Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of sodium fusidate ointment and mupirocin ointment in the treatment of bacteria-infected skin disease
2020-06-12YuanQinQianYi
Yuan Qin ,Qian Yi
1Department of Neurology,Daping Hospital,Army Medical University (Third Military Medical University),Chongqing 400042,China.
Abstract Objective:To evaluate the efficacy and safety of sodium fusidate ointment and mupirocin ointment in the treatment of bacteria-infected skin disease.Methods:The search terms “sodium fusidate ointment”,“mupirocin ointment”,“bacterial infection”,etc.were searched in the database of PubMed,EMbase,Cochrane,Web of Science,Wanfang,VIP,and CNKI.The search time was from inception to November 2019.Randomized controlled trials of sodium fusidate ointment and mupirocin ointment for the treatment of bacteria-infected skin disease were collected.Two studies independently performed literature screening,data extraction,and literature quality evaluation.Meta analysis was performed using RevMan 5.3 software.Results:A total of 14 literature were included,involving 1,825 patients,916 in the experimental group,and 909 in the control group.Meta analysis results showed that the total clinical effective rate of the experimental group (RR=1.12,95% CI (1.06,1.19), P <0.0001),degree of improvement in pruritus score (MD=-1.21,95% CI (-1.78,-0.64), P <0.0001),degree of improvement of eczema area and severity index score (MD=-2.47,95% CI (-3.92,-1.02), P=0.0008),and sensitivity rate of drug sensitivity test (RR=1.35,95% CI (1.24,1.46), P <0.00001) were better than those of control group.The incidence of adverse reactions(RR=0.18,95%CI(0.09,0.39),P <0.00001)was significantly smaller than that of control group.But the bacterial clearance rate (RR=1.22,95% CI (0.98,1.52), P=0.08) compared with the control group,the difference was not statistically significant.Conclusion:Sodium fusidate ointment is better than mupirocin ointment in the treatment of bacteria-infected skin disease,and it helps to improve the severity of disease and itching,and has good safety,which is worthy of clinical promotion.
Keywords:Sodium fusidate ointment,Mupirocin ointment,Bacterial infection,Meta analysis
Background
Bacteria-infected skin disease is a common clinical skin disease.Staphylococcus is the main pathogenic bacteria,which mainly causes skin infection symptoms,such as pustular sores,folliculitis and scabies.Such patients will experience clinical symptoms,such as pain,redness,pus,and so on [1].If patients with this type of disease are not effectively treated in a timely manner,it may lead to lymphadenopathy,fever,etc.,and even cause sepsis and death in severe cases [2].The drugs for clinical treatment of bacteria-infected skin disease are mainly sodium fusidate ointment and mupirocin ointment.However,the clinical efficacy of the two drugs in the treatment of bacteria-infected skin diseases is significantly different.In recent years,although the clinical reports about sodium fusidate ointment and mupirocin ointment on the treatment of bacteria-infected skin disease are increasing,the previous study included a smaller sample size and a longer history.Our study used systematic reviews and meta-analysis to comprehensively evaluate the efficacy and safety of sodium fusidate ointment and mupirocin ointment on bacteria-infected skin disease,in order to provide reference for clinical decision-making.
Materials and methods
Literature search
PubMed,EMBase,Cochrane,Web of Science,Wanfang,VIP,and CNKI were searched from inception to November 2019.Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of the efficacy and safety of sodium fusidate ointment and mupirocin ointment in the treatment of bacteria-infected skin disease were collected.Search terms were “sodium fusidate ointment”,“mupirocin ointment”,“bacterial infection”,and so on.Subject words and free words were combined to search.
Inclusion criteria
Study type.RCT,whether blind or not,language is limited to Chinese and English.
Types of participants.Patients diagnosed with bacteria-infected skin disease through bacterial culture;patients who were allergic to fusidic acid,mupirocin and similar chemical structure were excluded; patients with severe heart,liver,and kidney dysfunction,neurological diseases,mental illness and severe endocrine diseases,were also excluded.
Intervention measures.The experimental group was uniformly applied with sodium fusidate ointment,and the control group was uniformly applied with mupirocin ointment.The patients in the two groups were applied 2 to 3 times a day.Wash the affected area with potassium manganate solution before taking the medicine.
