Diagnostic Utility of Interferon-Gamma Release Assay in Tuberculous Lymphadenitis
2020-01-10XinchaoLiuSusuYeWenzeWangYueqiuZhangLifanZhangXiaochengPanZiyueZhouMiaoyanZhangJianghaoLiuZhiyongLiangXiaoqingLiu
Xinchao Liu,Susu Ye,Wenze Wang,Yueqiu Zhang,Lifan Zhang,3,Xiaocheng Pan,Ziyue Zhou,Miaoyan Zhang,Jianghao Liu,Zhiyong Liang,Xiaoqing Liu,3*
1Department of Infectious Diseases,Peking Union Medical College Hospital,
2Department of pathology,Peking Union Medical College Hospital,
3Clinical Epidemiology Unit,International Epidemiology Network,
4Department of Internal Medicine,Peking Union Medical College Hospital,Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences &Peking Union Medical College,Beijing 100730,China
Key words:Tuberculous lymphadenitis (TBL);T-SPOT.TB;diagnostic test;sensitivity;specificity
Objective The aim of this study was to evaluate the diagnostic performance of T-SPOT.TB for tuberculous lymphadenitis.Methods Suspected tuberculous lymphadenitis patients between September 2010 and September 2018 who had both peripheral blood T-SPOT.TB test and lymph node biopsy were retrospectively enrolled in this study.The cutoff value of T-SPOT.TB test for peripheral blood was set as 24 spot forming cell (SFC)/106 periphreral blood monocyte cell (PBMC) according to the instruction of testing kits.The gold standard for diagnosis of TBL was the combination of microbiology results,histopathology results and patient's response to anti-TB treatment.Diagnostic efficacy of T-SPOT.TB was evaluated,including sensitivity,specificity,accuracy,predictive values,and likelihood ratio.Results Among 91 patients who met the inclusion criteria,we excluded 8 cases with incomplete clinical information and 6 cases who lost to follow-up.According to the gold standard,there were 37 cases of true TBL (9 confirmed TBL and 28 probable TBL),30 cases of non-TBL,and 10 cases of clinically indeterminate diagnosis who were excluded from the final analyses.The T-SPOT.TB tests yielded 43 cases of positive response and 24 cases of negative response.The sensitivity,specificity,accuracy,positive predictive value (PPV),negative predictive value(NPV),positive likelihood ratio (PLR) and negative likelihood ratio (NLR) of peripheral blood T-SPOT.TB for diagnosing TBL were 89.2%,66.7%,79.1%,76.7%,83.3%,2.68 and 0.16,respectively.The number of SFCs of T-SPOT.TB in TBL patients [432(134-1264)/106 PBMCs]was higher than that in non-TBL patients [0 (0-30)/106 PBMCs]with a significant difference (Z=-5.306,P <0.001).Conclusion T-SPOT.TB is a rapid and simple diagnostic test for TBL with a high sensitivity and negative predictive value.
TUBERCULOSIS (TB),an infectious disease and serious health hazard,caused 1.2 million deaths among HIV-negative people in 2018 according to the World Health Organization (WHO).1China bears a high burden of TB in the world.According to the estimation of WHO,in 2016,China had 895 000 new infections of TB,which ranked only after India and Indonesia.Tuberculous lymphadenitis (TBL) is the most common extra-pulmonary tuberculosis,which accounts for 4.0% to 5.1% of all tuberculosis and 14.5% to 50.0% of extra-pulmonary tuberculosis cases.2-5The clinical manifestations of TBL can be atypical,and misdiagnosis is common.It usually requires tissue culture and pathological verification to make a definitive diagnosis.However,the cultivate yield from lymph node biopsy is usually extremely low,therefore it is paramount to develop a rapid,sensitive and less invasive diagnostic utility.
