籽用大麻性别连锁标记的验证及SCAR标记开发
2019-12-14赵铭森方书生陈瑶康红梅高金虎陈思远杨昕冯旭平张立武
赵铭森 方书生 陈瑶 康红梅 高金虎 陈思远 杨昕 冯旭平 张立武

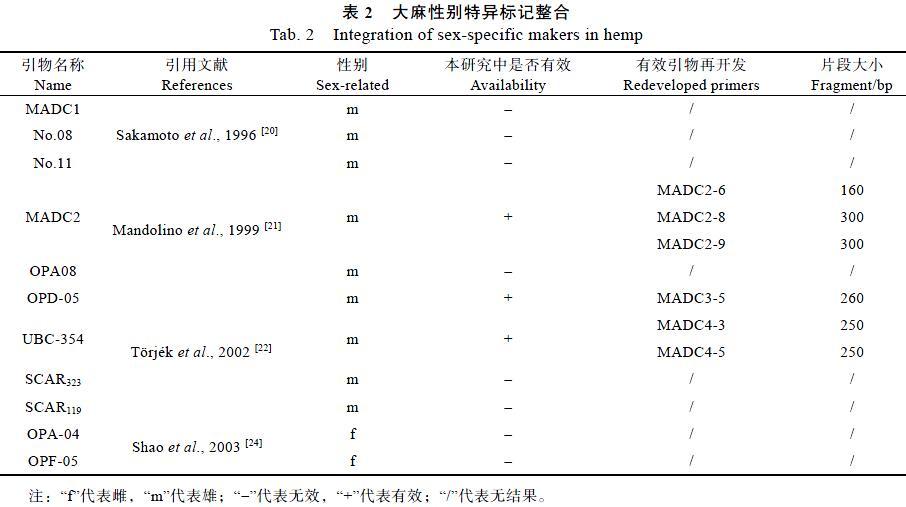
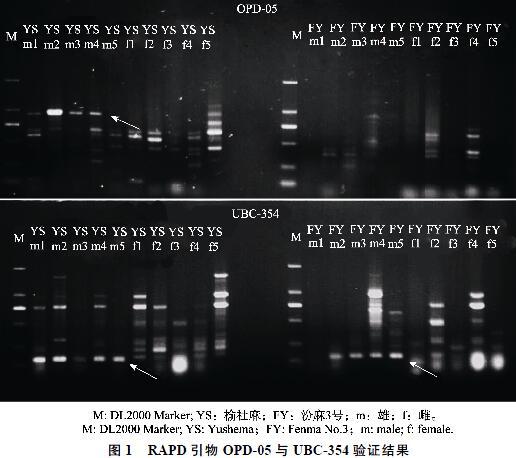
摘 要 大麻是雌雄異株的异花授粉作物,在苗期鉴定出植株的性别,对大麻育种及生产具有重要的意义。为开发与籽用大麻品种性别连锁的SCAR标记,本研究以汾麻3号、榆社麻和苍山麻为试验材料,研究已有的11个性别连锁标记在籽用大麻品种中的适用性。结果表明,3个标记(OPD-05、UBC-354和MADC2)在籽用大麻品种中呈雄性特异,尚未发现雌性特异条带。回收雄性特异条带并测序,根据测序结果新开发了6个SCAR标记,其中MADC2-8表现最好;进而利用123份已知性别的样本来检测MADC2-8的准确性,发现其平均准确性高达98.34%。该研究不仅丰富了大麻性别鉴定的分子标记,而且为大麻性别研究和实际应用奠定基础。
关键词 大麻;籽用品种;性染色体;SCAR;MADC中图分类号 S563.3 文献标识码 A
Evaluation of Markers Linked to Sex-specific and Development of SCAR Makers in Seed Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.)
