海藻生物保水剂吸水保水性能及抗冷冻性研究
2020-07-06严国富聂伟燕牛红艳李凯凯汤洁
严国富 聂伟燕 牛红艳 李凯凯 汤洁
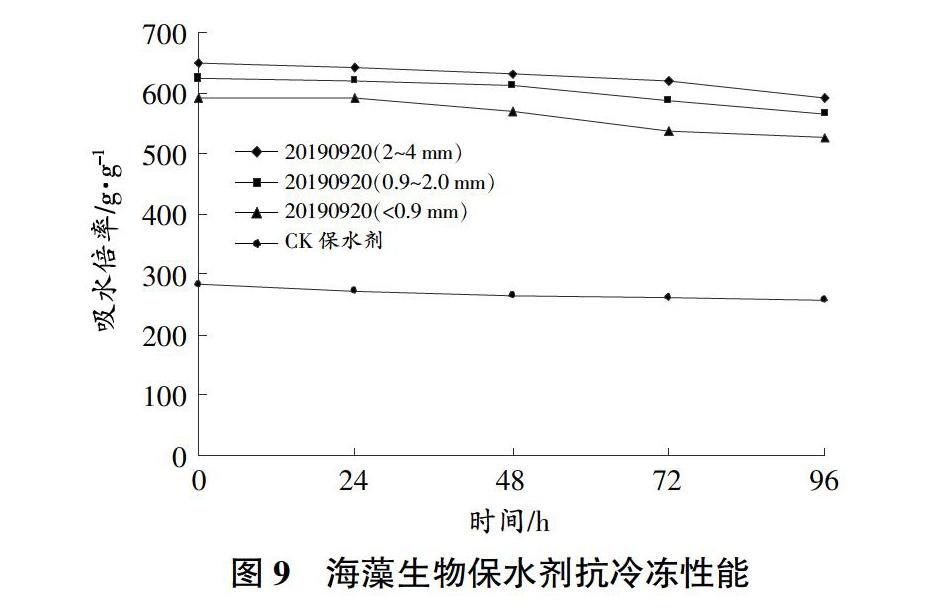
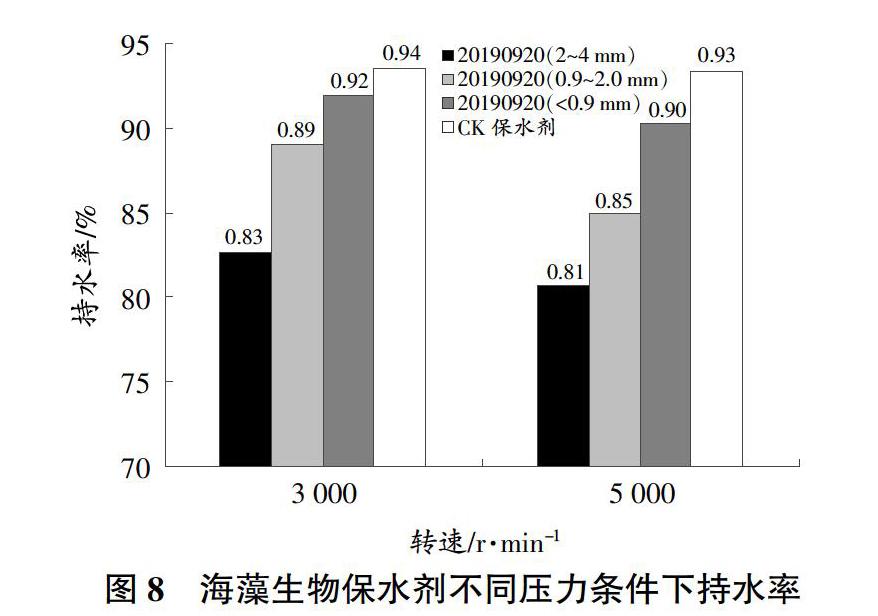
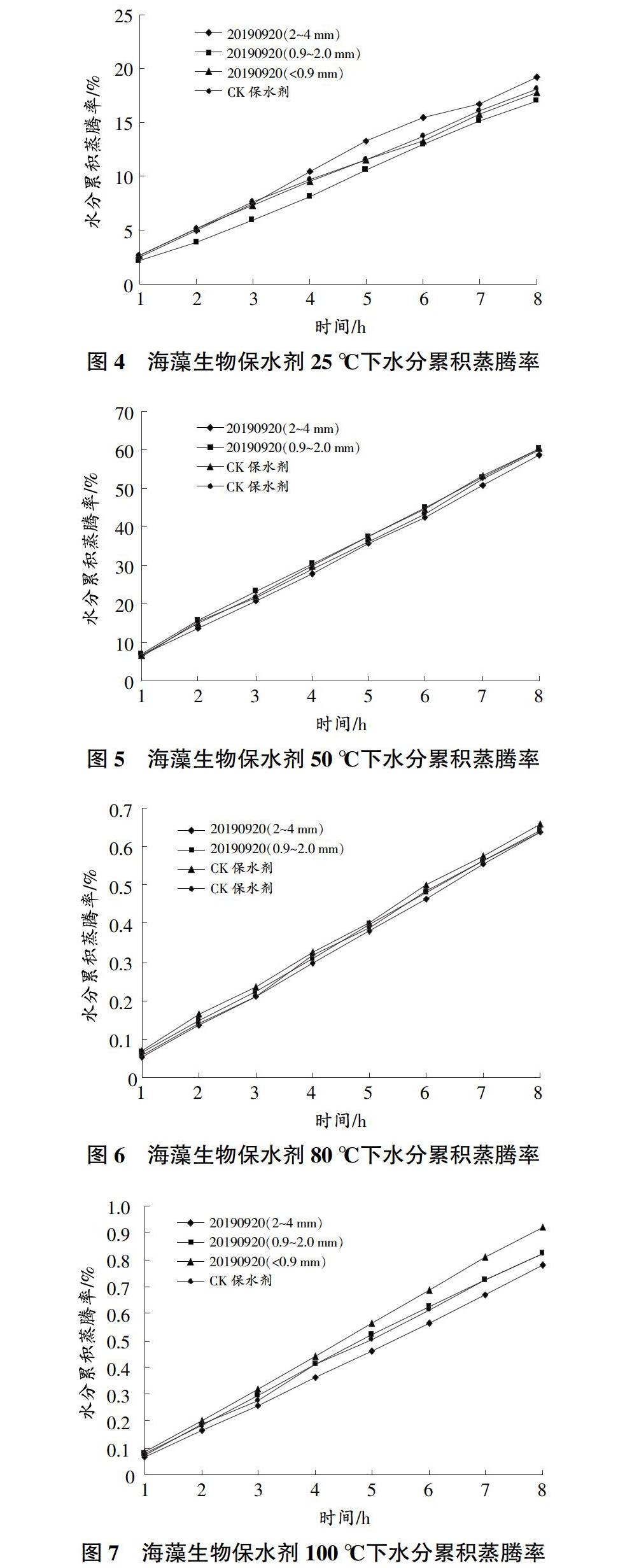
摘要 本文以褐藻(馬尾藻)中高含量的海藻多糖物质为研究对象,运用生物酶解技术和生化制备新工艺,将海藻多糖物质与丙烯酸进行共聚接枝交联,形成海藻多糖-聚丙烯酰胺共聚交联海藻生物保水剂,具有吸水倍数高、寿命长的优点。海藻生物保水剂充分吸水后,粒径为2~4 mm吸水倍率最高,为650.11 g/g。充分吸盐水后,粒径为0.9~2.0 mm吸盐水倍率最高,为61.29 g/g。在吸水前1 h内,粒径为0.9 mm吸水速率最快,所有粒径吸水9 h左右接近饱和。25 ℃条件下,粒径为2~4 mm水分蒸发较快;100 ℃条件下,水分累积蒸腾率粒径为2~4 mm最低,抗高温性能较好。相同转速不同保水剂之间加压0.5 h后,持水率表现为大粒径比小粒径高;不同转速下,3 000 r/min转速条件下保水剂的持水率略大于5 000 r/min,增加压力可降低保水剂持水率。随着冷冻时间的延长,保水剂的吸水倍率呈现下降趋势,但幅度较小,冷冻96 h后,粒径2~4 mm、粒径0.9~2.0 mm、粒径<0.9 mm吸水倍率分别下降9.09%、9.42%、11.04%。3种粒径海藻生物保水剂在冷冻后吸水倍率均可保持在500倍以上,具有较好的抗冷冻性。
关键词 海藻生物保水剂;吸水倍率;吸盐水倍率;抗高温性能;抗压性能;抗冷冻性能
中图分类号 TQ317 文献标识码 A
文章编号 1007-5739(2020)12-0190-03 开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID)
Study on Water Absorption and Water Retention Performance and Freezing Resistance of Seaweed Biological Water Retention Agent
YAN Guo-fu NIE Wei-yan NIU Hong-yan LI Kai-kai TANG Jie
(Beijing Leili Balanced Agricultural Development Co., Ltd., Beijing 101407)
Abstract In this paper, the high content of algae polysaccharides in brown algae (Sargasso algae) was used as the research object, by using the biological enzymolysis technology and the new biochemical preparation technology, the algal polysaccharide was copolymerized with acrylic acid to form the