Effects of Shenmai Injection (参麦注射液) Combined with Meglumine Adenosine Cyclophosphate Injection on Cardiac Function and Peripheral Serum Levels of TNF-α,TGF-β1 and IFN-γ in Patients with Viral Myocarditis
2020-02-20ZHENGDuoGUOWenjuan郭文娟ZHAOXuelian赵雪莲
ZHENG Duo (郑 铎), GUO Wen-juan (郭文娟), ZHAO Xue-lian (赵雪莲)
1. Department of Gerontology, Fushun Mining Bureau General Hospital, Fushun 113008, China
ABSTRACTObjective:To explore effects of Shenmai Injection (参麦注射液) combined with Meglumine Adenosine Cyclophosphate Injection on cardiac function and peripheral serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) and interferon-γ (IFN-γ) in patients with viral myocarditis. Methods:A total of 70 patients with viral myocarditis admitted in Cardiovascular Medicine Department of our hospital from June 2016 to June 2018 were selected and divided into a control group(treated with Meglumine Adenosine Cyclophosphate Injection) and an observation group (additionally treated with Shenmai Injection (参麦注射液) on the treatment basis of the control group) according to random number method, with 35 cases in each group. Before and after the treatment, cardiac functional indexes like cardiac index (CI), left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and left ventricular shortening fraction (FS), serum levels of TNF-α, TGF-β1 and IFN-γ, clinical efficacy and adverse reactions occurred in the 2 groups were recorded and compared. Results:Therapeutic effective rate in the observation group was 88.57%, higher than 68.57% in the control group (P < 0.05). After the treatment, cardiac functional indexes like CI, LVEF and FS were higher than those in the control group (P < 0.05). After the treatment,the serum expression levels of TNF-α and TGF-β1 were lower than those in the control group (P < 0.05),while the serum expression level of IFN-γ was higher than that in the control group (P < 0.05). There was no statistically significant difference in the adverse reaction rates between the 2 groups (P > 0.05).Conclusion:The treatment of patients with viral myocarditis by Shenmai Injection (参麦注射液) combined with Meglumine Adenosine Cyclophosphate Injection is more effective, reducing inflammation and restoring cardiac function.
KEYWORDS Viral myocarditis; Shenmai Injection (参麦注射液); Meglumine adenosine cyclophosphate
Viral myocarditis is a relatively common infectious cardiomyopathy at present[1]. Its clinical manifestations include fever, sore throat,palpitations, edema, etc. If not treated in time, it will cause heart failure, dyspnea, cardiogenic shock, and even death, which poses a serious threat to physical and mental health of patients[2]. At present, clinical use of Meglumine Adenosine Cyclophosphate Injection and other drugs for routine anti-infection and alleviation of myocardial inflammation is mainly for viral myocarditis[3], and the treatment combined with Shenmai Injection (参麦注射液) is relatively less. According to YE Shan-shan[4]and other studies, it is found that Shenmai Injection (参麦注射液) also has significant efficacy in the treatment of viral myocarditis. This study aims to compare the effects of different treatments on cardiac function and peripheral serum levels of TNF-α, TGF-β1 and IFN in patients with viral myocarditis, so as to provide guidance for clinical treatment.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
General Information
The cases were from 70 patients with viral myocarditis admitted to Cardiovascular Medicine Department in our hospital from June 2016 to June 2018. Inclusion criteria: (1) consent from hospital ethics committee and the patient, confirmed by puncture examination to be diagnosed as viral myocarditis[5]: ① isolated virus; ② viral nucleic acid detected by viral nucleic acid probe during early detection; ③ positive specific virus antibody; (2)from 18 to 75 years old; (3) no antibiotics or no infections occurred 6 months before the treatment;(4) clear consciousness, with certain understanding and cognitive ability; (5) no history of alcohol or drug abuse (6) complete clinical data; (7) those agreed to the study and signed the informed consent.Exclusion criteria: (1) lactation period, gestation period or gestation plan within 6 months; (2) nonviral myocarditis and other cardiovascular diseases;(3) history of hypertension, arthritis, diabetes and other chronic diseases or malignant tumors in other organs; (4) those with congenital heart, liver and kidney dysfunction; (5) those allergic to the drug in this study or those taking the drug without following requirements; (6) those who had received relevant treatment before the enrollment; (7) other acute infections or excessive use of antibiotics 30 d before the enrollment; (8) those disagreed with the study or did not sign the informed consent. A total of 70 patients were enrolled in the study. They were randomly divided into control group (treated with Meglumine Adenosine Cyclophosphate Injection)and observation group (additionally treated with Shenmai Injection (参麦注射液) on the treatment basis of the control group). No statistical significance in the difference of patients' general information (P >0.05). See Table 1.
