Metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma to the thyroid gland with widespread nodal involvement:A case report
2020-04-09XingZhangXinGuJiaGenLiXianJieHu
Xing Zhang,Xin Gu,Jia-Gen Li,Xian-Jie Hu
Xing Zhang,Department of Thyroid and Breast Surgery,The Affiliated People's Hospital of Ningbo University,Ningbo 315040,Zhejiang Province,China
Xin Gu,Department of Pathology,The Affiliated People’s Hospital of Ningbo University,Ningbo 315040,Zhejiang Province,China
Jia-Gen Li,Xian-Jie Hu,Department of Thyroid and Breast Surgery,The Affiliated People’s Hospital of Ningbo University,Ningbo 315040,Zhejiang Province,China
Abstract BACKGROUND Esophageal cancer is one of the most common causes of cancer-related death.Some patients with esophageal cancer have distant metastases at the time of diagnosis,but metastasis to the thyroid gland(MTG)and multifocal thyroid lesions alone are extremely rare.CASE SUMMARY In this case report,we present a case of a 69-year-old male with esophageal MTG.The patient visited our hospital for a routine body check-up,which revealed multifocal nodules in his thyroid lobes and enlarged cervical lymph nodes.A fine needle aspiration biopsy showed malignancies in both thyroid lesions and lymph nodes.The patient was initially diagnosed with primary bilateral thyroid cancer that spread to his lymph nodes,and a total thyroidectomy was performed.The histology showed MTG and therefore,a diagnostic work-up was implemented to determine the primary tumor.A fluorine-18-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography scan showed that the lower part of the esophagus and the lymph nodes in the neck,chest,and abdomen were involved.An esophagogastroscopy and corresponding pathology revealed distal esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.The esophageal MTG diagnosis was confirmed with pathological immunohistochemistry.CONCLUSION This case report highlights the difficulty in diagnosing esophageal MTG.Patients may have no malignancy history and be asymptomatic.Further diagnostic procedures are necessary after MTG is confirmed by cytology or histology,and the final diagnosis should be made according to the identification of the primary malignancy combined with pathological immunohistochemistry findings.
Key Words:Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma;Metastasis;Thyroid gland;Thyroidectomy;Lymph nodes;Case report
INTRODUCTION
Esophageal cancer is the ninth most common cancer worldwide,with 572034 new cases estimated in 2018,and the sixth leading cause of cancer-related death,with 508585 cases[1].Esophageal cancer distant metastases most commonly occur in the liver,followed by the lungs,bones,and brain[2].Metastasis to the thyroid gland(MTG)is rare,with reported in surgical series ranging from 1.4% to 3.0%[3].Esophageal malignancies are relatively rare sources of the thyroid metastases,compared to kidney and lung malignancies,and are only seen in 9% of patients with MTG[4].In the clinical setting,secondary thyroid tumors only present without concurrent primary cancer symptoms or known malignancy histories in patients with MTG,and this situation can perplex physicians.We present the case of a patient with metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma(ESCC)of a thyroid gland,which was initially misdiagnosed as primary thyroid cancer with cervical lymph node metastasis.After a thyroidectomy,esophageal MTG was confirmed by a fluorine-18-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography(FDG-PET-CT)combined with pathological immunohistochemistry.
CASE PRESENTATION
Chief complaints
An ever healthy 69-year-old Chinese male patient was hospitalized after a routine check-up that showed malignancy-suspected nodules in his bilateral thyroid lobes and enlarged cervical lymph nodes on both sides.
History of present illness
The patient was asymptomatic and received the treatment for the first time at our hospital.
History of past illness
The patient had an unremarkable past history except for diabetes and hypertension.
Physical examination
Physical examination revealed a 3.0 cm firm thyroid mass in the right thyroid lobe,and swollen neck lymph nodes were palpated on both sides.
