A Meta-analysis of Dachaihu Decoction combined with western medicine in the treatment of acute pancreatitis with the TCM syndrome of liver qi depression and liver-gallbladder dampness-heat
2020-02-14KaiBinSunXinYuZhangRongSun
Kai-Bin Sun,Xin-Yu Zhang,Rong Sun
1Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,College of Pharmaceutical Science,Jjinan 250355,China.
2Shandong University,Institute of Advanced Medical Sciences,Jinan 250012,China.
Abstract Backgroud:To evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety of Dachaihu Decoction in the treatment of acute pancreatitis (AP) with the traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) syndrome of liver qi depression and liver-gallbladder dampness-heat.Methods:We searched randomized controlled trials of Dachaihu Decoction in the treatment of AP with the TCM syndrome of liver qi depression and liver-gallbladder dampness-heat from databases in CNKI,WanFang,VIP,Embase,PubMed,and Cochrane Library (from established to August 2019).All the retrieved documents were imported into the Noteexpress software for screening and management,and the included documents were evaluated for quality and data extracted.Statistical analysis was performed with RevMan (version 5.3).Results:A total of 132 articles were retrieved and 8 studies were included to analysis,including 679 patients.Quality evaluation of included studies suggested that the quality of the literatures is generally not high.Meta-analysis showed that the total clinical effective rate of AP was higher in the treatment group than in the control group [OR=5.00,95% CI (2.86,8.73)],and the difference was statistically significant (P <0.00001).The patient's abdominal pain relief time [MD=-0.57,95% CI (-0.86,-0.27),P=0.0002],bloating relief time [MD=-0.71,95% CI (-1.05,-0.37),P =0.04],time of serum amylase returning to normal [MD=-1.00,95% CI (-1.60,-0.40),P=0.001]and time of urinary amylase returning to normal [MD=-1.62,95% CI (-2.88,-0.37),P=0.01]all lower than the control group.But there was no statistically significant difference between the treatment group and the control group at the first defecation time [MD=-0.86,95% CI (-1.75,-0.03),P=0.06].The patient's serum TNF-α levels on the 3rd [MD=-28.53,95% CI (-49.57,-7.49),P=0.008]and 7th day [MD=-26.13,95% CI(-49.76,-2.50),P=0.03]in the treatment group were statistically lower in the treatment group than in the control group.Similarly,the patient's serum IL-6 levels on the 3rd [MD=-6.62,95% CI (-12.49,-0.75),P=0.03]and 7th day [MD=-11.98,95% CI (-22.25,-1.71),P=0.02]were also statistically lower in the treatment group than in the control group.No serious complications or adverse reactions were observed.Conclusion:Dachaihu Decoction combined with western medicine in the treatment of AP with the TCM syndrome of liver qi depression and liver-gallbladder dampness-heat can improve clinical efficacy compared with western medicine alone.In addition,the combination therapy method is safe and can be used for syndrome differentiation of AP patients in the clinic.
Keywords:Dachaihu Decoction,Acute pancreatitis,Liver qi depression,Liver-gallbladder dampness-heat,Meta-analysis
Background
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is an inflammatory reaction with digestion,edema,bleeding and even necrosis of pancreatic tissue caused by a variety of causes.The incidence of AP is increasing year by year.The incidence of AP in Europe has reached 4.6-100 per ten thousand populations [1].There is no the disease name of AP in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM),and AP can be classified as“abdominal pain”,“stomach pain”and“spleen and chest pain”.The location of the disease involves spleen,stomach,liver and gallbladder,and the etiology is complex and various.The pathogenesis is mainly caused by the disorder of ascending and descending conduction of spleen and stomach,abnormal catharsis of liver and gallbladder,and qi blocking of viscera [2,3].In the clinic,Dachaihu decoction combined with routine western medicine is often used to treat AP [4,5].But it is not clear whether the application of Dachaihu decoction in the treatment of AP with syndrome types such as liver qi depression and damp-heat of liver and gallbladder can improve the clinical effective rate,reduce the mortality,relieve clinical symptoms,reduce amylase and inflammatory factors.
