The intervention effect of virtual reality technology on patients recovering from traumatic brain injury:a meta analysis
2020-01-01XiaoXiaoYangYuanYuanChenFanJieMeng
Xiao-Xiao Yang,Yuan-Yuan Chen,Fan-Jie Meng*
1Graduate college,Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Tianjin,301600,China.
2College of health engineering,Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Tianjin,301600,China.
Abstract
Key words:Virtual reality,Traumatic brain injury,Balance,Systematic review,Randomized controlled trial.
Introduction
Traumatic brain injury(TBI)is a brain injury caused by external force and is a common surgical emergency [1].Common defects after craniocerebralinjury include ataxia,postural instability,tremor,balance disorder and fine motor skills disorder,and even cognitive disorders[2].At present,the rehabilitation of brain trauma has made great progress,but there are still many patientswith balancedysfunction and motor dysfunction,which seriously affects the quality of life of patients[3].
Virtual reality(VR)is an artificial environment synthesized by computers,which enables users immersed in it to generate visual,listening,touch and other feelings,and obtain human-computer interaction experience in three-dimensional visual space,giving users the same impression as the real environment in the real world[4,5].VR can provide a rich and colorful scene environment and simulate a variety of real training programs to greatly mobilize the enthusiasm of patients in training[6].By creating a simulation model,the participants feel that the environment is real and allow direct interaction with the dynamic environment created by the computer.VR training technology has the characteristics of low cost,convenientuse,rich interestand repeatable operation,attracting patients to participate in the training [7].Studies have shown thatVR technology can improve balance function,postural control ability,motor function,daily life ability and other aspects of patients recovering from TBI,butithas notbeen proved by systematic evaluation.This study explored the effect of VR technology on the intervention of patients recovering from TBI and provided evidence-based evidenceto promotetheapplication ofVR technology in TBI.
Materials and methods
Inclusion criteria and exclusion criteria
Types of studies:the randomized controlled trials(RCTs)were included with out restriction of publication language.Master theses and conference papers were not included.
Types of participants:patients who meet the diagnostic criteria for traumatic brain injury and had been diagnosed by CT and MRI with clear consciousness and who were in recovery.There was no limitation on the type,stage and severity of traumatic brain injury.The injury caused by cerebrovascular accident cannot be included.There was no restriction on race,nationality,age or course of illness.
Types of interventions:the experimental group applied virtual reality technology training combined with conventional rehabilitation training.The rehabilitation system used by virtual reality technology had various modes such as upper and lower limb movement,walking posture,sitting posture,cognition and balance training.The patient accepted balance exercises and according to himself in the virtual scene.They needed to go up and down the stairs,skis,insert wood,open motorboat,wipe the table,play vegetable games and dodge shark games,which not only can exercise the flexibility and balance of the trunk,but also help to control the center of gravity.The control group adopted conventional rehabilitation training,including exercise therapy,occupational therapy and speech therapy,etc.
Outcome indicators:the assessment of indicators adopted the internationally used assessment tools.Balance function was evaluated according to Berg balance scale(BBS);motor function was assessed according to the Fugl-Meyer assessment scale(FMA);assessment of daily living ability was according to Barthel index(BI)assessment scale.Posture control ability assessment used body center of pressure(COP);mental state scores was evaluated according to mini-mental state examination(MMSE);timed up and go test was evaluated according to functional gait Assessment(FGA);unified balance scale was evaluated according to unified balance scale(UBS).
Exclusion criteria:(1)Other musculoskeletal and joint diseases that affect walking,such as osteoarthritis and fractures;(2)unstable condition;(3)serious dysfunction of heart,liver,kidney and other importantorgans;(4)non-Chinese and English literature;(5)repeated publications;(6)literature with too little report information to be used;(7)the study design does not conform to the randomized controlled trial;(8)literature review.
Search methods
The computer retrieved CNKI,VIP,Wan Fang,Embase,the Cochrane Library and Pub Med database.The retrieval period was from the establishment of the database to July 2019.Search strategies were:(virtual reality or virtual environment or video game or VR)and(cerebral trauma or brain trauma or brain injury or traumatic brain injury).Use all relevant keywords and keywords to search,if the abstract meets the inclusion criteria,further search and read the full text,and trace the references of the obtained.
