三支概念分析中的粒与知识结构
2020-04-29魏玲赵思雨
魏玲 赵思雨


摘要:三支概念分析是将三支决策思想引入形式概念分析产生的进行数据分析与知识发现的新工具。文中用三支决策思想从知识内涵角度阐述三支概念分析中的基本概念,进而用粒计算思想分别从对象和属性两个角度刻画三支概念分析的知识结构,最后将DIKW体系用于三支概念分析,给出三支概念分析的D-I-K/W漏斗模型。
关键词:三支概念分析;形式概念分析;三支决策;粒计算;DIKW体系
中图分类号:O29;TP18
DOI:10.16152/j.cnki.xdxbzr.2020-04-004开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID):
Granules and knowledge structure in three-way concept analysis
WEI Ling1,3, ZHAO Siyu1,2,3
(1.School of Mathematics, Northwest University, Xi′an 710127, China;
2.College of Mathematics and information Science, Xianyang Normal University, Xianyang 712000, China;
3.Institute of Concepts, Cognition and Intelligence, Northwest University, Xi′an 710127, China)
Abstract: Three-way concept analysis is a new tool for data analysis and knowledge discovery by introducing three-way decision into formal concept analysis. This paper expounds the basic concepts of 3WCA with 3WD thought from the perspective of knowledge intension. Then it describes the knowledge structure of 3WCA with granular computing from two perspectives of object and attribute. Finally, the DIKW hierarchy is applied to 3WCA, and the D-I-K/W funnel model of 3WCA is given.
Key words: three-way concept analysis; formal concept analysis; three-way decision; granular computing; DIKW hierarchy
形式概念分析理论(formal concept analysis,FCA)由德国数学家Wille于1982年提出[1]。FCA以包含对象集、属性集及二者二元关系的形式背景为基础,刻画了对象子集与属性子集间“共同具有”的关系,进而形成内涵与外延,形式化的完美表达了哲学中的正概念[2]。目前,形式概念分析在属性约简、规则获取、决策分析、数据挖掘等方面有很好的研究成果和应用[3-6]。
将三支决策理论(three-way decisions,3WD)[7]中的三分思想引入形式概念分析,Qi等提出了三支概念分析(three-way concept analysis,3WCA)[8]。Qi等在形式背景上定义负算子,并构造三支算子,将对象集或属性集三分,形成三支概念与三支概念格。负算子刻画了对象子集与属性子集间“共同不具有”的关系,其语义及运算方式与FCA中补背景的正算子吻合,同时也形式化的表达了哲学中的负概念。三支概念分析自2014年提出以来,得到了广泛认可,在基础理论研究[9-12]、三支概念格构造[13-15]、规则提取[16]、概念学习[17-18]、模糊三支概念分析[19]、不完备三支概念获取[20]及实际应用[21]等方面取得了诸多研究成果。
粒计算(granular computing,GrC)是由Zadeh于1979年提出的模糊信息粒发展而来的理论[22],强调研究背景与问题的粒化与层次分析,并在此基础上解决问题。目前许多学者将粒计算与形式概念分析结合,得到了丰富的研究成果[23-26]。Qi等基于形式背景从不同角度提出了5种粒,并研究了5种粒之间的关系,进而给出形式概念分析中的粒链条与粒层级[27]。这些粒在层次角度和语义角度都有所不同。这种研究方法对于从粒计算的角度解读三支概念分析很有借鉴意义。
数据-信息-知识-智慧(DIKW)体系是信息科学、计算机科学、管理科学、心理学、认知科学、哲学等诸多学科的基本概念之一[28-31]。数据、信息、知识、智慧之间的关系微妙而紧密,没有明确的界限。Yao结合三支决策的思想,将信息作为弱知识,给DIKW体系一个三层解释:D-I/K-W模型[32]。在三支概念分析中,形式背景是数据的一种载体,以数据为基础,可以从DIKW体系的角度对三支概念分析进行认知学习。
