Introduction Performance of Aornia melanocarpa in 4 Districts of Tianjin
2020-08-01ChenxiWANGJingyuanXIEYiPEIWenXUJiangliNIEYaSU
Chenxi WANG, Jingyuan XIE, Yi PEI*, Wen XU, Jiangli NIE, Ya SU
1. College of Horticulture and Landscape, Tianjin Agricultural University, Tianjin 300384, China; 2. College of Humanities and Social Sciences, Tianjin 300384, China
Abstract [Objectives] To enrich the species resources of Tianjin, Aornia melanocarpa was introduced and cultivated in 4 districts of Tianjin. [Methods] Two consecutive years of observation in 2018-2019 and research on the phenological period, high yield and fruit economic traits in 4 districts of Tianjin were carried out. [Results] The A. melanocarpa of the Linhai Jiayuan Experimental Site in Jinghai District has larger single fruit weight, higher nutrient composition, stronger plant growth, higher yield and storage stability, so this site can be used as a main planting base for large-scale planting of A. melanocarpa; the experimental site of Tianjin Agricultural University East Campus and the experimental site of Cuiping Lake Science Park of Jizhou District have a sour and astringent taste but relatively low yield, need to be processed as by-products in combination with market prices to determine whether to plant; the experimental site of Tianjin Agricultural University West Campus has low yield, small fruit and poor taste, and the planting effect is the worst among the four experimental sites. [Conclusions] From the overall economic traits of fruits, the fruits produced in the experimental site of Jinghai District have sufficient weight, high solid-acid ratio, and relatively high nutrient content, thus this experimental site can be used as large-scale cultivation base for A. melanocarpa.
Key words Aornia melanocarpa, Tianjin, Introduction
1 Introduction
Aorniamelanocarpais a deciduous shrub of theSorbusgenusin Rosaceae family. It is a precious tree species that integrates ecology, garden ornamentation, and medicinal health[1]. It was introduced by Liaoning Institute of Agriculture & Forestry in Arid Areas from the United States in the 1990s. With more than 20 years of trial planting, the growth results have performed well[2], and it is currently in the stage of promotion and development. The tree height can reach about 2 m, the leaves are single leaves alternate, flowers are white, the fruit is berry type, and it is dark purple after maturity[3], the fruit is slightly sweet and sour. Its fruit juice contains high concentration of anthocyanins, polyphenols and other nutrients, and has various effects such as anti-oxidation, anti-tumor and hypoglycemic effects[4]. As one of the four municipalities directly under the central government of China, Tianjin is also the largest open city and industrial and commercial city in northern China. Its economy is very developed, andA.melanocarpahas strong adaptability, early fruiting, high yield and high economic value[5], thus it is bound to have a very broad market prospect in Tianjin. In this experiment, we introducedA.melanocarpainto 4 districts of Tianjin for cultivation management, and measured its phenological period, growth amount and fruit quality, in order to provide a basic and theoretical guidance for the promotion and further development ofA.melanocarpain Tianjin.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Experimental materialsThe experimental material was 1-year-oldA.melanocarpaseedlings collected from Harbin of Heilongjiang Province, and were planted in four experimental bases in Tianjin in December 2017: the experimental site of Tianjin Agricultural University East Campus (hereinafter referred to as Xiqing 1 Experimental Site), Tianjin Agricultural University West Campus (hereinafter referred to as Xiqing 2 Experimental Site), Linhai Jiayuan Experimental Site in Jinghai District (hereinafter referred to as Jinghai District Experimental Site), and the experimental site of Cuiping Lake Science Park of Jizhou District (hereinafter referred to as Jizhou District Experimental Site).
2.2 General situation of experimental site
2.2.1Xiqing 1 Experimental Site. This experimental site is located in the east campus of Tianjin Agricultural University (39°05′ N, 117°06′ E), with an altitude of 4 m, a frost-free period of 210 d, sunshine hour of 2 699 h, extreme minimum temperature of -11.8 ℃ and average annual temperature of 16.6 ℃. The soil is clay loam , pH 9.27, soil organic matter content 1.61%, alkaline nitrogen content 91.52 mg/kg, available phosphorus content 108.5 mg/kg, available potassium content 211.27 mg/kg.
2.2.2Xiqing 2 Experimental Site. This experimental site is located in the the west campus of Tianjin Agricultural University (39°09′ N, 116°58′ E), with an altitude of 7 m, a frost-free period of 203 d, sunshine hour of 2 810 h, extreme minimum temperature of -14.8 ℃ and average annual temperature of 12.2 ℃. The soil is sand soil , pH 8.96, soil organic matter content 0.91%, alkaline nitrogen content 110.78 mg/kg, available phosphorus content 63.28 mg/kg, available potassium content 241.41 mg/kg.