Data extraction
Two investigators independently extracted data for the included trials using a standardized data extraction sheet,which included year,author,country,sample size,baseline characteristics of patients,duration of treatment,duration of disease,interventions and outcomes.Any discrepancies were resolved by discussion.
Risk of bias assessment
The risk of bias in the included studies was assessed by 2 researchers using the Cochrane manual tool for risk assessment of bias in RCTs.Seven items were included:generation of random order,concealment of random scheme allocation,blind method for research objects and intervention implementors,blind method for outcome evaluators,integrity of outcome indicator data,possibility of selective reporting of research results,and other sources of bias.The evaluator should make a low bias risk,high bias risk and unclear judgmentfor each project.If the research completely meets the standard,the methodology quality level is A;if the standard is partially met,the quality level of methodology is B;the study that completely failed to meet the quality standard was rated as C,and those with a methodology quality level of C were not included in this analysis.
Statistical analysis
RevMan 5.3 software was used for meta analysis of the data.Firstly,the X2test was used to test the heterogeneity among the literature results.If the detection results wereP>0.1 and I2<50%,there was no statistical heterogeneity.IfP<0.1,I2≥50%,no clinical heterogeneity was determined,the random effectmodel was adopted for meta-analysis.
Results
Search results
542 related articles were detected.The 120 articles wereexcluded by checking theNoteExpress software,after reading the title and abstract,46 articles were included,376 articles were excluded for no mention of VR,brain trauma,non-clinical trials.Further search and read the full text,exclude non-randomized controls and 39 articles were excluded due to non-randomized controlled trials or others and finally 7 articles were included.The detailed screening process was shown in f l ow diagram(Figure 1).The characteristics of included studies were summarized in Table 1.The included studies were published from 2014 through 2018.The studies included 386 participants,with sample sizes ranging from 20 to 120.The methodological quality of all 7 studies was grade B.
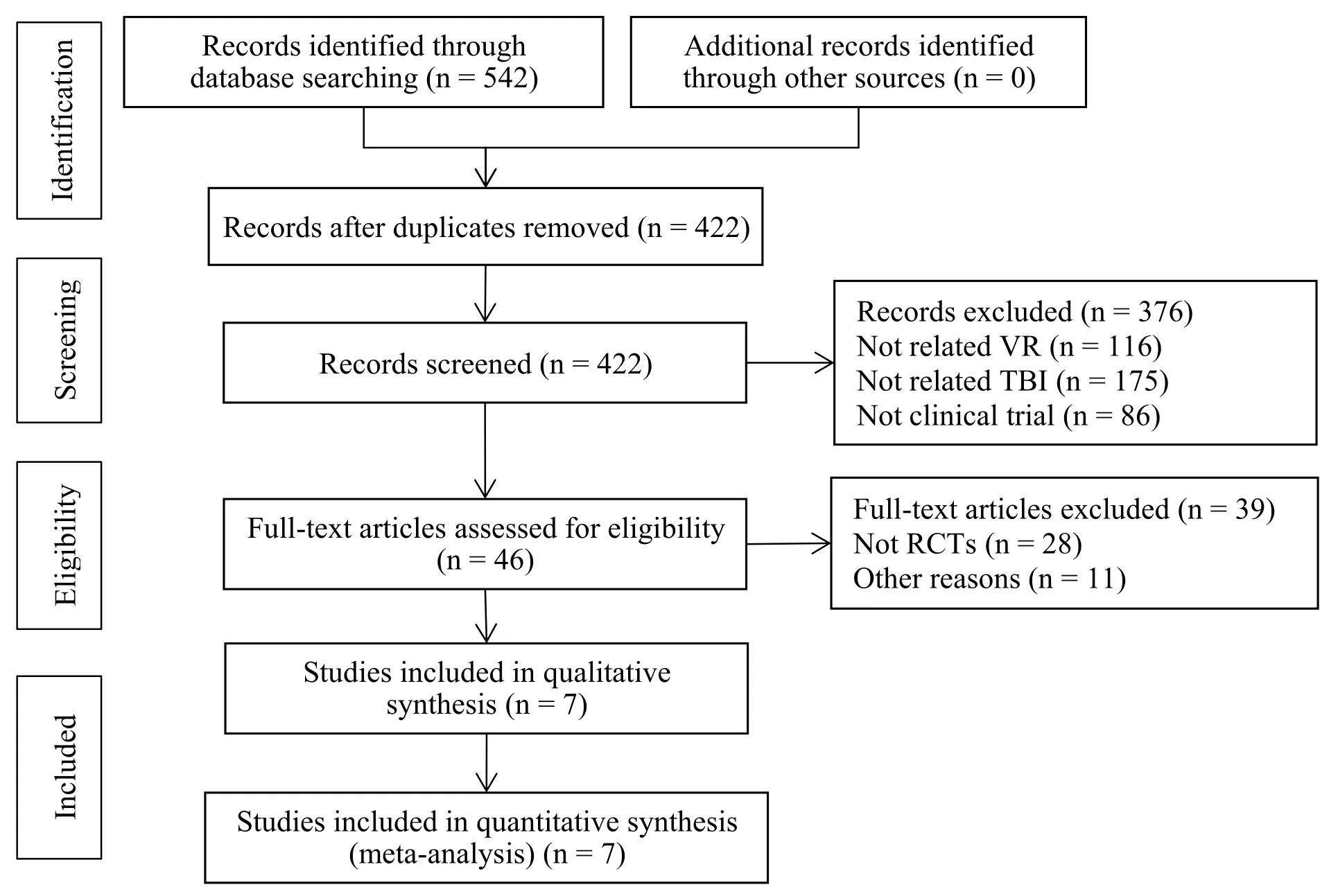
Figure 1 Literature screening process and results.TBI,traumatic brain injury;VR,virtual reality;RCTs,randomized controlled trials.
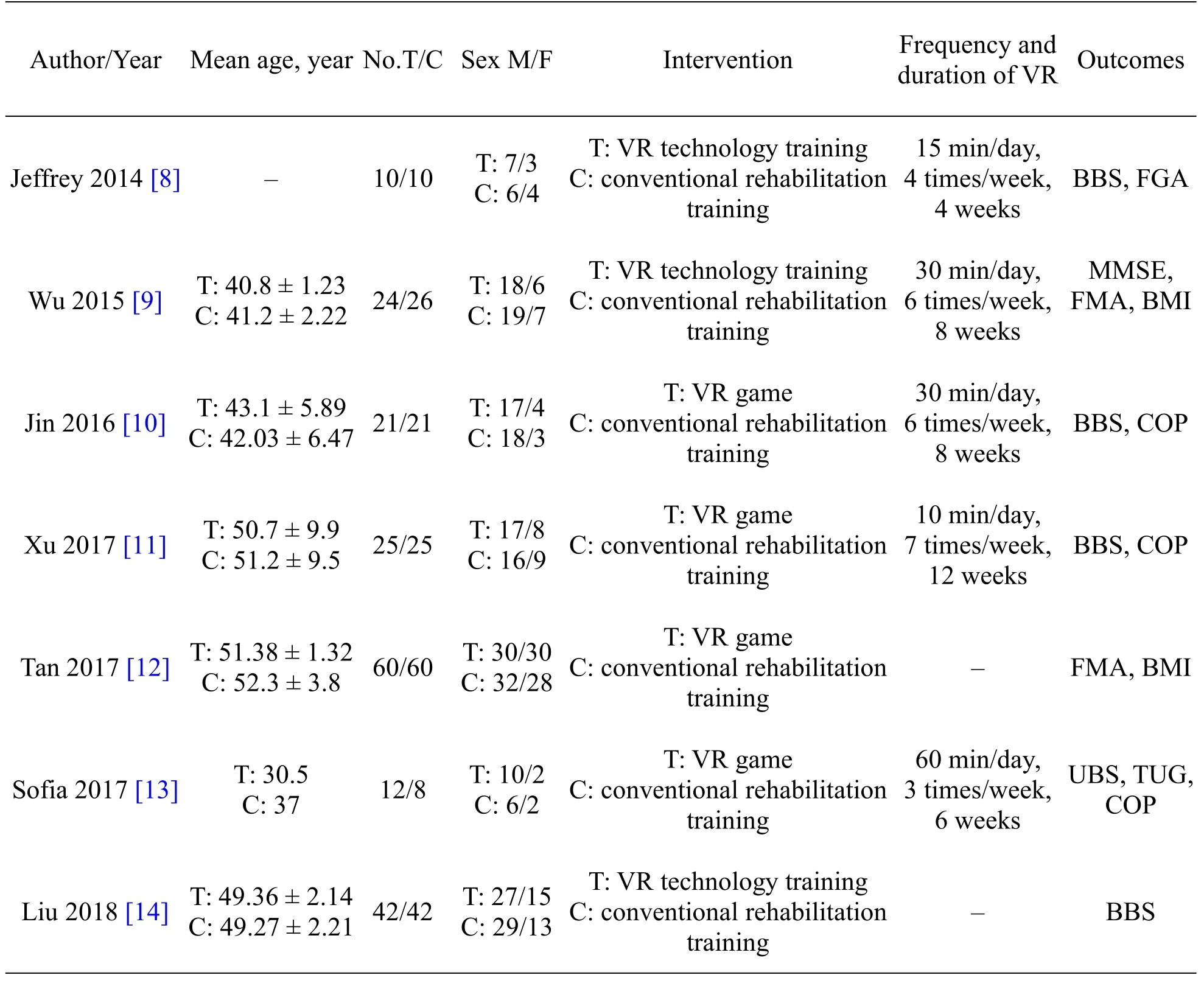
Table 1 Basic characteristics of the included studies
Effects on outcome indicators
Balance function.Four RCTs[8,10,11,14]assessed the balance ability including 98 patients in the experimental group and 98 patients in the controlgroup with BBS balancescale.The heterogeneity between the studies was not significant(P=0.91,I2=0%),so a fixed effect model was used.Meta-analysis showed that the difference between the two groups was statistically significant(MD=3.72,95%CI(2.61,4.83),P<0.001),suggesting that VR combined with routine rehabilitation training was significantly better in improving the balance function of patients with TBI(Figure 2).
Posture control ability.(1)Length of track motion:three RCTs[10,11,13]evaluated the length of trajectory exercise.58 patients were included in the experimental group and 54 patients in the control group.Meta-analysis showed that the heterogeneity between the studies was not significant(P=0.97,I2=0%),so a fixed effect model was used.Meta-analysis showed that the difference between the two groups was statistically significant(SMD=-0.80,95%CI(-1.19,-0.41),P<0.001),suggesting that VR combined with routine rehabilitation training can reduce the length of trajectory of patients with TBI.The aspect is obviously superior to the simple routine rehabilitation training(Figure 3).