Report on Screening Test of Dazhou Superior Ramie Germplasm Resources
2020-08-01YalingLIZhonggangCUIYunGOUZhaoxiaTANGYanYANGWenmeiWUZhonghuaZHANG
Yaling LI, Zhonggang CUI, Yun GOU, Zhaoxia TANG, Yan YANG, Wenmei WU, Zhonghua ZHANG
Sichuan Dazhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Dazhou 635000, China
Abstract [Objectives] To promote the development of the ramie industry in Dazhou City of Sichuan Province and provide a material basis for the breeding of new ramie varieties. [Methods] The Institute of Bast Fiber Crops of Dazhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences performed a screening test of excellent ramie germplasm resources from 2017 to 2019 to compare the growth, resistance, raw fiber yield and fiber fineness of the experimental materials. [Results] All the experimental materials showed strong growth potential, drought resistance and disease resistance. There were 8 kinds of resources with a fiber fineness greater than 2 000 m/g, of which 3 kinds of resource materials had a fiber fineness greater than 2 300 m/g; 12 kinds of resources has the raw fiber yield exceeding the control and 10 kinds of resources had the raw fiber yield ≥ 2 000 kg/ha; 3 kinds of resources met the requirements of the high-yield and high-quality indicators (fiber fineness exceeding 2 000 m/g and raw fiber yield ≥ 2 000 kg/ha), they were BD0718, BD1614 and BYL2. [Conclusions] These high-quality ramie resources can provide a rich resource base for the breeding of new ramie varieties.
Key words Ramie, Germplasm resources, Growth potential, Resistance, Raw fiber yield, Fiber fineness
1 Introduction
Ramie (Boehmerianivea(L.) Gaudich.) is Herbaceous perennial type plant inBoehmeriagenus of Urticaceae family. Ramie is an excellent natural fiber crop with traditional characteristics in China and an important raw material for the textile industry. Ramie has been cultivated as a fiber crop in China for more than 2 000 years. At present, China’s ramie production accounts for more than 90% of the world. Ramie has become China’s fine worsted natural fiber raw material second only to cotton. Dazhou is the main ramie production area in China and the main high-quality ramie production base for China’s linen textile enterprises. Its planting area and yield account for more than 95% of Sichuan Province and more than 65% of the whole China. The fiber quality ranks first in China. Ramie is also the most distinctive cash crop in Dazhou and the main source of farmers’ income. In order to promote the development of the ramie industry in Dazhou City, the Institute of Bast Fiber Crops of Dazhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences continues to strengthen the breeding of new varieties of ramie with high yield, high quality and high resistance. We performed field cultivation experiments on germplasm resources with good traits in the ramie germplasm resource nursery of the Institute of Bast Fiber Crops of Dazhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences, in the hope of selecting excellent germplasm resources and providing a material basis for the breeding of new ramie varieties.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Experimental materialsAll experimental materials were selected from the ramie germplasm resource nursery of the Institute of Bast Fiber Crops of Dazhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences. We surveyed and analyzed the traits of all germplasm resources in the ramie germplasm resource nursery, including the growth, appearance, and germination, and initially selected 30 kinds of germplasm resources with strong growth potential and good germination (as listed in Table 1). In April 2017, we conducted tender branch cutting for reproduction of these 30 kinds of resources.
2.2 Experiment designThe experiment used the plot comparison method, repeated twice, and the control variety (CK) adopted Zhongzhu No.2. They were transplanted in June 2017, the planting area of each experimental material was 10 m2, the planting specification was 50 cm × 60 cm, and the width between the plots was 90 cm; protection lines were arranged around the plots, and the experimental materials were randomly arranged. The plots were covered with mulch film and not uncovered throughout the year. In the fourth growing season after transplanting, we started to conduct corresponding data surveys on the experimental ramie germplasm materials. The test data collection cycle was 6 consecutive seasons in 2018-2019 for two consecutive years.
2.3 Experiment management
2.3.1Intertillage, weeding, and fertilizer application. During the growth of first ramie every year, weeds are prone to breeding, it is necessary to conduct weeding in a sunny day. Combined with intertillage, conduct top dressing one time, and apply 1.0 kg of urea for each plot. The fertilizer types, quantity, methods and time requirements of all plots should be consistent with each other, to reduce the experiment error.