Outcome indicators.(1) Evaluation of clinical symptoms:the patients' clinical symptoms and signs(including erythema,pimples,erosions,and purulent secretions,etc.) were scored before treatment and after 1 week of treatment,respectively; percentage=(total points before treatment-total points after treatment)/total points before treatment × 100%.(2) The clinical effects are divided into cured,markedly effective,effective,and ineffective.Cured patients are defined as the lesion completely disappears,and the bacterial culture is negative; markedly effective patients are those whose lesion tissue is obviously disappeared,the bacterial culture is negative,and the appearance of the lesion is restored ≥70%; effective patients are those with the disappeared lesion tissue and the positive bacteria culture,and the appearance of lesions recovered 30%-70%; invalid patients are defined as the lesion tissue is basically unchanged,bacterial culture was positive,and the appearance of lesions recovered <30%.Total clinical effectiveness=the number of cases (cured+markedly effective +effective)/ total cases × 100%.(3) Itching score:the patient's itching degree is scored,with a total of 0 to 3 points,which represent no itching,occasional itching,continuous itching,strong itching and affecting life,respectively.(4)Eczema area and severity index(EASI)score:EASI is scored according to the severity of bacteria-infected skin diseases.Evaluation content includes some symptoms of clinical skin lesions,such as epidermal shedding,erythema,lichenification,and edema.Zero to three points represent no signs and symptoms,presence of symptoms and signs while need to be carefully checked,clear symptoms and signs,obvious symptoms and signs,respectively.(5)Bacteriological efficacy:the rate of bacterial clearance=(number of positive bacteria before treatment-number of positive bacteria after treatment)/number of positive bacteria before treatment × 100%.(6) Safety assessment:safety assessment is evaluated by the incidence of adverse reactions.
Exclusion criteria
(1) Non-randomized controlled trial; (2) republished research; (3) the data report was incomplete and complete data could not be extracted; (4) the conventional treatment measures of the two groups were inconsistent.
Data extraction
Extraction articles were independently screened by two reviewers.If any objections were resolved through negotiation,refer to the opinions of third parties if necessary.The retrieved documents were imported into the document management software NoteExpress to remove duplicate documents.By reading the title and abstract,documents those didn't meet the inclusion criteria were removed.Then,the full text of the remaining documents were red.Finally,the included documents were determined according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria.The input data includes general information (author,year,sample size,etc.),intervention measures (sodium fusidate ointment and mupirocin ointment usage,dosage,course of treatment,etc.),and outcome indicators (total clinical effectiveness,adverse reaction rate,etc.).
Quality evaluation
According to the bias risk assessment method recommended in the Cochrane Systematic Review Manual 5.1.0,bias risk assessment was conducted for the inclusion of RCTs.Its main items mainly included randomization scheme,group hiding,blind method,incomplete data reporting,selectivity outcome reports,and other sources of bias.Each item was evaluated as“high”,“low”,and “unclear”.The included studies fully met the above entry criteria,suggesting that the risk of bias was minimal and the quality was “A”;some met the above entry criteria partly,suggesting that the risk of bias might be medium and the quality was “B”; if the studies didn't meet the above entry criteria at all,indicating that the risk of bias was high and the quality was“C”.
Statistical analysis
Meta-analysis was performed using RevMan 5.3 software.Binary variables were calculated using relative risk (RR),continuous variables were calculated using mean difference (MD),and 95%confidence interval(CI)was used as statistical analysis.Heterogeneity between studies uses the Q test and I2test.IfP >0.1 or I2<50%,the heterogeneity was considered to be low,and a fixed effect model was used for analysis; ifP≤0.1 or if I2≥50%,the heterogeneity was considered significant,and a random effect model was used to analyze the causes of heterogeneity.All combined results were statistically significant atP<0.05.Funnel plots were used to detect publication bias.
Results
Flow chart of literature search
A total of 106 literature were collected through relevant database searches.After reviewing,reading titles,abstracts and full text,14 papers [3-16] were finally included for meta-analysis.The flow chart of the literature screening is shown in Figure 1.