(2)Track moving speed:two RCTs[11,13]evaluated the trajectory movement speed.37 patients were included in the experimental group and 33 patients in the control group.Meta-analysis showed that the heterogeneity between the studies was not significant(P=0.83,I2=0%).Therefore,a fixed effect model was used.Meta-analysis showed that the difference between the two groups was statistically significant(SMD=-0.95,95%CI(-1.45,-0.45),P=0.0002),suggesting that VR combined with routine rehabilitation training can reduce the trajectory movement speed of patients with TBI.The aspect was obviously superior to the simple routine rehabilitation training.In one study,the anterior-posterior and posterior COP movements of the static biceps were evaluated.Descriptive analysis showed that the VR group was slower than the conventional rehabilitation group in the anteroposterior direction and left and right direction(Figure 4).(3)Peripheral area of the track:two RCTs[10,11]evaluated the peripheral area of the trajectory.46 patients were included in the experimental group and 46 patients in the control group.Meta-analysis showed that the heterogeneity between the studies was not significant(P=0.88,I2=0%).Therefore,a fixed effect model was used.Meta-analysis showed that the difference between the two groups was statistically significant(SMD=-0.69,95%CI(-1.11,-0.26),P=0.001],suggesting that VR combined with routine rehabilitation training can reduce the peripheral area of patients with TBI.The aspect was obviously superior to the simple routine rehabilitation training(Figure 5).