Table 1 Thirty kinds of experimental ramie resources
2.3.2Harvesting in suitable time. When the plant’s black stalk reaches 2/3, they can be harvested, and all the plots should be harvested on the same day. Test the seeds in accordance with the requirements, and calculate the yield of each plot after harvesting.
2.3.3Topdressing. After the harvest of each season of ramie, conduct timely topdressing once, 1.0 kg of compound fertilizer in each plot, and investigate the growth potential and resistance during the growing period.
2.3.4Winter cultivation. Conduct winter cultivation in the middle and late of December every year. During winter cultivation, apply 15 000 kg of rapeseed cake for 1 ha field combined with intertillage, ridge and cover the ramie stalk and well arrange the drainage ditches.
2.4 Survey itemsIn accordance with the principles and methods specified in theRamieGermplasmResourceDescriptionSpecificationandDataStandard, observe and make a record of the growth potential, order, growth uniformity, drought resistance, and tolerance to waterlogging, wind resistance, cold resistance, resistance to mosaic disease, and resistance to anthracnose of the experimental germplasm resources from the fourth growth season. The raw fiber yield identification method is carried out according to the standard ofEvaluationCriteriaforExcellentGermplasmResourcesofCrops-Ramie; 10 plants of each experimental germplasm material are harvested at the mature stage of each season, fiber is arranged according to the GB 5884-86RamieFiberCountTestMethod, and fiber fineness is determined using BEION F10 automatic fiber fineness tester. The data analysis adopts Excel 2007.
3 Results and analysis
