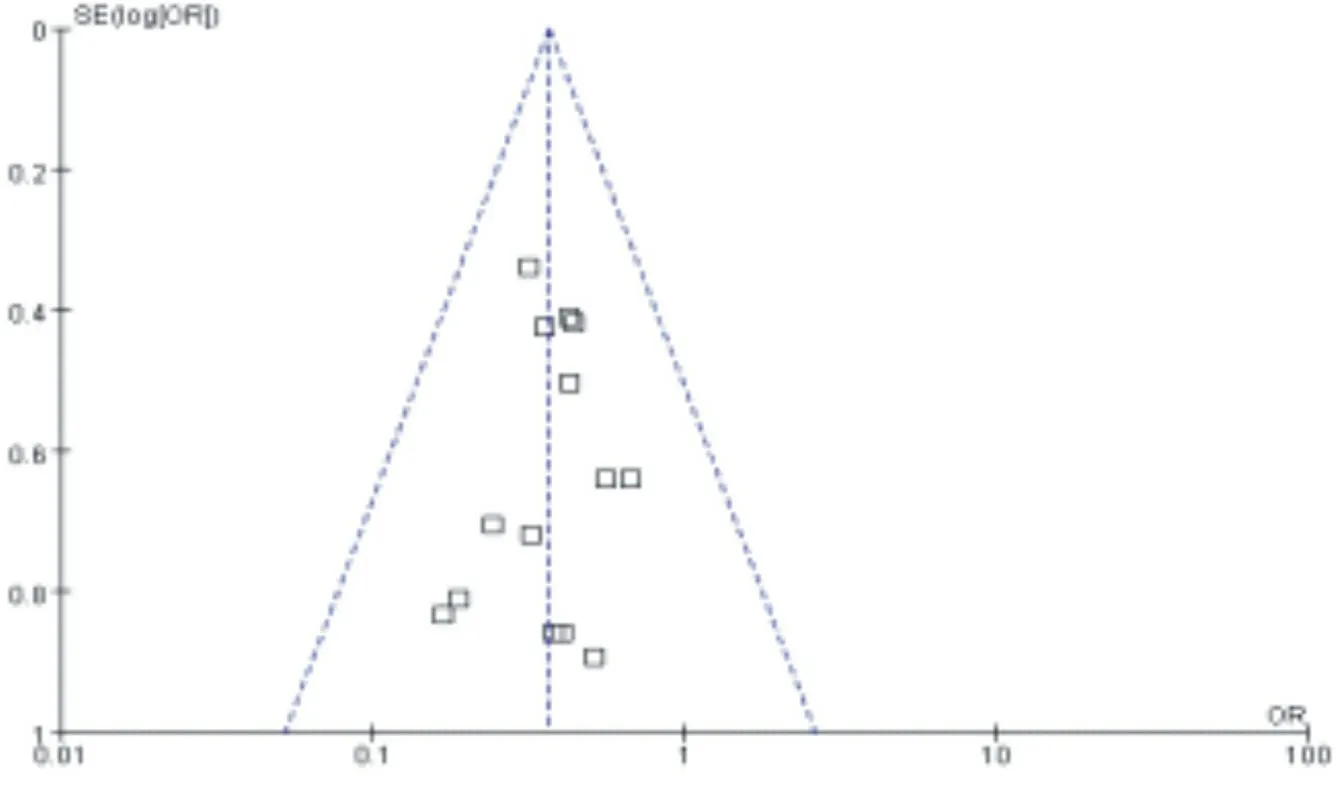
Figure 11. Inverted funnel plot of the incidence of MACE
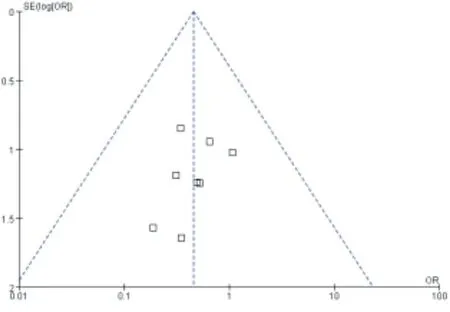
Figure 12. Inverted funnel plot of the incidence of target vessel revascularization
4. Discussion
4.1 safety Acute coronary syndrome (acutecoronary syndromes, ACS)
mainly unstable atherosclerotic plaques in the coronary artery rupture or coagulating material release in great quantities, cause the platelet aggregation and thrombosis in blood vessel complete or incomplete occlusion, blood vessels in patients with coronary artery lesions appear different degree of occlusion and cause myocardial ischemia, is the increasing incidence of cardiology, a critical case, [18] patients with complications and case fatality rate is high.. Non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome (nst-acs) has a high incidence in patients with acute coronary syndrome [19]. The literature indicates that in patients with non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome, whether or not there is hemodynamic instability, electrical storm or severe ischemia, The short-term or long-term benefits of stenting after coronary angiography reveal occlusion are positive.Therefore, interventional therapy is recommended for non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome patients without contraindications [20]. Antiplatelet agents are considered to be important drugs to reduce the complications and mortality of patients after cardiac intervention. By meta analysis results can be concluded that compared with clopidogrel drug group, on behalf of Greg los drug group can obviously reduce the major adverse cardiovascular events, angina symptoms, incident nonfatal heart infarction, heart failure, cardiac death, target vessels reascularization probability, in addition to the target vessel reascularization the rest have statistical significance. The incidence of dyspnea was increasing, which was statistically significant. At present, the mechanism of ticagrelor causing dyspnea is still unclear, which may be related to the following : (1) by blocking ENT1 on the cell membrane, ticagrelor increases the mass concentration of adenosine in the blood, and then stimulates the C fibers of the vagus nerve in the lung, causing difficulty in breathing. (2) ticagrelor group can inhibit the P2Y12 receptor in neurons and the tralilike response induced by ticagrelor. (3) cytosine arabinoid effect: ticagrelor is an adenosine triphosphate analogue, so it can stimulate the cytosine