基于动作单元的机电产品故障溯源诊断方法
2020-04-17鞠萍华柯磊冉琰王治超张威
鞠萍华 柯磊 冉琰 王治超 张威

摘 要:针对故障在复杂机电产品中传递发展的特点,提出了一种基于动作单元的机电产品故障溯源诊断方法. 按照“功能-运动-动作”对整机功能进行结构化分解得到基本的动作单元,并分析动作单元之间的传递过程;在此基础上建立以动作单元和故障现象为节点的贝叶斯网络模型,利用贝叶斯网络的推理算法,计算各个节点的发生概率并追溯最大概率路径,实现动作层的故障动作单元诊断及故障动作单元传播过程诊断;利用故障图对动作单元内部的故障模式及其传递发展过程进行描述,找到引起动作单元故障的根本原因. 通过对机电产品动作层和动作单元内部的诊断分析,实现故障现象到故障原因的溯源诊断. 将所提出的溯源诊断方法应用到某企业数控转台故障诊断中,结果表明,从运动的角度进行故障溯源诊断,能够有效地诊断出故障动作单元及其传播过程并反映出动作单元内部元件故障的传递发展过程,便于找到导致故障的根本原因,提高了对机电产品故障诊断的效率.
关键词:溯源诊断;结构化分解;动作单元;贝叶斯网络;故障图
中图分类号:TH165 文献标志码:A
Abstract:Aiming at the characteristic of the transmission and development of fault in complex electro-mechanical products,a method of fault root causes tracing analysis for electro-mechanical products based on action unit was proposed. Firstly,the transfer process between action units was analyzed after the basic action unit was obtained by structuring decomposition of the whole machine function which was “function-motion-action”. Then a Bayesian network model was established based on action unit and fault phenomenon,and combined with reasoning algorithm of Bayesian networks to calculate the occurrence rate of each node and trace the maximum probability path to diagnose the fault action unit and its propagation process at the motion level. To find out the root cause of the failure of the action unit,the fault graph was used to describe the failure model of fault action unit and its transfer and development process. The trace diagnosis from the fault phenomenon to the fault cause can be realized through the diagnosis and analysis at action layer and in the interior of action unit of complex electro-mechanical products. Finally,the method