蜂群无人机编队内无线紫外光协作避让算法
2020-04-01赵太飞史海泉李星善
赵太飞,高 鹏,史海泉,李星善
蜂群无人机编队内无线紫外光协作避让算法
赵太飞1,3*,高 鹏1,3,史海泉1,3,李星善2
1西安理工大学自动化与信息工程学院,陕西 西安 710048;2湖北航天技术研究院总体设计所,湖北 武汉 430040;3陕西省智能协同网络军民共建重点实验室,陕西 西安 710048
在战场复杂电磁环境下,保证蜂群无人机编队机间飞行安全和编队内可靠通信尤为重要。本文提出一种蜂群无人机编队内无线紫外光协作避让算法,结合无线紫外光覆盖特点设计紫外虚拟围栏避让策略,基于增强矢量场直方图法针对无人机在避让时的运动状态的代价函数进行改进,采用无迹卡尔曼预测器预测邻近无人机的飞行状态。在两种预测场景下的避让仿真中,结果表明,与增强矢量场直方图法进行对比,本文算法的整体运动轨迹平滑,局部避让时无明显抖动,避让路径总长度平均减少3.46%,总耗时平均减小18.94%,验证了蜂群无人机编队内无线紫外光协作避让算法的有效性。
蜂群无人机;无线紫外光;虚拟围栏;协作避让;轨迹预测;增强矢量场直方图法

1 引 言
蜂群无人机编队是由大量载荷不同、类型不同的无人机组成,根据战场环境调整编队内机群数量及队形以便执行隐秘侦察,重点突防等作战任务。蜂群无人机编队存在无人机机间密度大,对环境信息实时性要求高的特点[1]。由于各类型的电磁干扰无处不在,特别是电子对抗过程中无人机编队需要保持无线电静默以降低暴露风险,而无线“日盲”紫外光通信正好能满足这种通信方式的需求,其优势主要有背景噪声小、抗电磁干扰能力强、非直视通信、低功耗、高集成度、易于机载[2]。因此,采用“日盲”紫外光协作无人机编队飞行能为无人机编队在强电磁干扰环境中顺利执行任务提供有效保障。
路径规划是蜂群无人机编队顺利完成任务的前提,分为全局路径规划[3-7]和局部避让算法[8-10]。全局路径规划在已知环境信息的前提下通过各类算法实现规划,其优势在于路径平滑,避让效果好,缺点是不能适用于实时性高的场景,文献[5-7]中利用移动物体的运动状态预测很好地实现了全局路径规划。局部避让算法通过一定避让条件实现在线路径规划,其优势在于适用动态场景,但是其存在局部极小和路径抖动等缺点,较其他局部避让算法而言,增强矢量场直方图法易于实现,局部避让效果好,得到了广泛的应用。文献[11-13]通过结合全局路径规划算法和局部避让算法实现了在动态场景下的高鲁棒性的路径规划,大大减小了局部极小、路径抖动等问题,也克服了全局路径规划算法动态场景适应性的问题。本文主要针对基于无线紫外光通信的蜂群无人机编队,利用无线紫外光构建无人机安全范围内的环境直方图来避让和预警该区域内的邻近无人机,实现高鲁棒性、实时性更好无人机编队内的机间避让。
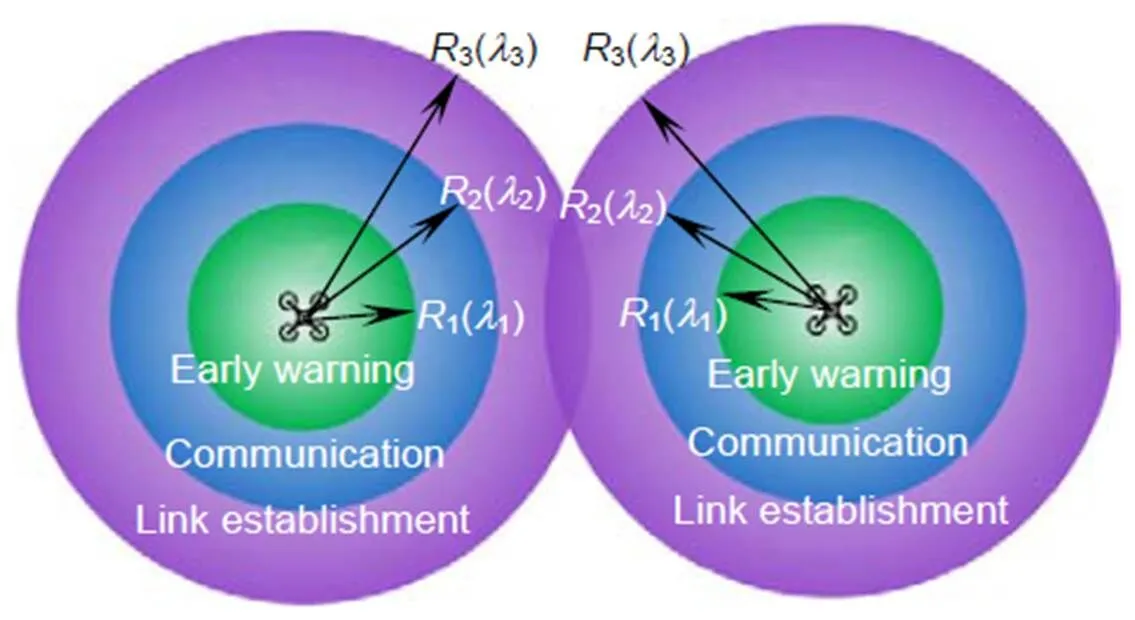
2 无线紫外光自主避让策略

