Mirror therapy:a potential rehabilitation treatment
2019-12-11XinLiuTianYangXingRanLiuShanShanYangGuoWeiWang
Xin Liu,Tian-Yang Xing,Ran Liu,Shan-Shan Yang,Guo-Wei Wang*
1Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,China.
Abstract
Keywords: Mirror therapy,Dyskinesia,Sensory disturbance,Cognitive impairment,Speech disorder
Introduction
Mirror therapy was first proposed by Ramachandran for the treatment of phantom limb pain after amputation [1].In the operation,patients with an amputated limb can use either a mirror or a mirror box to reflect an image of the intact limb; this provides the visual illusion that two intact limbs exist,which allowing the patient to imagine the movement of the amputated limb through the visual illusion,feedback and reality,combined with the rehabilitation training program[2].
The development of mirror therapy has been widely used today in all aspects of rehabilitation programs,such as the recovery of dysfunctions such as sensation,exercise and language,especially the improvement of pain and exercise capacity.This is a new boost in the healing process,and we can adopt new models to improve dysfunction and be highly viable and harmless.By reviewing the data,we have organized the following mechanisms for the action of mirror therapy and the application in the rehabilitation of various diseases as follows.
Mechanism of action of mirror therapy
At present,the mechanism of its action is not clear,and several mechanisms have been suggested to explain how mirror therapy works for motor recovery.
Activated mirror neuron
At the earliest,the mirror neuron was discovered by Rizzolatti,who discovered that when the monkey was performing a specific action and found that other people or monkeys were performing the action,some neurons appeared in the F5 area before the ventral movement(Figure 1).The discharge,so named it as a mirror neuron[3].Mirror neurons are a type of neuron that excites and regulates movement when an individual performs a specific motion action and observes similar behavior performed by others [4].Some studies have shown that the excitation of mirror neurons was also found in the ventral part of the frontal cortex of monkeys during the execution and observation of grip movements.In the subsequent experiments,mirror neurons were found in the vertebral small leaves [5],the main motor cortex [6],the ventral ventral region [7],and the lateral medial parietal lobe[8],where the core areas of action execution and observation are located(Figure 2).
The study of mirror neurons in humans was first found by Mukamelet al[9].Some neurons in the medial temporal lobe and auxiliary motor cortex produced action potentials when performing and observing actions.Numerous mirror neurons form the mirror neuron system(MNS),which controls the motion system through an“observation-motion matching mechanism”.This mechanism can effectively integrate exercise,observe and imagine these three neurophysiological processes.Mirror neuron system is also one of the important mechanisms of motor relearning[10].As a kind of psychological process without action,sports imagination has been proved to be beneficial to hemiplegia [11].The recovery of motor function by motor imagination therapy and exercise observation therapy is likely to promote functional reorganization and plasticity of the brain by activating the mirror neuron system [12].In the study of Buccino [13],functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) shows that the excitability of some brain functional areas,including mirror neuron system,is significantly increased in the process of imitation and learning.
When the same motion is reproduced,the mirror neurons are stimulated,so the motor neuron system plays an important role in the learning of motion [8].In mirror therapy,the movement of the contralateral side of the limb mirror allows the patient to observe the movement of the limb in the mirror and activate the mirror neuron by imagining that the affected limb is moving,thereby replacing the proprioception to a certain extent.The input,which plays an important role in the recovery of motor cortex function.In recent years,some scholars have confirmed through imaging that,compared with looking at one's own motion or others' motion,looking at one's own motion in the mirror has more active brain areas and a wider range[14].
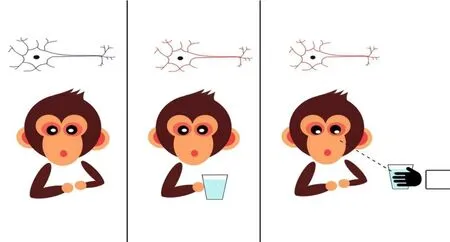
Figure 1 the possible mechanism of activating the mirror neuron to promote brain remodelin
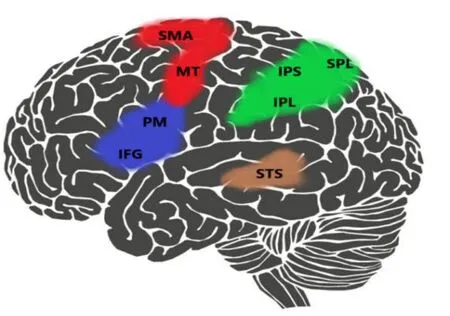
Figure 2 The mirror neurons in brain
Prevent the learned disuse of the affected limb
Long-term non-use of the limb will lead to a significant decline in limb function.In a case report,Rocca [15]pointed out that it was difficult to move the affected limb due to dysfunction and pain,which will lead to the compensatory use of the healthy side and the learned disuse of the affected limb.Mirror therapy can improve the presence of the affected limb through a mirrored visual illusion.Studies by fMRI have shown that mirror neurons can produce the same effect when the stimulus is reproduced [16],which is related to the recovery of the limbs.When mirror therapy is applied to allow patients to produce the illusion of correct response,repeated contact can significantly reduce learned disuse[17].