Interferon gamma release assay (IGRA),including QuantiFERON-TBGold and T-SPOT.TB,is based on cellular immune response,and has been introduced into the diagnosis of tuberculosis in recent years.It was reported that IGRA in the diagnosis of TBL had sensitivities of 78.8%-95.2% and specificities of 52%-95.5%.4,6-13The great varieties of these results are likely due to the inability to acquire both IGRA and lymph node biopsy simultaneously,and the small sample size in each study.Some studies were designed for all entities of extra-pulmonary tuberculosis,making them less specific for TBL evaluation.4,6,12,13This study was designed to explore the diagnostic utility of T-SPOT.TBin TBL by using results from tissue culture,pathology and clinical follow-up.
PATIENTS AND METHODS
Patient selection
This retrospective study was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board of the hospital (SK367) and patient information consents were waived.The study was designed to evaluate suspected TBL patients from Peking Union Medical College Hospital between September 2010 and September 2018.We retrospective searched databases to retrieve all inpatients and outpatients with both lymph node biopsy pathology and peripheral blood T-SPOT.TBresult.Histological diagnosis was obtained for the lymphadenopathy from all cases either by thoracic/abdominal surgery or by superficial lymph node biopsy.Clinical information including demographic characteristics,symptoms,underline conditions,sites of biopsy,etc.,were acquired through charter review.The inclusion criteria for patients were as follows:1.Age greater than 18 years old;2.at least one of the following manifestations:(1) symptoms of fever,weight loss,or night sweat;(2) peripheral lymph node swelling by physical examination;(3) lymph node enlargement confirmed by CT or MRI.Cases with insufficient charter information to make definitive diagnosis or lost to follow-up were excluded.
Two physicians specialized in infectious disease made categorization of patients' diagnosis independently based on patients' clinical manifestations,imaging findings,microbiology,pathology results,and therapeutic effect of anti-tuberculosis treatment in the follow up period without knowing T-SPOT.TBresults.For cases whose definitive diagnosis could not be reached from the initial visit,we further reviewed medical records of the following three months,or we followed up by phone call to determine anti-TB treatment response of the patient.When the two physicians perceived different opinions,a third specialist would be consulted for the final diagnosis.
Diagnostic categorization for TBL
The gold standard for TBL was the combination of microbiology result,pathology result,and patients' response to anti-tuberculosis treatment.Patients were categorized into 4 groups according to protocols in the study of Liao CHet al.3Confirmed TBL and probable TBL was considered as true TBL according to the gold standard.
1.Confirmed TBL:Mycobacterium tuberculosis(MTB) culturing of lymph node tissue is positive,or tissue Acid-fast staining is positive.
2.Probable TBL:histological findings are consistent with TBL (granulomatous inflammation and/or caseous necrosis and/or multinucleate giant cell),and the patient responds clinically and radiologically to anti-TB treatment.
3.Indeterminate TBL:do not meet the above diagnostic criteria or fail to reach a conclusive diagnosis during a 3-months follow-up.
4.Non-TB:alternative diagnosis is made,or there is clinical improvement without anti-TB treatment.
T-SPOT.TB test