The basic characteristics
Finally,14 articles [3-16] (1 English article [16] and 13 Chinese articles [3-15])were included in the study,involving 1,825 patients with 916 in the experimental group and 909 in the control group.Among them,14 included literature [3-16] described the the rate of clinical effectiveness and incidence of adverse reactions.Five articles [3,5,9,11,12] described the improvement of itching score.Six articles [3,5,9-12]described the EASI score.There articles [6,8,13]described the rate of drug sensitivity test.Five articles[6,8,13,15,16] were included and described the bacterial clearance rate and the observation time was 7-14 days.Baseline analysis was performed in the included studies,and the baselines were similar and comparable(Table 1).
Results of literature quality evaluation
According to the Cochrane Collaboration's bias risk assessment tool,bias risk assessment was performed on the included literature.The quality of the included literature was average,and the possibility of bias could not be ruled out.Of the 14 literature [3-16] included,only 3 were (TF172) described using random number method,1 paper[4]used envelope lottery method,and the rest of the paper only showed random grouping,without describing the specific allocation method.1 paper [16] described double-blind method,and the other papers were not mentioned subjects or outcome evaluators were blinded.The included outcome data were complete and there were no selective reporting results.Among them,5 articles with a quality of “A”[3,4,8,11,14] and 8 articles with a quality of “B”were included (TF176),one of the quality “C” [10](Figure 2).
Meta analysis results
The clinical total effective rate.The 14 literatures[3-16] included in the clinical total effectiveness meta-analysis were heterogeneous (P<0.00001,I2=74%),and a random effect model was used for meta-analysis.The results showed that the clinical total effective rate in sodium fusidate ointment group was significantly higher than that in the control group,and the difference between the two groups was statistically significant (RR=1.12,95% CI (1.06,1.19),P<0.0001)(Figure 3).
Incidence rate of adverse reactions.Reaction rates included 14 articles [3-16] with no statistically significant heterogeneity (P=0.98,I2=0%),and a fixed-effects model was used.Meta-analysis results showed that the incidence of adverse reactions in the sodium fusidate ointment group was significantly smaller than that in the mupirocin ointment group,and the difference was statistically significant (RR=0.18,95%CI(0.09,0.39),P <0.00001)(Figure 4).
Itching scores.Five literatures [3,5,9,11,12] were included with significant heterogeneity (P<0.00001,I2=98%),and a random effects model was used.Meta-analysis results showed that the improvement of itching score in sodium fusidate ointment group was significantly greater than that of mupirocin ointment group,and the difference was statistically significant(MD=-1.21,95% CI (-1.78,-0.64),P<0.0001)(Figure 5).
EASI score.Six literatures [3,5,9-12] were included with obvious heterogeneity (P<0.00001,I2=97%),and a random effect model was used.Meta analysis results showed that the degree of EASI score improvement of sodium fusidate ointment was significantly greater than that of mupirocin ointment group,and the difference was statistically significant(MD=-2.47,95% CI (-3.92,-1.02),P=0.0008)(Figure 6).
Drug susceptibility test.There articles [6,8,13]were included and the heterogeneity among the studies was not statistically significant (P=0.39,I2=0%),and a fixed effect model was used.Meta analysis results showed that the rate of the susceptibility test of the sodium fusidate ointment group was significantly greater than that of mupirocin ointment group,and the difference is statistically significant (RR=1.35,95%CI(1.24,1.46),P <0.00001)(Figure 7).
The bacterial clearance rate.Five literatures[6,8,13,15,16]were included with obvious heterogeneity (P<0.00001,I2=93%),and a random effect model was used.Meta-analysis results showed that sodium fusidate ointment the bacterial clearance rate was not statistically significant compared with the mupirocin ointment group (RR=1.22,95% CI (0.98,1.52),P=0.08)(Figure 8).
Publication Bias
RevMan 5.3 software was used to draw an inverted funnel plot for the clinical outcomes of the main outcome indicators to perform a publication bias test,as shown in Figure 9.Each research point was basically symmetrically distributed around,and most of the data points were located at the top of the funnel plot,but some data point outliers and individual scattered inside the funnel chart,suggesting the possibility of publication bias.It may be considered that the quality of the included literature was not high,and the negative result test had not been published.