This study used met-analysis method to evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety of Dachaihu Decoction in the treatment of AP with the TCM syndrome of liver qi depression and liver-gallbladder dampness-heat.This study will provide evidence of the selective application of Dachaihu Decoction in the treatment of AP.
Materials and methods
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria.①Research types:Randomized controlled trials (RCTs).② Study object:Patients who meet the diagnostic criteria of AP in western medicine and have clear syndrome differentiation in TCM.The patient's sex,age,race and course are not limited.③diagnostic criteria:Refer to the diagnostic criteria of AP in the consensus on Integrated traditional Chinese and Western Medicine for diagnosis and treatment of Acute pancreatitis (2017) [2].④Intervening measure:Control group including early fasting,gastrointestinal decompression,controlled rehydration,correction of water,electrolyte and acid-base balance disorders,use of omeprazole,octreotide,ulinastatin and endoscopic interventional therapy;Treatment group including control therapy methods and modified Dachaihu Decoction.⑤Outcome measures:Total clinical effective rate,mortality,incidence of complications,time for relief of abdominal pain,time for relief of abdominal distension,time for first defecation,time for amylase to return to normal,tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α),interleukin-6(IL-6).The nine indicators contain at least one.
Exclusion criteria.①non-RCTs or the clinical design is not rigorous.②Unable to extract data.③Retrospective studies or animal studies.④reviews articles,case report,conference papers.⑤studies with unclear TCM.
Searching and screening strategies
Published studies were retrieved from 6 databases.Chinese database include China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI),Wanfang Database,and VIP Data.English database include Embase,Pubmed and the Cochrane Library.Time is from established to May 2019.In Chinese database,the keywords were“大柴胡汤”,“急性胰腺炎”,“肝郁气滞”,“肝胆湿热”.In English databases,the keywords were“dachaihu decoction”and“acute pancreatitis”.All the retrieved literatures were imported into Noteexpress software,and two researchers,Sun Kaibin and Zhang Xinyu,read the literatures independently and screened them according to the inclusion and exclusion criterias.If there were differences,they were discussed with Sun Rong,the third researcher,and settled through negotiation.
Data extraction and quality evaluation
We extracted the data from the included studies.The quality evaluation items mainly include random method,allocation hiding,whether the blind method is used,integrity of outcome data,and selective reporting.We used Review Manager 5.3 software to make bar chart of bias risk.
Statistical method
We used the RevMan 5.3 software to meta-analysis.First,heterogeneity test was conducted among the results of each study (test level wasP<0.05).The fixed model was applied in the absence of heterogeneity (P> 0.1,I2< 50%).If there is statistical heterogeneity between the results (P≤ 0.1,I2≥ 50%),the source of heterogeneity is analyzed first.If heterogeneity is excluded,the fixed effect model is used.If not,the random effect model is use.Funnel chart was used to analyze the potential publication bias of the included studies.
Results
Retrieval result
As shown in Figure 1,a total of 132 studies were obtained in the initial examination and 8 RCTs were finally included after screening [6-13].
The characteristics and quality evaluation of included studies
8 RCTs totally include 679 patients.The outcome measures of included 8 studies include total clinical effective rate,incidence of complications,time for relief of abdominal pain,time for relief of abdominal distension,time for first defecation,time for amylase to return to normal,TNF-α and IL-6.No case fatality rate was reported in 8 studies.The basic information of the included studied is shown in Table 1.All studies grouped patients according to the random control principle,and one study [8]adopted the method of“random number table”.All the studies did not mention allocation concealment.Two studies used double-blind method [11]and single-blind method [6],respectively.
Other studies have not explained the implementation of the blind method.Six people lost follow-up in one study,and none of the other studies lost follow-up.The outcome data of all studies were complete and not selectively reported.One study [13]in other bias assessments may have high-risk bias.The detailed information of methodological quality of the included studies is listed in Figure 2 and Figure 3.