Daily living ability.Two RCTs[9,12]used BI to evaluate the ability of daily living.A total of 84 patients were included in the experimental group and 86 patients in the control group.Meta-analysis showed that the heterogeneity between the studies was not significant(P=0.16,I2=49%),so a fixed effect model was used.Meta-analysis showed that the difference between the two groups was statistically significant(MD=11.87,95%CI(10.42,13.32),P<0.001),suggesting that VR combined with routine rehabilitation training was superior in improving the daily living ability of patients with TBI(Figure 6).
Motion function.Two RCTs[9,12]used FMA to evaluate motor function.A total of 84 patients were included in the experimental group and 86 patients in the controlgroup.Meta-analysis showed that the heterogeneity between the studies was not significant(P=0.18,I2=43%),so a fixed effect model was used.Meta-analysis showed that the difference between the two groups was statistically significant(MD=3.83,95%CI(2.30,5.36),P<0.001),suggesting that VR combined with routine rehabilitation training was significantly better in improving the motor ability of patients with TBI(Figure 7).
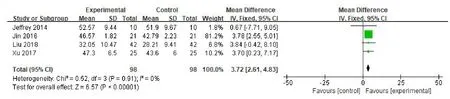
Figure 2 Meta-analysis of VR technology on balance ability of patients with TBI.TBI,traumatic brain injury;VR,virtual reality;CI,confidence interval;SD,standard deviation.
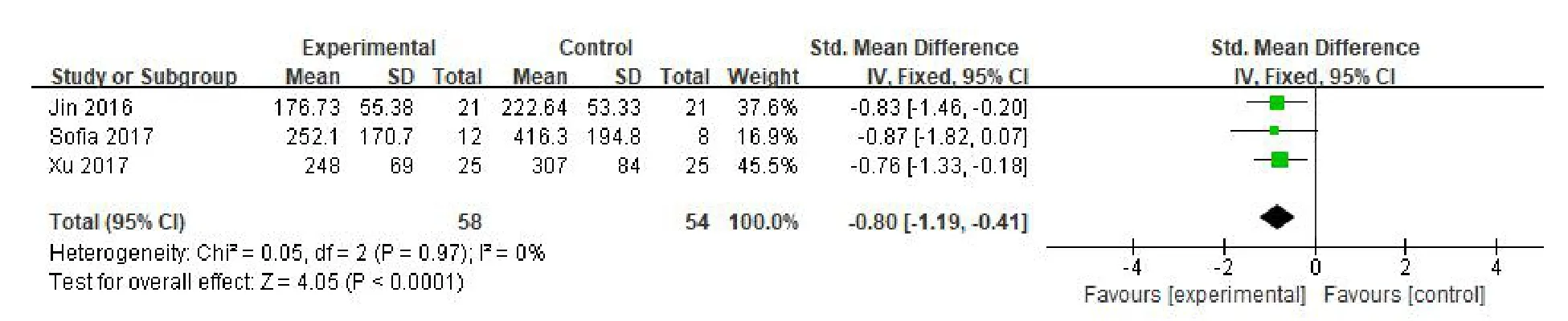
Figure 3 Meta-analysis of VR technology on the length of trajectory movement in patients with TBI.TBI,traumatic brain injury;VR,virtual reality;CI,confidence interval;SD,standard deviation
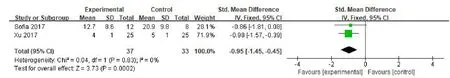
Figure 4 Meta-analysis of VR technology on trajectory movement speed of patients with TBI.TBI,traumatic brain injury;VR,virtual reality;CI,confidence interval;SD,standard deviation.