Laboratory examinations
The laboratory test results were normal for free triiodothyronine level(6.21 pmol/L,normal range 3.28-6.47 pmol/L),free thyroxine level(10.23 pmol/L,normal range 7.64-16.03 pmol/L),and thyroid-stimulating hormone level(1.79 mIU/L,normal range 0.51-5.91 mIU/L).The tumor markers levels were all in normal range.
Imaging examinations
Ultrasonography revealed multiple Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System 4c nodules in bilateral thyroid lobes(Figure 1).Neck contrast-enhanced computed tomography(CT)scan indicated multifocal disease in the thyroid lobes and enlarged cervical lymph nodes on both sides(Figure 2).
Further diagnostic work-up
The patient underwent a fine needle aspiration(FNA)biopsy of the thyroid lesions and neck lymph nodes,which showed malignant tumor cells in both(Figure 3).
FINAL DIAGNOSIS
The final diagnosis of MTG from ESCC was based on the immunohistochemical panel after thyroidectomy.
TREATMENT
The patient received a total thyroidectomy plus bilateral level VI lymph nodes dissection.The permanent section revealed metastatic squamous cell carcinoma in the thyroid gland.Therefore,further diagnostic procedures were performed to determine the primary carcinoma.A chest CT scan revealed mediastinal nodal involvement,and an abdominal ultrasound was negative.A postoperative FDG-PET-CT was performed,which showed that the lower part of the esophagus and the lymph nodes in the neck,chest,and abdomen were all involved(Figure 4).The patient underwent an esophagogastroscopy,and a lesion was noted in the distal esophagus,in which squamous cell carcinoma was confirmed by biopsy(Figure 5A).Immunohistochemistry of the thyroid lesions was consistent with features of metastatic ESCC(Figure 5B-H).The patient received four rounds of adjuvant chemotherapy of oxaliplatin combined with 5-fluorouracil every 3 wk and then withdrew due to the side effects.
OUTCOME AND FOLLOW-UP
He was followed up every 3 mo after discharge.At present,he is on traditional Chinese medicine and feels well 1 year after the diagnosis.
DISCUSSION
Although rare,esophageal MTG does occur.Physicians should keep in mind that it is necessary to perform further examinations of the cervical region when malignant,multifocal lesions in the thyroid gland are noted.MTG needs to be considered as a differential diagnosis,even in patients with no prior history of malignancy.MTG is generally regarded to result from the spread of a primary tumor by a hematogenous route.Despite its rich blood supply,the thyroid is a rare site for metastatic disease.This phenomenon is due to fast arterial flow that prevents cancer cell adhesion,and the high oxygen saturation and iodine content of the thyroid gland inhibit the growth of malignant cells[3].The incidence of MTG is low and amounts to 2%-3% of all malignant tumors of the thyroid[5].The most common primary malignancies that can metastasize to the thyroid gland are renal cell cancer,followed by lung cancer and breast cancer[6].MTG from esophageal cancer is extremely rare,and only a few sporadic cases have been reported in the literature thus far[7-10].To our knowledge,there has been no reported case of metastasis of esophageal cancer to the thyroid gland and widespread involvement of distant lymph nodes at the same time.

Figure 1 Right thyroid sonogram.A:Left thyroid sonogram;B:Both A and B show multifocal,hypoechoic,irregular,and calcified nodules in the thyroid gland(orange arrows).
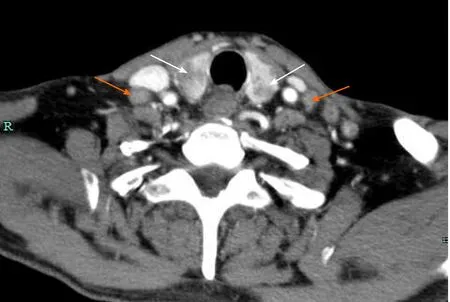
Figure 2 The enhanced contrast neck computed tomography scan shows lesions in the thyroid lobes(white arrows)and enlarged lymph nodes(orange arrows).