ZHAO Mingsen1,2, FANG Shusheng2,3*, CHEN Yao2,3, KANG Hongmei1, GAO Jinhu1, CHEN Siyuan2,3, YANG Xin2,3, FENG Xuping1, ZHANG Liwu2,3**
1. Institute of Economic Crops, Shanxi Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Taiyuan, Shanxi 030000, China; 2. Key Laboratory for Genetics, Breeding and Multiple Utilization of Crops, Ministry of Education / Fujian Key Laboratory for Crop Breeding by Design, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, Fuzhou, Fujian 350002, China; 3. Experiment Station of Jute and Kenaf in Southeast China, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs / Public Platform for Germplasm Resources of Bast Fiber Crops of Fujian, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, Fuzhou, Fujian 350002, China
Abstract Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) is a dioecious and cross pollinated plant. Sex identification of plants at seedling stage is of great significance for breeding and production in hemp. To develop new SCAR markers linked to sex-specific, three Chinese local seed hemp varieties, Fenma No.3, Yushema and Cangshanma, were used as the experimental materials to investigate the application of 11 markers linked to sex-specific in Chinese local seed hemp varieties in this study. The results showed that three makers (OPD-05 and UBC-354 as well as MADC2) were male-specific, while no female specific bands were found. Novel SCAR markers were developed on the basis of sequences of male specific bands. Among them, MADC2-8 was the best. Furthermore, 123 samples with known sex identification were used to assess the accuracy of MADC2-8. The average accuracy was 98.34%. These results would not only enrich the molecular markers linked to sex-specific, but also lay a foundation for the research and practical application of sex identification in hemp.
Keywords Cannabis sativa; seed variety; sex chromosome; SCAR; MADC
DOI10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2019.10.023
大麻(Cannabis sativaL.)为大麻科(Cannabinaceae)大麻属(CannabisL.),属短日照异花授粉作物,雌雄异株[1]。按栽培目的进行分类,大麻可分为纤用型(工业大麻)、籽用型(油用型)、药用型等。籽用型品种籽产量高,含油可达32%以上;纤用型品种麻皮产量高,出麻率高,纤维柔软、色白、有光泽;药用型品种花叶产量高,大麻二酚含量高[1-4]。大麻植株有雌株及雄株不同类型,不同性别的植株形态存在较大差异。大麻从种子萌发到开花一般需要3个月以上的时间,在此之前不能从形态上准确判断植株性别[5],只有在开花时才能从形态上准确判断植株性别,生产上通常采用多留苗,到时雄性植株开花后自然死亡,这样造成极大的浪费。因此,在苗期鉴定出植株的性别,对大麻育种及栽培均具有重要的意义。利用分子标记技术能够克服形态和生理生化指标受环境及发育阶段影响的缺点,从分子水平上在苗期鉴定出植株的性别。