arabinoid bronchus, resulting in adverse respiratory stress, bronchial constriction and dyspnea [21]. A large number of literatures mentioned that the symptoms of dyspnea in patients were relieved after prolonged treatment or symptomatic treatment such as antihistamine and spasmolysis. However, there were no cases of severe dyspnea or even death due to dyspnea. Compared with the clopidogrel group, the incidence of bleeding in the ticagrelor group increased. The bleeding mainly included gastrointestinal bleeding, gingival bleeding, nasal cavity bleeding, etc., but all of them were non-fatal and were relieved after treatment. However, deaths from massive bleeding have been reported in the clopidogrel group. The incidence of arrhythmia has an increasing trend, and there is no statistical difference. Arrhythmia in patients with bradyarrhythmia mainly bradyarrhythmia, may be associated with cardiac muscle Abnormal conduction function after injury. In summary, compared with the clopidogrel group, the ticagrelor group had higher safety in major adverse cardiovascular events, angina symptoms, and nonfatal myocardial infarction after medication. Although not as safe as clopidogrel in arrhythmia, hemorrhage and dyspnea, there were no fatal cases.
4.2 Limitations of system evaluation
Meta-analysis showed that the ticagrelor group was safer than the clopidogrel group. Due to the small number of cases of non-stsegment elevation acute coronary syndrome collected and treated with interventional therapy, the results of meta-analysis have certain limitations, which cannot replace large-scale randomized controlled trials and cannot represent the actual clinical effect. Therefore, with the increase of patient data, its safety and the number of patients included in the safety should be constantly updated.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Mechanism of Shenfu Decoction in the treatment of critically ill patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) based on network pharmacology
- Investigation and analysis of 14 034 college students on COVID-19 and its countermeasures and suggestions
- Effect of Tetrahydroberberine on improving vascular endothelial cell injury
- The relationship between polymorphisms of P-selectin genes and plasma P-selectin concentration with thrombosis in non-valvular atrial fibrillation of Kazakh ethnicity
- Super-minimal incision kidney transplantation: Report of 6 cases
- Relationship between nap and hypertension in adults: An updated meta-analysis