T-SPOT.TBis generally ordered for patients who frequently present fever,weight loss,night sweat,and elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR),suspecting for TB infection.We collected 4 ml heparin-anticoagulated venous blood from these patients,and blood samples were sent for T-SPOT.TBtest (Oxford Immunotec,Abingdon,UK) within 6 hours by a laboratory personnel who was blinded to patients' clinical data.T-SPOT.TButilized AIM-V (GIBCOTM AIM V Medium liquid,Invitrogen,USA) as negative control,phytohemagglutinin (PHA) as positive control,early secreted antigenic target 6-kDa protein (ESAT-6) and culture filtrate protein 10 (CFP-10) as specific antigens,respectively.Peripheral blood monocyte cells (PBMC)from each subject were separated and prepared at a concentration of 2.5×106/ml,and then plated (2.5×105per well) on a plate precoated with antibody against interferon γ.Plates were incubated 16-18 h at 37°C in 5% carbon dioxide.After incubation,wells were developed with a conjugate against the antibody and an enzyme substrate.Spot forming cells (SFCs) were counted with an automated ELISPOT reader (AID-ispot,Strassberg,Germany),with each SFC representing an antigen-specific T cell secreting interferon γ.The response was considered positive if the antigen well contained 6 or more spots and had twice the number of spots as seen in the negative control well,based on the T-SPOT.TBkit (Oxford Immunotec,Abingdon,UK)operating instruction.The background spots number should be less than 10 for the negative control well of PBMC and greater than 20 for the positive control well of PBMC.The cutoff value of T-SPOT.TBtest for peripheral blood was set as 24 SFC/106PBMC according to the test kits instruction.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 19.0 software (SPSS Inc,Chicago,IL).Normal distribution was determined by Kolmogorov-Smirnov tests.Continuous data with normal distribution was expressed as mean ± standard deviation,while non-normal distributional data was expressed as median and interquartile range.Classification data was expressed as percentage.T-test and Mann-Whitney U test were used to compare continuous variables of normal distribution and non-normal distribution,respectively.The 95%confidence interval (CI) was estimated from the binomial distribution.P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Characteristics of the subjects
From patients who had both T-SPOT.TBtest and lymph node biopsy pathology in our database,91 patients with suspicious tuberculous lymphadenitis were included in this study.Among them,we excluded 6 cases who are lost to follow-up and 8 cases with incomplete clinical information from analysis.The process of patient selection is illustrated in Figure 1.Of the remaining 77 patients,28 were male and 49 were female;their age ranged from 18 to 75 years old,with mean of 47.9±14.1 years old.The HIV serological antibody tests of all subjects were negative.There were 9 confirmed TBL cases,28 probable TBL cases,10 indeterminate TBL cases,and 30 non-TB cases.The clinical demographic characteristics of the enrolled patients are shown in Table 1.
The diagnostic performance of T-SPOT.TB for TBL
Of the enrolled 77 patients,according to the gold standard,37 patients were true positive of TBL (9 confirmed TBL cases and 28 probable TBL cases),30 cases were true negative of TBL (non-TBL).The indeterminate TBL cases (n=10) were excluded from the diagnostic test.Of 37 TBL cases,T-SPOT.TBwas positive in 33 cases,with the sensitivity of 89.2% (95%CI:73.6%-96.5%).In 30 non-TBL patients,20 cases were negative by T-SPOT.TB,with the specificity of 66.7% (95%CI:47.1%-82.1%) (Table 2).The accuracy of T-SPOT.TBfor TBL was 79.1%.The positive predictive value,negative predictive value,positive likelihood ratio and negative likelihood ratio of T-SPOT.TBfor TBL were 76.7% (95%CI:61.0%-87.7%),83.3% (95%CI:61.8%-94.5%),2.68 (95%CI:1.59-4.49) and 0.16 (95%CI:0.06-0.42),respectively.
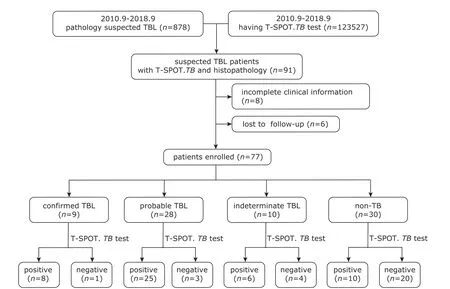
Figure 1.The flow chart of enrolling patients in the study.TBL,tuberculous lymphadenosis;TB,tuberculosis.
The number of IFN-γ-secreting T cells(SFCs,Spot Forming Cells) in peripheral blood
The number of ESAT-6 antigens in the TBL group and the non-TBL group were 236 (48-508) SFCs/106PBMCs and 0(0-0) SFCs/106PBMCs,respectively (Z=-5.274,P<0.001) (Figure 2).The number of CFP-10 antigens in the TBL group and the non-TBL group were 148 (36-690) SFCs/106PBMCs and 0 (0-28) SFCs/106PBMCs,respectively (Z=-4.630,P<0.001).Thetuberculosis mycobacteriaspecific antigen T-SPOT.TBSFCs,which was the sum of ESAT-6 and CFP-10 SFCs,of the TBL group and the non-TBL group were 432(134-1264) SFCs/106PBMCs and 0 (0-30) SFCs/106PBMCs,respectively (Z=-5.306,P<0.001).