By facilitating motor pathways
The facilitative motor neural pathway is mainly based on the theory of interactive hemisphere inhibition.Under normal circumstances,the inhibition and promotion of bilateral brains is in a dynamic equilibrium.When the side brain is damaged due to various reasons,the balance is destroyed,and the contralateral brain is too inhibited to the affected side,thereby making the recovery of the affected side difficult [18].Through mirror therapy,patients could active limbs to achieve the illusion of bilateral activities,thereby restoring motor function[19].
Clinical applications of mirror therapy
Mirror therapy improves motor dysfunction
Mirror therapy could improve the motor function and reshape the primary motor cortex by mirroring the neuron system,allowing the patient to imagine the affected side by observing the mirror image of the healthy side.Through physical activity and repeated training of intracortical inhibition signals,which can improve motor function of the affected limb [20].At the present stage,mirror therapy is mainly used for motor function damage after stroke,but it also has a certain effect in improving the exercise retardation of Parkinson's patients,the abnormal movement of children with cerebral palsy,and the recovery of motor function of shoulder joint capsule.
Post-stroke motor dysfunction.With the increasing aging of the world population,strokes with high morbidity,high mortality and high disability rate have successfully “promoted” one of the three major diseases that endanger human health,seriously affecting the quality of life of patients.Limb motor dysfunction after stroke is the focus and difficulty in rehabilitation training.Mirror therapy as a newer rehabilitation training method plays its unique advantage in relieving this problem[21].
Upper limb dysfunction.Mirrored treatment was performed on post-stroke patients with hemiplegia.patients with hemiplegia place their hands on the table with a plane mirror in the middle of the hands to observe the mirrored upper limbs during the movement of the upper limbs.The training is conducted for 20 minutes each time,once a day,every Friday,for 4 weeks.The fugl meyer assessment (FMA) was used to to assess the upper limb function before and after the mirror therapy intervention.After therapy,FMA showed a significant improvement from 29.5 ± 12.4 to 36.5 ± 15.5 (P<0.05).which shows that mirror therapy can be used as an effective intervention to improve the function of upper limbs in stroke patients with hemiplegia.Kojima[22]and others found that the combination of mirror therapy and electromyography-triggered neuromuscular stimulation(ETMS) can effectively increase the feasibility of upper limb movement after stroke.Studies by Young-Rim Paik[23] and Amasyali SY [24] had also demonstrated that both mirror therapy and neuromuscular stimulation can effectively alleviate the development of upper limb function in patients with stroke.
Lower extremity dysfunction.Motor dysfunction is a major problem and phenomenon in the sequela of stroke.Mirror therapy can effectively alleviate dyskinesia in the early stage,which has an important impact on its daily activities and the return to family and society.Salhab G[25] measured the range of dorsiflexion,lower limb sensorimotor function and walking duration compared with specular therapy combined with electrical stimulation (ES) and traditional rehabilitation therapy.Experiments showed that the combined group improved the lower extremity motor function after stroke.Experiments by Xu Q [26] and others had also demonstrated that combination of mirror therapy and neuromuscular electrical stimulation can improve walking ability and reduce sagging in patients with camphor stroke.TS In [27] experimentally demonstrated that for stroke patients,visual feedback from the mirror resulted in a significant reduction in posture sway on a more unstable surface,but increased sway distance and speed.The combination of mirror neuron activation and traditional stroke physiotherapy can enhance the recovery of lower extremity motor function of stroke patients.Broderick P [28] found that mirror therapy can significantly improve muscle tension and lower limb balance.
Dyskinesia in other diseases.Slowness of movement and involuntary tremors in the fingers are the typical performance of Parkinson patients.Gaia Bonassi [29]combined Mirror Visual Feedback (MVF) therapy with exercise training to improve the excitability of primary motor cortex(M1s)by which improved the movements of affected(untrained)finger in PD patients.
