New Variants of Wild Red-fleshed Kiwifruit in Jiugongshan Region and Their Application Prospect
2020-07-31GuorongMAOQingjiaMAO
Guorong MAO, Qingjia MAO
1. College of Horticulture and Gardening, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434025, China; 2. Administrative Commission of Jiugongshan National Nature Reserve of Hubei Xianning, Tongshan 437600, China
Abstract The collection of wild kiwifruit germplasms has already proved its worth with the development of valuable new kiwifruit cultivars. Through field investigation and consulting the existing literature, this paper illustrates that Jiugongshan region in China is a unique gene bank of excellent wild kiwifruit germplasm resources on the boundary between Hubei and Jiangxi provinces. It is also one of the important birthplaces of breeding materials for new kiwifruit cultivars in China. The paper introduces the main characteristics of two wild red-fleshed kiwifruit germplasms discovered in this region, and one of them is a new large-fruited variant of wild red-fleshed kiwifruit. The main fruit qualities of the large-fruited form are that short fruit stalk, large fruit (the maximum fresh fruit mass of about 81.2 g), moderate sweetness and sourness, reddish to red inner pericarp, the ripe fruit soluble solids content 14.10%, total sugar 8.84%, total acid 1.18%, vitamin C 644.3 mg/kg. It is expected to be cultivated into a new edible cultivar(line) or ornamental and edible cultivar(line) of Actinidia chinensis, which has a broad prospect of development and utilization.
Key words Wild red-fleshed kiwifruit, Short fruit stalk, Jiugongshan region
1 Introduction
China is the original home of kiwifruit and is considered the center of species diversity and of evolution of the genusActinidia. Jiugongshan region, mainly including Jiugongshan Mountain in Xianning, Hubei Province and its adjacent areas:Tongshan County, Chongyang County, Yangxin County in Hubei Province, as well as Wuning County and Xiushui County in Jiangxi Province[1], is also one of the important birthplaces of new kiwifruit cultivar breeding materials. Jiugongshan Mountain (29°19′N-29°29′N, 114°23′E-114°48′E) lies in the middle part of the Mufu Mountains on the boundary of Hubei and Jiangxi. It is now composed of two parts: Jiugongshan National Nature Reserve and National Scenic Spot in Xianning, Hubei Province, with a small overlap in the middle. The highest elevation is 1 656.7 m, the climate is warm and humid, and the natural conditions are superior, so it is a very suitable distribution area for the growth of kiwifruit. Hubei and Jiangxi are one of the concentrated distribution areas of kiwifruit in China. The Jiugongshan region on the boundary of Hubei and Jiangxi is a rich gene bank with excellent wild kiwifruit germplasm resources. The current Chinese kiwifruit cultivars are most of selections directly from the wild. There are more than 10 new cultivars(lines) ofA.chinensiswhose maternal plants or hybrid parents come from this region[1-4]. Among Chinese new kiwifruit cultivars, ‘Jintao’ originating from this region, is the first case of fruit cultivar whose propagating right can be successfully transferred to a foreign company. This region has made outstanding contribution to the exploration of wild kiwifruit genetic resources and to the breeding of new cultivars in China.
Red-fleshed kiwifruit is a variant ofA.chinensisvar.chinensis,which has a small number, narrow and scattered distribution in nature. In 1979, the wild red-fleshed kiwifruit was found in northwest Jiangxi[5]. From 2010 to 2011, Sui Liyunetal. collected an accession of the wild red-fleshed kiwifruit germplasm in Jiugongshan region, but the fruit was probably small[6]. Red-fleshed kiwifruit is "the third generation" of new kiwifruit cultivars cultivated at home and abroad after green- and yellow-fleshed kiwifruit. Among the three kinds of kiwifruit with green, yellow and red flesh, only red-fleshed kiwifruit contains anthocyanin, but no anthocyanin is found in green- and yellow-fleshed cultivars[7]. Foods rich in anthocyanins prevent several chronic diseases and many other disorders, such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, diabetes and obesity. Anthocyanins have very important nutritional and pharmacological values, such as improving eyesight, delaying aging, preventing and reducing the occurrence of cardiovascular disease and cancer[8]. This specific germplasm characteristic of red-fleshed kiwifruit has played a more important role in kiwifruit production and consumption. In recent years, the large area planting of excellent cultivars of red-fleshed kiwifruit such as ‘Hongyang’ has led to a diversified pattern of green-, yellow- and red-fleshed kiwifruit in the international kiwifruit market[9], and it has become more and more popular to the producers and consumers. This paper focuses on the newly discovered wild red-fleshed kiwifruit in this region, mainly including 2 kinds of different sizes of fruits, in order to attract more attention at home and abroad to Jiugongshan region, a natural "gene treasury" ofA.chinensisPlanch., and to provide a new evidence for further strengthening the conservation, development and utilization of the rare germplasm resources.