DISCUSSION
Tuberculosis is an important threatening for public health.Tuberculous lymphadenitis is one of the most common extra pulmonary tuberculosis.The clinical manifestations of tuberculous lymphadenitis are mostly non-specific,which makes the definitive diagnosis quite challenging.At present,the most commonly used test forMycobacterium tuberculosisinfection is still the tuberculin skin test.But its low sensitivity and low specificity,14,15potential influenced by bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccination and environmental mycobacterial infection,not being applicable in immunosuppressed patients and severe tuberculosis patients,have limited its universal clinical application.
Ever since Koch discoveredMycobacterium tuberculosisin 1882,acid-fast staining has been the cornerstone of tuberculosis diagnosis.16The number ofMycobacterium tuberculosisin tissue samples needs to be greater than 104/ml to yield a positive acid-fast staining result.However,tuberculous lymphadenitis usually contains very fewMycobacterium tuberculosis,which makes the sensitivity of acid-fast staining in diagnosing TBL extremely low (0-40%).17,18Also,non-tuberculous mycobacterium can be acid-fast positive.We found only 9 out of 37 TBL patients (24.3%)were positive for acid-fast staining in this study.Mycobacterium tuberculosisculture and identification is still the gold standard,which usually takes 4-6 weeks to isolate,and the positive rate of culturing can be as low as 30%-67.2%.19PCR can be a useful method in diagnosingMycobacterium tuberculosisinfection,with sensitivities and specificities of 88%-90.3% and 82%-100%,respectively,20-22and the result can be ob-tained in a few hours.However,PCR in diagnosing TBL requires invasive methods for sampling,professional staff and advanced laboratory facilities.Furthermore,it cannot determine whether theMycobacterium tuberculosisin tissue is alive or not.23,24