本文主要從三种不同的角度对三支概念分析进行认识学习。首先是三支决策的角度,用三分的思想解读三支概念分析;其次是粒计算的角度,从不同语义出发提出5种粒并研究其关系;最后是DIKW体系角度,利用DIKW模型分析三支概念分析,并给出适于3WCA的D-I-K/W模型。
4 认知漏斗——知识获取角度
根据现代知识体系形成的相关理论,数据经过整理成为信息,信息经过系统化成为知识,而知识是智慧的源泉。这就是著名的DIKW(Data-to-Information-to-Knowledge-to-Wisdom)理论。这一体系关于数据、信息、知识、智慧之间的层次递进在信息科学、计算机科学、认知科学、哲学等诸多学科中得到了普遍认可[28-31]。
在DIKW體系中,数据作为一些事实的集合,本身并不能表现出任何意义,只有当通过某种方式对数据进行组织和分析时,才成为有意义的信息。信息经过筛选、综合等系统化处理,上升为可以解决较为复杂问题的知识。而智慧是对知识的有效利用,关注的是事物发展的未来。
DIKW体系一般以如图8所示的金字塔模型呈现。最底层的数据是金字塔庞大的基石,而智慧则是其顶端相当小的一部分。自下而上看金字塔,体现的是复杂性、抽象性、意义与价值的提升。
Rowley将金字塔模型颠倒,给出了DIKW体系的漏斗模型[28]。漏斗模型可以更加生动的体现数据逐渐集中、提炼、凝缩,成为有价值的智慧的过程。
然而,在人们的认知当中,由于数据、信息、知识及智慧四个层次中任何两个相邻级别之间可能不存在明确的边界,故其定义或解释并没有绝对一致的看法。至于DIKW 体系分为几层合适,也没有固定的说法。比如,有数据-信息-知识的三层结构DIK模型[28],也有数据-信息-知识-理解-智慧这样的五层结构[30]。但是,复杂的结构虽然会提供更为详细的信息或更为细节化的描述,却也会增加理解的难度。数据、信息及知识、智慧之间的分离是存在一致性的,而信息在某种角度可以被看作是一种弱知识[31]。因此,Yao基于三支决策理论认为,三层是最基本的结构,他将信息与知识合并,给出了如图9所示的DIKW的三层解释:D-I/K-W模型[32]。
在3WCA中,形式背景、三支概念(格)及规则(决策)是三个基本概念。将原始数据以二维表的形式储存在形式背景中,包括一些具体的对象、属性及二者之间的二元关系,是数据层面。通过对形式背景的学习,可得到具体的三支概念及由三支概念构建的三支概念格,这是对原始数据进行了挖掘和提炼,获得的初步认识,是信息层面。最终由这些概念,可学习出规则、决策,是可以应用的知识和智慧层面。
由此,研究认为,在3WCA框架下,知识与智慧之间的区别难以界定,D-I-K-W漏斗模型更接近D-I-K/W漏斗模型。从这一角度来说,DIKW体系可被理解为如图10所示的D-I-K/W三层结构。虽然这种理解不同于Yao的D-I/K-W漏斗模型呈现的语义,但这种三层结构其本质仍是三支决策理论在3WCA认知层次上的一种呈现。
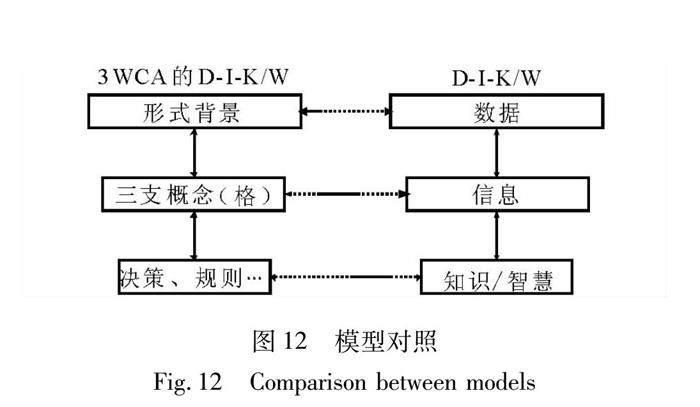
针对3WCA的D-I-K/W漏斗模型可具体表达为如图11所示的形式。图12则给出一般D-I-K/W模型与3WCA框架下具体模型之间的对应关系。
5 结 语
三支概念分析将三支决策的思想引入形式概念分析,是对形式概念分析的扩展,也是三支决策理论的一个具体模型。本文首先基于三支决策,从知识内涵的角度阐述三支概念格中的三分;其次基于粒计算,从知识结构的角度提出3WCA上的五种粒,研究其关系;最后基于DIKW体系,从知识获取的角度对3WCA进一步认知,给出3WCA自身的D-I-K/W漏斗模型。
3WCA的产生,隐含了大量的研究课题。如,如何更进一步将3WCA与三支决策理论、粒计算、认知科学等进行交叉研究,都是3WCA研究领域内富含理论意义与研究价值的新问题。
3WCA的研究尚在起步阶段,期待对这一研究方向感兴趣的同行学者提出并解决更多的新问题,共同推动了3WCA的研究。
参考文献:
[1] WILLE R. Restructuring lattice theory: An approach based on hierarchies of concepts [C]∥RIVAL I.Ordered Sets.Dordrecht-Boston:Reidel,1982: 445-470.
[2] 金岳霖. 形式逻辑[M]. 北京: 人民出版社, 1979.
[3] 张文修, 魏玲, 祁建军. 概念格的属性约简理论与方法 [J].中国科学E辑: 信息科学, 2005, 35(6): 628-639.
ZHANG W X,WEI L,QI J J.Attribute reduction theory and approach to concept lattice[J].Science in China Series F:Information Science,2005,48(6):713-726.