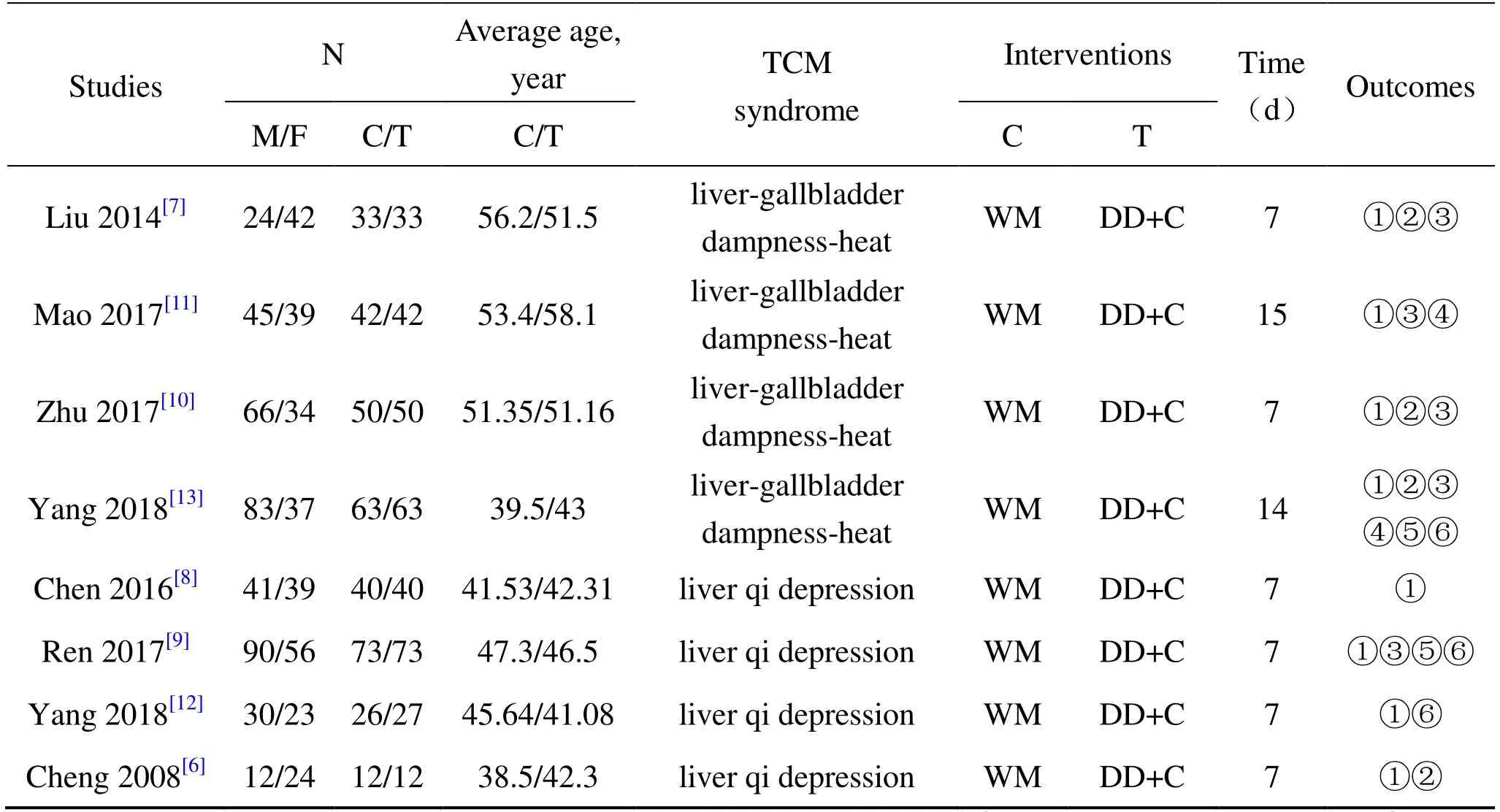
Table 1 General information of included studies
Meta-analysis results
The total effective rate.The total effective rate was reported in 8 studies,including 337 cases in the treatment group and 336 cases in the control group.There was no significant heterogeneity among the studies (P= 0.93,I2=0%),so we used the fixed model to meta-analysis.The meta-analysis results showed that the total clinical effective rate of AP was higher in the treatment group than the control group[OR=5.00,95% CI (2.86,8.73)],and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.00001) (Figure 4).