3.1 Growth traits and resistance comparison of the experimental materialsThrough the investigation of the growth traits of three seasons of ramie every year (Table 2), we found that 5 materials in the experimental resources showed quite strong growth (the material number was 11, 14, 18, 22, 25), and other experimental materials showed strong growth; the growth order of the 2 materials (the material number was 3 and 18) was quite order, and the other materials were order; the growth uniformity of the 2 materials (the material number was 3 and 20) was quite uniform, and other materials were uniform. As to the resistance (Table 3), we found that there were 4 test materials with quite strong wind resistance, numbered 2, 9, 12, 13 respectively, and other materials showed strong wind resistance; all materials showed quite strong drought resistance; through the investigation of the resistance of the experimental resources to waterlogging in the rainy season, it was found that all the materials showed intermediate resistance; through the cold resistance investigation, we found that all the experimental materials showed strong cold resistance. In the disease resistance investigation, we found that all the experimental materials did not appear to be infected with mosaic virus and anthrax virus.
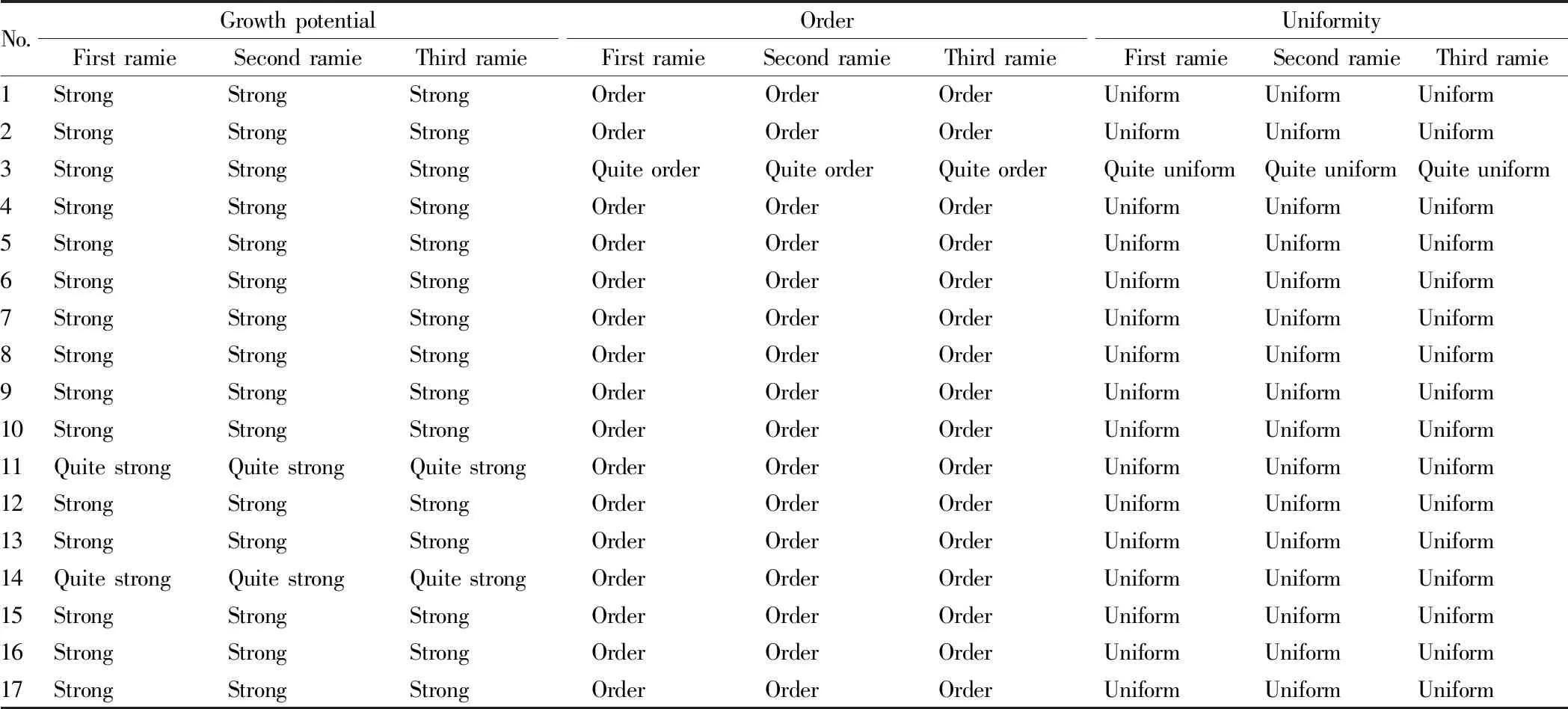
Table 2 Growth traits of the experimental materials
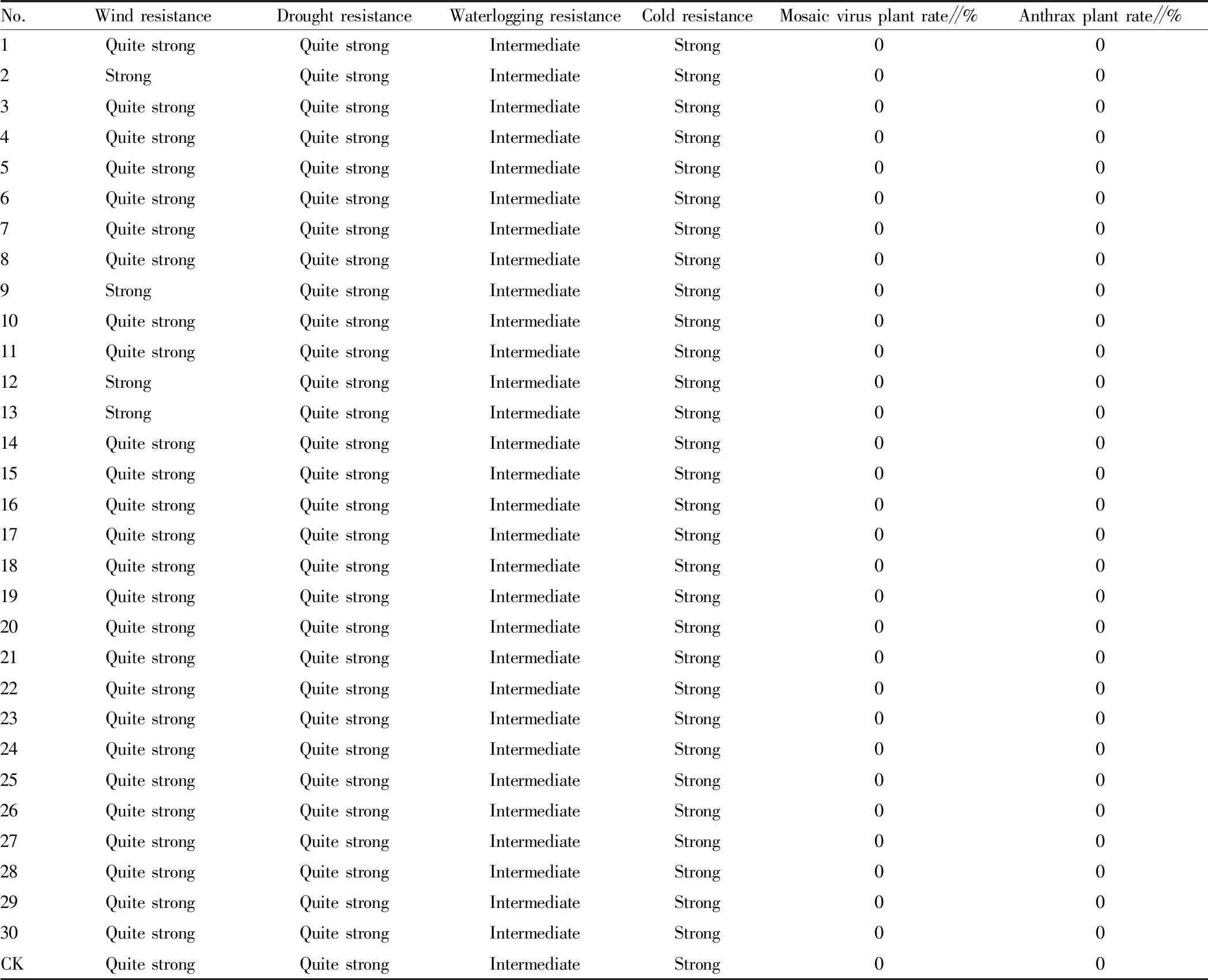
Table 3 Resistance comparison of the experimental materials
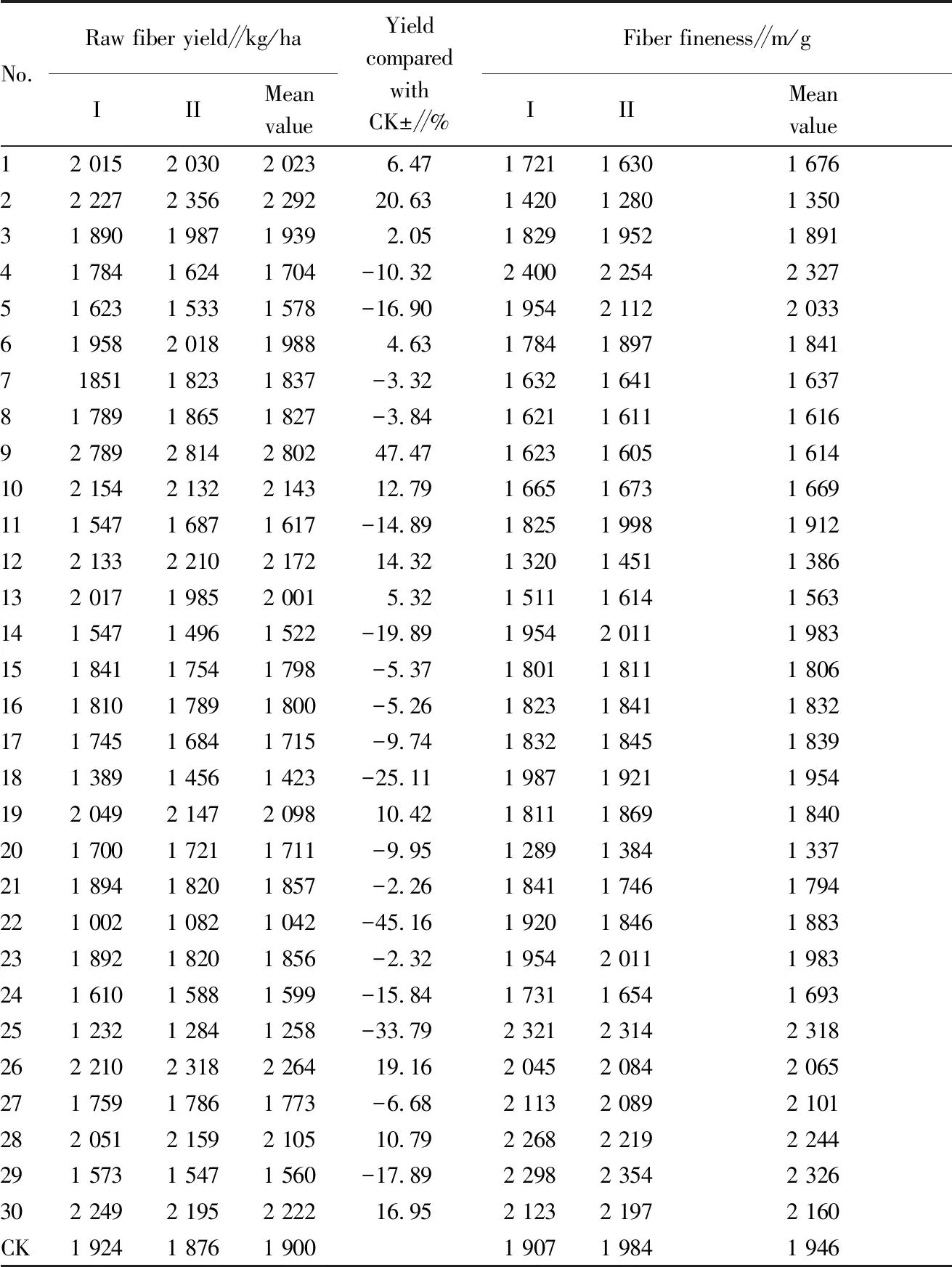
Table 4 Raw fiber yield and fiber fineness of experimental materials
3.2 Comparison of raw fiber yield and fiber fineness of experimental materialsThrough analyzing the raw fiber yield and fiber fineness of all the experimental materials for two years and six seasons (Table 4), we found that the raw fiber yield of 12 resources increased compared with