[4] SHAO M W, LEUNG Y, WU W Z. Rule acquisition and complexity reduction in formal decision contexts [J]. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning, 2014, 55(1): 259-274.
[5] LI J H, REN Y, MEI C L, et al. A comparative study of multigranulation rough sets and concept lattices via rule acquisition [J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2016, 91: 152-164.
[6] LI W, WEI L. Data dimension reduction based on concept lattices in image mining [C]∥Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery, 2009: 369-373.
[7] YAO Y Y. Three-way decision: An interpretation of rules in rough set theory [C]∥WEN P, LI Y, POLKOWSKI L, et al.Rough Sets and Knowledge Technology (Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 5589).Gold Coast, Australia, 2009: 642-649.
[8] QI J J, WEI L, YAO Y Y. Three-way formal concept analysis[C]∥MIAO D Q, PEDRYCZ W, SLEZAK D, et al.Rough Sets and Knowledge Technology (Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 8818).Shanghai, China, 2014: 732-741.
[9] QI J J, QIAN T, WEI L. The connections between three-way and classical concept lattices [J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2016, 91: 143-151.
[10]REN R S, WEI L. The attribute reductions of three-way concept lattices [J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2016, 99: 92-102.
[11]YU H Y, LI Q G, CAI M J. Characteristics of three-way concept lattices and three-way rough concept lattices [J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2018, 146: 181-189.
[12]魏玲, 高乐, 祁建军. 三支概念分析研究现状与展望[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 49(4): 527-537.
WEI L, GAO L, QI J J. Review and outlooks of three-way concept analysis [J].Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 49(4): 527-537.
[13]祁建军, 汪文威. 多线程并行构建三支概念 [J].西安交通大学学报, 2017, 51(3): 116-121.
QI J J, WANG W W. A multithreaded parallel algorithm for constructing three-way concepts[J].Journal of Xi′an Jiaotong University, 2017, 51(3): 116-121.
[14]QIAN T, WEI L, QI J J. Constructing three-way concept lattices based on apposition and subposition of formal contexts [J].Knowledge-Based Systems, 2017, 116: 39-48.
[15]王明, 魏玲. 基于K-Modes聚類的OE-概念格压缩 [J]. 模式识别与人工智能, 2018, 31(8): 704-714.