Methods
(1) Both groups of patients maintained absolute bed rest during the treatment. Lowflow oxygen and ECG monitoring were opened.Vitamin C was given (Huazhong Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., specification of 0.1 g 100 tablets,SFDA approval number H42020614), 0.2 g/time, 3 times/d. If accompanied by arrhythmia,Propafenone Hydrochloride Tablets were given(Shandong Renhetang Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.,specification of 50 mg 50 tablets, SFDA approval number H37020793), 300-600 mg/d, divided into 4-6 times/d. (2) The control group was given Meglumine Adenosine Cyclophosphate Injection(Hunan Hansen Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.,specification of 2 mL:30 mg, SFDA approval number H20045035) for intravenous drip, adding this product to 250 mL-500 mL 5% glucose injection for dilution, 60 mg/time, 1 time/d, continuous treatment for 14 d. (3) The observation group was additionally treated with Shenmai Injection (参麦注射液) on the treatment basis of the control group. The Shenmai Injection (参麦注射液) (Chiatai Qingchunbao Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., specification of 20 mL,SFDA approval number Z33020020) was used for intravenous drip, and it was diluted with 250 mL-500 mL 5% glucose injection, 20 mL/time, 1 time/d. According to actual situation of the patients, the speed of drip was regulated to low speed, with continuous treatment for 14 d.
Efficacy Evaluation Criteria
Recovery: clinical symptoms disappeared,normal heart rate, partial recovery of ST-T changes,and premature beat decreased by more than 85%in ECG review; effective: clinical symptoms basically disappeared, basically normal heart rate, partially recovery of ST-T changes, premature beat decreased by 50%-85% in ECG review; invalid: no significant improvement in clinical symptoms, abnormal heart rate, no significant improvement in ST-T changes,and premature beat decreased by less than 50% in ECG review. Effective rate = (recovery + effective)/total number of cases × 100%.
Observation Index
(1) Before and after the treatment, 2 mL of fasting venous blood of each patient in the 2groups was taken in the early morning. Cardiac functional indexes like cardiac index (CI), left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and left ventricular shortening fraction (FS) were measured by pureview cx50 Puller echocardiography machine(produced by Philips, the Netherlands), and they were compared. (2) Before and after the treatment,5 mL of fasting venous blood of each patient in the 2 groups was taken in the early morning. The blood was centrifuged at 1500 r/min for 10 min.After the separation of serum, serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) and interferon-γ (IFN-γ) were detected by double antibody sandwich method and related kits (produced by Shanghai Enzyme-linked Biotechnology Co., Ltd.). (3) After the end of the treatment, adverse reactions in the 2 groups were recorded in detail.

Table 1. Comparison of General Information between the 2 Groups

Table 2. Comparison of Clinical Efficacy between the 2 Groups (n (%))
Table 3. Comparison of Main Cardiac Functional Indexes between the 2 Groups before and after the Treatment
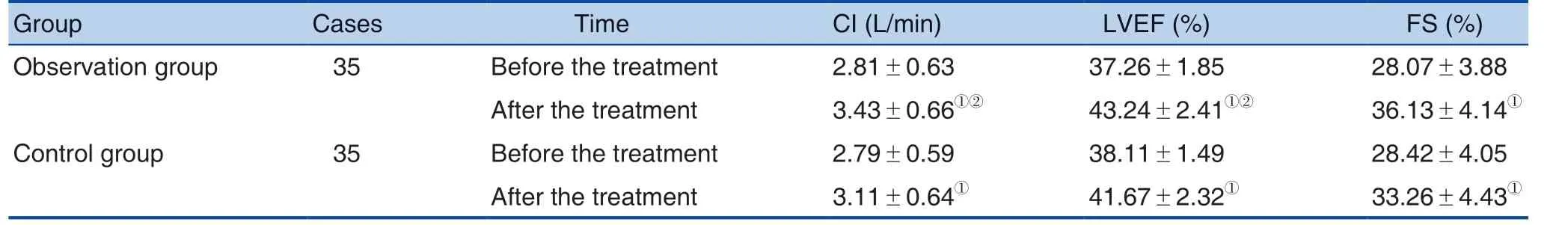
Table 3. Comparison of Main Cardiac Functional Indexes between the 2 Groups before and after the Treatment
Note: ①Compared with before the treatment, P < 0.05; ②Compared with the control group after the treatment, P < 0.05.
