乳腺钼靶摄影与3.0T磁共振对乳腺癌的诊断意义
2020-02-07李小淑
李小淑
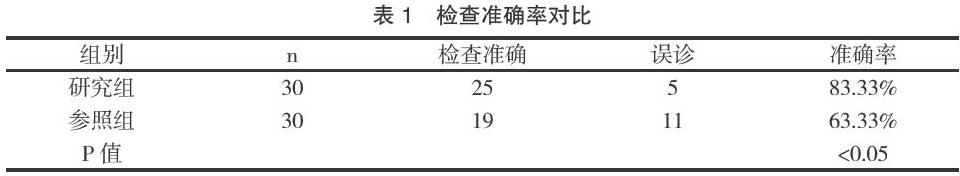
【摘 要】目的:分析乳腺钼靶摄影与3.0T磁共振对乳腺癌中的诊断效果。方法:选取60例乳腺癌患者作为本次实验的研究对象,在入组后,将患者按照诊断方式的不同随机分配为研究组和参照组,每组30例患者,其中,参照组采用钼靶摄影,观察组使用3.0T磁共振,对比两种诊断方式的准确率。 结果:在实验后发现,采用3.0T磁共振诊断的研究组,诊断准确25例,准确率(83.33%);而使用钼靶摄影的参照组,准确检测例数19例,准确率(63.33%)。组间差较大,有明显可比性,(P<0.05)。结论:在乳腺癌的检查诊断中,采用3.0T磁共振,准确率较高,且在检测过程中,并不会辐射太强而影响患者的身体,因此,应用价值较高。
【关键词】乳腺癌;钼靶摄影;3.0T磁共振;诊断准确率
【中图分类号】R737.9 【文献识别码】B【文章编号】1002-8714(2020)01-0006-01
【Abstract】 Objective: To analyze the diagnostic effect of mammography and 3.0T magnetic resonance in breast cancer. Methods: 60 patients with breast cancer were selected as the subjects of this experiment. After being enrolled in the study group, the patients were randomly assigned to the study group and the reference group according to the different d stic methods. According to the different diagnostic methods, the patients were randomly assigned to the reference group and the research group, 30 patients in each group. Among them, molybdenum target photography was used in the control group and 3.0 was used in vation group. T-magnetic resonance imaging was used to compare the accuracy of the two diagnostic methods. Results: After the experiment, 25 cases were diagnosed rately by 3.0T magnetic resonance (MR), the accurac 83.33%, while 19 cases were detected accurately by mol target photography (MR), the accuracy rate was 63.33%. The differen groups was significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion: In the di of breast cancer, 3.0T magnetic resonance imaging has a high accuracy, and in the detection process, the radiation will not be too strong to affect the patients body, so it has a high application value.
【Key words】breast cancer; molybdenum target radiography; 3.0T magnetic resonance; diagnostic accuracy
1 资料与方法
1.1一般资料
在本次对照实验中,共有60例研究对象,均为乳腺癌患者,入组后,根据不同的诊断方式将其分为了研究组和参照组。60例患者中,最小年龄39岁,最大年龄67岁,平均年龄(54.39±2.08)岁,对比患者的一般资料,无较大差异,不具备可比性,(P>0.05)。
1.2方法
参照组采用钼靶摄影,设备采用GE X光机,并严格按照操作规范调整焦点、焦距,并采用激光相机进行图像打印,将扫描位置设定为双侧乳腺斜位、轴位摄影。研究组使用3.0T磁共振诊断,护理人员要将检查过程中的注意事项告知患者,并协助其保持俯卧位,将扫描位置、扫描间距、层厚等设定完毕后开始检测[1]。
1.3观察指标
以两种诊断方式的诊断准确率作为观察指标。
1.4统计学处理
实验过程中,数据间的分析处理使用SPSS22.0,诊断准确率(%),以(P>0.05)表示无可比性。
2 结果
在实验后发现,采用3.0T磁共振诊断的研究组,诊断准确25例,准确率(83.33%);而使用钼靶摄影的参照组,准确检测例数19例,准确率(63.33%)。组间差较大,有明显可比性,(P<0.05)。
2.1
3 讨论
准确的诊断是治疗的前提,对于乳腺癌的诊断主要有3.0T磁共振和钼靶摄影,据其应用效果来看,3.0T磁共振的效果更好,可以通过其先进的磁共振技术,立体的、全面的扫描病症部位,准确定位病灶;而钼靶摄影虽然在乳腺癌诊断方面的应用率也较高,但在立体性、致密性方面較差,因此诊断效果略有不足[2]。
由实验结果来看,3.0T磁共振的诊断准确率更高,研究组的准确率为(83.33%),参照组仅为(63.33%),(P<0.05),由此可见,3.0T磁共振在乳腺癌检测方面应用价值较高,适宜在临床上广泛推广。
参考文献
[1] 王思佳,吴金萍. 彩色多普勒超声成像和乳腺X线摄影对早期乳腺癌诊断价值的对比[J]. 河北医学,2016,22(01):78-81.
[2] 荆彦平,高峥嵘,骆宾,张俊,南晓东,辛欣,张焱,程敬亮. MRI、钼靶摄影、超声对乳腺癌术前评估的价值及比较[J]. 现代肿瘤医学,2015,23(03):400-403.