1) 安全飞行:通过判断,在下一个运动周期邻近无人机处在链路建立区内并且正在远离,此时判定邻近无人机为安全飞行状态。
2) 一般危险:通过判断在下一个运动周期邻近无人机处于通信区内,但(+2)的周期内处于预警区,标记该无人机为潜在危险。
3) 紧急避让:通过判断在下一个运动周期邻近无人机处于预警区内,当前时刻必须执行局部避让。紧急避让状态下,通过最佳方向采样和最佳速度采样提供局部避让路径,再通过筛选出代价最小的避让路径,最终实现了机间自主避让。

图1 无线紫外光虚拟围栏模型
当无人机之间互相接收到波长为2的光信号时,双方开始通信;当无人机之间互相接收到波长为1的光信号时,无人机之间开始执行自保程序。
3 基于无线紫外光的增强矢量场直方图法
3.1 无人机运动模型


图2 无人机运动模型
Fig. 2 UAV motion model
通过转换关系可求得在大地坐标系下任意无人机运动到点时的位置信息为


无人机运动时的速度和位移可由以下公式表示:


3.2 基于无线紫外光虚拟围栏的直方图构建



其中:




图3 无线紫外光虚拟围栏直方图
Fig. 3 Wireless ultraviolet virtual fence histogram




3.3 无人机飞行方向的最优选择
虚拟围栏直方图本质上是一个无线紫外光虚拟围栏覆盖范围内的可飞行区域集合,需要通过一些约束条件筛选出适合飞行的区域。原有算法通过设定可飞行区域的边界值,比较二者差值与阈值之间的关系筛选最佳运动方向,但是对于无人机来说,这种选择运动方向存在一定局限性,下一时刻对当前时刻的影响并未考虑,为此,需要通过预测邻近无人机在下一时刻的飞行状态,结合该状态选择当前时刻无人机的运动方向。而无人机系统是非常复杂的非线性系统[17],并且利用无线紫外光设备提供无人机机间距离、方位角时也存在误差。为了提高避让的精准度,本文将利用无迹卡尔曼预测器预测邻近无人机的飞行轨迹及运动状态以便于运动方向的选择。
设无人机作匀变速运动,由于无线紫外光设备及运动系统自身均含高斯白噪声,则运动状态方程()和观测方程()[18]可表示为
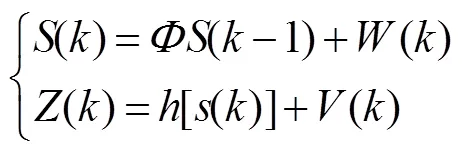
式中:()表示无人机系统所包含的高斯白噪声,其具有协方差阵。()表示观测状态下的高斯白噪声,其具有协方差阵。


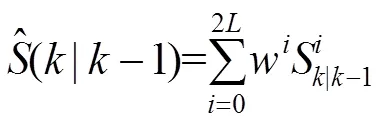















图4 基于无线紫外光的避让流程图
4 算法仿真结果与分析
4.1 仿真参数设置
避让算法参数如表1所示。无人机状态预测时系统噪声()具有协方差,()具有协方差阵,分别如下:

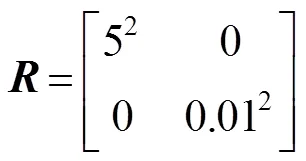
()和()二者不相关,采样次数=50次,采样时间=1 s。表2所示为各个运动状态预测初始参数。
4.2 避让算法对比分析
在算法对比中,矢量场直方图避让算法(VFH+)为局部避让算法,故存在局部极小的问题,并且原算法的路径锯齿程度明显,路径不平滑。增强矢量场直方图法(VFH*)为利用A*算法全局搜索关键避让信息,局部避让采用矢量场直方图的避让算法,该算法虽利用A*算法获取了全局地图信息,但是对于无人机蜂群这类高动态应用场景存在环境信息更新不及时影响避让效果等问题。基于此,提出了虚拟围栏避让算法(UAVF),本算法为考虑当前运动物体的运动状态和运动物体运动状态预测的局部避让算法。由于VFH+只适合于静态障碍物的局部避让,在此将轨迹预测后的位置状态离线显示在地图中,查看其避让轨迹状态。在场景一下,选取了近前30 s的轨迹,因为会遇发生在前30 s内。在场景二下,选取了近前50 s的轨迹。图5(a)为场景一中局部避让轨迹图,图5(b)为场景一中避让轨迹局部放大图,图6(a)场景二中局部避让轨迹图,图6(b)为场景二中避让轨迹局部放大图。
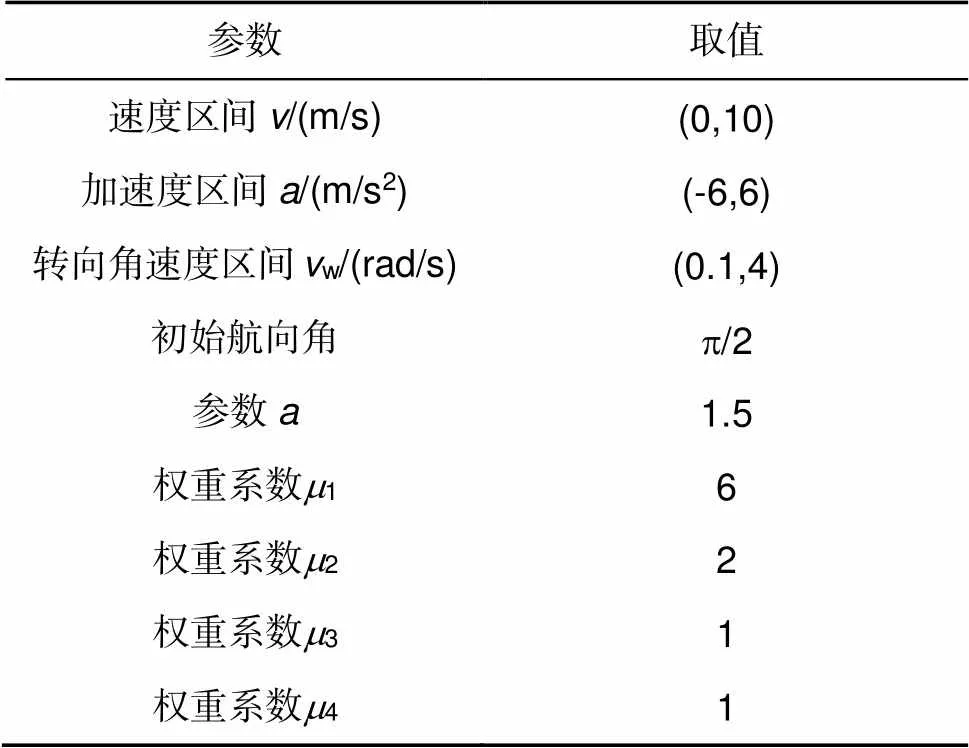
表1 避让算法参数