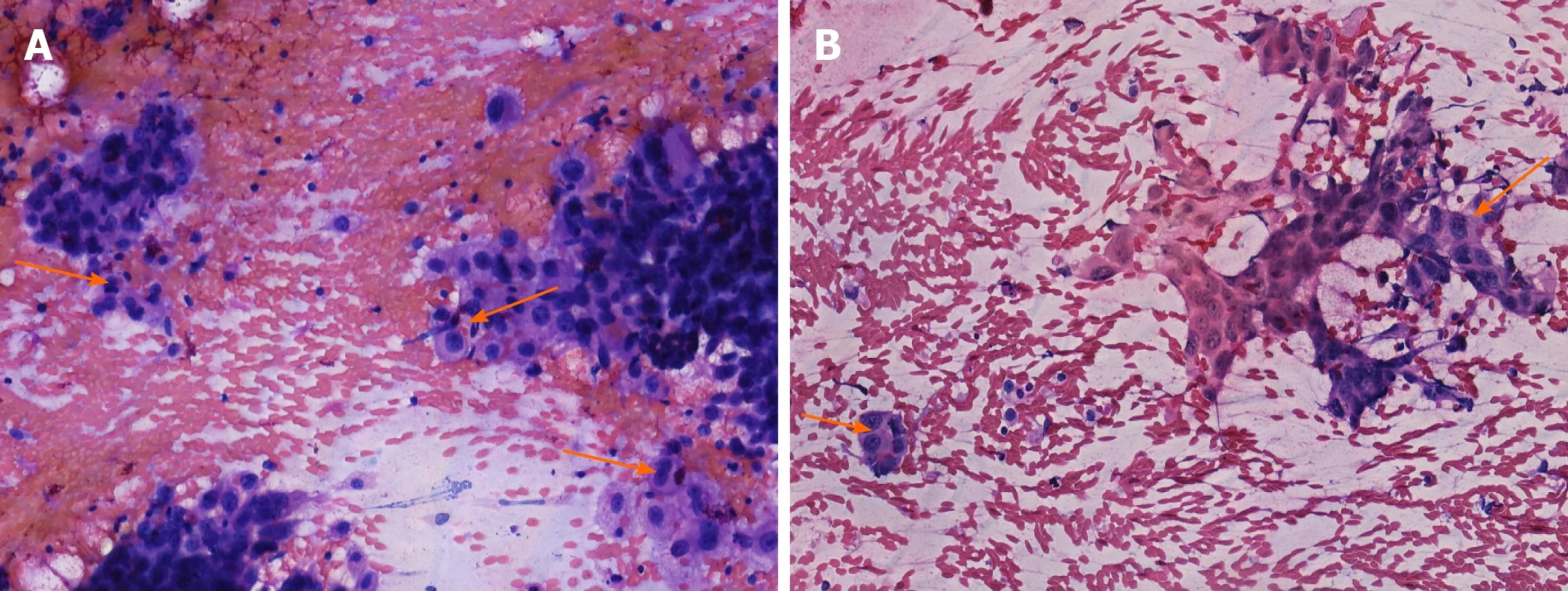
Figure 3 Fine needle aspiration cytology of the thyroid lesions stained with hematoxylin and eosin(× 200).A:It shows malignant tumor cells(orange arrows);B:It shows malignant tumor cells(orange arrows).
Metastatic disease that involves the thyroid gland may pose a diagnostic challenge.At presentation,MTG may share similarities with primary thyroid tumors,and most patients are asymptomatic[11].MTG may be the sole presentation,without any primary tumor-related symptoms or previous malignancy history.This patient with MTG lacked symptoms of advanced-stage esophageal cancer like dysphagia,weight loss,and chest pain.The thyroid masses and neck nodal involvement were the only positive findings at the initial imaging and physical examination before the surgery.The fine needle aspiration cytology did not reveal MTG as well.Preoperative fine needle aspiration cytology is a reliable approach to establish the diagnosis.However,it has limitations with regard to distinguishing MTG from primary thyroid carcinoma.Therefore,this disease can confuse surgeons and masquerade the primary thyroid cancer metastases to cervical lymph nodes.Even after the thyroidectomy,the permanent section showed MTG.It was not an easy task to determine the primary tumor,and the work-up diagnostic procedures helped locate the primary tumor.