关于大麻性别,前人早在20世纪初就展开了研究。Hirata等[6]发现大麻是有2个异型性染色体的雌雄异型植株,Yamada等[7]指出大麻雌株有2个X染色体,雄株有1个X染色体和1个Y染色体。Warmke等[8]研究表明,常染色体并不参与大麻性别表达,其性别表达差异与X、Y染色体上分别携带雌性和雄性表达的基因有关。大麻的核型是由9对常染色体和1对性染色体(X和Y)[9-10],其性别表达是由Y染色体控制[11-12]。而同大麻亲缘关系最近的啤酒花(Humulus lupulus)性别却受X染色体与常染色体比值影响 [13-14]。在其他物种中如黄瓜,其性别性状可以由一个大片段DNA序列拷贝数决定[15],而在大麻中将转座子和序列拷贝数与表型性状相关联仍然是个挑战[16]。但有研究显示,大麻性别分化跟反转座子存在着相关性[17-18]。Faux等[19]首次整合了雌雄异株和雌雄同株的连锁图谱,并进行了QTL分析,将雌雄同株性别基因定位到X染色体上。鉴于大麻植株性别鉴定的经济效益,前人还开发出性别特异的分子标记用于雌雄单株的早期鉴定,如Saka m oto[20]、Mandolino[21]利用RAPD技术分别开发出雄性特异SCAR标记MADC1(730 bp)、MADC2(390 bp);T?rjék等[22]也开发出雄性特异标记MADC5(323 bp)和MADC6(119 bp)。宋书娟等[23]和Shao等[24]分别用RAPD引物OPX09、OPA04和OPF05得出雌性特异的带型。尽管前人开发了一些性别连锁的标记,但是这些研究主要集中在纤用和药用大麻,是否适用于籽用大麻品种还属未知。
本研究以籽用大麻为材料,验证已有的性别连锁标记在籽用大麻的适用性,并开发SCAR标记。
1 材料与方法
1.1材料
2018年2月1日在福建省三明市福建农林大学洋中科教基地玻璃温室内分2个小区种植榆社麻和汾麻3号,钢架大棚中种植榆社麻,每个品种随机挑选100株苗编号挂牌,取幼嫩叶片于10 mL离心管中,保存于–80 ℃冰箱备用;待其开花后,记录编号单株性别并统计其品种的雌雄单株总数。
1.2方法
1.2.1 DNA提取 利用改良CTAB法提取基因組DNA[25],1.2%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测DNA质量,紫外分光光度计测定其浓度并统一稀释为50 ng/L,作为模版保存于-20 ℃备用。
1.2.2 引物选择及PCR扩增 选用前人文献中性别鉴定相关引物[20-22,24],送至福州擎科生物科技有限公司合成。利用榆社麻和汾麻3号两个品种的雌雄单株各5个作为模版,进行PCR扩增。RAPD引物PCR反应体系为10 μL,含2?TaqMaster Mix(试剂购自上海进岸生物科技有限公司)3.8 μL、ddH2O 3.8 μL、10 μmol/L引物0.4 μL,DNA模版2 μL;SCAR引物PCR反应体系10 μL,含2?TaqMaster mix 3.8 μL、ddH2O 3.8 μL、10 μmol/L引物对左右各0.2 μL,DNA模版2 μL。
雖然本研究开发的标记与雄性高度连锁,但试验材料选用的品种还是较少,下一步有必要扩大品种数及品种类型,验证新开发的性别连锁标记是否具有广泛适用性。在验证前人开发的分子标记中,并未发现雌性特异的条带。因此,在本研究的基础上,有必要通过集团分离分析法结合测序技术对大麻群体进行分析,进一步开发雌性特异分子标记甚至雌雄同株特异标记,进而利用多重PCR反应[32]快速鉴定出大麻三种性别。
4 结论
本研究验证了3个性别连锁标记适用于中国地方籽用大麻品种,并新开发出6个雄性特异SCAR标记,其中,MADC2-8在中国地方籽用大麻品种中准确率高达98.34%。这些标记可用于籽用大麻早期性别田间鉴定。
参考文献
[1] 熊和平. 麻类作物育种学[M]. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社, 2008: 297-318.
[2] 孙小寅, 管映亭, 温桂清, 等. 大麻纤维的性能及其应用研究[J]. 纺织学报, 2001, 22(4): 34-36, 3.
[3] ElSohly M A, Slade D. Chemical constituents of marijuana: The complex mixture of natural cannabinoids[J]. Life Sciences, 2005, 78(5): 539-548.
[4] Radwan M M, Ross S A, Slade D,et al. Isolation and characterization of new cannabis constituents from a high potency variety[J]. Planta Medica, 2008, 74(3): 267-272.
[5] 王玉富, 粟建光, 赵立宁. 大麻的性别分化及其分子生物学研究进展[J]. 中国麻业, 2006, 28(3): 117-119.
[6] Hirata K. Sex determination in hemp (Cannabis sativaL.)[J]. Journal of Genet, 1927, 19(1): 65-79.
[7] Yamada I. The sex-chromosome ofCannabis sativa L.[J]. Seiken Ziho, 1943, 2: 64-68.
[8] Warmke H E, Davidson H. Polyploid investigation[J]. Year Book of the Carnegie Institution of Washinton, 1944, 43: 135-139.
[9] Sakamoto K, Akiyama Y, Fukui K,et al. Characterization; genome sizes and morphology of sex chromosomes in hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) [J]. Cytologia(Tokyo), 1998, 63(4): 459-464.
[10] Divashuk M G, Alexandrov O S, Razumova O V,et al. Molecular cytogenetic characterization of the dioeciousCannabis sativawith an XY chromosome sex determination system[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(1): e85118.