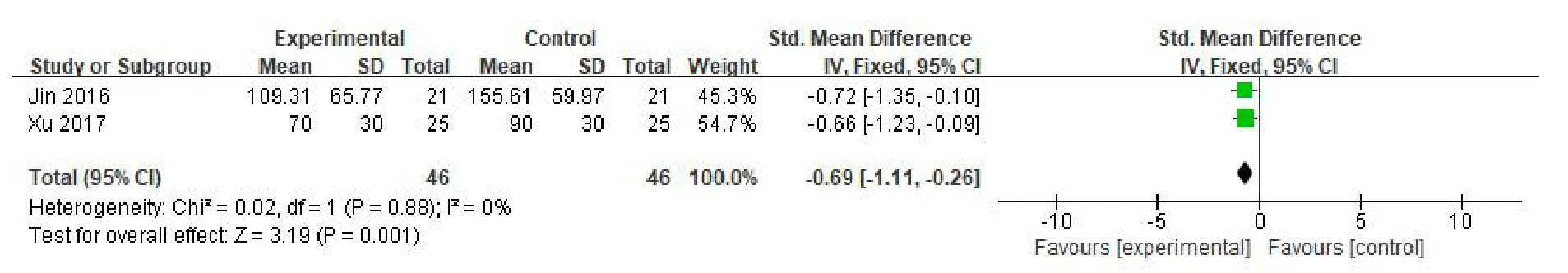
Figure 5 Meta-analysis of VR technology on the peripheral area of patients with TBI.TBI,traumatic brain injury;VR,virtual reality;CI,confidence interval;SD,standard deviation.
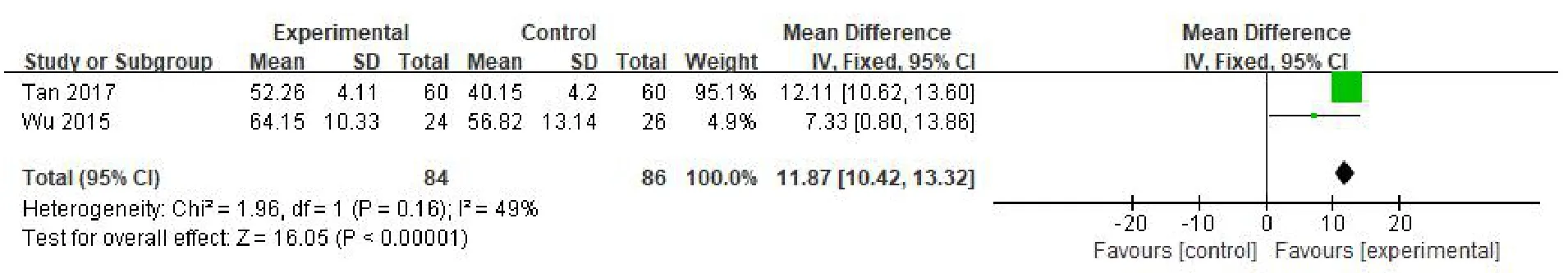
Figure 6 Meta-analysis of VR technology on daily living ability of patients with TBI.TBI,traumatic brain injury;VR,virtual reality;CI,confidence interval;SD,standard deviation
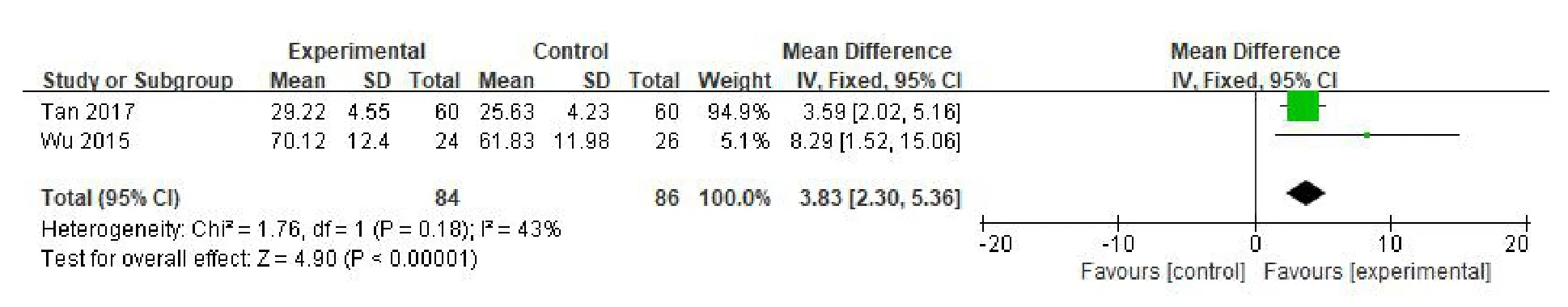
Figure 7 Meta-analysis of VR technology on motion function of patients with TBI.TBI,traumatic brain injury;VR,virtual reality;CI,confidence interval;SD,standard deviation
Discussion
The meta results showed that VR technology can improve the balance function,posture control ability,daily living activity ability and exercise ability of patients with TBI.The recent researches maybe explained the reasons.(1)VR technology for repeated training of traumatic limbs of the brain can produce effective synaptic enhancement and increase exercise-induced neural plasticity[15].(2)VR technology was more patient and consistent than the therapist,and patients with brain trauma can repeatedly imitate the practice according to their own situation.Due to the high similarity between the virtual environment and the real environment,the rehabilitation function obtained in the virtual environment can be easily converted into the real environment,which was beneficial to the patient's own function recovery[16].(3)According to the feedback information of the obtained therapeutic effect,the state and effect of the patient's treatment were known,and the therapist had a certain effect on grasping the patient's condition.(4)VR technology was interesting,interactive and imaginative,which can stimulate the enthusiasm ofcerebraltrauma patients to participate in treatment.
The postural control ability included in this paper was measured by human body pressure of center(COP),including track motion length,track motion speed and track peripheral area.Track motion length,that was,the shaking degree of the subject,the smaller the length,the better the stability.Trajectory velocity,that was,the degree of center of gravity transfer of the subject,the smaller the velocity,the better the stability.The peripheral area of the track,that was,the region in which the center of gravity of the subject moves,was smaller and more stable[11].