Group Cases Time CI (L/min) LVEF (%) FS (%)Observation group 35 Before the treatment 2.81±0.63 37.26±1.85 28.07±3.88 After the treatment 3.43±0.66①② 43.24±2.41①② 36.13±4.14①Control group 35 Before the treatment 2.79±0.59 38.11±1.49 28.42±4.05 After the treatment 3.11±0.64① 41.67±2.32① 33.26±4.43①
Statistical Methods
SPSS 18.0 statistical software was used for data analysis. Count data was expressed by the number of cases or percentage. The χ2test was used. Measurement data was expressed by"x-±s". The t test was used for comparison between groups, and rank sum test was used for comparison of ranked data between groups. P < 0.05 was considered as that there was statistically significant difference.
RESULTS
Comparison of Clinical Efficacy between the 2 Groups
Therapeutic effective rate in the observation group was 88.57%, and the total effective rate in the control group was 68.57%. The difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). See Table 2.
Comparison of Main Cardiac Functional Indexes between the 2 Groups before and after the Treatment
There was no significant difference in the CI,LVEF and FS between the 2 groups before the treatment (P > 0.05). The above indexes were significantly increased after the treatment, and the increase in the observation group was significantly higher than that in the control group (P < 0.05). See Table 3.
Comparison of Serum TNF-α, TGF-β1 and IFN-γ between the 2 Groups before and after the Treatment
There was no significant difference in the serum levels of TNF-α, TGF-β1 and IFN-γ between the 2 groups before the treatment (P > 0.05). After the treatment, the levels of serum TNF-α and TGF-β1 in the 2 groups were lower than those before the treatment (P < 0.05), and the decrease in the observation group was more significant than that in the control group, with statistically significant difference (P < 0.05); the IFN-γ level in the observation group was higher than that in the control group (P < 0.05). See Table 4.
Comparison of Adverse Reaction Incidence between the 2 Groups
The incidence of adverse reactions in the observation group was 11.43%, and the incidence ofadverse reactions in the control group was 17.14%.The difference was not statistically significant(P > 0.05). See Table 5.
Table 4. Comparison of Serum TNF-α, TGF-β1 and IFN-γ between the 2 Groups before and after the Treatment (n,

Table 4. Comparison of Serum TNF-α, TGF-β1 and IFN-γ between the 2 Groups before and after the Treatment (n,
Note: ①Compared with before the treatment, P < 0.05; ②Compared with the control group after the treatment, P < 0.05.
Group Cases Time TNF-α (ng/mL) TGF-β1 (ng/mL) IFN-γ (ng/mL)Observation group 35 Before the treatment 2.79±0.39 4.89±1.24 0.82±0.39 After the treatment 1.53±0.21①② 2.71±0.62①② 1.28±0.44①②Control group 35 Before the treatment 2.86±0.47 4.77±1.19 0.84±0.43 After the treatment 1.91±0.17① 3.12±0.84① 1.06±0.42①

Table 5. Comparison of Adverse Reaction Incidence between the 2 Groups (n (%))
DISCUSSION
Viral myocarditis is one of the common cardiovascular diseases, and the incidence rate is increasing year by year[6]. At present, patients with viral myocarditis are often improved their prognosis by conventional anti-infective therapy with Meglumine Adenosine Cyclophosphate Injection and related adjuvant therapy[7]. The main component of Meglumine Adenosine Cyclophosphate Injection is adenosine cyclophosphate, and the excipient is meglumine. Related studies have confirmed that the use of Meglumine Adenosine Cyclophosphate Injection can increase myocardial contractility and decrease myocardial oxygen consumption,and it has significant improvement on heart pumping function and sinus node P cell function[8].According to WANG Shu-yun's study[9], the efficacy of meglumine adenosine cyclophosphate in the treatment of viral myocarditis is significant,effectively relieving the pain of patients.