[11] Shepdard H L, Parker J S, Dabby P,et al. Sexual development and sex chromosomes in hop[J]. New Phytologist, 2000, 148(3): 397-411.
[12] Vyskot B, Hobza R. Gender in plants: sex chromosomes are emerging from the fog[J]. Trends in Genetics, 2004, 20(9): 432-438.
[13] Westergaard M. The Mechanism of sex determination in dioecious flowering plants[J]. Advances in Genetics, 1958, 9: 217-281.
[14] Ming R, Bendahmane A, Renner S S. Sex chromosomes in land plants[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2011, 62: 485-514.
[15] Zhang Z, Mao L, Chen H,et al. Genome-wide mapping of structural variations reveals a copy number variant that determines reproductive morphology in Cucumber[J]. The Plant Cell, 2015, 27(6): 1595-1604.
[16] Pisupati R, Vergara D, Kane N C. Diversity and evolution of the repetitive genomic content inCannabis sativa[J]. BMC genomics, 2018, 19(1): 156.
[17] Sakamoto K, Ohmido N, Fukui K, et al. Site-specific accumulation of a LINE-like retrotransposon in a sex chromosome of the dioecious plantCannabis sativa[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2000, 44(6): 723-732.
[18] Sakamoto K, Abe T, Matsuyama T, et al. RAPD markers encoding retrotransposable elements are linked to the male sex inCannabis sativaL.[J]. Genome, 2005, 48(5): 931-936.
[19] Faux A M, Draye X, Flamand M C, et al. Identification of QTLs for sex expression in dioecious and monoecious hemp (Cannabis sativaL.) [J]. Euphytica, 2016, 209(2): 357-376.
[20] Sakamoto K SK, Komeda Y, Kamada H,et al. A male-associated DNA sequence in a dioecious plant,Cannabis sativa[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 1996, 36(8): 1549-1554.
[21] Mandolino G, CarbonicA, Forapani S, et al. Identification of DNA markers linked to the male sex in dioecious hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) [J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 1999, 98(1): 86-92.
[22] T?rjék O, Bucherna N, Kiss E, et al. Novel male-specific molecular markers (MADC5, MADC6) in hemp[J]. Euphytica, 2002, 127(2): 209-218.
[23] 宋书娟, 刘 卉, 邵 宏. 大麻性别连锁的特异DNA标记的初步研究[J]. 中国药物依赖性杂志, 2002, 11(3): 182-184.
[24] Shao H, Song S J, Clarke R C. Female-associated DNA polymorphisms of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) [J]. Journal of Industrial Hemp, 2003, 8(1): 5-9.
[25] 徐建堂, 祁建民, 方平平, 等. CTAB法提取红麻总DNA技术优化与ISSR和SRAP扩增效果[J]. 中国麻业科學, 2007, 29(4): 179-183.
[26] Flachowskyes H, Weber W E, Peil A. Application of AFLP for the detection of sex-specific markers in hemp[J]. Plant Breeding, 2001, 120(4): 305-309.
[27] 陈其军, 韩玉珍, 傅永福, 等. 大麻性别的RAPD和SCAR分子标记[J]. 植物生理学报, 2001, 27(2): 173-178.
[28] Mandolino G, Carboni A, Bagatta M, et al. Occurrence and frequency of putatively Y chromosome linked DNA markers inCannabis sativa L.[J]. Euphytica, 2002, 126(2): 211-218.
[29] Peil A, Flachowsky H, Schumann E, et al. Sex-linked AFLP markers indicate a pseudoautosomal region in hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) [J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2003, 107(1): 102-109.
[30] Moliterni C V M, Cattivelli L, Ranalli P, et al. The sexual differentiation ofCannabis sativa L.. A morphological and molecular study[J]. Euphytica, 2004, 140(1-2): 95-106.
[31] 吕佳淑, 赵立宁, 臧巩固, 等. 大麻性别相关AFLP分子标记筛选[J]. 湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 36(2): 123-127.
[32] 何尧声, 沈文涛, 黎小瑛, 等. 利用多重PCR技术快速鉴定番木瓜性别[J]. 热带作物学报, 2008, 29(3): 347-351.