表2 运动状态初始参数

图5 (a) 场景一中局部避让轨迹;(b) 场景一中避让轨迹局部放大

图6 (a) 场景二中局部避让轨迹;(b) 场景二中避让轨迹局部放大图
从图5(a)中可以观察出,三类算法均可安全完成局部避让,并最终到达目的地。从图5(b)中可以看出,由于UAVF考虑了自身运动速度及在避让时的机间距离的冗余,局部避让时路径平滑且转向平缓,机间距离保持良好,无明显轨迹抖动。VFH+由于未能提前获知运动物体的运动状态,选择从障碍物的下一个前进方向避让,在实际情况中,极有可能在会遇时出现碰撞,而且避让时出现了明显的抖动。VFH*虽然提前全局搜索适合路径,并在局部完成避让,但是从开始搜索路径到避让,局部路径较长,有转向角度。仿真中,VFH*算法共耗时36.01 s,路径总长度570 m;VFH+算法路径总长度529 m,共耗时31.45 s;UAVF算法共耗时29.23 s,路径总长度398 m。相比VFH*算法,总路径长度减少3.02%,总耗时减少18.82%。
图6(a)表明,三类算法均可安全完成局部避让,并最终到达目的地。从图6(b)可以观察出,由于VFH+在离线规划中未能找到合适避让方向,故从出发开始选择绕过最远端物体到达终点,总耗时费42.97 s,路径总长度860 m。VFH*和UAVF均能很好地完成局部避让,但相比VFH*,UAVF轨迹平滑,转向角度较小。VFH*总耗时47.48 s,路径长度离794 m;UAVF总耗时38.43 s,路径总长度763 m。与VFH*相比,UAVF耗时减少19.06%,路径总长度减少3.90%
4.3 运动状态预测性能分析