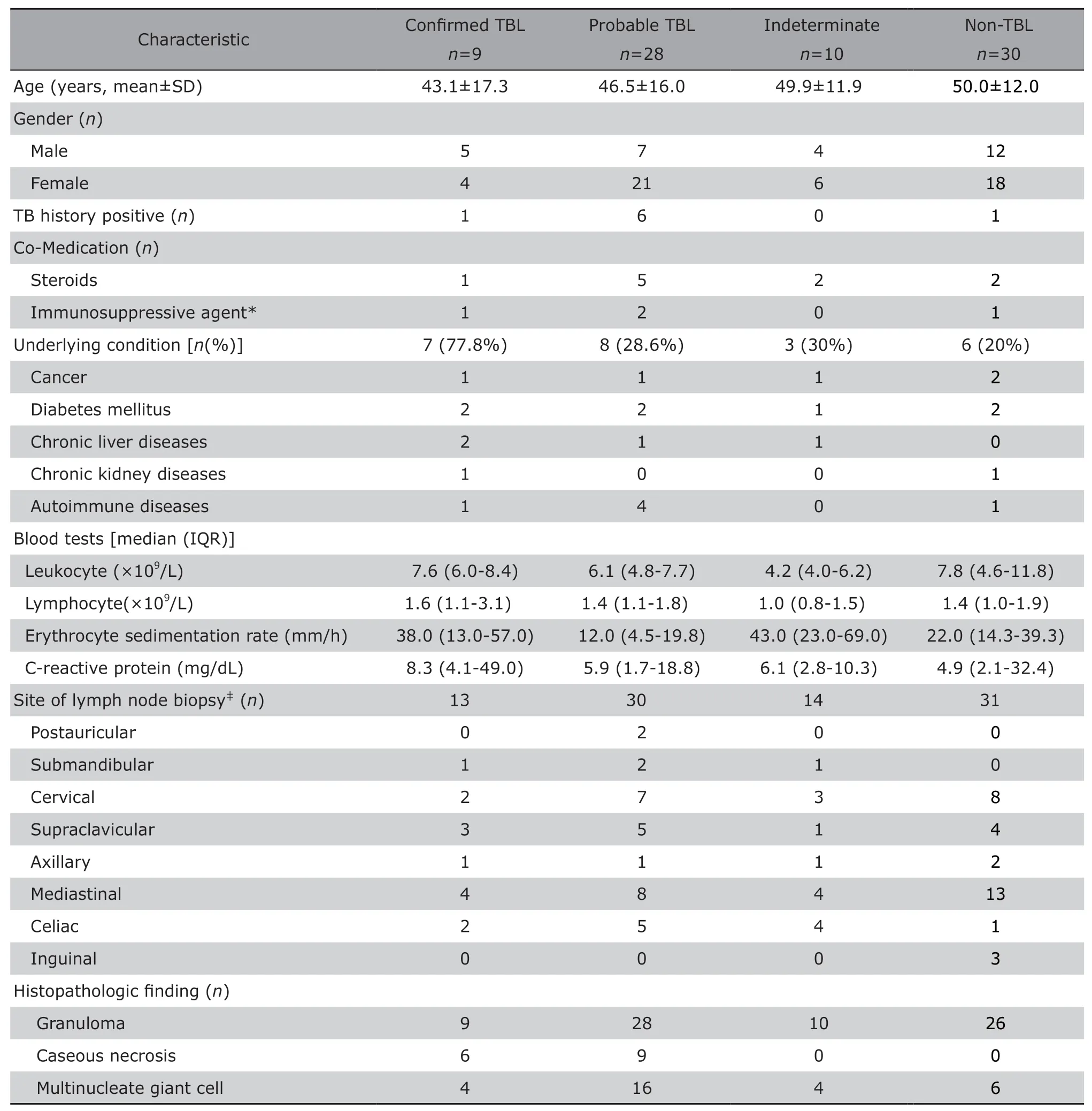
Table 1.Demographic and clinical characteristics of suspected TBL patients enrolled (n=77)
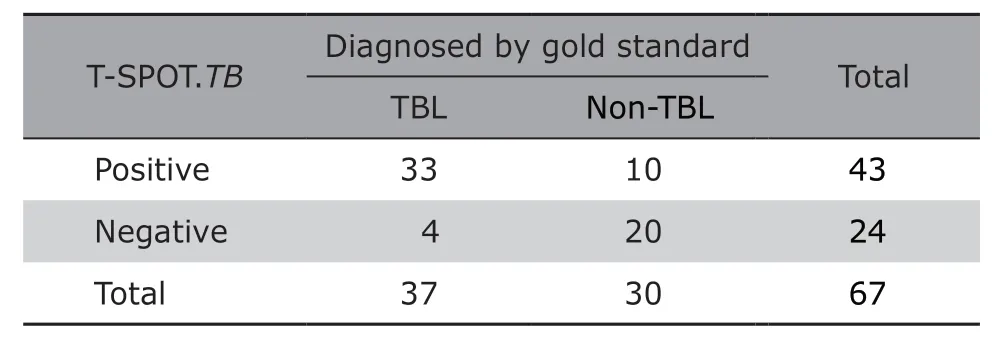
Table 2.Diagnostic yields of T-SPOT.TB for the suspected tuberculous lymphadenitis
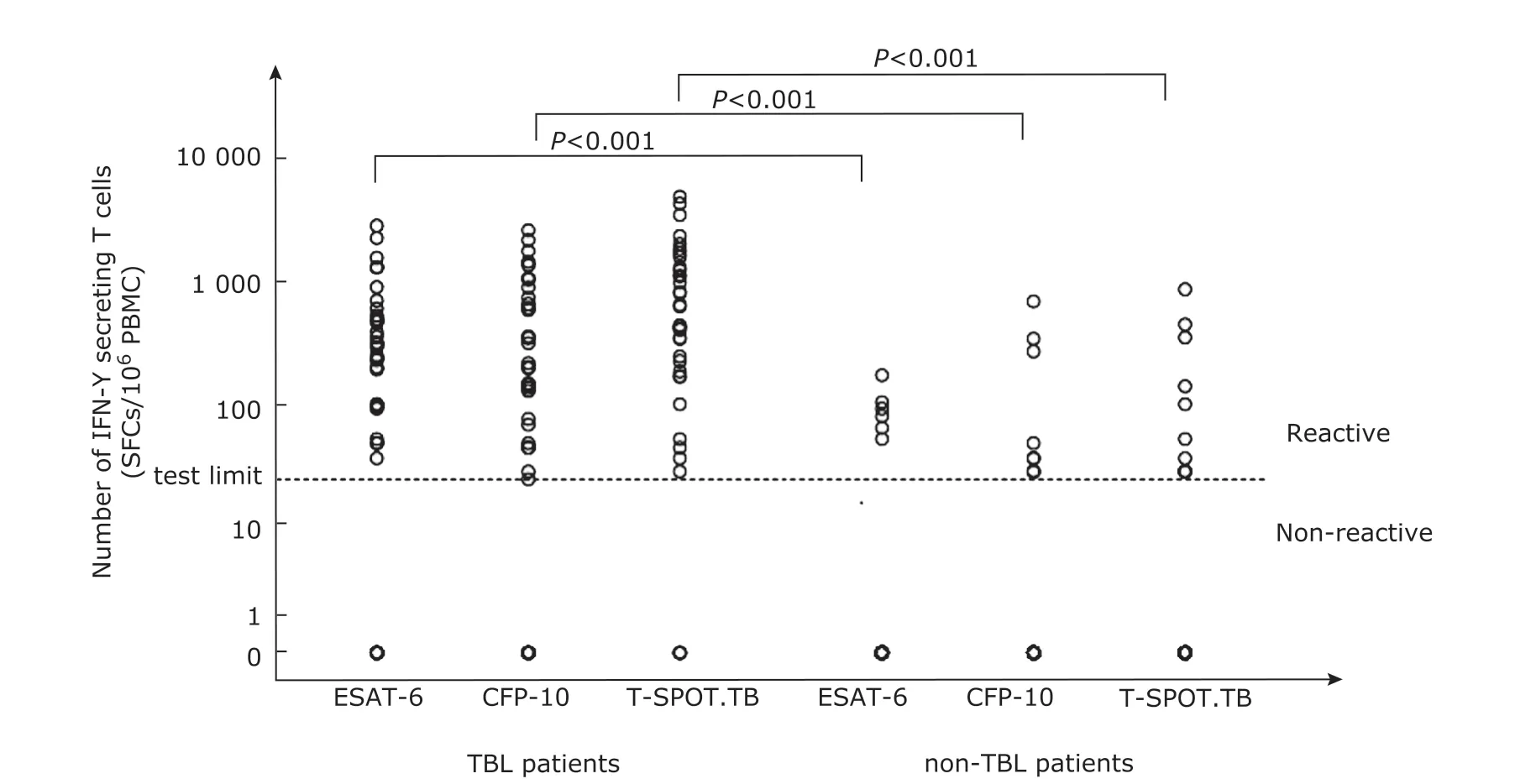
Figure 2.The number of mycobacterium tuberculosis specific IFN-γ secreting T cells in peripheral blood of TBL patients and non-TBL patients.Significant difference in the number of ESAT-6,CFP-10 and total T-SPOT.TB spots between TBL group and the non-TB group (all P<0.001).The segmentation line indicates the threshold value of T-SPOT.TB (24 SFCs/106 PBMC).Results below the threshold were all present as 0.ESAT-6,early secreted antigenic target 6-kDa protein;CFP-10,culture filtrate protein 10.