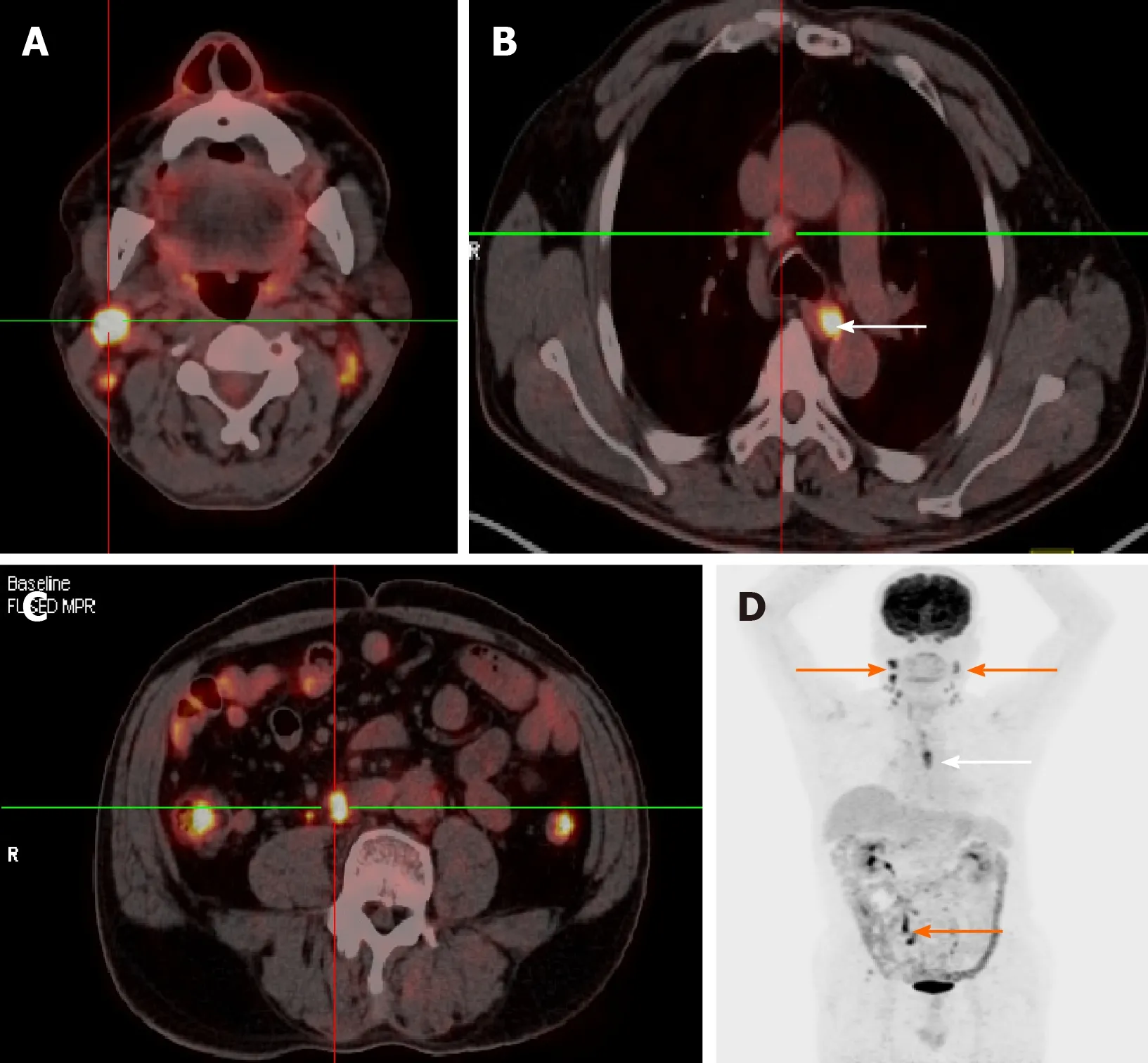
Figure 4 Fluorine-18-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography-computed tomography fused transaxial images(A-C)and maximum intensity projection(D).A and C:They show the uptake nodal focus(center of crossing);B:It shows an enlarged lymph node(center of crossing)and esophageal lesion(white arrow);D:It shows widespread lymph node involvement(orange arrows)and an esophageal lesion(white arrow).