algal polysaccharide polyacrylamide copolymerized cross-linked algal biological water retention agent, which had the advantages of high water absorption multiple and long service life. After the seaweed biological water retention agent fully absorbed water, the water absorption rate was the highest (650.11 g/g) when the particle size was 2-4 mm. After the salt water was fully absorbed, and the rate of salt water absorption was highest (61.29 g/g) when the particle size was 0.9-2.0 mm. In the first hour before water absorption, the water absorption rate of the particle size <0.9 mm was the fastest, and all particle sizes were close to saturation after 9 h of water absorption. Under the condition of 25 ℃, the water with a particle size of 2-4 mm evaporates faster;under the condition of 100 ℃, the cumulative water evaporation rate was the lowest with a size of 2-4 mm, and the high temperature resistance was better. After pressurization for 0.5 h, the water retention rate of the large particle size was higher than that of the small particle size between different water-retaining agents at the same speed;at different speeds, the water retention rate of the water-retaining agent at 3 000 r/min was slightly greater than that of 5 000 r/min, increasing pressure could reduce the water holding capacity of the water-retaining agent. With the extension of freezing time, the water absorption rate of the water-retaining agent showed a downward trend, but the amplitude was relatively small. After 96 h hours of freezing, the water absorption rates of particle size 2-4 mm, particle size 0.9-2.0 mm and particle size <0.9 mm decreased by 9.09%, 9.42% and 11.04%, respectively. The three kinds of algae biological water-retaining agents can keep the water absorption rate above 500 times after freezing, and have good freezing resistance.
Key words seaweed biological water retaining agent; water absorption rate; salt water absorption rate; high temperature resistance; compression resistance; freezing resistance
干旱是制约我国农业生产与发展的一个重要因素,水资源的合理开发与利用迫在眉睫。保水剂是一种化学抗旱节水材料,可以提高土壤持水力、改良土壤结构、吸附土壤速效养分、减少养分的淋溶流失,实现保水保肥的作用。目前,保水剂的生产开始向复合化及多功能方向发展[1]。
保水剂最早是美国人从玉米上研制而成。保水剂分为丙烯酰胺-丙烯酸盐共聚交联物(聚丙烯酰胺、聚丙烯酸钠、聚丙烯酸钾、聚丙烯酸铵等)和淀粉接枝丙烯酸盐共聚交联物(淀粉接枝丙烯酸盐)两大类。保水剂亲水性很强,能够反复吸水、释水,从而增强土壤的水分保持能力,以供植物吸收和利用。在吸水初始,保水剂吸水速率达到最大,随后逐渐减小并趋于溶胀平衡,吸水倍率与溶液浓度、保水剂粒径及吸水次数有关[2]。
海藻生物保水剂以褐藻(马尾藻)中高含量的海藻多糖物质为研究对象,运用生物酶解技术和生化制备新工艺,将海藻多糖物质与丙烯酸进行共聚接枝交联,形成海藻多糖-聚丙烯酰胺共聚交联海藻生物保水剂,具有吸水倍数高、寿命长的优点。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料及仪器
海藻生物保水剂(20190920批次)(2~4 mm,0.9~2.0 mm,<0.9 mm),北京雷力平衡农业发展有限公司自制;保水剂,外购,北京汉力淼新技术有限公司;氯化钠(NaCl),分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