of fault root causes tracing analysis based on action unit was used to deal with the root cause of the NC rotary table of some machining center,the results show that the proposed traceability diagnosis method can effectively diagnose the fault action unit and its propagation process,and reflect the transmission and development process of the internal components of the action unit from the angle of motion,which is convenient to find out the root cause of the fault and improve the efficiency of fault diagnosis for electro-mechanical products.
Key words:root causes tracing analysis;the structural decomposition;action unit;Bayesian networks;fault graph
機电产品从投入运行到损坏的整个过程中,由于系统的复杂性,其状态变化呈现出模糊不确定的特点[1-2],这一特点增加了对机电产品故障进行准确诊断的难度. 如何在具有模糊不确定性特点的状态变化过程中,准确快速地诊断出机电产品故障的原因,尽快恢复生产,已成为学术界和工业界关注的焦点[3].
2.1.2 基于动作单元的贝叶斯网络建模及推理
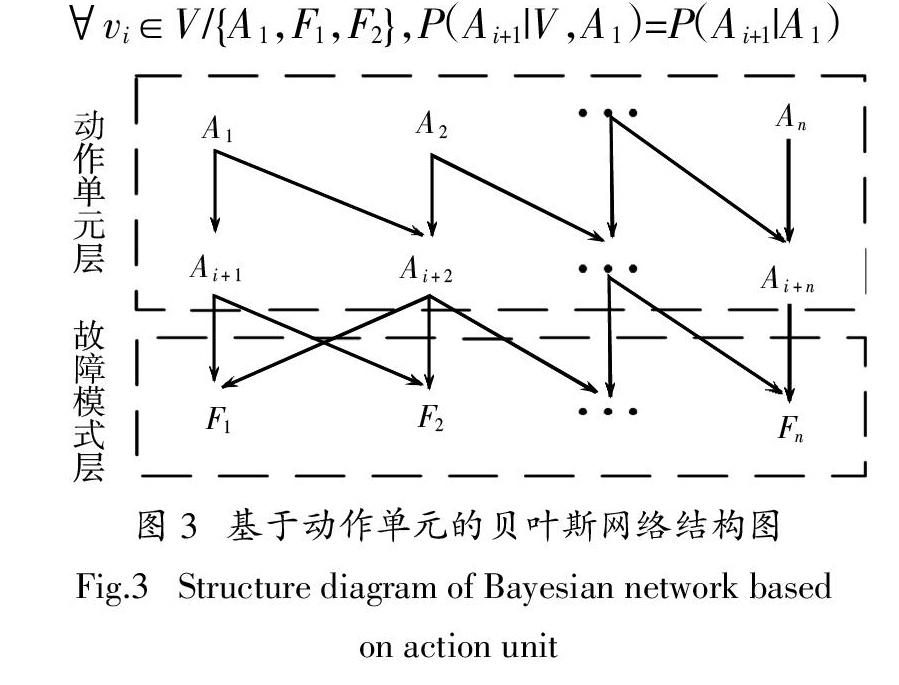
以动作单元和故障现象为节点,建立基于動作单元的贝叶斯网络图. 如图3所示,A表示动作单元;An为Ai+n父节点,表示为An出现故障时,可能会导致Ai+n发生故障;F表示故障现象;Ai+n为Fn的直系父节点,表示出现某一故障现象Fn可能由动作单元Ai+n引起. 在图3的动作单元贝叶斯网络结构图中,满足如下假设:给定节点Xi条件独立于在其父节点给定后的任意非Xi子代任意节点,如节点Ai+1,在给定其父节点A1时,节点Ai+1条件独立于除F1、F2外的其他任意节点[19],表示为:
当建立好图3所示动作单元的贝叶斯网络之后,结合图2,对故障动作单元进行推理,思路和步骤如下:
步骤1 确定故障现象、运行工况及统计数据作为诊断证据,结合领域专家知识确定出动作单元发生故障的先验条件.
步骤2 计算动作单元发生故障的后验概率,包括单个动作单元的后验概率和多个动作单元组合的后验概率情况.
步骤3 确定最大后验概率并通过最大后验概率追溯最大概率路径,诊断出导致故障发生的动作单元及其传递影响路径.
2.2 基于动作单元的故障图分析
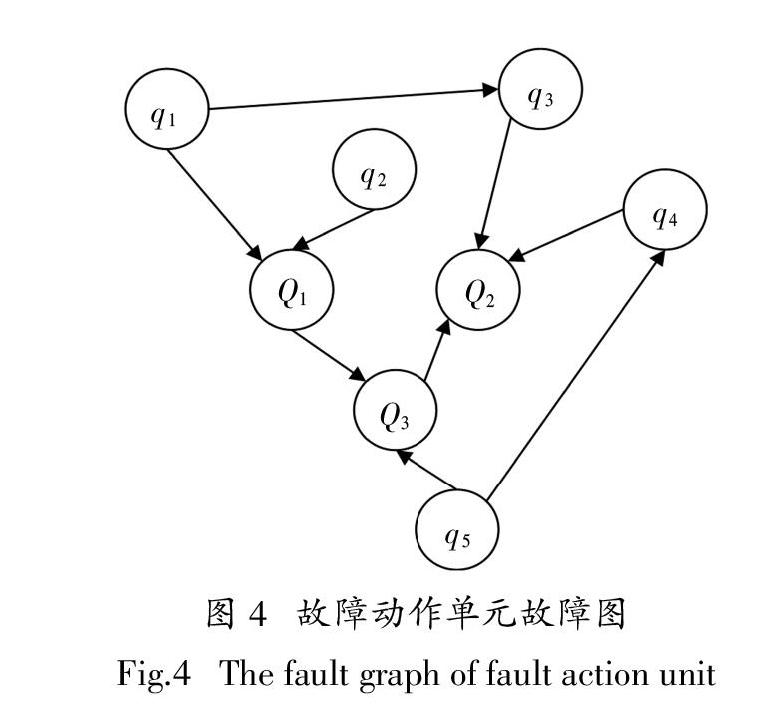
通过2.1节的诊断分析,得到故障动作单元及其传递路径. 为了诊断出故障的根本原因,还需要对导致动作单元故障的原因进行分析. 故障图能够反映出节点之间的层次关系和传递关系,因此本文利用故障图对故障动作单元层内部的故障传递发展进行描述. 如图4所示,Q1、Q2、Q3为故障动作单元的故障模式;q1、q2、q3、q4、q5为故障基本事件,通过该图可以判断出故障模式及故障传递和发展的过程,从而分析出影响单元故障的基本事件,找到导致故障发生的根本原因,完成故障溯源诊断.
3 实例分析
以某机床的数控转台故障诊断为例,建立基于动作单元的故障溯源诊断模型,对文中提出的溯源诊断方法进行应用说明.