图7与图8中的无人机真实轨迹和预测轨迹均为Matlab仿真所得。图7(a)为场景一中的预测轨迹图,从图中可以看出,真实值与预测值整体拟合度较高,但是局部相对误差依然存在。图7(b),7(c)为场景一中的预测轨迹局部放大图,放大比例基本相同,顺序为从左上到右下。图7(b)是预测刚开始时局部放大,可以看出由于采用次数少,相对误差比较明显。图7(c)预测次数在25~30左右,相对误差减少。综合两幅图可以分析出,由于预测次数的增加,相对误差在逐渐减小,最后趋于稳定。在场景一的预测中,相对距离误差最大不超过6.83 m,相对速度误差最大不超过1.88 m/s,相对加速度误差最大不超过0.17 m/s2。
图8(a)为场景二中的预测轨迹图,从图中可以看出,真实值与预测值整体拟合度较高,但是局部相对误差明显。图8(b),8(c)为场景二中的轨迹局部放大图,放大比例基本相同,顺序为左下到右上。图8(b)是预测刚开始时的局部放大图,可以看出,由于刚开始预测,相对误差非常明显,图8(c)是预测次数在15~25左右,相对误差减少幅度大。综合两幅局部放大图可以分析出,随着预测次数的增加,相对误差在减小,最后趋于稳定。在场景二的预测中,相对距离误差最大不超过8.19 m,相对速度误差最大不超过0.82 m/s,相对加速度误差最大不超过0.11 m/s2。两次状态下的相对误差平均值如表3所示。
5 结 论
本算法考虑了蜂群无人机编队内无线紫外光隐秘通信的覆盖特点,提出了无线紫外光虚拟围栏避让策略。基于传统增强矢量场直方图法,通过增加速度采样改进代价函数,结合无迹卡尔曼预测器预测编队内其他无人机运动状态,实现了蜂群无人机编队飞行时的协作避让。仿真结果表明,与传统算法相比,本算法在两种场景中的避让总路径长度平均减少3.46%,总耗时平均减小18.94%。该算法能够在未获取全局地图的情况下,通过无线紫外光设备及无人机运动状态预测实现协作避让。
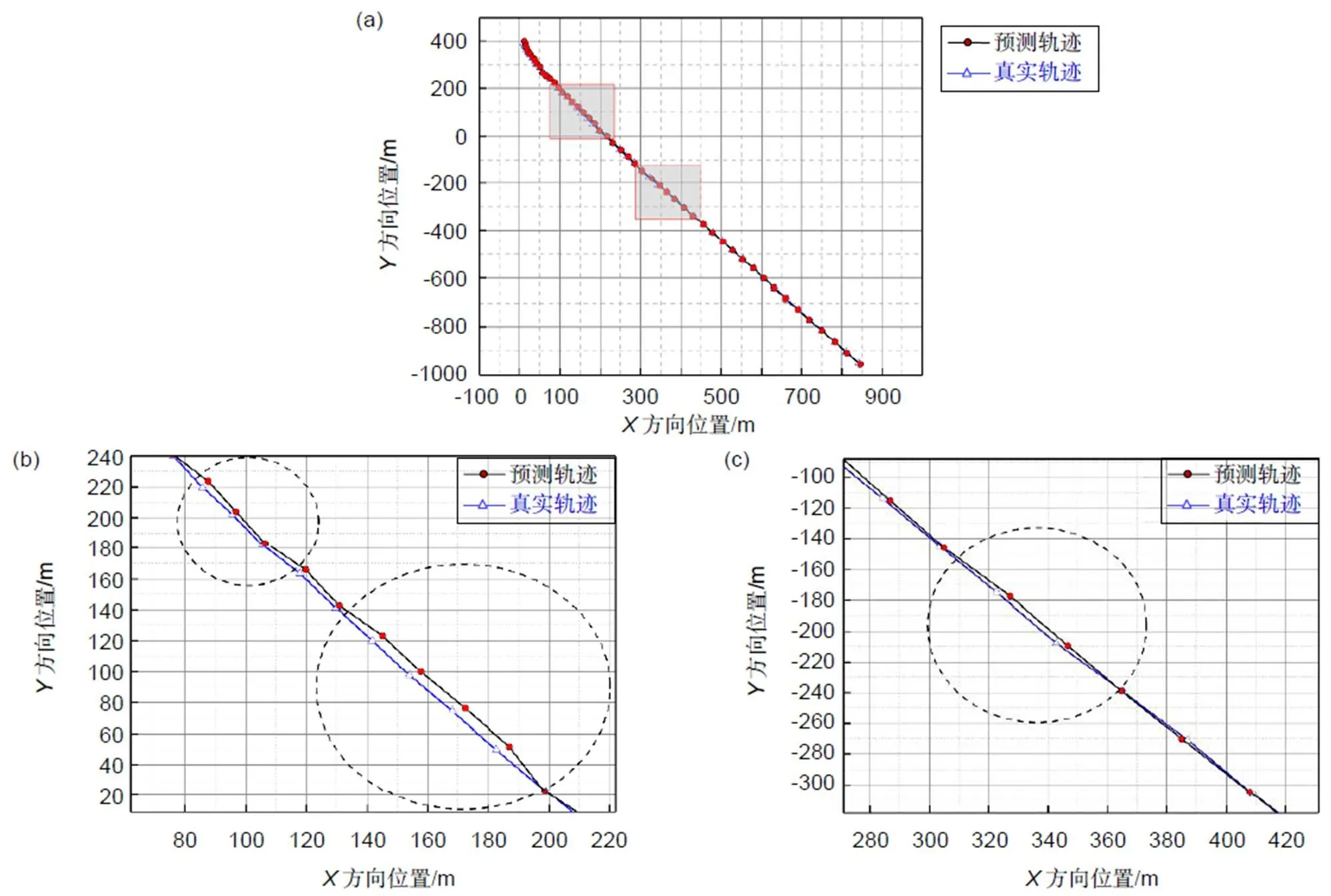
图7 (a) 场景一中的预测轨迹;(b) 第一次局部放大;(c) 第二次局部放大