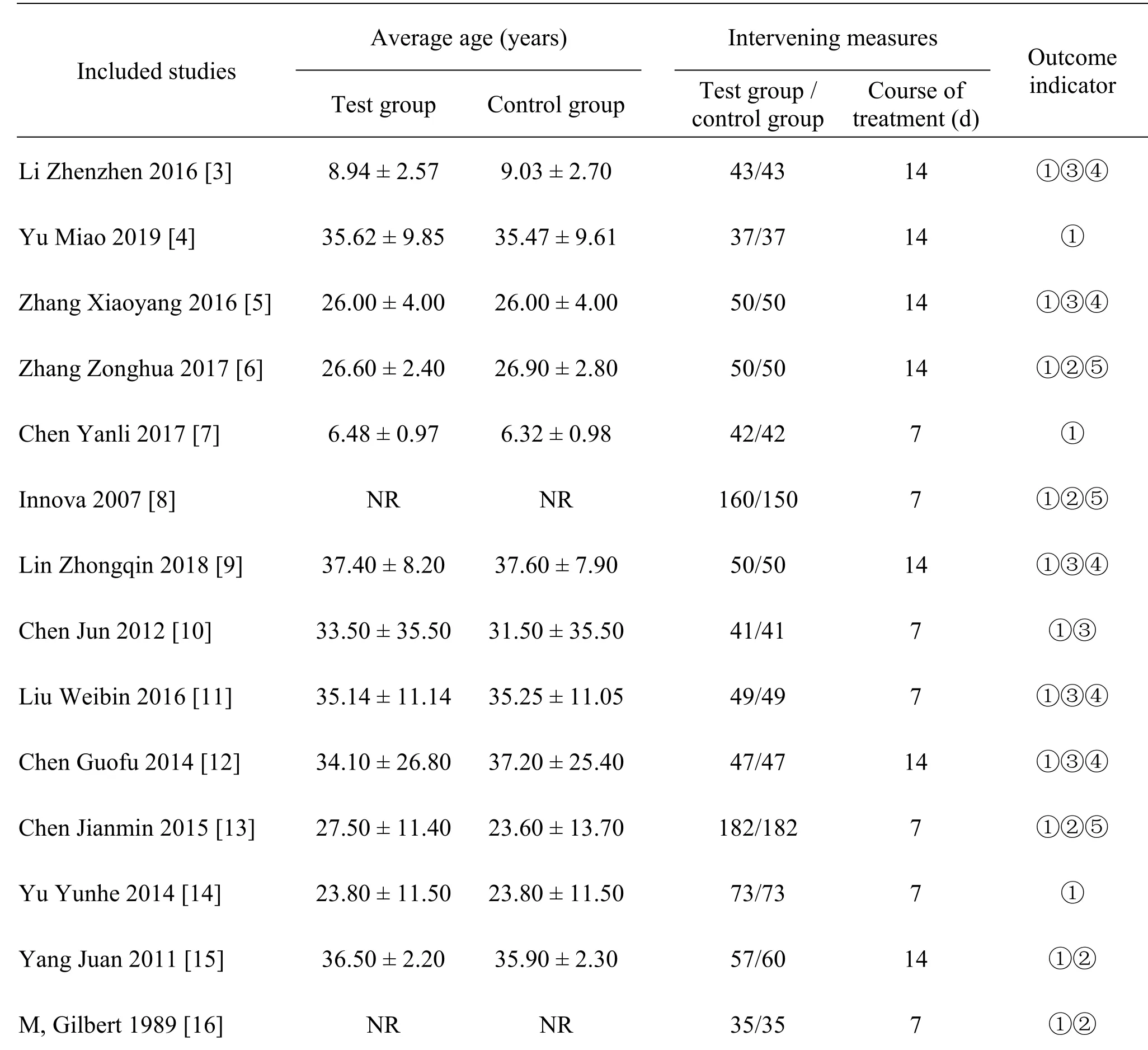
Table 1 Basic information table of included literature
Discussion
Bacteria-infected skin diseases mainly include primary bacterial infectious skin diseases and secondary bacterial infectious skin diseases.They are caused by a single bacterium and occur on normal skin.They are called primary bacterial infectious skin diseases.Infections on existing diseased skin are called secondary bacterial skin infections [17].With the widespread application of antibiotics,the increase of resistant strains has led to an upward trend in patients with bacterial infectious skin diseases [18].Streptococcus and staphylococcus are the main pathogenic bacteria,which are highly toxic and easily penetrate into the skin of patients.Once invaded,they can easily cause diseases such as folliculitis,abscess and paronychia,if they penetrate deep skin tissues medium,it is easy to cause erysipelas,and severe cases can cause rheumatoid arthritis and nephritis,which seriously threaten patients' health and quality of life[19].Mupirocin ointment is a spectrum antibacterial drug with a wide range of effects,but the long-term effect is not obvious.Sodium fusidate ointment is a high-efficiency,narrow-spectrum antibiotic,which is contained in the fermentation liquid of fusidic acid lipid balls.Made by extraction,it has strong sensitivity in bacteriostasis,and it is ideal for sterilizing anaerobic bacteria such as Gram bacteria,Corynebacterium,Staphylococcus epidermidis,and sodium fusidate ointment has strong penetrability and can penetrates deep into the skin to remove bacteria quickly and effectively[20].