2.2.3Jinghai District Experimental Site. This experimental site is located in a farm house of Linhai Jiayuan in Jinghai District (38°09′ N, 116°09′ E), with an altitude of 7 m, a frost-free period of 171 d, sunshine hour of 2 699 h, extreme minimum temperature of -17.3 ℃ and average annual temperature of 11.8 ℃. The soil is clay loam, pH 8.68, soil organic matter content 2.15%, alkaline nitrogen content 69.84 mg/kg, available phosphorus content 55.10 mg/kg, available potassium content 199.22 mg/kg.
2.2.4Jizhou District Experimental Site. This experimental site is located in Cuiping Lake Science Park of Jizhou District (40°01′ N, 117°30′ E), with an altitude of 132 m, a frost-free period of 195 d, sunshine hour of 2 900 h, extreme minimum temperature of -14.8 ℃ and average annual temperature of 12.2 ℃. The soil is gravel clay, pH 7.86, soil organic matter content 2.01%, alkaline nitrogen content 130.05 mg/kg, available phosphorus content 61.97 mg/kg, available potassium content 129.89 mg/kg.
2.3 Experiment designA.melanocarpaseedlings were planted in December 2017, with row spacing of 0.5 m×0.5 m, planted in ridges and furrows, and 200 plants were planted in each experimental site, and strict field management was performed. Each experimental site was arranged with 3 repetitions, each time repeated 10 plants and all plants were marked with cards.
2.4 Measurement of itemsWe investigated and described the phenological period, high yield potential, and fruit economic traits ofA.melanocarpa. The phenological period research used the visual survey method[6]. After the fruit is ripe, 30 fruits were randomly picked from each experimental site to determine the weight of single fruit and titratable acid. The content of soluble solids was determined by WYT handheld refractometer; the content of titratable acid was determined by acid-base titration[7]; Vc content was determined by 2,6-dichlorophenol-indophenol method[8]; anthocyanin content was extracted by ethanol; total phenol and total flavonoids were determined by ultraviolet colorimetric method[9].
3 Results and analysis
3.1 Phenological periodFrom Table 1, it can be seen that the buds ofA.melanocarpadifferentiated and leaf extension started in mid-April in Xiqing 1 Experimental Site. They began to grow slightly in late April, bloomed in early May, fruit set in early June, ripened in early August, and leaves started falling in Late October. It took 193 d from bud to leaf falling in late October. It took 115 d from bud differentiation to fruit ripening, the florescence was about 13 d, and about 64 d from fruit setting to fruit ripening. The buds ofA.melanocarpadifferentiated and leaf extension started in late April in Xiqing 2 Experimental Site. They began to grow slightly in early May, bloomed in mid-May, fruit set in mid-June, ripened in late August, and leaves started falling in early October. It took 170 d from bud differentiation to leaf falling. It took 127 d from bud differentiation to fruit ripening, the florescence was about 18 d, and about 66 d from fruit setting to fruit ripening. The buds ofA.melanocarpadifferentiated and leaf extension started in mid-April in Jinghai District Experimental Site. They began to grow slightly in late April, bloomed in mid-May, fruit set in early June, ripened in mid-August, and leaves started falling in late October. It took 199 d from bud differentiation to leaf falling. It took 124 d from bud differentiation to fruit ripening, the florescence was about 19 d, and about 67 d from fruit setting to fruit ripening. The buds ofA.melanocarpadifferentiated and leaf extension started in mid-April in Jizhou District Experimental Site. They began to grow slightly in early May, bloomed in late May, fruit set in mid-June, ripened in late August, and leaves started falling in mid-October. It took 187 d from bud to leaf falling. It took 131 d from bud differentiation to fruit ripening, the florescence was about 19 d, and about 66 d from fruit setting to fruit ripening. The experimental results show that the development period ofA.melanocarpaplanted in the Xiqing 1 Experimental Site and Jinghai District Experimental Site was relatively close, and the occurrence time was earlier than the Jizhou District Experimental Site, and the development period of the Xiqing 2 Experimental Site was the latest.

Table 1 Performance of phenological period of Aornia melanocarpa in districts of Tianjin
3.2 High yield potentialAccording to Table 2 and combined with the air temperature and soil physical and chemical properties of each experimental site, it can be seen that the leaf length ofA.melanocarpain Xiqing 1 Experimental Site and Jinghai District Experimental Site had no significant difference, while the leaf length ofA.melanocarpain Jizhou District Experimental Site was only 5.887 cm, which was only higher than 5.227 cm of Xiqing 2 Experimental Site, showing a very significant difference from Xiqing 1 Experimental Site and Xiqing 2 Experimental Site. The leaf width ofA.melanocarpain Jinghai District Experimental Site was significantly different from that in Xiqing 1 Experimental Site, but it was very different from the other two experimental sites. The narrowest leaf width ofA.melanocarpain Jizhou District Experimental Site was 3.173 cm. In terms of the data of flowers, the number of flowers in single branch in Xiqing 2 Experimental Site was the smallest among the four experimental sites, only 11, which was significantly different from the other three experimental sites. As to the corolla diameter and pedicel length, Xiqing 2 Experimental Site was also the lowest of the four experimental sites, and significantly different from the other three experimental sites. In terms of fruiting, the single branch fruiting rate and per unit area yield in the Jinghai District Experimental Site were the highest among the four experimental sites, and the per unit area output value of Xiqing 2 Experimental Site was only one-eighth of that in the Jinghai test site.