图8 (a)场景二中的预测轨迹;(b)第一次局部放大;(c) 第二次局部放大

表3 相对误差平均值
[1] Yu L, Wei P, Ma Z L,. Analysis on the development of foreign army anti-bee colony drone technology[J]., 2017(12): 26–30.
于力, 魏平, 马振利, 等. 外军反蜂群无人机技术发展分析[J]. 飞航导弹, 2017(12): 26–30.
[2] Luo C. The study of signal processing and design of base band system for non-line-of-sight optical communication[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2011.
罗畅. 非视距光通信信号处理研究与基带系统设计[D]. 北京: 中国科学院研究生院, 2011.
[3] Tan Y Y, Li Y, Zhou J,. Path replanning approach for UAV based on A* algorithm in complex environment[J]., 2017, 39(6): 1268–1273.
谭雁英, 李洋, 周军, 等. 复杂环境下基于A*算法的无人机路径再规划[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2017, 39(6): 1268–1273.
[4] Mac T T, Copot C, Tran D T,. A hierarchical global path planning approach for mobile robots based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization[J]., 2017, 59: 68–76.
[5] Roberge V, Tarbouchi M, Labonte G. Comparison of parallel genetic algorithm and particle swarm optimization for real-time UAV path planning[J]., 2013, 9(1): 132–141.
[6] Wu Z Y, Li J H, Zuo J M,. Path planning of UAVs based on collision probability and Kalman filter[J]., 2018, 6: 34237–34245.
[7] Chen Y B, Luo G C, Mei Y S,. UAV path planning using artificial potential field method updated by optimal control theory[J]., 2016, 47(6): 1407–1420.
[8] Qu P R, Xue J R, Ma L,. A constrained VFH algorithm for motion planning of autonomous vehicles[C]//, 2015.
[9] Babinec A, Duchoň F, Dekan M,. VFH*TDT (VFH* with time dependent tree): a new laser rangefinder based obstacle avoidance method designed for environment with non-static obstacles[J]., 2014, 62(8): 1098–1115.
[10] Zhang Y Y, Qu D, Ke J,. Dynamic obstacle avoidance for USV based on velocity obstacle and dynamic window method[J]., 2017, 23(1): 1–16.
张洋洋, 瞿栋, 柯俊, 等. 基于速度障碍法和动态窗口法的无人水面艇动态避障[J]. 上海大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 23(1): 1–16.
[11] Ji J, Khajepour A, Melek W W,. Path planning and tracking for vehicle collision avoidance based on model predictive control with multiconstraints[J]., 2017, 66(2): 952–964.
[12] Cui R X, Li Y, Yan W S. Mutual information-based multi-AUV path planning for scalar field sampling using multidimensional RRT[J]., 2016, 46(7): 993–1004.
[13] da Silva Arantes J, da Silva Arantes M, Toledo C F M,. Heuristic and genetic algorithm approaches for UAV path planning under critical situation[J]., 2017, 26(1): 1760008.
[14] Zhao T F, Yu X X, Bao H,. Ranging and positioning method using wireless solar blind ultraviolet[J]., 2017, 25(9): 2324–2332.
赵太飞, 余叙叙, 包鹤, 等. 无线日盲紫外光测距定位方法[J]. 光学精密工程, 2017, 25(9): 2324–2332.
[15] Zhang Y L, Zhao C P, Yan H. Path planning for unmanned aerial vehicles using improved bidirectional A* and vector field histogram algorithm[J]., 2019, 19(4): 179–184.
张亚兰, 赵成萍, 严华. 基于改进双向A*和向量场直方图算法的无人机航路规划[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2019, 19(4): 179–184.
[16] Sun Y Z, Xiao S D, Pan S F,. VFH algorithm for obstacle avoidance based on Kalman Filter[J]., 2015, 29(4): 373–377, 398.
孙扬智, 肖世德, 潘绍飞, 等. 融合卡尔曼滤波的VFH避障算法[J]. 江苏科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 29(4): 373–377, 398.
[17] Dai R, Cochran J, Jr. Path planning and state estimation for unmanned aerial vehicles in hostile environments[J]., 2010, 33(2): 595–601.
[18] Guan Y Z, Song C L, Dong H J. Path planning of the free-floating manipulator for capturing a moving target[J]., 2017, 39(6): 803–811.
关英姿, 宋春林, 董惠娟. 空间自由漂浮机器人对运动目标抓捕的路径规划[J]. 机器人, 2017, 39(6): 803–811.
An algorithm for the bee colony drone to use wireless ultraviolet for cooperative obstacle avoidance
Zhao Taifei1,3*, Gao Peng1,3, Shi Haiquan1,3, Li Xingshan2
1Faculty of Automation and Information Engineering, Xi¢an University of Technology, Xi¢an, Shaanxi 710048, China;2General Design Institute of Hubei Academy of Aerospace Technology, Wuhan, Hubei 430040, China;3Shanxi Civil-Military Integration Key Laboratory of Intelligence Collaborative Networks, Xi¢an, Shaanxi 710048, China
Wireless UV virtual fence model
Overview:Uninhabited aerial vehicles (UAVs) are widely used not only in civil fields such as power inspection and environmental monitoring, but also in military applications such as reconnaissance, surveillance and confusion. The drone “bee colony” is composed of a group of small unmanned aerial vehicles that work together independently. It has excellent features such as low cost, high damage resistance, good sensing ability, strong collaboration ability and functional distribution, which can improve the efficiency of completing task. In the complex electromagnetic environment of the battlefield, it is especially important to ensure the flight safety between the formation of the drone group and the reliable communication within the formation. The advantages of wireless ultraviolet communication mainly include small background noise, strong anti-electromagnetic interference capability, all-weather non-direct view communication, low power consumption, high integration, easy to load, etc., which can meet the communication requirements in this environment.