The results of this study show that in terms of clinical effectiveness,the clinical effectiveness of sodium fusidate ointment is significantly higher than that of mupirocin ointment,and the difference is statistically significant,compared with Ye Xia[21]and other research results are consistent.In terms of the degree of improvement in the EASI score and itching degree score,before treatment,patients in the sodium fusidate ointment group and patients in the mupirocin ointment group were compared with each other in terms of the EASI score and itching degree score significance.After treatment,the improvement of the EASI score and itching score of the patients in the sodium fusidate ointment group was significantly better than that in the mupirocin ointment group.The gap was statistically significant,suggesting that the sodium fusidate ointment in the clinical symptoms and signs of patients In terms of improvement,it is better than mupirocin ointment.In the sensitivity rate of the susceptibility test,the sensitivity rate of the sodium fusidate ointment group is significantly greater than that of the mupirocin ointment group,the difference is statistically significant,suggesting that the sodium fusidate ointment The antibacterial effect is obvious.In addition,in terms of the incidence of adverse drug reactions,the incidence of adverse reactions in the sodium fusidate ointment group is significantly smaller than that of the mupirocin ointment group,the difference is statistically significant,and the adverse reactions in the two groups are local itching.Burning sensation,no serious adverse reactions,can be relieved on its own,suggesting that sodium fusidate ointment is safer.However,in terms of bacterial clearance rate,there is no statistical difference between the sodium fusidate ointment group and the mupirocin ointment group .This may be related to the small sample size of the included studies.
From the search results of this meta-analysis,there are certain limitations in this study.(1)This study only retrieved Chinese and English literature,and literature in other languages were not included,and there may be language bias.(2) Clinical studies abroad in recent years there are few randomized controlled studies,and most of the domestic study designs are of low quality and lack of rigor.The meta-analysis is heterogeneous.Due to the limited data provided in the included literature,further analysis is not possible.(3) Include the literature of this meta-analysis five articles of grade“A”[3,4,8,11,14],eight articles of grade“B”[5-7,9,12,13,15,16],one article of grade “C” [10],there are documents of grades B and C of varying degrees bias.
In summary,sodium fusidate ointment has good clinical efficacy in treating bacterial infectious skin diseases,and rarely has adverse reactions.The adverse reactions are mainly mild local itching and burning sensation,which can usually be relieved by itself without the need for withdrawal of the drug.If severe irritation or allergic reactions occur,the drug should be stopped and replaced with other appropriate drugs.However,due to the low quality of the included literature and the publication bias,large-scale and high-quality RCTs are still needed for further confirmation.
杂志排行
Clinical Research Communications的其它文章
- Insight into the post-hospital syndrome
- Optimal cut-off and assessment of survival days are needed in risk factors for COVID-19 mortality
- Visual analysis of advance care planning related studies
- Traditional Chinese medicine treatment of immune-related pneumonia caused by PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors
- Research progress of acupuncture in the treatment of Parkinson's disease