After all other routine examinations are negative for the primary tumor,FDG-PETCT usually is the final resort;in some patients,the primary tumors cannot be found[4].Although the indication of surgery for metastatic thyroid carcinomas is uncertain and does not impact overall survival,in some patients with MTG,a total thyroidectomy is warranted[12-14].Especially for MTG multifocal disease,a total thyroidectomy should be considered and may achieve control of the central neck[6].Furthermore,definitive histology by surgical excision may be required to confirm the diagnosis[15].
The differential diagnoses of MTG of ESCC include primary squamous cell carcinoma(PSCC)of the thyroid and mucoepidermoid thyroid carcinoma(MEC).PSCC of the thyroid resembles anaplastic thyroid carcinoma in clinical presentation.Patients with PSCC of the thyroid present with rapidly increasing neck mass invading the adjacent structures.Besides patients’ history,immunohistochemical panel is useful in diagnosing MTG.PSCC as well as squamous carcinoma component in association with other thyroid carcinomas have been shown to be positive for paired box gene 8(PAX-8)protein[16].Like anaplastic thyroid carcinoma,PSCC shows a high frequency of P53 overexpression[17].In this case,PAX-8 and P53 were negative.The microscopic features of multifocal tumor nests along the vessels found in this case indicate MTG as well.The immunohistology characteristics of MEC generally demonstrate positive for thyroid transcription factor-1(TTF1)and thyroglobulin.In this case,TTF1 and thyroglobulin were both negative.Furthermore,the immunohistochemical staining was positive for CK5/6 and P40.Combined with the results of FDG-PET-CT and esophagogastroscopy,the diagnosis of MTG from ESCC was confirmed.
CONCLUSION
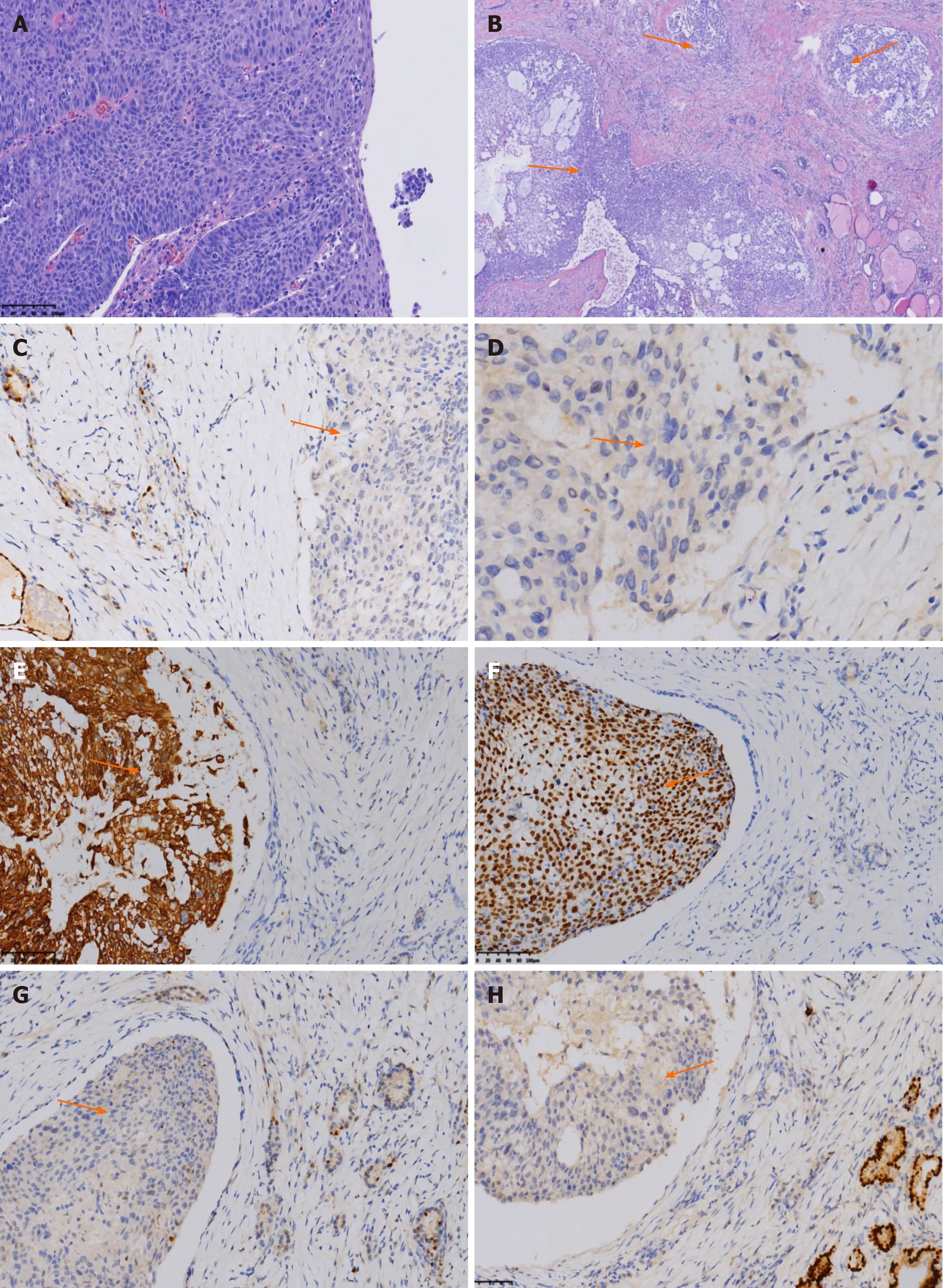