This paper proposes an algorithm for collaborative avoidance using wireless ultraviolet light between drones in a bee colony drone formation. Through combining avoidance algorithm with the characteristics of wireless ultraviolet light coverage, a wireless ultraviolet virtual fence avoidance strategy is proposed. Considering the relationship between the enhanced vector field histogram method and its own motion state to improve the cost function and verify the effectiveness of the avoidance algorithm.The unscented Kalman filter predictor is used to predict the flight state of the adjacent drone in order to achieve safe and efficient avoidance. Through computer simulation in two prediction scenarios, the results show that the improved enhanced vector field histogram method has smooth overall motion trajectory and good avoidance effect. Compared with the original algorithm, this algorithm has no obvious jitter when it is partially avoided, the turning arc is large and there is no sharp turn. It is more suitable for the actual application and reduces the path length and time consumption.In summary, in the complex battlefield environment, the bee swarm drone can not only use airborne wireless ultraviolet equipment to achieve stable network communication,it can also use improved enhanced vector field methods based on wireless ultraviolet light to enable efficient avoidance between drones in a bee colony drone formation.
Citation: Zhao T F, Gao P, Shi H Q,An algorithm for the bee colony drone to use wireless ultraviolet for cooperative obstacle avoidance[J]., 2020, 47(3): 190505
An algorithm for the bee colony drone to use wireless ultraviolet for cooperative obstacle avoidance
Zhao Taifei1,3*, Gao Peng1,3, Shi Haiquan1,3, Li Xingshan2
1School of Automation and Information Engineering, Xi¢an University of Technology, Xi¢an, Shaanxi 710048, China;2General Design Institute of Hubei Academy of Aerospace Technology, Wuhan, Hubei 430040, China;3Shanxi Civil-Military Integration Key Laboratory of Intelligence Collaborative Networks, Xi¢an, Shaanxi 710048, China
For complex battlefield environments, it is especially important to ensure the safety of flight between uninhabited aerial vehicles (UAV) formations and reliable communication within the formation. This paper proposes an algorithm for collaborative avoidance using wireless ultraviolet light between drones in a bee colony drone formation. Combined with the above algorithm and using the characteristics of wireless ultraviolet light coverage, the avoidance strategy of ultraviolet virtual fence is designed. And by enhancing the vector field histogram method to improve the cost function of the state of motion of the drone when performing mutual avoidance. In addition, the algorithm uses the unscented Kalman filter to predict the flight status of nearby uninhabited aerial vehicles. The simulation results show that in the avoidance simulations of the two prediction scenarios, the overall motion trajectory of this algorithm is smoother than that of the enhance vector field histogram method. At the same time, there is no obvious jitter when local avoidance occurs, the total length of the avoidance path is reduced by 3.46% on average, and the total time consumption is reduced by 18.94%. This verifies that the wireless ultraviolet cooperative avoidance algorithm in a bee colony drone formation is effective.
colony drone; wireless ultraviolete; virtual fence; cooperative obstacle avoidance; trajectory prediction; enhanced vector
V279+.2;TN929.1
A
10.12086/oee.2020.190505
: Zhao T F, Gao P, Shi H Q,. An algorithm for the bee colony drone to use wireless ultraviolet for cooperative obstacle avoidance[J]., 2020,47(3): 190505
2019-08-26;
2019-09-26
国家自然科学基金资助项目(61971345,U1433110);陕西省教育厅服务地方专项计划项目(17JF024);西安市科学计划项目(CXY1835(4));陕西省重点产业链创新计划项目(2017ZDCXL-GY-05-03);西安市碑林区科技计划项目(GX1921)
赵太飞(1978-),男,博士,教授,主要从事网络通信与自组织网络技术的研究。E-mail:tfz@xaut.edu.cn
赵太飞,高鹏,史海泉,等. 蜂群无人机编队内无线紫外光协作避让算法[J]. 光电工程,2020,47(3): 190505
Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (61971345, U1433110), Shaanxi Provincial Department of Education Service Local Special Project (17JF024), Xi¢an Science Project (CXY1835(4)), Shaanxi Provincial Key Industry Chain Innovation Project (2017ZDCXL-GY-05-03), and Xi¢an Beilin District Science and Technology Plan Project (GX1921)
* E-mail: tfz@xaut.edu.cn