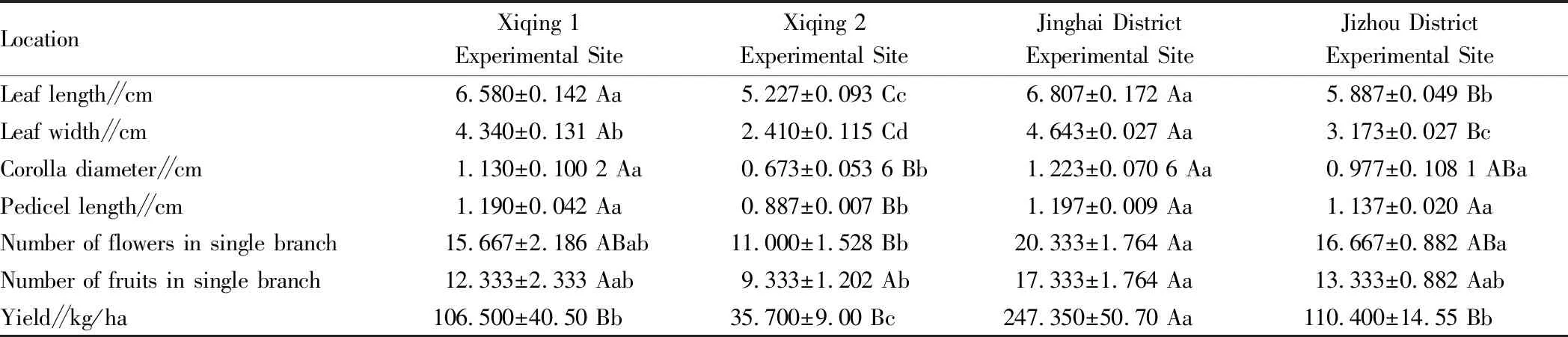
Table 2 Static growth indicators of Aornia melanocarpa
3.4 Economic traits of fruitsSoluble solids and titratable acid are two independent traits that can control the flavor quality of fruit[10], the solid-acid ratio is proportional to the fruit taste[11], and the Vc content and anthocyanin content reflect the nutritional value of fruit. The results showed that Jinghai District Experimental Site had the largest fruit, with an average single fruit weight of 0.9511 g, and Xiqing 2 Experimental Site had the smallest fruit, with an average single fruit weight of 0.654 g; the largest solid-acid ratio came from the fruit produced in Jinghai Experimental Site, which had a sweet and sour taste and relatively high nutritional value, the solid-acid ratio produced in the remaining three experimental sites was basically the same, the taste was sour and astringent, and the fruit nutritional value of Xiqing 2 Experimental Site was the lowest. The fruit hardness of the four experimental sites was in the intermediate and upper level, and the fruit hanging time was longer, and all were resistant to storage and transportation.

Table 3 Economic traits of Aornia melanocarpa fruit in four experimental sites
4 Conclusions and discussions
Through two consecutive years of introduction and cultivation experiments, it was found thatA.melanocarpagrows normally in 4 districts of Tianjin.A.melanocarpais very easy to take root, so cutting, tissue culture and seed propagation are feasible[12]. The orchard should be provided with with sufficient sunlight and good drainage, have suitable climatic conditions, frost-free period of more than 120 d and annual precipitation about 700 mm, the soil quality is mainly loam, the soil pH is about 8.5, and the thickness of the soil layer is more than 30 cm. The survival rate of planting in spring is high. After planting, water well enough and cover with the plastic film. Since this tree species was introduced from the Northeast, and the survival rate after natural overwintering is relatively high. However, for the sham seedlings, the root system needs to be trimmed to remove the moldy and diseased roots, and the root system should be properly soaked before planting[13]. From the overall economic traits of fruits, the fruits produced in the experimental site of Jinghai District have sufficient weight, high solid-acid ratio, and relatively high nutrient content, thus this experimental site can be used as large-scale cultivation base forA.melanocarpa. The fruits produced in the Xiqing 1 Experimental Site and Jizhou District Experimental Site have a sour and astringent taste, and the yield is relatively low, so they need to be processed as by-products and combined with market prices to decide whether to plant in these two sites. In the four experimental sites,A.melanocarpaplanted in Xiqing 2 Experimental Site not only has relatively short plants, but also has low yield, small fruit and poor taste, the planting effect is the worst in the four experimental sites.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- A Preliminary Study on the Teaching Evaluation Language of Art Teachers in Rural Middle Schools
- An Analysis on the Forestry Technology Work after Afforestation
- About KIT
- Empirical Study on Relationship between Income Structure and Consumption of Rural Residents in Jiangsu
- Conservative Breeding of Debao Pony in Nanning, Guangxi
- Effects of Nano Chinese Herbal Medicine Feed Additive on Growth Performance, Meat Quality and Disease Resistance of Chickens