2 Superior variant characteristics of wild red-fleshed kiwifruit
Wild red-fleshed kiwifruit germplasms are at least identified to belong to threeActinidiataxa (A.arguta,A.chinensisandA.deliciosa)[6]. Since June 2, 2011, the new red-fleshed germplasms belonged toA.chinensisin wild kiwifruit populations have been found in Jiugongshan region of altitude of more than 800 m, mainly including the large-fruited wild red-fleshed kiwifruit and the small-fruited wild red-fleshed kiwifruit. Among them, the large-fruited wild red-fleshed kiwifruit(also called as superior var-iant of red-fleshed kiwifruit, SVRK for short) is very precious and rare. "J4" is an accession of the large-fruited wild red-fleshed kiwifruit (SVRK) discovered in Jiugongshan region.
2.1 Fruit mass and fruit stalk length of SVRK"J4" average fresh fruit mass and fruit stalk length of 25 fruits picked on the same day were about 49.0 g and 2.3 cm, respectively; the average fruit length was 5.0 cm, and the average transverse and side diameter was 3.8 and 3.5 cm, respectively. Among them, the number of medium-sized fruits of 40-50 g accounted for 60% of the total, the number of large fruits of above 50 g accounted for 32%, and the mass of the largest fresh fruit (Fig. 1A) was about 81.2 g. The fruits of "J4" are medium to large among the wild red-fleshed kiwifruit found so far.
2.2 Comparison of fruit size between SVRK and small-fruited red-fleshed kiwifruit10 large fruits and 10 medium-sized fruits were randomly selected from the wild small-fruited red-fleshed kiwifruit picked in the Jiugongshan region on the same day, and the average fresh fruit mass was 23.5 g; 10 large fruits, 10 medium-sized fruits and 10 small fruits were randomly selected, and the average transverse diameter was 2.9 cm, the average fruit stalk length was 3.0 cm. Before the fruits of the wild small-fruited red-fleshed kiwifruit were picked for 3 days the "J4" fruits were picked and randomly selected for measurement. "J4" average fresh fruit mass(20 fruits) was 37.4 g, and the average transverse diameter(30 fruits) was 3.4 cm, 59.1% and 17.2% higher than that of the former, respectively. The "J4" fruit was significantly larger than the former, but "J4" average fruit stalk length(30 fruits) was 2.0 cm, 50% shorter than the former. T-test showed that the differences between them in fresh fruit mass, transverse diameter size and fruit stalk length were very significant (P<0.01).
2.3 The intensity and spread of red color for the inner pericarp of SVRKThe red scores for intensity of red-fleshed kiwifruit are divided into 1-5 grades according to the red color degree of the inner pericarp, and the highest class is H5. The red score for intensity of the largest fruit of "J4" was H2 (red grade 2; Fig. 1B). After indoor storage and ripening, the reddest inner pericarp score could reach H4 (red grade 4; Fig. 1C). This showed that the red color degree of the inner pericarp of the same wild red-fleshed kiwifruit was irregular and varied greatly. After ripening, the "J4" average red score of 20 good fruits was H3-(near red grade 3),which was between Fig. 1B and Fig. 1C. The red inner pericarp of "J4" showed a banded distribution, that is, there was a red banded spread of about 0.3 cm along the locules, and it was not radial along the locules outside the core like ‘Hongyang’ kiwifruit.