The main components of Shenmai Injection (参麦注射液) are Radix Ginseng Rubra (Hong Shen)and Radix Ophiopogonis (Mai Dong). Radix Ginseng Rubra (Hong Shen) has the effect of nourishing spleen and replenishing qi. Radix Ophiopogonis(Mai Dong) has the effect of nourishing yin and moistening lung. Modern pharmacological studies have shown that[10]Shenmai Injection (参麦注射液)can increase cardiac output. When the concentration is < 1 mg/kg, it can increase blood pressure,while it is > 1 mg/kg, it can dilate blood vessels,decrease blood pressure, and have significant antiinflammatory effects for non-specific inflammation.According to LUO Jin-guang[11]and other studies,Shenmai Injection (参麦注射液) can not only rapidly decrease myocardial damage caused by viral infection, but also relieve related inflammatory reaction, and help the recovery of cardiac function.
This study found that after the treatment,the therapeutic effective rates in the observation group and the control group were 88.57% and 68.57%, respectively, and that in the observation group was higher than that in the control group(P < 0.05), indicating the use of Shenmai Injection(参麦注射液) combined with Meglumine Adenosine Cyclophosphate Injection was more effective in the treatment. According to Wang Xingfen's study[12],Shenmai Injection (参麦注射液) combined with Meglumine Adenosine Cyclophosphate Injection had significant effect on viral myocarditis, which was consistent with the results of this study. After the treatment, the recovery level of cardiac functional indexes like CI, LVEF and FS in the observation group was higher than that in the control group(P < 0.05), indicating that combination therapy would be more conducive to the recovery of cardiac function in patients. QIU Xi-jun[13]and other studies found that the combination therapy could effectively improve cardiac function of patients, which was consistent with the results of their study.
The most common pathogen of viral myocarditis is Coxsackie virus, which is a common virus that not only causes inflammatory damage in patients, but also induces the patient's immune system to produce a variety of cytokines, while the serum expression levels of TNF-α, TGF-β1 and IFN-γ are common laboratory test indexes for viral myocarditis, and it is fast and accurate for the diagnosis of the disease and the identification of pathogens[14]. At the same time, this study also found that after the treatment, the serum levels of TNF-α and TGF-β1 in the observation group were lower than those in the control group (P < 0.05), and the expression level of IFN-γ was higher than that in the control group (P < 0.05). This is because IFN-γ has effects of antivirus and promoting autoimmunity.The higher its expression level, the higher the immunity. According to Chen Rui's study[15], the expression levels of TNF-α and TGF-β1 in patients with viral myocarditis were on the high side, the IFN-γ expression level was on the low side, and the incidence of systemic inflammatory response was higher; after the treatment, the above expression levels would return to normal levels, and the conclusion was consistent with this study.
In summary, the use of Shenmai Injection (参麦注射液) combined with Meglumine Adenosine Cyclophosphate Injection compared with Meglumine Adenosine Cyclophosphate Injection treatment has a more significant clinical effect, contribute to the recovery of cardiac function, effectively decrease serum TNF-α and TGF-β1 levels, and increase IFN-γ level. This study still needs to perform study with higher quality and large-sample clinical data to further confirm clinical efficacy of the 2 medicines.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
World Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine的其它文章
- World Federation of Chinese Medicine Societies Center for Translation
- New Year's Message
- INSTRUCTION FOR AUTHORS
- Professor YANG Yu-fei's Experience on the Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine Treatment Strategy for Advanced Colorectal Cancer
- Two Definitions of Life Will Highlight on Physiological Understanding of Six Meridians
- Clinical Study on CT-guided Modified Akupotomye in the Treatment of Lumbar Nerve Posterior Branch Compression