3.1 动作单元的构建
对某型号加工中心的数控转台进行结构分解,得到整机的最小动作单元,分解结构如图5所示. 由图5可知,转台分度功能和性能需要转台升降运动、转台回转运动、托板夹紧松开运动正常工作来保证. 转台回转运动要正常工作,需要蜗杆转动单元、涡轮转动单元、回转体转动单元按照顺序正常动作;托板夹紧松开运动需要活塞移动单元、拉爪移动单元、顶杆移动单元按照顺序正常动作. 任一动作单元出现故障,就会导致转台分度功能和性能得不到保障,便会以某种故障现象表现出来.
3.2 动作单元贝叶斯网络
根据实验记录及售后记录,得到该型号机床数控转台的故障模式如表1所示. 这些故障模式可能单个存在,也可能同时存在. 由于组成动作单元的任一零件故障会导致动作单元不能正常动作,在这里将动作单元不能正常动作归为动作单元故障.
结合分解得到的动作单元和故障模式之间及动作单元与动作单元之间的相关关系,建立网络结构图,如图6所示.
结合企业的数据和领域专家确定出先验概率,并计算后验概率、建立贝叶斯网络概率表,如表2所示.
3.3 故障动作单元推理诊断
某次故障中,该数控转台的工作台发生倾斜(F4),以此为例,对引起该现象可能的动作单元进行推理诊断. 导致该现象发生的直接动作单元是A4、A6动作单元. 而导致A4动作单元不能正常动作的原因是自身或A3动作单元引起,A3动作单元不能正常动作的原因是由自身或A2动作单元引起;A6动作单元不能正常动作的原因由自身或A5或A7动作单元引起. 利用表2数据计算在工作台发生倾斜情况下的相关动作单元的后验概率,最大概率路径即为诊断结果,如表3所示.
3.4 动作单元的故障图
由表3可以得出,导致F4故障发生的动作单元为A6,而导致A6动作单元不能正常动作的是A5动作单元. 根据分析得到动作单元的传递影响路径为A5-A6-F4 . 为了分析A5、A6动作单元之间的故障传递发展过程,现基于A5、A6动作单元进行故障图分析,分别如图7和表4所示.
3.5 基于动作单元的故障溯源推理
通过前文的分析,结合图5、6、7和表4的分析,得出:该数控转台出现工作台倾斜这一故障现象的直接原因是动作单元A6出现故障不能正常动作,而动作单元A6出现不能正常动作的原因除了自身外,还来自于A5动作单元的影响,因此需要重点对A5、A6动作单元进行检查. 经检查发现A6动作单元出现无动作(M9)的情况(正常状况下应该有松开动作),但是拉爪并未损坏;根据图7对动作单元内部故障传递发展的描述进行相关排查,发现活塞无动作(M2)并且活塞外部有液压油渗出(M4),因此对活塞进行拆解,发现其密封圈已经损坏(f2),和实际情况相符.
4 结 论
根据故障在复杂机电产品中的传递发展特点,对整机进行结构化分解得到最基本的动作单元. 在此基础上,先建立以动作单元为节点的贝叶斯诊断模型在动作层对故障动作单元及其传递影响过程进行诊断;接着建立故障图对动作单元内部的故障传递发展进行描述,通过对动作层和动作单元内部故障发展过程的刻画和推理诊断,为找出故障的根本原因提供了方向,能够较快地实现故障现象到故障根本原因的溯源,对消除产品故障,提高产品运行效率具有重要意义.
参考文献
[1] 孙秋冬,郭维芹,周政新. 发电机绝缘故障模糊诊断专家系统的设计[J]. 电力系统自动化,2006,30(23):94—96.
SUN Q D,GUO W Q,ZHOU Z X. Fuzzy expert system design for insulation fault diagnosis in generator[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems,2006,30(23):94—96.(In Chinese)
[2] 楊苹,吴捷,冯永新. 200 MW汽轮发电机组振动故障的模糊诊断系统[J]. 电力系统自动化,2001(1):45—49.
YANG P,WU J,FENG Y X. Fuzzy fault diagnosis system for a 200 MW turbo-generator set[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems,2001(1):45—49.(In Chinese)
[3] 雷亚国,贾峰,孔德同,等. 大数据下机械智能故障诊断的机遇与挑战[J]. 机械工程学报,2018,54(5):94—104.
LEI Y G,JIA F,KONG D T,et al. Opportunities and challenges of machinery intelligent fault diagnosis in big data era[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2018,54(5):94—104.(In Chinese)
[4] 张家良,曹建福,高峰,等. 基于非线性频谱数据驱动的动态系统故障诊断方法[J]. 控制与决策,2014,29(1):168—171.