Evaluation index of curative effect.4 studies [6,7,10,13]reported patient's abdominal pain relief time and 3 studies [7,10,13]reported bloating relief time.2 studies [7,10]reported the first defecation time.4 studies [7,9,10,13]reported the time of serum amylase returning to normal and 3 [7,9,10]reported the time of urinary amylase returning to normal.Heterogeneity test showed that all the studies had heterogeneity,and the heterogeneity was not eliminated after excluding the literature one by one,so the random effect model was adopted.The results showed that in the treatment group,patient's abdominal pain relief time [MD=-0.57,95% CI (-0.86,-0.27),P=0.0002],bloating relief time [MD=-0.71,95% CI (-1.05,-0.37),P=0.04],time of serum amylase returning to normal [MD=-1.00,95% CI(-1.60,-0.40),P=0.001]and time of urinary amylase returning to normal [MD=-1.62,95% CI (-2.88,-0.37),P=0.01]all lower than the control group.But there was no statistically significant difference between the treatment group and the control group at the first defecation time [MD=-0.86,95% CI (-1.75,-0.03),P=0.06](Figure 5).
Level of inflammatory cytokines.2 studies [9,13]reported the TNF-α levels on the 3rd and 7th day after treatment.3 studies [9,12,13]reported the IL-6 levels on the 3rd and 7th day after treatment.Heterogeneity test showed that all the studies had heterogeneity,and the heterogeneity was not eliminated after excluding the literature one by one,so the random effect model was adopted.Resultsshowed that patient's serum TNF-α levels on the 3rd [MD=-28.53,95% CI(-49.57,-7.49),P=0.008]and 7th day [MD=-23.13,95% CI (-49.76,-2.50),P=0.03]in the treatment group were statistically lower in the treatment group than in the control group (Figure 6).Similarly,the patient's serum IL-6 levels on the 3rd [MD=-6.62,95% CI (-12.49,-0.75),P=0.03]and 7th day [MD=-11.98,95% CI (-22.25,-1.71),P=0.02]were also statistically lower in the treatment group than in the control group.
Complications and adverse reactions.Two studies reported complications and adverse reactions during treatment,while the other six studies did not mention.Guohong Yang [13]pointed out that during the treatment,no abnormalities of liver and kidney function,electrolytes and ECG were found,and no serious adverse reactions were found.The combination treatment was safe and reliable.Jiansheng Mao [11]pointed out that during the treatment,there was 1 case of acute respiratory distress,1 case of pancreatic cysts and 1 case of shock in the treatment group,and a total of 3 cases with complications occurred.The incidence of complications was 7.14% in the treatment group.In the control group,there were 3 cases of acute respiratory distress,1 case of pancreatic cysts,3 cases of shock,2 cases of gastrointestinal bleeding,and 4 cases of infection.A total of 13 patients had complications.The complication rate was 33.33% in the control group.
Publication bias
Less than 10 articles were included in this study,so there was no publication bias analysis.