Children with unilateral spastic cerebral palsy (CP)usually have a mirror image,an involuntary imitation of unilateral autonomous movement of the contralateral upper limb.Kuo HC [30] and others explored the neurophysiological mechanisms and functional effects of mirror therapy in children and unilateral CP and proposed that mirror therapy can alleviate the dyskinesia of children with cerebral palsy.
Bayon-Calatayud M [31] compared the effects of mirror therapy and physiotherapy on the range of motor activity.Experiments showed that two groups of patients were found by active wrist extension and Quick-DASH(arm,shoulder and hand disability) functional recovery assessment.The range of motion of the wrist was improved but there was no significant difference in activity between groups.
Başkaya MC[32]and others had demonstrated through experiments that mirror therapy combined with physical therapy seems to be an effective treatment to relieve shoulder pain,improve shoulder ROM,shoulder function and adhesion in patients with adhesive joint capsule.
Mirror therapy for sensory dysfunction
Mirror therapy is mainly used to treat pain in sensory dysfunction.The following mainly introduces pain caused by diseases such as phantom limb pain and complex local pain syndrome.
Phantom limb pain.Pain is an alarm that reminds us of abnormal physical functioning,but sometimes pain also deceives us in an illusory form.Phantom limb pain(PLP)is neuropathic pain without physical injury.It means that the amputated patient still feels the presence of an amputation and will feel pain of different nature continuously or intermittently.The onset of PLP can be long or short,and the incidence is high [34].the amputated patients are prone to pain due to psychological disorders caused by missing limbs.Mirror therapy is an effective intervention for slowing PLP.During the mirror-therapeutic intervention of the PLP,individualized observation of the patient is performed to move the unaffected upper or lower limbs of the patient into a particular mirror frame or to block the patient from observing the affected limb [35].After a 4-week mirror treatment and a 12-week follow-up assessment,Hashikuar Ramadugu [40] found that mirror therapy can significantly reduce the frequency of pain and gradually convert persistent or intermittent pain into transient pain or painlessness.Sacha B.Finn [36] grouped 15 minutes of mirroring therapy per day to treat PLP and found that visual input affected the activation of mirror neurons through which reduced the perception of pain.Beth D.Darnall [37] provided his patient Jonathan with a self-contained mirror therapy at home.Compared to his previous treatment,mirror therapy relieved his pain and improved his ability to control the disease,reducing its dependence on opioids.Wang Fengyi [38] found that mirror therapy can not significantly alleviate phantom limb pain,but its auxiliary role cannot be ignored and it can be combined with other treatments to improve its efficacy in a meta-analysis.
Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS).CPRS is an abnormal syndrome that causes spontaneous,traumatic symptoms of pain,sensation,autonomic nerves,exercise or nutrition [39].Studies have shown that the remission of acute pain in CPRS can be achieved by mirror visual feedback,which is based on the reorganization of the primary somatosensory cortex,but once converted to chronic pain,the treatment effect is not as good as before.Janet Het al.Bultitude used mirror image therapy for patients with SM to treat their CPRS.During the treatment progresses,the pain gradually diminished and becomes painless,but the pain recured after one week of treatment stoppage,ever more seriously,it can lead to limb pain in the same position on the contralateral side.Therefore,the time and frequency of mirror therapy are critical to the efficacy,and rest and training time should be established.Jiang Jie [41] treated pain caused by shoulder-shoulder syndrome (SHS) after stroke with mirror image therapy and found the good effects on the pain,which may prove that the mechanism of mirror therapy was mainly related to brain remodeling.
Other pain.In addition,Richard W.Willy [42] used a full-length gait retraining method to change the variable peak hip adduction to greatly improve pain.Xie Na [43]used mirror image therapy for breast cancer postoperative persistent pain,which can relieve a certain degree of pain,but there was no conclusive evidence for further clinical application.
Mirror therapy improves cognitive dysfunction
Any factor that causes functional and structural abnormalities in the cerebral cortex can lead to cognitive impairment.Since the brain functions are complex and different types of cognitive impairment are interrelated,one aspect of cognitive impairment can lead to another or more aspects of cognitive impairment.Current treatments are symptomatic treatment,which was no improvement in cognitive abnormalities.Recent researches found the adventages of mirror therapy on the cognitive dysfunction caused by the brain injury and stroke.