In recent years,IFN-γ release assays (IGRA)have been developed for screening tuberculosis infections,including whole blood IFN-γ enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (QuantiFERON-TB Gold) and enzyme-linked immunospot assay (T-SPOT.TB).T-SPOT.TBis a new immunological diagnostic tool for the detection ofMycobacterium tuberculosisinfection.It is not influenced by BCG vaccination and most infections of non-tuberculous mycobacteria.The sensitivity of T-SPOT.TBis also high in that one specific T lymphocytes can be detected in every 1 million peripheral blood mononuclear cells,and the entire detection process only takes 2 days.25According to the peripheral blood T-SPOT.TBresult in current study,the number of spot forming cells was significantly higher in TBL patients than in the non-TBL patients.Peripheral blood T-SPOT.TBshowed a good sensitivity (89.2%) but a relative low specificity (66.7%) for diagnosis of TBL.These results were comparable with that in previous reports where T-SPOT.TBin diagnosing TBL had sensitivities of 81%-95%,specificities of 52%-80%.10-13It was reported that the false negative T-SPOT.TBresults might be associated with elderly age,serious comorbidities such as liver cirrhosis,and other underlying diseases.26,27Thus,T-SPOT.TBresult should be interpreted discreetly in these population.In the current study,4 cases of 37 TBL patients were T-SPOT.TBnegative.
We found that peripheral blood T-SPOT.TBhad a good negative predictive value (83.3%) for TBL,which was high,and this was consistent with the study result of Jiaet al.10who reported a negative predictive value as high as 95.9%.Therefore,T-SPOT.TBmay have a great value in excluding the diagnosis of TBL.Of the non-TBL group,10 patients had positive T-SPOT.TBresults (FPR,33.3%),but only one of them had a history of tuberculosis.We speculate that these cases may have latent tuberculosis infections.Gao and colleagues reported a high prevalence of latent tuberculosis in China,28with the QuantiFERON-TB positive rate being 13%-20%,which may explain the relatively low specificity of T-SPOT.TBin diagnosing TBL.
In this study,the number of T cells that responded to ESAT-6 in the TBL patients appeared to be higher than the number of T cells that responded to CFP-10,but the difference was not statistically significant.Similar findings were reported in female genital tuberculosis patients29and in active TB infection populations.30However,as these studies are not specifically targeting patients of TBL,more TBL specific researches are needed.
TBL is generally considered to be prevalent mainly in children.However,to our clinical experience in recent year,it is commonly seen in people of 20-40 years old,especially in women.The gender preference was documented in this study as well.The reason women are more susceptible to TBL is still unclear.Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-10 may play a role.31CD4+lymphocyte counts,endocrinal factors,socioeconomic factors,and cultural factors might also be involved in the gender difference.32The most commonly involved lymph node of TBL in our study was mediastinal lymph nodes (32.4%),followed by cervical lymph nodes(24.3%),supraclavicular lymph nodes (21.6%).Jiaet al.found that the most commonly involved lymph node was cervical lymph nodes (86.7%),followed by axillary lymph nodes (6.0%) and inguinal lymph nodes(3.6%).10The inconsistency in this aspect may be largely associated with differences in patients characteristics of the healthcare facilities,where the hospital of the current study receives more complicated and severe cases with enlargement of deep lymph nodes.
Our study has several limitations.This is a retrospective study and the sample size is relatively small,which may introduce bias that leads to either over or under-estimation of the final outcome.In addition,as the healthcare institution where study was conducted is the National Center for Difficult and Complicated Cases,patients in this study are generally severe or complicated cases,the results should be applied with caution when T-SPOT.TBbeing applied to hospitals with different patient characteristics.It is necessary to perform multi-centric large sample-sized studies to further evaluate the diagnostic value of T-SPOT.TB.
In summary,the study suggests that T-SPOT.TBmay be considered as a simple,rapid,highly sensitive tool for TBL diagnosis with good negative predictive value.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declared no conflict of interests.
Article information
Part of results in this study were presented by poster at the IDWeek conference 2017,San Diego.
杂志排行
Chinese Medical Sciences Journal的其它文章
- Bevacizumab Combined with Icotinib Overcomes Osimertinib Resistance in a Patient of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- An Optimized Protocol of Azoxymethane-Dextran Sodium Sulfate Induced Colorectal Tumor Model in Mice
- Ontology:Footstone for Strong Artificial Intelligence
- Antagonistic Effects of N-acetylcysteine on Mitogenactivated Protein Kinase Pathway Activation,Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Responses in Rats with PM2.5Induced Lung Injuries
- Physiological Variables Associated with the Development of Acute Mountain Sickness
- A Single-center Retrospective Cohort Study on Cesarean Section under General Anesthesia