Discussion
As a common disease in clinical gastroenterology,AP is a complicated disease with varied changes.Early loss of treatment on AP is prone to develop into severe acute pancreatitis (SAP),which endangers human health.Ulinastatin,octreotide,cimetidine,antibiotics,antioxidants,and calcitonin are currently used in clinical treatment,but no drug can significantly reduce the short-term mortality of AP [14].The clinical application of TCM to treat or prevent its attack is gaining more and more attention.Dachaihu Decoction consists of eight TCM herbs,includingRadix Bupleuri,Scutellariae Radix,Radix Rhei Et Rhizome,Aurantii Fructus Immaturus,Arum Ternatum Thunb.,PaeoniaeRadix Alba,Jujubae FructusandZingiber Officinale Roscoe.In the prescription,Radix Bupleuriis Jun herb and is good at soothing the liver to relieve depression and reconcile Shaoyang.The minister medicineScutellariae Radixis used to remove the evil of Shaoyang.The light use ofRadix Rhei Et RhizomeandAurantii Fructus Immaturusis actually a minister of medicine for clearing heat of Yangming and promoting the circulation of qi.Radix Rhei Et Rhizomewater extract [15]and emodin and other free anthraquinones[16,17]have good effects on rat models of AP.Network pharmacology research shows that chemical components such as quercetin,luteolin,behenol,baicalein,and emodin may be the main functional substance basis of Dachaihu Decoction in the treatment of AP.Many experimental studies have shown that these components have good Anti-inflammatory activity [18].
The results of this study showed that compared with conventional treatment of western medicine,the combined application of Dachaihu Decoction for the treatment of AP with the TCM syndrome of liver qi depression and liver-gallbladder dampness-heat can improve clinical efficacy,and play a positive role in alleviating abdominal pain,alleviating abdominal distension,promoting the normalization of serum and urine amylase and can significantly reduce the levels of inflammatory factors such as TNF-α and IL-6.However,there is no significant difference between the two treatment schemes for the time of first defecation.In terms of adverse reactions and complications,Yang Guohong [13]found no serious adverse reactions.
Mao Jiansheng [11]pointed out that the incidence of complications in the Dachaihutang treatment group was significantly lower than that in the western medicine treatment group.Two studies further confirmed the safety and efficacy of clinical combination of Dachaihu Decoction and conventional treatment of western medicine.The results suggest that the use of Dachaihu Decoction to treat AP with the TCM syndrome of liver qi depression and liver-gallbladder dampness-heat is safe and effective under the guidance of the theory of TCM.Therefore,this combination can be used clinically.The early stage of AP is from onset to about 10 days.The clinical TCM syndromes are mostly liver qi depression and liver-gallbladder dampness-heat [3,19].Therefore,the treatment of Dachaihu Decoction should be applied early in the onset of AP.
The limited sample size and quality of the studies included in this article increased the risk of bias in this systematic review.Therefore,higher quality clinical trials and more clinical samples are needed to confirm the clinical efficacy and safety of Dachaihu Decoction in the treatment of AP with the TCM syndrome of liver qi depression and liver-gallbladder dampness-heat.Literature quality evaluation showed that the quality of included studies was low,mainly focusing on the two aspects of allocation concealment and blind implementation,suggesting that future clinical research should strictly follow the principle of RCTs when conditions permit.The results showed that there was no heterogeneity in the total clinical effectiveness of the studies,but there was heterogeneity in clinical efficacy and other indicators.Heterogeneity was not eliminated after excluding the articles one by one.We analyzed that the heterogeneity may be caused by the inconsistency in the detection methods of biochemical indicators and the inconsistencies in the determination criteria of observation indicators,which suggests that in future clinical studies,it is necessary to use uniform methods and implement uniform standards.TCM has its own unique theoretical system.Academician Wang Yongyan and others [20,21]believe that syndrome differentiation is the core theory of TCM,but most of the literature does not explicitly include the symptom characterization of cases.In summary,clinical research of TCM should be guided by the theory of TCM,strictly follow the principle of randomized control,and adopt unified methods and standards to provide more high-quality clinical studies and provide detailed references for accurate clinical medication.In addition,for AP,the mortality rate is a more important than effective rate.But no mortality rate was reported in the included studies.So,it is recommended that future clinical studies of AP should report mortality rate.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Drug Combination Therapy的其它文章
- Traditional Chinese medicine combined with low-dose glucocorticoid for treating nephrotic syndrome:A case report
- Analysis of compatibility rules and mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine for preventing and treating postoperative recurrence of bladder cancer
- Jianpi Bushen Recipe affects epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma through TGF-β and Twist
- CDK4/6 inhibitors in the treatment of hormone receptor-positive,HER2-negative advanced breast cancer