the control, of which 7 resources increased by more than 10%, and the material numbers were 2, 9, 10, 12, 19, 26, 30, respectively; especially the materials with the numbers 2 and 9, the raw fiber yield increased by 20.63% and 47.47% compared with the control; 10 materials with the raw fiber yield exceeded 2 000 kg/ha, the numbers were 1, 2, 9, 10, 12, 13, 19, 26, 28, 30, respectively, among which the raw fiber yield of material 9 was as high as 2 802 kg/ha. Among all experimental materials, 11 materials had the fiber fineness higher than the control (1 946 m/g), numbered 4, 5, 14, 18, 23, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, of which 8 materials had the fiber fineness exceeding 2 000 m/g (material numbers were 4, 5, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, respectively), especially the fineness of material 4, 25, 29 exceeding 2 300 m/g, specifically 2 327, 2 318, and 2 326 m/g.
4 Conclusions and discussions
According to the experimental results, among all the experimental materials, 7 resource materials meet the high yield indicator and have strong resistance, namely RC2014, BD1604, GZ-1, 2007-female parent 6, BD0718, BD1614, and BYL2, all show strong growth, order and uniformity; 8 materials (No.4, 5, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30) meet the high quality indicator (fiber fineness ≥ 2 000 m/g), showing strong resistance. In summary, there are 3 resources that meet the high-yield and high-quality indicators (fiber fineness ≥ 2 000 m/g, raw fiber yield ≥ 2 000 kg/ha), namely BD0718, BD1614, BYL2, with strong resistance and excellent growth potential. These high quality ramie materials are expected to provide a rich resource base for the breeding of new ramie varieties. At present, the utilization of ramie is