Figure 5 Fine needle aspiration cytology of the thyroid lesions stained with hematoxylin and eosin(× 200)and the immunohistochemical features.A:Permanent section of the esophagus stained with hematoxylin and eosin shows esophageal squamous cell carcinoma(× 200);B:Histology of MTG stained with hematoxylin and eosin shows multifocal tumor nests(orange arrow)(× 40);C:Immunohistochemical negative staining of metastasis to the thyroid gland(MTG)for thyroid transcription factor-1(orange arrow)(× 200);D:Immunohistochemical negative staining of MTG for thyroglobulin(orange arrow)(× 200);E:Immunohistochemical positive staining of MTG for CK5/6(orange arrow)(× 200);F:Immunohistochemical positive staining of MTG for P40(orange arrow)(× 200);G:Immunohistochemical negative staining of MTG for(orange arrow)(× 200);H:Immunohistochemical negative staining of MTG for paired box gene 8(orange arrow)(× 200).
It is difficult to determine the primary tumor when patients with esophageal MTG are asymptomatic and have no previous malignancies.Further diagnostic procedures are necessary after MTG is confirmed by cytology or histology,and the final diagnosis should be made according to the identification of the primary malignancy combined with pathological immunohistochemistry findings.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We acknowledge the work of the nurses and doctors of The Affiliated People’s Hospital of Ningbo University involved in the surgery and the following treatment.
杂志排行
World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Role of monoclonal antibody drugs in the treatment of COVID-19
- Review of simulation model for education of point-of-care ultrasound using easy-to-make tools
- Liver injury in COVID-19:A minireview
- Transanal minimally invasive surgery vs endoscopic mucosal resection for rectal benign tumors and rectal carcinoids:A retrospective analysis
- Impact of mTOR gene polymorphisms and gene-tea interaction on susceptibility to tuberculosis
- Establishment and validation of a nomogram to predict the risk of ovarian metastasis in gastric cancer:Based on a large cohort