Cognitive dysfunction after the brain injury.The left side of the body caused by the right brain injury is ignored [17].The mirror neurons in the mirror system mainly play a role in controlling movement (especially the movement of the hand) and observing the same movement,and the position of the mirror nerve system in the brain is mainly in the lower frontal lobe and the anterior motor cortex and parietal lobules.The right brain injury site of the patient is in the right occipital lobe and parietal lobe [44],so there is a good rehabilitation for the treatment of the left hemisphere in the left half of the body that ignores the MNS mechanism.After three weeks of continuous training,we found that video rehabilitation therapy based on MNS was helpful to reduce the neglect of half-space in middle-aged and elderly people.The results of the experiment are undoubtedly successful,and the MNS mechanism gives doctors and patients more choices and reintegration hope for future rehabilitation in the half-side of the body.
Stroke.According to the research of Mao Huimin [45],two groups of experimental subjects were rehabilitated using the MNST V1.0 therapeutic apparauts for 8 weeks.The patien's cognitive and Activities of Daily Living assessments were followed using the MoCA and Wisconsin card sorting tests.The results showed that the treatment group was superior to the control group.
In the known data experimental group,it was obtained that the superiority of MVF treatment was derived from the activation of the MSN portion of the brain.In the case of cognitive damage after brain injury,if the brain damage part and MSN have a certain overlap or most overlap,then in the rehabilitation of cognitive direction,the therapeutic effect of MVF is not achieved in traditional cognitive therapy.This is of great significance for patients to be able to re-enter society earlier and to enhance the efficiency of social rehabilitation.
In the future,we can explore more about the application and benefits of MVF treatment for more types of cognitive diseases.And more detailed sub-regions in the MSN section of the brain for comparison and experimentation to achieve specific quantitative rehabilitation criteria.In addition,the application of MSN as a mechanism of rehabilitation can be developed,and the combination of human and machine makes the quantitative rehabilitation better.
Mirror therapy improves speech dysfunction
Aphasia.Although MNS-targeted action observation therapy has been applied to the treatment of motor dysfunction,sensory dysfunction,and cognitive dysfunction,there are also a small number of data studies showing that mirror therapy has a good therapeutic effect on lexical retrieval and general language function of aphasia patients.These neural system networks are activated when individuals perform learning actions by performing mimicry,observation,and motor imaging,enabling people to (re)learn damaged functions by activating these related internal actions [46].Chen WL[47] found that hand repetitive motion combined with dynamic object observation can improve the language function of patients with aphasia by analyzing the naming test of language function and action.Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) also indicates that hand repetitive motion can activate related fields of MNS (including speech regions).Yang JP[48] also analyzed the effects of mirror therapy on post-stroke exercise aphasia through fMRI technology.
Autism.Autism is also known as the child autism spectrum disorder,also known as autism.In the early development of MNS dysfunction,a series of injuries characterized by autism spectrum disorder(ASD) may be caused,including imitation,mental theory,and social communication defects [49].Recent experimental data showed that patients with ASD had defects in goal-directed behavior and emotional expression communication.Whether the patient was in a quiet state or not,his organization's motor behavior and speech expression exchanges show an abnormal state [50].Dapretto [51] through fMRI examination found that children with autism and normal children in the immature facial expression and emotional expression,autistic children's performance is worse than normal children.Therefore,early dysfunction of the mirror neuron system can provide a basis for the diagnosis of autism.Similar results were reported by Martineau [52] and Oberman LM [53].Therefore,it is concluded that the functional recovery of mirror neurons had a certain effect on the enhancement of verbal expression and communication in autistic patients.
Conclusion
As a safety and operable therapy,mirror therapy is very helpful for the recovery of stroke,the relief of pain,and the improvement of cognitive dysfunction and speech dysfunction though activating mirror neuron.It is a supplementary treatment in the rehabilitation process,which is very conducive to the widespread use and application.However,in the current mirror therapy studies,the experimental data were not detailed,lacking multiple types of experiments and matched control group with the existence of unexplained and inevitable contingency.
In the future,we need to pay more attention to mirror therapy,and carefully quantify the effect of mirror therapy.In addition,we can also develop more applications of the mirror neuron system based on the traditional mirror therapy and provide new rehabilitation services for people with dysfunction.
杂志排行
TMR Non-Drug Therapy的其它文章
- Hidden in the hands-the special inner Bagua acupoints for pediatric massage
- Non-drug therapies for acute gouty arthritis treatment
- Quality evaluation and content analysis of non-drug guidelines on risk factors of secondary prevention of myocardial infarction
- The impact of inspiratory muscle training on exercise capacity and inspiratory muscle strength in heart failure patients: a meta-analysis
- Mirror therapy,an important but underappreciated rehabilitation treatment