Nervous system diseases were prone to patient balance and gaitdefects.The limitationsof balance and gait limit the activities and quality of life of patients'daily lives.More and more evidence now showed that VR technology was good for improving the balance and gait of patients with nervous system[17].Today,VR technology is widely used to treat patients with neurological diseases,such as acute and chronic stroke[18],Parkinson's disease[19],multiple sclerosis[20].Brain trauma is often caused by traumatic injuries such as blunt trauma,penetrating wounds,etc.The recovery period of brain trauma is longer than that of other acquired injuries and neurological diseases[21].Patients have obstacles in balance and exercise for a long time in the future.Long-term traditional rehabilitation training can easily lead to fatigue and burnout,which leads to low enthusiasm for training.VR technology provides a variety of training programs.Patients can be functionally trained “in an immersive manner”,greatly improving the patient's exercise compliance and thus promoting the recovery of patient function[22].
This meta-analysis found that the frequency of intervention with VR technology in patients with TBI included in the study and the intervention time were inconsistent.The time varied from 10-60 minutes;the frequency was 2-3 times a week,and the most was 6 times a week,so it is impossible to determine which was the best treatment.In view of the fact that VR technology and treatment programs were still in the development and research stage,and the number of RCTs was small,in the future research,more precise RCTs such as multi-center,large samples,and intervention methods can be used to further evaluate the effect.
In conclusion,VR technology can significantly improve the balance function,daily living ability,motor function and postural control ability of patients recovering from cerebral trauma.However,this paper also had limitations,as the number of included researches are few,so the sample size was also small.Moreover,the included patients in the RCTs were medium quality,the generation,allocation,concealment,withdrawal and loss of follow-up of random schemes were not mentioned in some literatures,and patients had different disease duration,treatment scheme design,and intervention methods rely on different equipment or technical platform,which will affect the study effect a larger sample size,high quality research,with a prolong ending index evaluation etc.,was needed to support the conclusion.