水浴锅,DZKW-S-4,北京市永光明医疗仪器厂;天平,AL204,梅特勒-托利多仪器(上海)有限公司;电冰箱,BCD-2016TEM,合肥美的荣事达电冰箱有限公司;电热鼓风干燥箱,101-2ABS,北京市永光明医疗仪器厂;标准试验筛,孔径0.18 mm。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 海藻生物保水剂吸水倍率的测定。称取1 g海藻生物保水剂,置于2 000 mL烧杯中,加入1 000 mL水,搅拌5 min,静置30 min,直至样品充分吸水膨胀。将凝胶状样品移入已知质量的标准试验筛中,自然过滤10 min。将试验筛倾斜放置,再过滤10 min。称量试验筛和凝胶状样品的质量。按式(1)计算保水倍率:
v=■(1)
式中:v—吸清水倍率(g/g),m1—吸清水后质量(g),m2—吸清水前质量(g)。
1.2.2 海藻生物保水剂吸盐水(0.9%NaCl)倍率的测定。称取1 g海藻生物保水剂,置于500 mL烧杯中,加入200 mL 0.9%NaCl溶液,搅拌5 min,静置30 min,直至样品充分吸0.9% NaCl溶液膨胀。将凝胶状样品移入已知质量的标准试验筛中,自然过滤10min。将试验筛倾斜放置,再过滤10 min。称量试验筛和凝胶状样品的质量。按式(2)计算保水倍率:
V=■(2)
式中:V—吸鹽水倍率(g/g),M1—吸盐水后质量(g),M2—吸盐水前质量(g)。
1.2.3 海藻生物保水剂吸水速率测试。准确称取1 g海藻生物保水剂试样于烧杯中,加入足够量的水,每隔0.5 h称一下保水剂的质量,计算其吸水倍率,直至保水剂吸水倍率基本保持不变为止,绘制出吸水倍率随时间变化的曲线图。
1.2.4 海藻生物保水剂高温保水性能测试。称取一定质量吸水达到饱和的保水剂,记其质量为N,分别静置在25、50、80、100 ℃条件下,每隔0.5 h称质量,记其质量为n[3]。按式(3)计算保水率:
B(%)=n /N×100(3)
1.2.5 海藻生物保水剂加压保水性能测试。称取一定质量吸水达到饱和的保水剂,记其质量为W。分别放在转速为3 000、5 000 r/min的离心机中离心30 min,取出后用吸水纸将游离水吸除后再称质量,记其质量为w[4]。按式(4)计算保水率:
C(%)=w/W×100(4)
1.2.6 海藻生物保水剂抗冷冻测试。分别称取0.1 g(精确到0.001 g)保水剂样品5份装入自封袋内,放入-20 ℃冰箱内冷冻。分别于0、24、48、72、96 h后取出样品,进行吸水性能测试[5]。
2 结果与分析
2.1 海藻生物保水剂吸水倍率
由图1可知,0.5 h时,吸水倍率表现为20190920(<0.9 mm)>20190920(0.9~2.0 mm)>CK保水剂>20190920(2~4 mm),其中前三者在0.5 h的吸水倍率均达100 g/g以上,20190920(<0.9 mm)在0.5 h的吸水倍率高达420 g/g。充分吸水后,保水剂吸水倍率表现为20190920(2~4 mm)>20190920(0.9~2.0 mm)>20190920(<0.9 mm)>CK保水剂。
2.2 海藻生物保水剂吸盐水倍率
由图2可知,吸盐水0.5 h时,保水剂吸盐水倍率表现为20190920(<0.9 mm)>20190920(0.9~2.0 mm)>20190920(2~4 mm)>CK保水剂,其中前两者的吸盐水倍率>30 g/g。充分吸盐水后,吸盐水倍率表现为20190920(0.9~2.0 mm)>20190920(2~4 mm)>20190920(<0.9 mm)>CK保水剂,吸盐水倍率均高于30 g/g。