Fig.1 The largest fruit (A, B) and the reddest inner pericarp(C) of "J4" SVRK from Jiugongshan region
2.4 Comparison of main fruit qualities between SVRK and ‘Hongyang’ kiwifruitThe maximum fresh fruit mass of "J4" and ‘Hongyang’ kiwifruit[10]was 81.2 and 87.0 g, respectively, indicating that the maximum fresh fruit mass of the former in the wild conditions was similar to that of the latter under good artificial cultivation conditions. The comparison of other main fruit qualities between the two is shown in Table 1.

Table 1 The main fruit qualities of "J4" red-fleshed kiwifruit and Hongyang kiwifruit
2.5 Genetic characteristics of large fruit and short fruit stalk of SVRKIn 2017, the branches of "J4" were used as scion to be grafted on a 7-year-old rootstock at a low altitude of about 30 m in Jingzhou City, Jianghan Plain; the F1generation of top grafting of "J4" (hereinafter referred to as "J4F1") began to produce fruits in the second year; in the third year (2019), one of the "J4F1" branches produced a total of 17 fruits, the inner pericarp was yellowish green, the maximum fresh fruit mass was 100.0 g, and the average fresh fruit mass was 81.0 g. It was the largest by artificial planting at low altitude in recent years (Table 2). This showed that the large-fruited characteristic of "J4" was heritable and had a tendency to become larger, so it was a very precious hybrid parent material of large-fruited red-fleshed kiwifruit. When "J4F1" was planted at low altitude in Tongshan County, Hubei Province in 2017, its short fruit stalk characteristic was also heritable and it was 31% shorter than that of the control ‘Hongyang’ kiwifruit. In other years, the fruit characters of "J4F1" with short fruit stalk and ‘Hongyang’ and ‘Donghong’ kiwifruit with long fruit stalk are shown in Table 2.
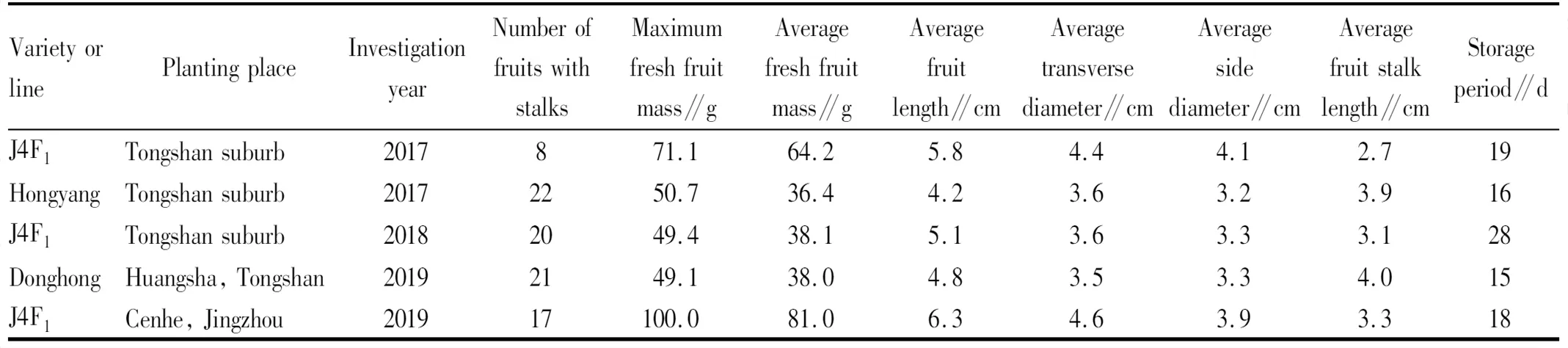
Table 2 Fruit characters of "J4F1" and Hongyang and Donghong kiwifruit
2.6 Taxonomic status and Chinese naming of SVRK
2.6.1Changes in taxonomic status of red-fleshed kiwifruit. Red-fleshed kiwifruit was discovered at 1 150 m altitude in Wufeng County, Hubei Province in 1980. The differences between red-fleshed kiwifruit andA.chinensisvar.chinensisform.chinensisare that the former single fruit stalk is long (4-5 cm), the fruit is small (transverse diameter of about 3 cm), and the color of the inner pericarp is reddish. In 1982, it was classified asA.chinensisvar.chinensisform.rufopulpa[11], and then raised toA.chinensisvar.rufopulpa[12]. According to the latest revision of the genusActinidia, the taxonomic units under the species ofA.chinensisinclude onlyA.chinensisvar.chinensis,A.chinensisvar.deliciosaandA.chinensisvar.setosa[9,13].