ZHANG J L,CAO J F,GAO F,et al. Fault diagnosis approach of dynamic system based on data driven of nonlinear spectrum[J]. Control and Decision,2014,29(1):168—171.(In Chinese)
[5] BOUCHACHIA A. Adaptive computational intelligence for dynamical system[C]//Intelligence for Nonlinear Dynamics and Synchronization. France,Atlantis:Atlantis Press,2010:3—20.
[6] 任岩,毕亚雄,王德宽,等. 风电机组传动链的故障树智能诊断技术[J]. 排灌机械工程学报,2016,34(4):328—331.
REN Y,BI Y X,WANG D K,et al. Fault tree intelligent diagnosis technology for wind turbine drivetrain[J]. Journal of Drainage and Irrigation Machinery Engineering,2016,34(4):328—331.(In Chinese)
[7] 姜万录,刘思远. 多特征信息融合的贝叶斯网络故障诊断方法研究[J]. 中国机械工程,2010,21(8):940—945.
JIANG W L,LIU S Y. Fault diagnosis approach study of Bayesian networks based on multi-characteristic information fusion[J]. Chinese Mechanical Engineering,2010,21(8):940—945.(In Chinese)
[8] 李宏梅,佟为明,程树康. 基于贝叶斯网络的信息融合汽车网络故障诊断方法[J]. 汽车工程,2015,37(10):1190—1194.
LI H M,TONG W M,CHEN S K. Fault diagnosis method of automotive Network with Bayesian network-based Information Fusion [J]. Automotive Engineering,2015,37(10):1190—1194. (In Chinese)
[9] 李金艳,余忠华,徐宣国. 信息不完备情况下多因素工序质量诊断方法[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报,2016,48(7):88—93.
LI J Y,YU Z H,XU X G. Diagnosis method of multi-cause process quality under incomplete information[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology,2016,48(7):88—93. (In Chinese)
[10] 王瑛,李菲. 基于集成权重和贝叶斯模型的科技奖励评价[J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版),2016,43(7):151—156.
WANG Y,LI F. Evaluation of science and technological achievements based on integrated weight and Bayesian network[J]. Journal of Hunan University(Natural Sciences),2016,43(7):151—156.(In Chinese)
[11] 陳东宁,姚成玉. 基于模糊贝叶斯网络的多态系统可靠性分析及在液压系统中的应用[J]. 机械工程学报,2012,48(16):175—183.
CHEN D N,YAO C Y. Reliability analysis of multi-state system based on fuzzy Bayesian networks and application in hydraulic system[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2012,48(16):175-183.(In Chinese)
[12] 宋志平,李应红,屈裕安. 描述复杂系统故障关系的条件故障图[J]. 系统工程与电子技术,2003,25(1):116—118.
SONG Z P,LI Y H,QU Y A. Conditional trouble graph for describing fault relation of a complex system[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics,2003,25(1):116—118.(In Chinese)
[13] 刘勇,蒲树祯,曹泽翰,等. 基于故障图模型的故障诊断方法研究[J]. 小型微型计算机系统,2006,27(9):1741—1745.
LIU Y,PU S Z,CAO Z H,et al. Research on fault diagnostic method based the fault graph model[J]. MiNi-Micro Systems,2006,27(9):1741—1745.(In Chinese)
[14] 韩光臣,孙树栋,王军强,等. 复杂系统模糊概率故障图模型研究[J]. 中国机械工程,2005,16(9):801—804.
HAN G C,SUN S D,WANG J Q,et al. Research on fault graph model of complex system based on fuzzy probability[J]. Chinese Mechanical Engineering,2005,16(9):801—804.(In Chinese)
[15] RAN Y,ZHANG G B,ZHANG L. Quality characteristic association analysis of computer numerical control machine tool based on meta-action assembly unit [J]. Advances in Mechanical Engineering,2016,8(1):1—10.
[16] 姜洪权,王金宇,高建民,等. 面向复杂系统故障溯源的SDG-FG模型建模方法[J]. 计算机集成制造系统,2015,21(3) :749—757.
JIANG H Q,WANG J Y,GAO J M,et al. Modeling method for SDG-FG model oriented to fault root causes tracing analysis of complex electromechanical system[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems,2015,21(3):749—757.(In Chinese)
[17] WEBER P,MEDINA O G,SIMON C,et al. Overview on Bayesian networks applications for dependability,risk analysis and maintenance area[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence,2012,25(4):671—682.
[18] ZHAO S Q. Power distribution system reliability evaluation by D-S evidence inference and Bayesian network method[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE 11th International Conference on Probabilistic Methods Applied to Power Systems. Singapore:IEEE,2010:654—658.
[19] MAHADEVAN S,ZHANG R,SMITH N. Bayesian network for system reliability reassessment[J]. Structural Safety,2001,23:231—251.