WANG M, WEI L. OE-concept lattice compression based on K-modes clustering [J].Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2018, 31(8): 704-714.
[16]WEI L, LIU L, QI J J, et al. Rules acquisition of formal decision contexts based on three-way concept lattices[J]. Information Sciences, 2020, 516: 529-544.
[17]LI J H, HUANG C C, QI J J, et al. Three-way cognitive concept learning via multi-granularity [J]. Information Sciences, 2017, 378(1): 244-263.
[18]HUANG C C, LI J H, MEI C L, et al. Three-way concept learning based on cognitive operators: An information fusion viewpoint [J]. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning, 2017, 83:218-242.
[19]HE X L, WEI L, SHE Y H. L-fuzzy concept analysis for three-way decisions:Basic definitions and fuzzy inference mechanisms [J]. International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics, 2018, 9(11): 1857-1867.
[20]YAO Y Y. Interval sets and three-way concept analysis in incomplete contexts [J]. International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics, 2017, 8(1): 3-20.
[21]YAO Y Y. Three-way conflict analysis: Reformulations and extensions of the Pawlak model [J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2019, 180: 26-37.
[22]ZADEH L A. Toward a theory of fuzzy information granulation and its centrality in human reasoning and fuzzy logic [J]. Fuzzy Sets and Systems,1997,90(2):111-127.
[23]苗夺谦,王国胤,刘清等. 粒计算: 过去、现在与展望[M]. 北京: 科学出版社,2007.
[24]智慧来, 李金海. 基于必然属性分析的粒描述[J].计算机学报, 2018, 41(12): 68-85.
ZHI H L, LI J H. Granule description based on necessary attribute analysis[J].Chinese Journal of Computers, 2018, 41(12): 68-85.
[25]WU W Z, LEUNG Y, MI J S. Granular computing and knowledge reduction in formal contexts [J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2009, 21(10): 1461-1474.
[26]李金海, 吳伟志. 形式概念分析的粒计算方法及其研究展望[J].山东大学学报(理学版), 2017(7): 1-12.
LI J H, WU W Z. Granular computing approach for formal concept analysis and its research outlooks[J].Journal of Shandong University(Natural Science), 2017(7): 1-12.
[27]QI J J, WEI L, WAN Q. Multi-level granularity in formal concept analysis[J]. Granular Computing, 2019, 4 (3): 351-362.
[28]ROWLEY J. The wisdom hierarchy:Representations of the DIKW hierarchy[J].Journal of Information Science, 2007, 33(2):163-180.
[29]ZELENY M. Management support systems:Towards integrated knowledge management[J]. Human Systems Management, 1987,7(1):59-70.
[30]ACKOFF R L. From data to wisdom[J]. Journal of Applied Systems Analysis, 1989, 16:3-9.
[31]FRICK M. The knowledge pyramid:A critique of the DIKW hierarchy[J].Journal of Information Science, 2009, 35(2):131-142.
[32]YAO Y Y. Tri-level thinking: Models of three-way decision[J]. International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics, 2020, 11(5): 947-959.
[33]DAVEY B A, PRIESTLEY H A. Introduction to lattices and order[M].Cambridge:Cambridge University Press, 2002.
(编 辑 张 欢)
作者简介:
魏玲,西北大学数学学院三级教授,博士生导师。西北大学概念、认知与智能研究中心主任,中国人工智能学会粒计算与知识发现专业委员会常务委员、知识工程与分布智能专业委员会委员。曾在香港中文大学、加拿大里贾那大学进行访问研究。主要从事形式概念分析、粗糙集理论、三支决策理论等方面的研究与教学工作。先后主持国家自然科学基金青年项目与面上项目4项,获陕西高等学校科学技术一等奖1项,合作出版著作两部。在《中国科学》,IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics等国内外期刊和国际会议发表论文70余篇,其中ESI高被引论文2篇,论文曾获2007 年“中国百篇最具影响国内学术论文”及2016 年中国科学杂志社“十年经典文章”。