2.6.2The naming of SVRK for convenience of communication. According to the characteristics of "J4" newly found in the Jiugongshan region, such as short fruit stalk, large fruit and reddish to red inner pericarp, it is likely to be a new variant of red-fleshed kiwifruit under the taxonomic unit ofA.chinensisvar.chinensis,which needs to be further identified. In order to distinguish it from the red-fleshed kiwifruit cultivars with long fruit stalk such as ‘Hongyang’ and ‘Donghong’, and to facilitate the communication of scientific research, we draw lessons from the previous naming method of Jinggangshan kiwifruit (A.chinensisvar.chinensisform.jinggangshanensis)[11-12]to tentatively name this possibly new variant Jiugongshan kiwifruit, whose Latin name isA.chinensisvar.chinensisform.jiugongshanensis. The differences between Jiugongshan kiwifruit andA.chinensisvar.chinensisform.chinensisare that the former single fruit stalk is short (less than 4 cm), the fruit is large (both transverse and side diameters are more than 3 cm), and the inner pericarp color of the fruit is reddish to red. Although the small-fruited red-fleshed kiwifruit comes from Jiugongshan region, it does not belong to Jiugongshan kiwifruit because it is small in fruit size (transverse diameter of less than 3 cm) , and is also different from the red-fleshed kiwifruit found in Wufeng County because its single fruit stalk is shorter (the length is 3.0 cm below 4-5 cm).
3 Application prospect
Red-fleshed kiwifruit is a unique germplasm resource of wild kiwifruit in China, and it is also a very precious breeding material. Whether it is a new variety bred directly from red-fleshed kiwifruit, or a new variety bred by crossing red-fleshed kiwifruit gene with other species, it has very high economic value[8]. Since 1978 Chinese red-fleshed kiwifruit cultivars ofA.chinensisbred by means of selection of superior variant from wild kiwifruit populations are very rare, such as ‘Chuhong’[14], but it has set a successful example for the sustainable exploitation and utilization of wild kiwifruit germplasm resources in China. This has a great impact on the cultivar structure and industrial sustainable development of kiwifruit in China. The "J4" SVRK, which is a new variant ofA.chinensisfound in Jiugongshan region, is suitable for planting in windy areas because of its short fruit stalk. In 2017 the scion of "J4" SVRK was grafted on the rootstock ofA.chinesisvar.deliciosain Jianghan Plain of low altitude. Compared with red-fleshed kiwifruit cultivars such as ‘Hongyang’, ‘Donghong’ and ‘Chuhong’, "J4F1" is large in fruit size , and its tastes are moderately sour and sweet; it has medium quality, high storability and beautiful fruit shape and is easy to peel; its early fruiting and high yield are good, growth vigor and adaptability are also strong. In 2019 (the very severe drought year) its drought resistance was prominent. The "J4" SVRK has nutritional value, landscape value and ecological value, and it is expected to be cultivated into a new edible female cultivar(line) or ornamental and edible variety(line) ofA.chinensis. Although its red characteristic of the inner pericarp color is not shown when "J4" is grafted and planted at low altitude area, but it can at least provide a new excellent breeding material with large-fruited red-fleshed gene for cross breeding. As for the small-fruited wild red-fleshed kiwifruit from Jiugongshan region, it would be grafted and planted at some scientific research bases forexsituconservation or used as other application. We hope that exciting new cultivars ofA.chinensiswill derived from the two new variants of the wild red-fleshed kiwifruit discovered in Chinese Jiugongshan region by different breeding methods.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- A Preliminary Study on the Teaching Evaluation Language of Art Teachers in Rural Middle Schools
- An Analysis on the Forestry Technology Work after Afforestation
- About KIT
- Empirical Study on Relationship between Income Structure and Consumption of Rural Residents in Jiangsu
- Conservative Breeding of Debao Pony in Nanning, Guangxi
- Effects of Nano Chinese Herbal Medicine Feed Additive on Growth Performance, Meat Quality and Disease Resistance of Chickens