concentrated on fiber utilization, and it is also actively explored in ramie feeding, soil and water conservation, and heavy metal pollution restoration. According to the different purposes of ramie utilization, the traits of ramie germplasm resources in cultivar selection are also different. For example, in terms of fiber use, it is recommended to emphasize traits such as resistance, raw fiber yield and fiber quality. In the aspect of feeding, it is necessary to pay attention to the traits such as biological yield, nutritional quality characteristics and cutting tolerance. As to the application of soil and water conservation, it is required to focus on the degree of root development, barren tolerance and drought resistance. In the remediation of heavy metal pollution, it is recommended to stress the degree of root development, stress tolerance, the ability to concentrate heavy metals, and biological yield. These require ramie researchers to carry out comprehensive and in-depth research on ramie germplasm traits. The study of germplasm resources is a basic work. Only after getting a comprehensive understanding of resource traits, can we make full and reasonable use of excellent germplasm resources.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Empirical Study on Relationship between Income Structure and Consumption of Rural Residents in Jiangsu
- Tillage Effect and Development Prospect of Fenlong Farming Tools with "Drill"
- Estimation of Economic and Ecological Value of Raising Sheep in Pastoral Area
- Construction of Platform-based Business Ecosystem
- Analysis of Industrial Transformation of Resource-based Towns in Qingyang City: Taking Qingcheng County as an Example
- Treatment Effect of Pig Manure-derived Biochar-based Metal Catalyst for Pig Breeding Wastewater
